The global market for specialty glass, including high-performance materials like Pyroceram, has witnessed steady expansion driven by rising demand in consumer appliances, semiconductor manufacturing, and high-temperature industrial applications. According to Grand View Research, the global glass ceramics market size was valued at USD 4.8 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.2% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by the increasing adoption of heat-resistant, low-expansion materials in cookware, electronics, and renewable energy systems. As innovation in thermal and mechanical performance becomes a differentiator, Pyroceram—a lithium aluminosilicate glass-ceramic known for its exceptional thermal shock resistance and durability—has emerged as a material of choice across industries. With key players investing in R&D and scaling production capabilities, the competitive landscape is evolving rapidly. Below are the top five Pyroceram glass manufacturers leading the market through technological expertise, global supply networks, and strategic partnerships.
Top 5 Pyroceram Glass Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Pyroceram ceramic glass
Domain Est. 2012
Website: vattiglass.com
Key Highlights: A highly professional manufacturer and supplier of glass and glass products,main dealing with tempered glass, insulated glass, laminated glass, solar glass, ……
#2 Corning Pyroceram
Domain Est. 1991
Website: corning.com
Key Highlights: Corning Pyroceram glass-ceramic material is opaque, light gray in color, and has high strength, high elastic modulus, and uniform dielectric properties….
#3 Corning® PYROCERAM® Glass Ceramic
Domain Est. 1997
Website: sgpinc.com
Key Highlights: PYROCERAM® is widely used for residential applications such as fireplace and wood burning stove windows, oven windows, broiler windows and other such appliances ……
#4 Pyroceram Glass, Heat Proof Glass
Domain Est. 2001
Website: onedayglass.com
Key Highlights: PyroCeram is a heat-resistant glass-ceramic that can tolerate exceptionally high temperatures. In actuality, it is a transparent version of ceramic….
#5 GUIDE TO CORNING VISIONS AND ARC VITROCERAMIC …
Website: leclair.vision
Key Highlights: Visions is made of a material belonging to the Pyroceram family of vitroceramics (glass-ceramics). It features thermal characteristics similar to Corning ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Pyroceram Glass
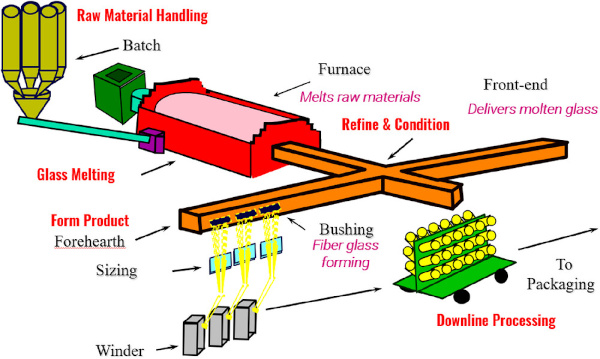
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Pyroceram Glass
Pyroceram glass, a proprietary lithium aluminosilicate glass-ceramic material originally developed by Corning, continues to play a specialized yet critical role across multiple industries. As we approach 2026, several key market trends are shaping the demand, applications, and competitive landscape for Pyroceram and similar glass-ceramic materials.
1. Resurgence in Consumer Durables: Smart Appliances & Cooktops
The smart home and connected kitchen markets are driving renewed interest in durable, aesthetically pleasing materials. Pyroceram’s combination of thermal shock resistance, scratch resistance, and sleek appearance makes it ideal for:
– High-End Induction Cooktops: Demand is rising as consumers upgrade to energy-efficient cooking surfaces. Pyroceram remains the material of choice for premium brands due to its ability to withstand rapid temperature changes and maintain a cleanable surface.
– Smart Oven Doors and Control Panels: With the growth of IoT-integrated appliances, manufacturers are using Pyroceram for touch-sensitive control interfaces and viewing windows that resist heat and fingerprints.
– Luxury Tableware and Fireplaces: Niche markets in designer home goods are adopting Pyroceram for modern fireplace screens and durable, heat-resistant tabletops.
Market Impact: Steady growth (CAGR ~4–6%) in the consumer appliances segment through 2026, supported by premiumization trends in emerging economies.
2. Expansion into High-Tech and Electronics
Pyroceram’s low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) and dielectric properties are attracting attention in advanced electronics:
– Semiconductor Manufacturing Equipment: Used in wafer handling components and thermal management systems where dimensional stability under heat is critical.
– 5G Infrastructure and Photonics: Potential use in substrates and insulators for high-frequency communication devices due to its electromagnetic transparency and thermal resilience.
– LED and Microdisplay Technologies: As next-gen displays (e.g., microLED) require heat dissipation and optical clarity, Pyroceram is being evaluated for encapsulation and support structures.
Market Impact: Emerging applications could increase demand from the electronics sector by 8–10% annually by 2026, though volumes remain smaller than consumer markets.
3. Sustainability and Recycling Pressures
Environmental regulations are pushing manufacturers toward sustainable materials:
– Recyclability Challenges: Unlike standard glass, Pyroceram is not easily recyclable due to its crystalline structure. This is prompting R&D into more sustainable compositions and end-of-life processing.
– Energy Efficiency in Production: Companies are investing in lower-carbon manufacturing processes to meet ESG goals, which may affect supply chain costs and pricing.
Market Impact: Regulatory scrutiny may slow adoption in eco-sensitive regions unless greener alternatives or closed-loop recycling are developed by 2026.
4. Competitive Landscape and Material Substitution
While Pyroceram remains a benchmark, competitors are emerging:
– Alternative Glass-Ceramics: Materials like Schott’s CERAN® and Nippon Electric Glass’s products offer comparable performance, increasing competition in cooktop and industrial markets.
– Advanced Composites and Ceramics: In aerospace and defense, materials such as silicon carbide or carbon-fiber-reinforced ceramics are challenging Pyroceram in extreme environments.
– Patent Expiry and Generic Production: As foundational patents expire, lower-cost producers in Asia are entering the market with similar lithium aluminosilicate glass-ceramics.
Market Impact: Price pressure may grow, especially in commoditized applications, but brand loyalty and performance in high-reliability uses will sustain premium segments.
5. Geopolitical and Supply Chain Dynamics
Raw material sourcing (e.g., lithium, alumina) is becoming more volatile:
– Lithium Demand Surge: Driven by EVs and batteries, lithium prices may impact Pyroceram production costs.
– Regional Manufacturing Shifts: Companies are diversifying production to North America and Southeast Asia to reduce reliance on single-source suppliers, affecting global supply chains.
Market Impact: Potential for cost fluctuations and supply constraints in 2025–2026, prompting vertical integration or long-term supply agreements.
Conclusion
By 2026, the Pyroceram glass market is expected to experience moderate growth, driven by innovation in smart appliances and electronics, tempered by sustainability challenges and competition. While not a mass-market material, its unique properties ensure continued relevance in high-performance and premium applications. Success will depend on manufacturers’ ability to innovate sustainably, manage supply chain risks, and differentiate from newer glass-ceramic alternatives.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Pyroceram Glass (Quality, IP)
Sourcing genuine Pyroceram® glass—trademarked by Corning Inc.—requires careful attention to both quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) compliance. Falling into common pitfalls can result in substandard materials, legal exposure, and reputational damage. Below are key risks to avoid:
1. Confusing Pyroceram with Generic Glass-Ceramic Materials
Pitfall: Assuming that any glass-ceramic with similar thermal or mechanical properties is equivalent to authentic Pyroceram.
Risk: Pyroceram is a proprietary glass-ceramic material developed by Corning with specific composition, microstructure, and performance characteristics. Generic alternatives may not match its thermal shock resistance, strength, or long-term durability.
Mitigation: Verify the material’s exact composition and processing history. Request certification or test data from the supplier. Only source from authorized Corning distributors or licensed partners.
2. Purchasing Counterfeit or Misrepresented Products
Pitfall: Acquiring materials labeled as “Pyroceram” from unauthorized vendors, particularly through online marketplaces or third-party suppliers.
Risk: These products may be counterfeit, inferior imitations, or misrepresented glass-ceramics. They often lack the rigorous quality control and performance validation of genuine Pyroceram.
Mitigation: Confirm supplier authorization directly with Corning. Request batch-specific documentation, including material traceability and compliance certificates. Avoid suppliers offering unusually low prices or vague technical specifications.
3. Overlooking Intellectual Property Rights
Pitfall: Using the term “Pyroceram” in product descriptions, marketing, or technical documentation without proper licensing.
Risk: “Pyroceram” is a registered trademark of Corning Inc. Unauthorized use may constitute trademark infringement, leading to cease-and-desist letters, legal action, or financial penalties.
Mitigation: Use generic terms like “glass-ceramic material” or “ceramic glass” unless you are an authorized licensee. Always include proper trademark attributions if permitted under agreement.
4. Inadequate Quality Control and Testing
Pitfall: Failing to implement incoming inspection protocols or relying solely on supplier claims.
Risk: Even legitimate sources may ship inconsistent batches. Without proper testing, defects such as microcracks, inhomogeneities, or deviations in thermal expansion may go undetected.
Mitigation: Establish a quality control checklist including visual inspection, dimensional accuracy, and performance testing (e.g., thermal cycling, impact resistance). Work with suppliers who provide full material test reports (MTRs).
5. Ignoring Application-Specific Requirements
Pitfall: Assuming one type of Pyroceram suits all applications.
Risk: Pyroceram comes in various formulations (e.g., different grades for cookware, industrial, or aerospace use). Using the wrong grade can lead to premature failure.
Mitigation: Clearly define your technical requirements (e.g., maximum operating temperature, coefficient of thermal expansion, optical clarity). Consult Corning’s technical data sheets or application engineers to ensure compatibility.
6. Supply Chain Transparency Gaps
Pitfall: Sourcing through multiple intermediaries without visibility into the material’s origin.
Risk: Increases exposure to counterfeit goods, recycled scrap, or diverted production not intended for your region or application.
Mitigation: Demand full supply chain traceability. Prefer direct relationships with Corning or tier-one authorized distributors. Include audit rights in procurement contracts where feasible.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls, organizations can ensure they source genuine, high-quality Pyroceram glass while respecting intellectual property and minimizing technical and legal risks.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Pyroceram Glass
Overview of Pyroceram Glass
Pyroceram is a lithium aluminosilicate-based glass-ceramic material known for its exceptional thermal shock resistance, low coefficient of thermal expansion, high mechanical strength, and optical clarity. Commonly used in cookware, aerospace components, and high-performance industrial applications, Pyroceram requires specialized handling, storage, and compliance considerations throughout the supply chain.
Regulatory Classification and Compliance
Pyroceram glass is generally classified as a non-hazardous solid material under major international regulations when in its finished, stable form. However, compliance obligations vary by region and application. Key regulatory frameworks include:
- GHS (Globally Harmonized System): Pyroceram is typically not classified as hazardous under GHS criteria for physical, health, or environmental hazards. Safety Data Sheets (SDS) should still be available and compliant with local GHS implementations.
- REACH (EU): Pyroceram is not listed as a Substance of Very High Concern (SVHC). Suppliers must confirm compliance with REACH Article 33 (communication in the supply chain) if applicable.
- TSCA (USA): Pyroceram is considered an existing chemical under TSCA and does not require pre-manufacture notification (PMN) when produced or imported in standard forms.
- RoHS & WEEE Compliance: For electronic or electrical applications, ensure Pyroceram components meet RoHS restrictions on hazardous substances and are marked appropriately for WEEE recycling.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Due to its durability, Pyroceram glass still requires careful packaging to prevent chipping, scratching, or fracture during transport:
- Use rigid, shock-absorbent packaging such as double-walled cardboard boxes with foam inserts or custom molded trays.
- Individual pieces should be separated using non-abrasive materials (e.g., bubble wrap, foam sheets).
- Clearly label packages as “Fragile” and “Handle with Care” to alert handlers.
- Avoid stacking heavy loads directly on packaged Pyroceram units. Use pallets and secure with stretch wrap or strapping.
Storage Conditions
To maintain material integrity:
- Store in a dry, climate-controlled environment with temperatures between 15°C and 30°C (59°F–86°F).
- Avoid prolonged exposure to high humidity, which may affect surface finishes or packaging.
- Keep materials off the floor using pallets or shelving to prevent contamination and water damage.
- Protect from direct sunlight and UV exposure if stored long-term, particularly for optically sensitive applications.
Transportation Guidelines
Pyroceram glass can be shipped via air, sea, or land freight, but proper documentation and packaging are essential:
- Air Freight (IATA): No special hazardous labeling required; standard cargo procedures apply. Confirm packaging meets IATA’s drop and vibration testing standards.
- Sea Freight (IMDG): Not regulated as dangerous goods under IMDG Code. Use moisture-resistant wrapping to prevent condensation damage in containers.
- Ground Transport (DOT, ADR): No hazardous classification under DOT or ADR for finished Pyroceram products. Use secure load-securing methods to prevent shifting.
Import/Export Documentation
Ensure all shipments include:
- Commercial Invoice specifying product name, quantity, value, and HS Code (typically 7013.99 or 7019.90 depending on form and use).
- Packing List with detailed itemization.
- Certificate of Origin if required by trade agreements.
- SDS (Safety Data Sheet) for customs or customer requirements.
- Verify import restrictions or labeling requirements in the destination country, especially for consumer goods.
Waste Disposal and Recycling
Pyroceram is inert and non-toxic in solid form. Disposal should follow local waste regulations:
- Non-hazardous waste streams are typically acceptable for landfill (where permitted).
- Recycling is encouraged; contact specialized glass or ceramic recyclers for processing options.
- Dust generated during cutting or machining may require respiratory protection and proper ventilation (OSHA/NIOSH guidelines apply to particulate exposure).
Emergency Response
Although Pyroceram is non-combustible and chemically stable:
- In case of breakage, clean up fragments using mechanical means (not compressed air) to avoid airborne particles.
- Wear cut-resistant gloves and eye protection during cleanup.
- No special firefighting measures are needed—Pyroceram does not burn or emit toxic fumes under normal conditions.
Supplier and Quality Assurance
To ensure compliance and performance:
- Source Pyroceram from certified suppliers with quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001).
- Request material certifications including composition, thermal properties, and test reports.
- Conduct incoming inspections for damage and dimensional accuracy.
Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance management for Pyroceram glass ensures safety, regulatory adherence, and product integrity. By following these guidelines for packaging, transport, storage, and documentation, organizations can minimize risks and maintain efficient supply chain operations. Always consult local regulations and conduct periodic compliance audits to stay current with evolving requirements.
Conclusion on Sourcing Pyroceram Glass
Sourcing Pyroceram glass requires a strategic approach due to its specialized composition, high-performance characteristics, and limited availability. As a lithium aluminosilicate-based glass-ceramic known for exceptional thermal shock resistance, low thermal expansion, and mechanical strength, Pyroceram is typically used in demanding applications such as aerospace, defense, laboratory equipment, and high-temperature industrial systems.
Direct sourcing from the original manufacturer, Corning Inc., or its authorized partners, remains the most reliable method to ensure material authenticity, consistent quality, and technical support. However, due to proprietary control and potential supply constraints, alternative routes such as certified distributors, specialized glass fabricators, or secondary market suppliers may be considered—though with careful verification of material specifications and traceability.
Challenges in sourcing include long lead times, minimum order quantities, and cost implications, particularly for custom shapes or sizes. Therefore, early engagement with suppliers, clear technical specifications, and consideration of substitute materials (such as other glass-ceramics like Zerodur or Robax, if application permits) can aid in supply chain resilience.
In conclusion, successful sourcing of Pyroceram glass hinges on establishing trusted supplier relationships, understanding technical and regulatory requirements, and planning for adequate lead times. For critical applications, prioritizing authenticity and performance over cost is essential to ensure functional reliability and safety.