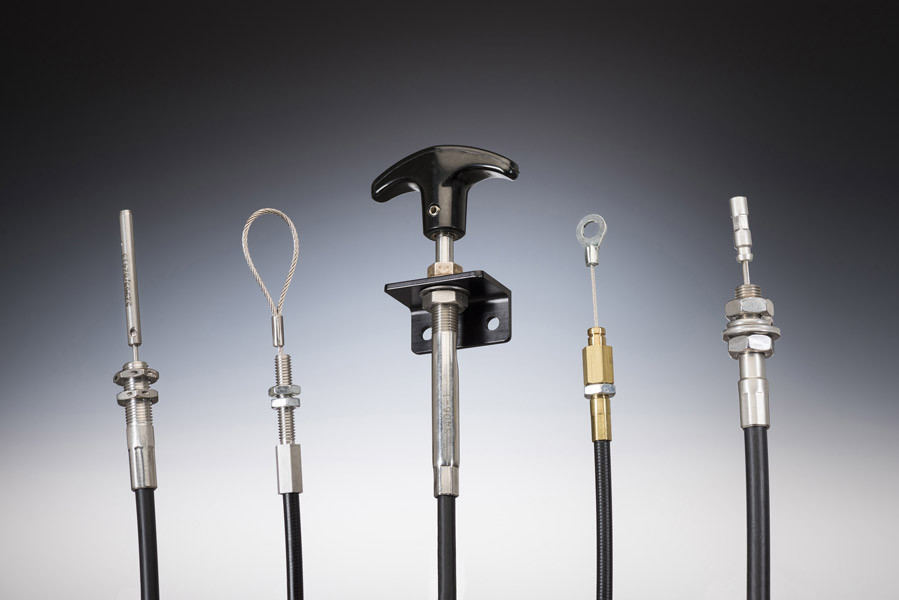
The global push pull control cables market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand across automotive, aerospace, industrial machinery, and medical device sectors. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global control cables market was valued at approximately USD 2.1 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 4.5% through 2029. This expansion is fueled by increasing automation, precision engineering requirements, and the need for reliable mechanical actuation in complex systems. Push pull control cables, known for their durability, accuracy, and low maintenance, are becoming integral components in both traditional and emerging applications, from throttle and clutch systems in vehicles to robotic surgical devices. As industries prioritize efficiency and performance, leading manufacturers are investing in advanced materials, miniaturization, and customization capabilities. In this competitive landscape, the top eight push pull control cable manufacturers have distinguished themselves through innovation, global supply chain reach, and stringent quality certifications—setting the benchmark for reliability and technical excellence.
Top 8 Push Pull Control Cables Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Push Pull Control Cables for Automotive, Marine & Industrial Uses
Domain Est. 1998
Website: safety.com.tw
Key Highlights: As a trusted push-pull cable manufacturer, we specialize in designing and producing high-performance push-pull cables, push-pull wires, and complete ……
#2 Push Pull Control Cable Assemblies
Domain Est. 2000
Website: tylermadison.com
Key Highlights: Leading manufacturer & supplier of push and pull cables, custom control cables and control cable assemblies. Our experienced and knowledgeable engineers are ……
#3 Control Cable & Push Pull Cable Assemblies & Expertise
Domain Est. 1997
Website: savacable.com
Key Highlights: Sava continues that legacy as a manufacturer of the world’s finest control cables, push-pull components, push-pull cable end fittings, and conduit….
#4 High Efficiency Push Pull Control Cables
Domain Est. 1998
Website: glendinningprods.com
Key Highlights: Glendinning manufactures a wide variety of high efficiency push-pull control cables. With unlimited cable combinations,Glendinning has the cable for you!…
#5 Control Cables
Domain Est. 1999
Website: bergencable.com
Key Highlights: As an industry leader in manufacturing control cables, Bergen Cable has the capabilities to produce control cables suited to a diverse range of applications….
#6 Push-Pull Cables
Domain Est. 2000
Website: cablecraft.com
Key Highlights: As the design leader in push-pull cables and controls, Cablecraft has provided engineered solutions for a myriad of applications throughout our history….
#7 Push
Domain Est. 2002
Website: lexcocable.com
Key Highlights: Lexco Cable manufactures a wide range of push pull controls for remote access latch releases, safety breaks, automotive hood releases, gaming industry ……
#8 Control Cables, Push Pull Cables, Push Pull Control Cables, Morse …
Domain Est. 2004
Website: cccables.com
Key Highlights: Push Pull Control Cables are available in various mounting configurations, travel or stroke length, overall length and temperature options….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Push Pull Control Cables
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Push Pull Control Cables
Market Overview
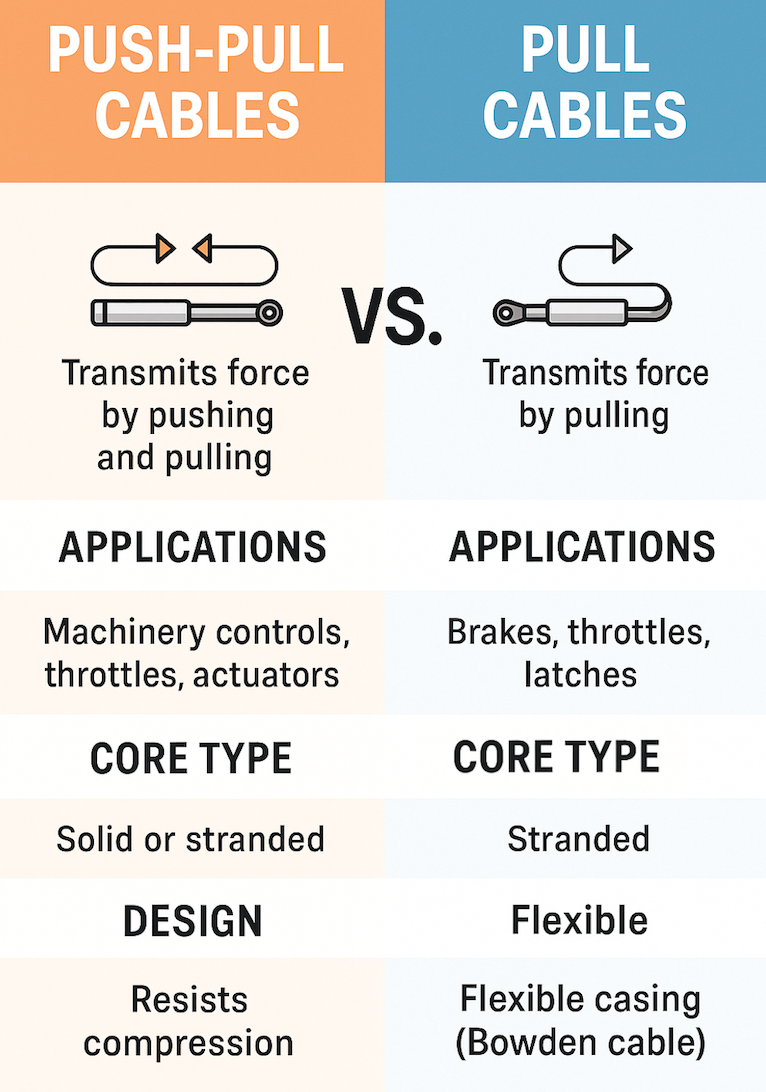
Push pull control cables are mechanical linkages used to transmit force and motion in a wide range of applications, including automotive, aerospace, industrial machinery, medical devices, and agriculture. These cables operate by transferring linear motion from one point to another, often enabling precise control in confined or complex systems. As industries continue to evolve toward automation, lightweight design, and energy efficiency, the demand for reliable and durable control solutions remains strong. The global push pull control cable market is expected to grow steadily by 2026, driven by technological advancements, increasing industrial automation, and the expansion of end-use sectors.
Key Market Drivers
1. Growth in the Automotive Sector
The automotive industry remains the largest consumer of push pull control cables, particularly for throttle, clutch, and gear shift mechanisms. Despite the shift toward electric vehicles (EVs), which often utilize electronic controls, many internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles and hybrid models still rely on mechanical systems. Furthermore, certain EV components—such as emergency brakes and manual override systems—continue to use push pull cables. As emerging markets expand their vehicle production, demand for cost-effective and reliable mechanical controls is expected to remain robust through 2026.
2. Expansion in Industrial Automation
Manufacturing and industrial processes are increasingly adopting automated systems that require precise mechanical actuation. Push pull cables are used in robotics, conveyor systems, and control panels where electronic sensors may not be suitable due to environmental conditions (e.g., high heat, dust, or electromagnetic interference). The trend toward Industry 4.0 and smart factories will continue to integrate mechanical components with digital monitoring, enhancing the relevance of durable control cables.
3. Aerospace and Defense Applications
The aerospace and defense sectors rely on push pull control systems for flight control surfaces, landing gear, and cabin mechanisms. These industries demand high-reliability components that perform under extreme conditions. As global defense spending increases and commercial aviation recovers post-pandemic, the need for certified, high-performance cables is expected to rise. Innovations in lightweight composite materials and corrosion-resistant coatings will further boost adoption in this sector by 2026.
4. Medical Device Integration
Push pull cables are increasingly used in medical equipment such as surgical robots, imaging systems, and adjustable hospital beds. Their ability to provide precise, smooth motion in sterile or space-constrained environments makes them ideal for life-critical devices. With aging populations and growing healthcare investments, the medical technology segment will contribute to market growth through 2026.
Technological Advancements
Material Innovation
Manufacturers are investing in advanced materials such as high-strength stainless steel, PTFE-coated wires, and composite sheaths to improve durability, reduce friction, and resist environmental degradation. These enhancements extend cable lifespan and reduce maintenance, making them more attractive in high-cycle applications.
Miniaturization and Customization
As equipment becomes more compact, especially in robotics and medical devices, there is growing demand for smaller, customizable push pull cables. OEMs are increasingly seeking tailored solutions with specific lengths, termination types, and force tolerances. This trend toward customization is expected to drive supplier innovation and strengthen customer relationships.
Integration with Smart Systems
While push pull cables are inherently mechanical, integration with sensors and IoT platforms allows for real-time monitoring of cable wear, tension, and performance. By 2026, hybrid systems that combine mechanical reliability with digital feedback will become more common, especially in predictive maintenance applications.
Regional Outlook
- Asia-Pacific: The fastest-growing region due to expanding manufacturing bases in China, India, and Southeast Asia. Rising automotive production and industrial automation investments will fuel demand.
- North America: Steady growth driven by aerospace, defense, and medical technology sectors. Emphasis on high-quality, certified components supports premium product adoption.
- Europe: Growth tempered by electrification trends in automotive, but strong demand in industrial machinery and renewable energy (e.g., wind turbine controls) will sustain the market.
- Rest of World: Emerging markets in Latin America and the Middle East show potential, particularly in agriculture and construction equipment.
Challenges and Risks
- Competition from Electronic Controls: Increased use of electronic throttle control (ETC) and drive-by-wire systems threatens traditional cable applications, especially in passenger vehicles.
- Supply Chain Volatility: Fluctuations in raw material prices (e.g., steel, plastics) and logistics disruptions can impact production costs and delivery timelines.
- Regulatory Compliance: Stringent safety and environmental standards in automotive and aerospace sectors require continuous certification and testing, increasing entry barriers for new players.
Competitive Landscape
The push pull control cable market is moderately consolidated, with key players including Belden Inc., The L.S. Starrett Company, S.S. White Technologies, and IMI Precision Engineering. These companies are focusing on R&D, strategic partnerships, and geographic expansion to strengthen their market positions. Smaller niche manufacturers are gaining traction by offering specialized, high-precision cables for medical and aerospace applications.
Conclusion
By 2026, the push pull control cable market will continue to evolve in response to technological change and shifting industry demands. While facing competition from electronic alternatives, mechanical cables retain critical advantages in reliability, cost, and performance under extreme conditions. Growth will be driven by industrial automation, aerospace, and medical applications, with innovation in materials and smart integration shaping the future. Companies that invest in customization, sustainability, and digital compatibility will be best positioned to capture value in this resilient and evolving market.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Push-Pull Control Cables: Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
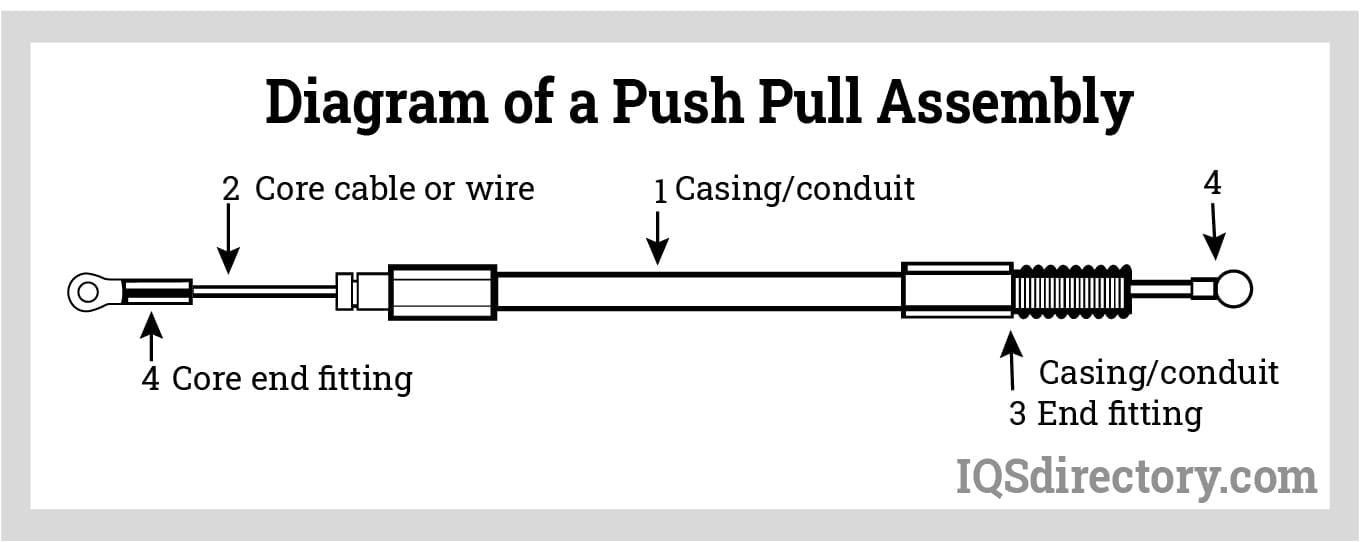
Sourcing push-pull control cables—commonly used in automotive, aerospace, industrial machinery, and medical devices—requires careful due diligence to avoid compromising performance, safety, and legal compliance. Two major areas of risk are product quality and intellectual property (IP) infringement. Below are common pitfalls in these areas.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inadequate Material Specifications
One of the most frequent issues is sourcing cables made from substandard materials. Low-cost suppliers may use inferior-grade stainless steel, plastic sheathing, or lubricants that degrade under temperature extremes, vibration, or chemical exposure. This leads to premature failure, increased maintenance, and potential safety hazards.
2. Inconsistent Manufacturing Tolerances
Push-pull cables require precise tolerances to ensure smooth operation and correct force transmission. Poorly manufactured cables often exhibit inconsistent cable length, core stiffness, or housing alignment, resulting in poor fitment or unreliable performance in critical applications.
3. Lack of Environmental Resistance
Many sourced cables fail under real-world conditions because they lack proper sealing or corrosion resistance. Buyers may overlook Ingress Protection (IP) ratings, assuming all cables are weatherproof. Without proper IP67 or IP68 ratings, cables can fail in humid, dusty, or washdown environments.
4. Insufficient Testing and Certification
Suppliers—especially from unverified sources—may not conduct proper functional, fatigue, or environmental testing. Absence of third-party certifications (e.g., ISO, UL, or automotive-specific standards) increases the risk of field failures and non-compliance.
5. Counterfeit or Reconditioned Components
In global supply chains, counterfeit cables—often refurbished or rebranded—are a growing concern. These cables may appear identical but lack the durability, traceability, or safety approvals of genuine parts.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
1. Design Infringement
Many push-pull control cables are protected by patents, especially those with unique internal mechanisms, ergonomic handles, or specialized end fittings. Sourcing generic versions that closely mimic patented designs can lead to IP litigation, product recalls, or customs seizures.
2. Unauthorized OEM Replicas
Some suppliers produce near-identical copies of OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) cables without licensing. These clones may save costs upfront but expose buyers to legal liability, especially if used in regulated industries like aviation or medical devices.
3. Lack of IP Documentation
Reputable suppliers provide IP clearance documentation or design licenses. Failing to request or verify this information increases the risk of unintentional infringement. Buyers assume liability even if the supplier misrepresented the product’s legal status.
4. Gray Market Sourcing
Purchasing from unauthorized distributors or gray market channels may result in genuine parts being sold outside their intended region, potentially violating distribution agreements or voiding warranty and IP protections.
Best Practices to Mitigate Risks
- Verify supplier credentials and request quality certifications (ISO 9001, IATF 16949, etc.).
- Demand test reports for environmental resistance, cycle life, and force performance.
- Inspect sample units for material quality, build consistency, and IP rating compliance.
- Conduct IP due diligence by reviewing patents and requiring legal assurances from suppliers.
- Use trusted procurement channels and avoid overly low bids that may indicate counterfeit or infringing goods.
By addressing these quality and IP pitfalls proactively, businesses can ensure reliable performance and legal compliance when sourcing push-pull control cables.
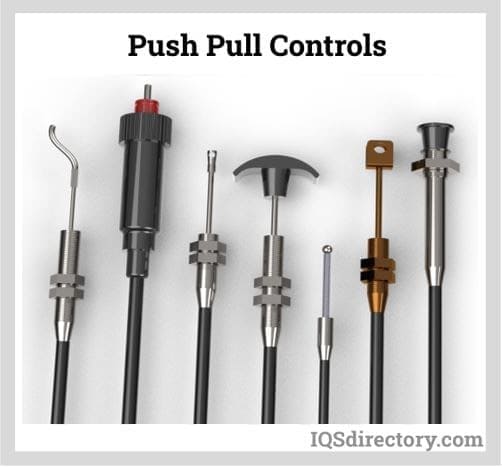

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Push Pull Control Cables
Overview
Push pull control cables are mechanical actuation components used across industries such as automotive, aerospace, industrial machinery, and medical devices. Proper logistics handling and regulatory compliance are essential to ensure product integrity, safety, and adherence to international trade standards.
Packaging & Handling
- Protective Packaging: Use anti-static, moisture-resistant materials to prevent corrosion and damage during transit.
- Labeling: Clearly label packages with part numbers, quantities, handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “Do Not Bend”), and country of origin.
- Cable Coiling: Cables should be coiled loosely with a minimum bend radius to prevent kinking or internal wire damage. Use spools or reels where applicable.
- Storage Conditions: Store in dry, temperature-controlled environments (typically 15–30°C, 30–60% RH) away from direct sunlight and chemicals.
Transportation Requirements
- Mode of Transport: Suitable for air, sea, or ground freight. Choose based on urgency, cost, and destination.
- Hazard Classification: Push pull control cables are generally non-hazardous. However, verify if any metallic or coated components require special handling.
- Export Packaging Standards: Comply with ISTA or ASTM standards for drop, vibration, and compression testing where required.
- Documentation: Include commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading/air waybill, and any required export declarations.
Regulatory Compliance
- RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances): Ensure cables comply with EU Directive 2011/65/EU, limiting the use of lead, cadmium, mercury, and other hazardous materials.
- REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals): Confirm that all materials used are registered and compliant with EC 1907/2006.
- Conflict Minerals (Dodd-Frank Act Section 1502): Disclose the sourcing of tin, tantalum, tungsten, and gold (3TG) if applicable, especially for U.S. markets.
- ITAR/EAR (U.S. Export Regulations): Determine if cables fall under export-controlled technologies. Most standard cables are EAR99 (low concern), but verify based on end-use.
Customs & Import/Export Procedures
- HS Code Classification: Typically classified under HS code 8708.29 (for automotive controls) or 8538.90 (electrical control parts), depending on application. Confirm with local customs authorities.
- Certificates of Origin: Required for preferential tariff treatment under trade agreements (e.g., USMCA, EU-FTA).
- Import Duties & Taxes: Research destination country tariffs, VAT, and any anti-dumping measures.
- Product Certification: Depending on region and application, cables may require UL, CE, ISO 9001, or other certifications.
Industry-Specific Considerations
- Automotive: Must meet OEM specifications (e.g., Ford WSK, GM GMW) and often require PPAP documentation.
- Aerospace: Subject to AS9100 standards and may require traceability (batch/lot tracking) and material certifications (e.g., MIL-DTL-83420).
- Medical Devices: If used in medical equipment, cables must comply with ISO 13485 and FDA 21 CFR Part 820 (QSR).
Returns & Reverse Logistics
- Establish a clear process for handling non-conforming or damaged shipments.
- Require return authorization (RMA) numbers and original packaging for all returns.
- Inspect returned items for damage and document reasons for return to improve quality and logistics planning.
Summary
Effective logistics and compliance for push pull control cables require attention to packaging, transportation standards, regulatory requirements, and industry-specific certifications. Proactive documentation and adherence to international regulations ensure smooth global distribution and minimize supply chain disruptions.
Conclusion for Sourcing Push-Pull Control Cables:
Sourcing push-pull control cables requires a strategic approach that balances performance requirements, cost-efficiency, and supply chain reliability. These precision components play a critical role in transmitting mechanical force and motion across various industries—including aerospace, automotive, medical devices, and industrial machinery—making quality and consistency paramount.
Key considerations in the sourcing process include material specifications, customization needs, durability under operational conditions (such as temperature, vibration, and environmental exposure), and compliance with relevant industry standards (e.g., ISO, ASTM, or MIL-SPEC). Engaging with reputable suppliers who offer technical expertise, rigorous quality control, and the ability to support low-volume custom designs or high-volume production is essential.
Additionally, evaluating lead times, geographic proximity, and long-term scalability helps mitigate supply chain risks. Building strong supplier relationships, conducting thorough supplier audits, and implementing clear communication channels contribute to consistent product quality and on-time delivery.
In conclusion, successful sourcing of push-pull control cables involves a comprehensive assessment of technical, operational, and logistical factors. By prioritizing quality, reliability, and collaboration with trusted manufacturers, organizations can ensure optimal performance of their systems and maintain a competitive edge in their respective markets.