The global automotive emissions control market, which includes critical components such as purge canister vent valves, is experiencing steady expansion driven by tightening environmental regulations and the rising production of fuel-efficient vehicles. According to Mordor Intelligence, the automotive emission control system market was valued at USD 37.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.2% from 2024 to 2029. A key contributor to this growth is the increasing demand for evaporative emission (EVAP) system components—among them, purge canister vent valves—which play an essential role in minimizing hydrocarbon emissions by managing fuel vapor release from the fuel tank to the engine’s intake manifold. As automakers prioritize compliance with Euro 7, Tier 3, and China 6 emission standards, the need for high-performance valves from reliable manufacturers has intensified. This has positioned leading suppliers at the forefront of innovation and market share expansion. The following analysis highlights the top seven purge canister vent valve manufacturers shaping the industry through technological expertise, global reach, and strategic partnerships.
Top 7 Purge Canister Vent Valve Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Canister Purge Valve
Domain Est. 2004
Website: boschautoparts.com
Key Highlights: Bosch is the Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) for this application; OE Technology provides the correct function and calibration to ensure trouble-free ……
#2 Canister Purge Valves
Domain Est. 2000
Website: standardbrand.com
Key Highlights: Standard® offers a line of canister purge solenoids/valves to help with your emission system repairs in addition to canister vent solenoids. Our high-grade ……
#3 Vapor Canister Purge Valve
Domain Est. 2001
Website: dormanproducts.com
Key Highlights: Engineered for a perfect fit and plug-and-play installation, this vapor canister purge valve is a direct replacement for the original equipment purge valve….
#4 Vapor Canister Vent Valves
Domain Est. 2002
Website: motorad.com
Key Highlights: MotoRad’s vapor canister vent valves are durable and well-constructed to enhance the system’s reliability, prevent vapor loss, and ensure that emissions are ……
#5 EVAP Solenoids and Valves
Domain Est. 2005
Website: bwdbrand.com
Key Highlights: Canister Purge Valves In addition to canister vent solenoids, we offer a line of canister purge solenoids/valves to help with your emission system repairs….
#6 Honda 17310
Domain Est. 2007
Website: hondapartsnow.com
Key Highlights: In stock 1–4 day deliveryWhen conditions allow, the PCM opens the canister purge valve, letting vapors mix with the air/fuel mixture to be burned. The EVAP system includes the cani…
#7 Purge Valve
Domain Est. 2016
Website: tu-lok.com
Key Highlights: When the valve is stuck the Vapor Canister Purge Valve is an emission control component that allows the engine to intake the required amount of fuel vapors into ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Purge Canister Vent Valve
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Purge Canister Vent Valve
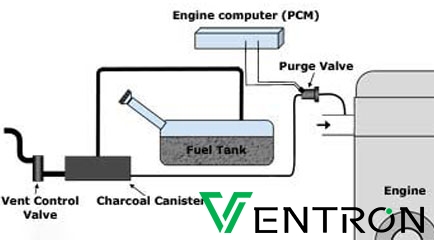
The global market for purge canister vent valves is poised for notable evolution by 2026, driven by stringent emissions regulations, advancements in vehicle electrification, and the continued demand for internal combustion engine (ICE) efficiency improvements. These valves—critical components in evaporative emission control (EVAP) systems—regulate the flow of fuel vapors from the charcoal canister to the engine intake manifold, preventing hydrocarbon release into the atmosphere.
-
Regulatory Pressure Driving Demand
By 2026, increasingly strict emissions standards from regulatory bodies such as the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), European Union’s Euro 7 standards, and China’s CN6b mandates will compel automakers to enhance EVAP system performance. This will sustain and potentially increase demand for high-precision purge canister vent valves capable of meeting tighter leak detection and vapor management requirements. -
Hybrid Vehicle Growth as a Key Driver
While the shift toward electric vehicles (EVs) may reduce reliance on traditional EVAP components, the expanding hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) and plug-in hybrid (PHEV) segment will sustain demand for purge valves. Most hybrids still utilize gasoline engines and fuel tanks, necessitating effective evaporative emission control. As automakers launch new hybrid platforms to meet carbon targets, vent valve integration will remain essential. -
Technological Innovation and Smart Valves
The 2026 market will likely see increased adoption of electronically controlled smart purge valves, offering real-time diagnostics, improved sealing, and integration with onboard diagnostic systems (OBD-II and beyond). These advanced valves support predictive maintenance and enhanced emissions monitoring—key features expected under next-generation vehicle software architectures. -
Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific, particularly China and India, will emerge as high-growth regions due to rising vehicle production and tightening emissions norms. North America and Europe will lead in adopting advanced valve technologies, driven by regulatory rigor and consumer demand for cleaner vehicles. Meanwhile, supply chain localization and nearshoring trends may influence manufacturing footprints for valve producers. -
Consolidation and Competition Among Suppliers
Tier-1 suppliers such as Bosch, Denso, Continental, and Keihin are expected to strengthen their market positions through R&D investments and strategic partnerships. Smaller manufacturers may face pressure to innovate or consolidate, especially as demand shifts toward higher-performance, lightweight, and cost-effective designs. -
Sustainability and Material Innovation
Environmental considerations will push manufacturers to adopt recyclable and heat-resistant materials in valve construction. Reduced part weight and longer service life will align with broader automotive sustainability goals, including end-of-life vehicle recycling.
In summary, the 2026 purge canister vent valve market will be shaped by regulatory mandates, hybrid vehicle expansion, technological sophistication, and regional growth disparities. While full electrification poses a long-term challenge, the transition period will ensure continued relevance and innovation in this niche but critical automotive component segment.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Purge Canister Vent Valves (Quality & IP)
Sourcing Purge Canister Vent Valves (also known as Canister Vent Solenoids or Purge Valves) presents significant challenges, particularly concerning quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to costly failures, warranty claims, reputational damage, and legal exposure.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
-
Inconsistent Performance & Premature Failure:
- Pitfall: Suppliers, especially lower-tier or non-authorized ones, may use substandard materials (e.g., inferior plastics, weak springs, low-grade seals) or inconsistent manufacturing processes. This leads to valves failing to open/close reliably, sticking, leaking, or degrading rapidly under heat, vibration, and fuel vapor exposure.
- Consequence: Failed evaporative emissions tests (EVAP), check engine lights (P0440, P0455, etc.), poor fuel economy, and customer dissatisfaction. High warranty return rates increase TCO.
-
Non-Compliance with OEM Specifications:
- Pitfall: Sourced valves may not meet the precise electrical characteristics (resistance, inductance), flow rates (crack pressure, full open flow), response times, or durability requirements (thermal cycling, vibration resistance, salt spray) mandated by the OEM. “Generic” or “compatible” parts often cut corners.
- Consequence: Malfunctions in the EVAP system, potential failure to pass regulatory emissions tests (e.g., FTP, SFTP), and vehicle drivability issues. Can lead to non-compliance penalties.
-
Poor Sealing and Leak Paths:
- Pitfall: Inadequate sealing materials, improper molding, or poor assembly can create micro-leaks in the valve body, diaphragm, or electrical connector. Fuel vapors escaping compromise the entire EVAP system’s integrity.
- Consequence: Persistent EVAP system leaks, triggering diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and failing emissions inspections. Difficult to diagnose and repair.
-
Inadequate Environmental Resistance:
- Pitfall: Valves sourced from suppliers without rigorous environmental testing capabilities may degrade quickly due to under-hood temperatures, humidity, road salt, or exposure to fuel additives and contaminants.
- Consequence: Reduced lifespan, unexpected failures, and increased field returns, especially in harsh operating conditions.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
-
Sourcing Counterfeit or Pirated Components:
- Pitfall: Unwittingly procuring valves that are illegal copies of genuine OEM parts, often bearing fake trademarks or packaging. These frequently originate from unauthorized manufacturers violating design patents and trademarks.
- Consequence: Direct legal liability for the buyer (contributory infringement), severe reputational damage (“We sold fake parts”), potential seizures by customs, and high risk of catastrophic quality failures. Warranty obligations become a nightmare.
-
Infringement of Design and Utility Patents:
- Pitfall: Selecting a valve design (e.g., specific internal geometry, actuator mechanism, connector design) that is protected by active patents held by the OEM or another Tier 1 supplier, even if sourced from a legitimate-looking supplier.
- Consequence: Risk of patent infringement lawsuits, injunctions halting production/sales, significant financial damages (potentially triple damages for willful infringement), and forced redesign costs.
-
Lack of Robust IP Due Diligence:
- Pitfall: Failing to verify the supplier’s right to manufacture and sell the specific valve design. Not requiring warranties of non-infringement or proof of licensing agreements. Relying solely on supplier claims without independent verification.
- Consequence: Exposure to significant legal and financial risk. The “innocent purchaser” defense is often weak or nonexistent in patent/copyright cases. Responsibility ultimately lies with the party putting the product into commerce.
-
Ambiguous or Inadequate IP Clauses in Contracts:
- Pitfall: Supplier contracts lacking clear, strong IP indemnification clauses, warranties of non-infringement, and provisions for handling IP disputes. Not securing rights to any improvements made by the supplier.
- Consequence: Left holding the bag if an infringement claim arises. Difficulty recovering legal costs and damages from the supplier. Uncertainty over ownership of modified designs.
Mitigation Strategies:
* Source from Authorized OEM Suppliers: Prioritize Tier 1 suppliers or authorized aftermarket manufacturers with direct OEM relationships.
* Rigorous Qualification & Auditing: Conduct thorough supplier audits (quality systems, manufacturing processes, material traceability) and demand comprehensive test data (performance, durability, environmental).
* Comprehensive IP Due Diligence: Conduct patent searches, require suppliers to provide proof of freedom-to-operate (FTO) or valid licenses, and include strong IP warranties and indemnification in contracts.
* Robust Quality Agreements: Implement detailed quality agreements with clear specifications, AQL levels, and failure mode requirements.
* Sample Testing & Validation: Perform independent bench and vehicle testing on sourced valves before full-scale adoption.
Ignoring these quality and IP pitfalls when sourcing Purge Canister Vent Valves can lead to far greater costs and risks than any initial savings achieved. A proactive, diligent approach is essential.
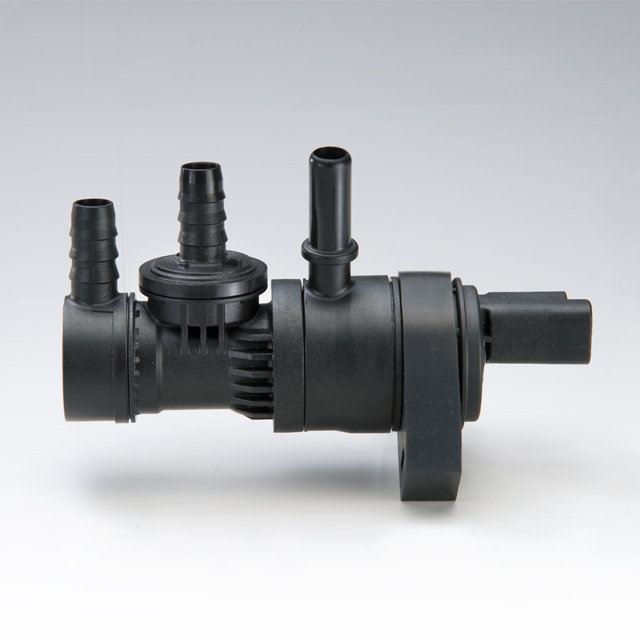

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Purge Canister Vent Valve
This guide outlines the key logistics and compliance considerations for the handling, transportation, storage, and regulatory adherence of Purge Canister Vent Valves, critical components in automotive evaporative emission control (EVAP) systems.
H2.1 Regulatory Compliance Framework
- Emissions Regulations (Primary):
- EPA (USA): Must comply with 40 CFR Part 86 (Control of Air Pollution from New Motor Vehicles and New Motor Vehicle Engines) and relevant state regulations (e.g., California Air Resources Board – CARB). Valves are integral to meeting evaporative emission standards (e.g., diurnal, hot soak, running loss).
- EU: Must comply with Euro 6d (and future Euro 7) regulations (Regulation (EU) 2017/1151, 2018/858). Specific requirements are defined in UNECE Regulations (e.g., Reg 83, Reg 101).
- Other Markets: Adhere to local regulations (e.g., China VI, Japan Post New Long-Term, India BS-VI). Requirements often mirror EPA or EU standards.
- Product Safety & Environmental Standards:
- RoHS (EU/China/Asia): Restriction of Hazardous Substances. Ensure valve materials comply with limits on Pb, Cd, Hg, Cr(VI), PBB, PBDE, and DEHP, BBP, DBP, DIBP.
- REACH (EU): Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals. Confirm no Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC) above thresholds are present. Provide Safety Data Sheets (SDS) if required.
- ELV (EU): End-of-Life Vehicles Directive. Requires design for recyclability and declaration of hazardous substances.
- Conflict Minerals (US Dodd-Frank SEC Rule 1502, EU Conflict Minerals Regulation): Report on the use of Tin, Tantalum, Tungsten, Gold (3TG) sourced from conflict-affected areas if applicable.
- Quality & Traceability:
- IATF 16949: Mandatory automotive quality management system standard. Requires rigorous process control, documentation, and traceability (e.g., lot tracking, serialization if required by OEM).
- OEM-Specific Requirements: Major automakers (e.g., Ford Q1, GM GP-12, VW Formel Q, Toyota TQI) have additional quality, packaging, labeling, and reporting requirements that must be met.
- Export Controls:
- Verify if technology or components are subject to export restrictions (e.g., EAR – Export Administration Regulations, ITAR – International Traffic in Arms Regulations, though rare for standard automotive parts). Obtain necessary licenses for restricted destinations.
H2.2 Logistics & Supply Chain Management
- Packaging:
- Protection: Use static-dissipative or conductive packaging (e.g., pink poly, metallized shielding bags) to prevent electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage to sensitive components (solenoids, sensors). Ensure robust outer packaging (corrugated boxes) for physical protection.
- Containment: Prevent contamination (dust, moisture, oils). Use sealed bags with desiccants if required for humidity control.
- Labeling: Comply with shipping regulations (see H2.3) and include essential information: Part Number, Revision Level, Lot/Batch Number, Quantity, Date Code, Manufacturer, Customer PO Number, Handling Symbols (e.g., ESD-sensitive, fragile).
- Sustainability: Optimize packaging size/weight and use recyclable materials where possible.
- Storage:
- Environment: Store in a clean, dry, temperature-controlled environment (typically 15°C – 30°C, 30% – 70% RH unless specified otherwise). Avoid direct sunlight and sources of heat, vibration, or corrosive fumes.
- ESD Protection: Store within ESD-protected areas (EPAs) using grounded shelving and handling procedures.
- Rotation: Implement FIFO (First-In, First-Out) or FEFO (First-Expired, First-Out) inventory management to prevent age-out of materials or components.
- Segregation: Store compliant vs. non-compliant (e.g., suspect, quarantined) material separately with clear identification.
- Transportation:
- Mode: Primarily Less-Than-Truckload (LTL) or Full Truckload (FTL) for regional, air freight for urgent international, ocean freight for large volumes internationally.
- Handling: Train personnel on ESD-safe handling. Use appropriate material handling equipment (MHE) to prevent dropping or crushing. Secure loads within vehicles.
- Tracking: Utilize shipment tracking (e.g., via carrier portals, TMS) for visibility and timely delivery.
- Cold Chain (Rare): Generally not required unless specific material sensitivity exists.
- Inventory Management:
- Maintain accurate real-time inventory levels (WMS).
- Track lot/batch numbers for full traceability (crucial for recalls and compliance reporting).
- Implement cycle counting and regular audits.
H2.3 Hazardous Materials & Shipping Compliance
- Classification: Purge Canister Vent Valves are typically NOT classified as hazardous materials (dangerous goods) for transport under major regulations (e.g., UN Model Regulations, IATA DGR, IMDG Code, 49 CFR) when empty and packaged for normal distribution.
- Key Points:
- No Pressurized Gas: Valves are shipped in a non-operational state, not pressurized.
- No Significant Hazardous Substances: While containing small amounts of regulated substances (e.g., lead solder under RoHS exemption 7(c)-I, specific plastics), these are generally not present in quantities or forms that trigger dangerous goods classification for the assembled valve.
- Contamination Risk: Valves must be shipped clean and dry. Residual fuel or significant hydrocarbon contamination could potentially classify them as hazardous (e.g., Class 3 Flammable Liquid, UN 1993), but this is highly unlikely for new, manufactured valves.
- Shipping Documentation:
- Bill of Lading (BOL): Standard commercial document.
- Commercial Invoice: Required for international shipments (declares value, description, HS code).
- Packing List: Details contents, weights, dimensions, marks/numbers.
- Certificates: Provide IATF 16949 certification, RoHS/REACH compliance declarations (DoC), and specific test reports (e.g., flow, leak, durability) as required by customers or regulations upon request. NOT typically required on every shipment.
- Safety Data Sheet (SDS): Generally NOT required for the finished valve assembly under GHS/CLP, as it’s not classified as hazardous. An SDS might exist for the materials used in manufacturing, but not for the final product shipped.
- Labeling for Transport: Standard shipping labels (address, handling marks, customer labels) are sufficient. No hazardous material labels (e.g., diamond labels, UN numbers) are required under normal circumstances.
H2.4 Key Actions & Best Practices
- Verify Customer Requirements: Obtain and strictly adhere to the specific packaging, labeling, testing, documentation, and quality requirements of each OEM/customer.
- Maintain Documentation: Keep comprehensive, up-to-date records for compliance (certificates, test reports, RoHS/REACH DoCs, conflict minerals reports, IATF 16949 audit records, lot traceability logs).
- ESD Program: Implement and audit a robust ESD control program throughout the supply chain (manufacturing, warehouse, shipping).
- Supplier Management: Ensure all sub-suppliers (e.g., for solenoids, gaskets, plastics) meet necessary compliance standards (RoHS, REACH, quality).
- Training: Regularly train logistics, warehouse, and quality personnel on handling procedures, ESD safety, and compliance requirements.
- Recall Preparedness: Have a clear process for traceability and rapid recall execution if non-conforming material is identified.
- Regulatory Monitoring: Stay informed about changes in emissions, chemical, safety, and trade regulations globally.
Disclaimer: This guide provides general information. Specific requirements can vary significantly based on the exact valve design, materials, destination country, customer, and regulatory interpretations. Always consult the latest official regulations and customer specifications for definitive compliance.
Conclusion for Sourcing Purge Canister Vent Valve:
After a comprehensive evaluation of suppliers, cost structures, quality standards, and supply chain reliability, sourcing the purge canister vent valve from a qualified manufacturer that meets OEM specifications is both feasible and strategic. Selecting a supplier with ISO/TS 16949 certification, proven experience in automotive emissions components, and strong quality assurance processes ensures compliance with emission regulations and vehicle performance requirements. Additionally, considering total cost of ownership—including unit price, logistics, lead times, and warranty support—enables long-term supply stability and cost efficiency.
In conclusion, by partnering with a reliable supplier that demonstrates technical capability, consistent quality, and responsive service, the procurement of purge canister vent valves can support vehicle reliability, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency across production and after-sales operations. Ongoing supplier performance monitoring and continuous improvement initiatives will further enhance supply chain resilience and product integrity.