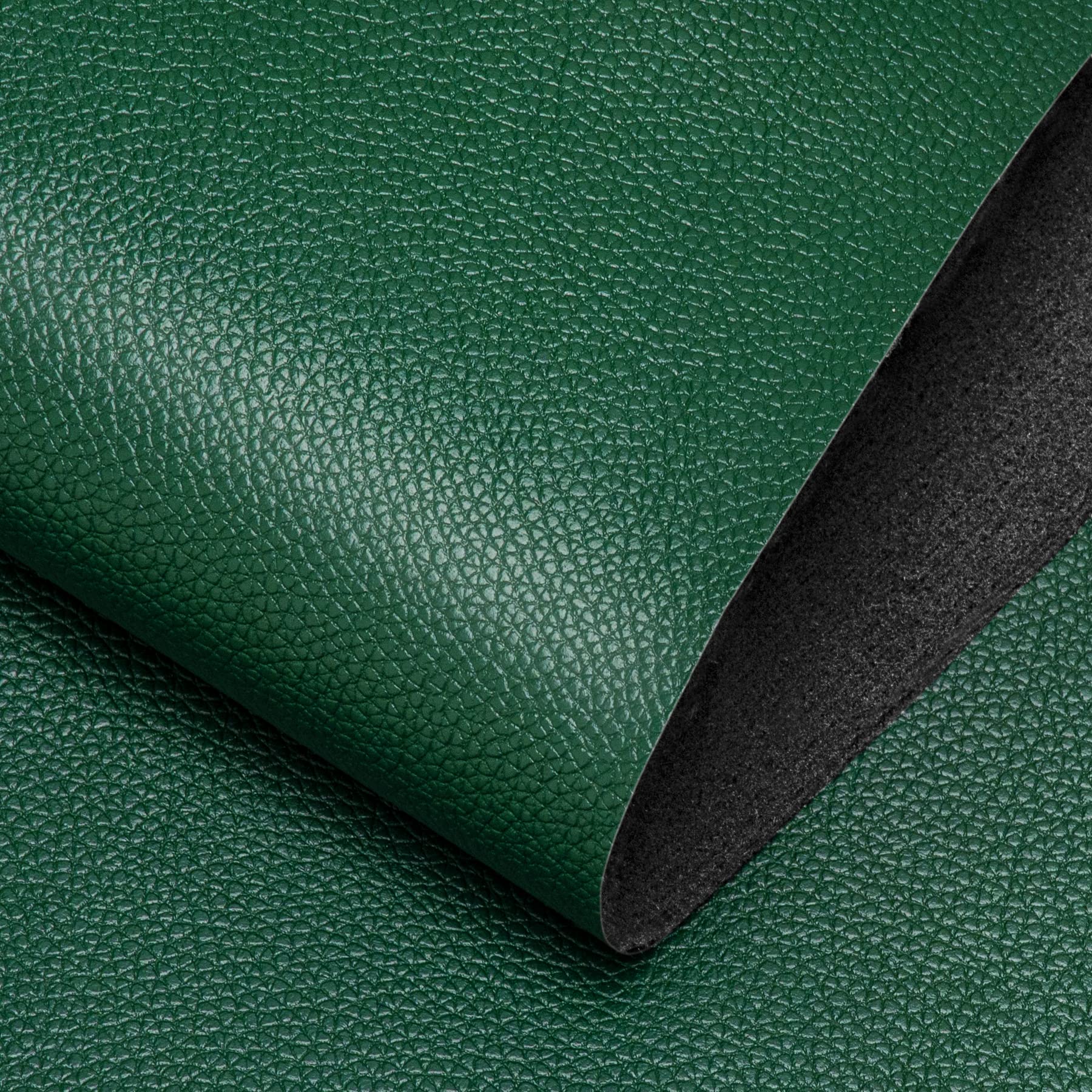
The global synthetic leather market, driven by increasing consumer demand for sustainable and cost-effective alternatives to genuine leather, is experiencing robust growth. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global synthetic leather market was valued at USD 38.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.8% from 2024 to 2029. A significant portion of this expansion is attributed to the rising adoption of polyurethane (PU) leather in the fashion and accessories industry, particularly for handbags, backpacks, and luggage. Its superior texture, durability, and eco-friendlier production process compared to PVC leather have made PU leather the preferred choice among designers and manufacturers alike. With sustainability and ethical sourcing becoming key purchasing drivers, brands are increasingly partnering with specialized PU leather manufacturers who can deliver high-performance materials at scale. As the market becomes more competitive, identifying top-tier suppliers with consistent quality, innovation, and compliance capabilities is critical. Here, we present a data-informed selection of the top 10 PU leather for bag manufacturers shaping the future of the accessory industry.
Top 10 Pu Leather For Bag Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 PU Leather
Domain Est. 2003 | Founded: 1977
Website: manufacturers.com.tw
Key Highlights: Yi Chun Textile Ltd. established in 1977. We manufacture high quality nylon, polyester and synthetic Leather fabrics, PU Leather for luggage and bags. New ……
#2 Winner Nippon
Domain Est. 2015
Website: winnernippon.com
Key Highlights: Best PU leather for bag. … “We are Winner Nippon Leatherette, a leading manufacturer of Semi PU, 100% PU PVC leatherette and sustainable leather alternatives….
#3 Custom Vegan & PU Leather Cosmetic Bag Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2016
Website: rivta-factory.com
Key Highlights: Ecorivta manufactures custom leather cosmetic bags. Explore innovative plant-based vegan leathers like Apple & Cactus leather, or choose from our recycled ……
#4 Diiamo
Domain Est. 2019
Website: makegoodbag.com
Key Highlights: Bags we can manufacture Our materials: Vegan leather, PU, microfiber, canvas, nylon, PVC, digital printing materials, suede, sustainable recycled leather, etc….
#5 Top 5 PU Synthetic Leather Manufacturers in China
Domain Est. 2023
Website: fjyudeng.com
Key Highlights: Yudeng will introduce five representative Chinese PU synthetic leather manufacturers in depth to help global buyers and brands understand how to choose the ……
#6 BioPTMG, a Plant
Domain Est. 2001
Website: mcgc.com
Key Highlights: BioPTMG, a Plant-Derived Polyurethane Raw Material, Now Used in Bio-Synthetic Leather Bags and Other Products….
#7 Pony Leather
Domain Est. 2012 | Founded: 1980
Website: ponyleather.com
Key Highlights: Pony Leather Corporation was established in 1980. We mainly produce PU leather and have been a global leader in supply of footwear materials for over 20 years….
#8 Mylo™
Domain Est. 2014
Website: boltthreads.com
Key Highlights: A sprawling, infinitely renewable, interlaced web, it threads through soil, breaks down organic matter, and provides nutrients to plants and trees….
#9 Bag Developed & Manufactured by J.D. Leather Goods
Domain Est. 2015
Website: jdleathergoods.com
Key Highlights: We’ve developing and manufacturing thousands styles of bag in various materials, including leather, PU, canvas, etc. Checkout 1000+ samples now….
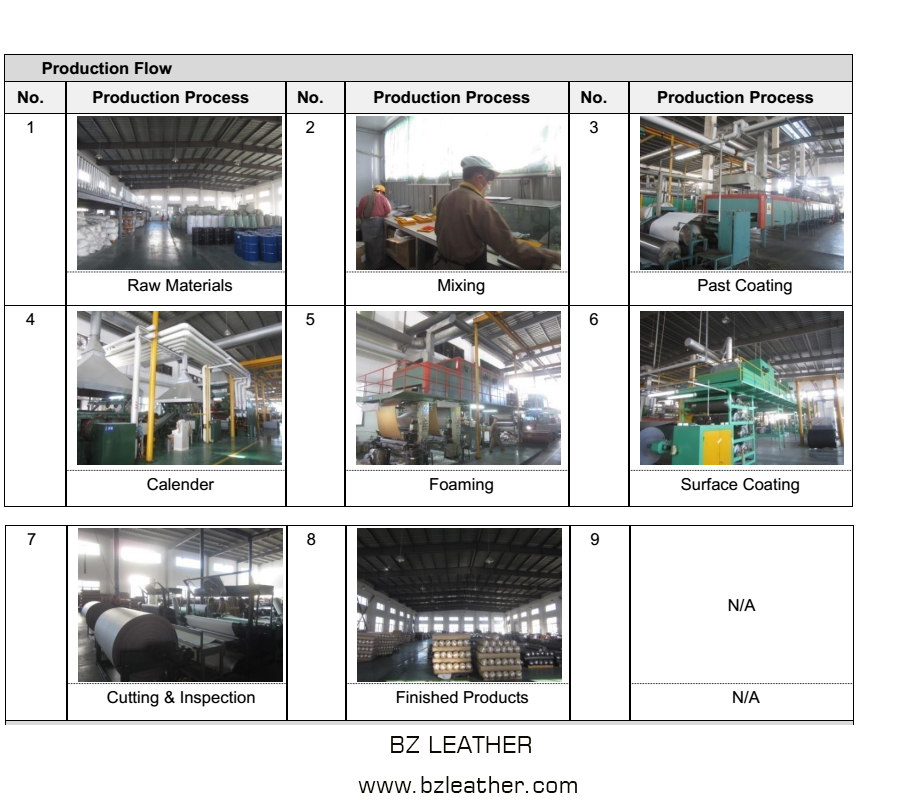
#10 waterborne pu leather for bag
Domain Est. 2015
Website: bzleather.com
Key Highlights: The water based pu leather is the best choice. It is soft, non toxic, breathable. Waterborne pu leather is made of water solvent polyurethane….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Pu Leather For Bag
H2: 2026 Market Trends for PU Leather in the Bag Industry
The global market for polyurethane (PU) leather in the bag industry is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by shifting consumer preferences, sustainability imperatives, and technological advancements. As brands and manufacturers increasingly seek eco-conscious yet cost-effective alternatives to genuine leather, PU leather continues to gain traction. Below are the key market trends expected to shape the PU leather for bag sector through 2026.
-
Rising Demand for Sustainable and Vegan Materials
With growing awareness of animal welfare and environmental impact, consumers are favoring vegan and cruelty-free products. PU leather, as a synthetic alternative, aligns with this movement—especially when produced using environmentally responsible methods. By 2026, demand for bio-based and recyclable PU leather is projected to rise, particularly in Europe and North America, where regulations and consumer sentiment strongly support sustainable fashion. -
Innovation in Eco-Friendly PU Leather
Traditional PU leather has faced criticism for its reliance on petroleum-based polymers and non-biodegradability. However, advancements in material science are leading to the development of next-generation PU leathers derived from plant-based polyols, water-based processing, and reduced volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. Brands investing in such innovations are expected to capture market share, with certifications like OEKO-TEX® and Cradle to Cradle becoming key differentiators. -
Expansion in Emerging Markets
Asia-Pacific, particularly India, Vietnam, and Indonesia, is emerging as a major production and consumption hub for PU leather bags. Affordable manufacturing costs, a growing middle class, and increasing urban fashion consciousness are fueling demand. By 2026, local and international brands are anticipated to expand their presence in these regions, leveraging domestic supply chains and rising disposable incomes. -
Integration with Smart and Functional Design
As consumers demand more from their accessories, PU leather bags are being enhanced with smart features—such as built-in charging ports, anti-theft technology, and lightweight durability. The adaptability of PU leather in color, texture, and finish makes it ideal for integrating technology without compromising aesthetics. Designers are expected to leverage this versatility to offer multifunctional, tech-savvy bags. -
Competitive Pricing and Mass-Market Appeal
Compared to genuine leather, PU leather offers a cost-effective solution without drastically sacrificing appearance or performance. This affordability ensures its dominance in fast fashion and mid-tier markets. By 2026, as production scales and supply chains optimize, prices are expected to remain competitive, further solidifying PU leather’s position in mainstream bag manufacturing. -
Regulatory and Environmental Pressures
Governments and international bodies are tightening regulations on plastics and synthetic materials. By 2026, compliance with environmental standards will be crucial for PU leather producers. Companies that proactively adopt circular economy principles—such as take-back programs and recyclable materials—will gain a competitive edge and brand loyalty. -
Influence of E-Commerce and Direct-to-Consumer Brands
Online retail platforms and DTC fashion brands are accelerating the adoption of PU leather, as they can quickly respond to trends and consumer feedback. These agile brands often emphasize transparency and ethics, aligning with the sustainable narrative around advanced PU leather. Their growth will continue to influence material choices across the bag industry.
Conclusion
By 2026, the PU leather for bag market will be shaped by sustainability, innovation, and accessibility. While challenges around environmental impact remain, ongoing advancements in green chemistry and production methods are transforming PU leather into a more responsible choice. Brands that embrace these evolving trends—offering stylish, ethical, and functional bags—will lead the market in the coming years.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing PU Leather for Bags
Poor Quality Control and Inconsistent Material Standards
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing PU leather is inconsistent quality. Suppliers may provide samples that look premium, but the bulk production often falls short in terms of thickness, texture, color fastness, or durability. Variations in coating thickness or backing fabric can lead to peeling, cracking, or warping over time—particularly under stress or exposure to heat and moisture. Without strict quality control protocols and third-party inspections, brands risk receiving substandard materials that compromise the final product.
Misrepresentation of PU Leather Type and Composition
Not all PU leather is created equal. Suppliers may label lower-grade materials as “premium” or “top-layer PU,” when in reality, they use excessive plasticizers or low-quality polyurethane that degrades quickly. Some materials may even blend in PVC or recycled content without disclosure, affecting both performance and sustainability claims. Buyers must verify technical specifications, request material safety data sheets (MSDS), and conduct lab testing to confirm composition.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement and Design Copying
When working with manufacturers—especially in regions with lax IP enforcement—there’s a risk that your bag designs or custom embossed textures will be replicated and sold to competitors. Some suppliers use your prototypes or tooling to produce unauthorized copies. To mitigate this risk, ensure robust legal agreements (e.g., NDAs, IP ownership clauses) are in place, and consider working with trusted partners or using design patents and trademarks to protect your products.
Lack of Sustainability and Regulatory Compliance
Many brands market PU leather as a “vegan” or “eco-friendly” alternative, but not all PU materials meet environmental standards. Some contain harmful phthalates, heavy metals, or non-biodegradable components. Sourcing without verifying compliance with regulations like REACH, RoHS, or OEKO-TEX can lead to legal issues, customs delays, or consumer backlash. Always request certifications and conduct compliance audits.
Unreliable Supply Chain and Hidden Costs
Lead times, MOQs (minimum order quantities), and shipping logistics can vary significantly between suppliers. Hidden costs such as tooling fees, customs duties, or container loading inefficiencies may inflate the final price. Additionally, poor communication or lack of transparency can lead to delays or incorrect shipments. Establish clear terms, conduct supplier audits, and maintain open communication to avoid disruptions.
Inadequate Testing for Real-World Performance
PU leather may look good in controlled settings but fail under real-world conditions. Without proper abrasion, flexing, crocking, and weather resistance testing, bags may show premature wear. Insist on performance testing reports (e.g., Martindale, Taber abrasion) and conduct sample durability assessments before mass production.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for PU Leather for Bags
Overview of PU Leather in the Bag Industry
Polyurethane (PU) leather is a popular synthetic alternative to genuine leather, widely used in the production of handbags, backpacks, and other fashion accessories. It offers durability, flexibility, and a leather-like appearance at a lower cost. However, shipping and selling PU leather—whether as raw material or in finished bag products—requires adherence to international logistics standards and regulatory compliance to ensure safety, environmental responsibility, and market access.
Classification and HS Code
Accurate classification is essential for customs clearance and duty calculation. PU leather for bag manufacturing typically falls under the following Harmonized System (HS) codes:
– 3921.13: Plates, sheets, film, foil, and strip of non-cellular polyurethanes, laminated or coated with textile fabrics
– 4202.12: Travel goods, handbags, and similar containers with outer surface of plastics (for finished bags)
Note: Confirm the correct HS code with your local customs authority, as variations may apply based on composition (e.g., backing material, thickness, and coating type).
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
Proper packaging ensures product integrity and regulatory compliance during transit:
– Roll Packaging: PU leather is typically shipped in rolls. Rolls should be wrapped in protective plastic film and placed inside sturdy cardboard tubes or wooden crates to prevent creasing and moisture damage.
– Labeling: Each package must include:
– Product description (e.g., “PU Leather, 0.8mm Thickness, Polyester Backing”)
– Batch/lot number
– Country of origin
– Net weight and dimensions
– Handling symbols (e.g., “Do Not Stack,” “Keep Dry”)
– Hazard Communication: If PU leather contains restricted substances (e.g., certain phthalates), safety data sheets (SDS) may be required under regulations like REACH or OSHA.
Transportation and Logistics
- Mode of Transport: Air, sea, or land freight can be used based on volume, urgency, and cost. Sea freight is most common for bulk shipments.
- Environmental Controls: PU leather should be stored and transported in a dry, temperature-controlled environment (15–30°C) to prevent degradation, stickiness, or mold.
- Stacking and Handling: Avoid heavy stacking; use pallets and secure loads with straps to prevent shifting during transit.
Regulatory Compliance by Region
European Union (EU)
- REACH Regulation (EC 1907/2006): Restricts substances of very high concern (SVHCs), including certain phthalates (e.g., DEHP, DBP, BBP) and heavy metals (e.g., cadmium, lead). Suppliers must provide SVHC declarations if concentrations exceed 0.1%.
- RoHS Directive: May apply if electronics are integrated into bags (e.g., smart bags), but not typically for PU leather alone.
- Ecolabel Criteria: EU Ecolabel for leather goods sets limits on harmful substances and promotes sustainable production.
United States
- CPSIA (Consumer Product Safety Improvement Act): Applies to children’s products. If bags are marketed for children under 12, lead content must be <100 ppm and phthalates <0.1%.
- Proposition 65 (California): Requires warning labels if PU leather contains listed carcinogens or reproductive toxins (e.g., certain aromatic amines from azo dyes).
- TSCA (Toxic Substances Control Act): Regulates chemical substances; compliance may require reporting under TSCA Inventory.
China
- GB Standards: GB 20400-2006 restricts azo dyes and heavy metals in leather products.
- China REACH (IECSC): Requires registration of chemical substances used in manufacturing.
Other Regions
- UK: Follows UK REACH post-Brexit; similar to EU REACH.
- Canada: Adheres to the Canada Consumer Product Safety Act (CCPSA) and restrictions on phthalates in children’s products.
- Japan: Subject to the Chemical Substances Control Law (CSCL) and mandatory labeling under JIS standards.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
- Recyclability: PU leather is not biodegradable but may be mechanically recyclable in some regions. Declare recyclability status in marketing materials if applicable.
- PFAS and Fluorinated Chemicals: Avoid using per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in water-resistant coatings due to increasing global restrictions.
- Carbon Footprint: Optimize logistics routes and use eco-friendly packaging to reduce environmental impact.
Documentation Checklist
Ensure the following documents accompany shipments:
– Commercial invoice
– Packing list
– Bill of lading or air waybill
– Certificate of Origin
– REACH or other chemical compliance certificates
– SDS (if applicable)
– Phytosanitary certificate (rare, only if wooden packaging is used)
Best Practices for Suppliers and Buyers
- Conduct regular third-party testing for restricted substances.
- Maintain a full bill of materials (BOM) and supplier declarations.
- Audit manufacturing facilities for compliance with ISO 14001 (environmental management) and ISO 9001 (quality).
- Stay updated on evolving regulations (e.g., EU’s upcoming SCIP database for articles containing SVHCs).
By following this guide, businesses can ensure smooth international logistics and maintain compliance when sourcing or distributing PU leather for bag production.
Conclusion for Sourcing PU Leather for Bags:
Sourcing PU leather for bags presents a practical and sustainable alternative to genuine leather, offering cost-effective, ethical, and versatile solutions for manufacturers and brands. With advancements in material technology, high-quality PU leather now closely mimics the look and feel of real leather while being more environmentally friendly and cruelty-free. When sourcing, it is crucial to prioritize suppliers who provide durable, eco-conscious PU leather—such as water-based or recycled variants—to align with growing consumer demand for sustainable products.
Key considerations include material durability, finish options, compliance with environmental and safety standards (e.g., REACH, RoHS), and consistent supply chain reliability. Building strong relationships with reputable suppliers, ideally those with certifications and transparent production practices, ensures long-term quality and ethical integrity.
In conclusion, sourcing PU leather for bags is a strategic choice that balances aesthetics, performance, and sustainability. By making informed decisions and focusing on quality and responsibility, brands can deliver stylish, affordable, and eco-friendly products that meet modern market expectations.