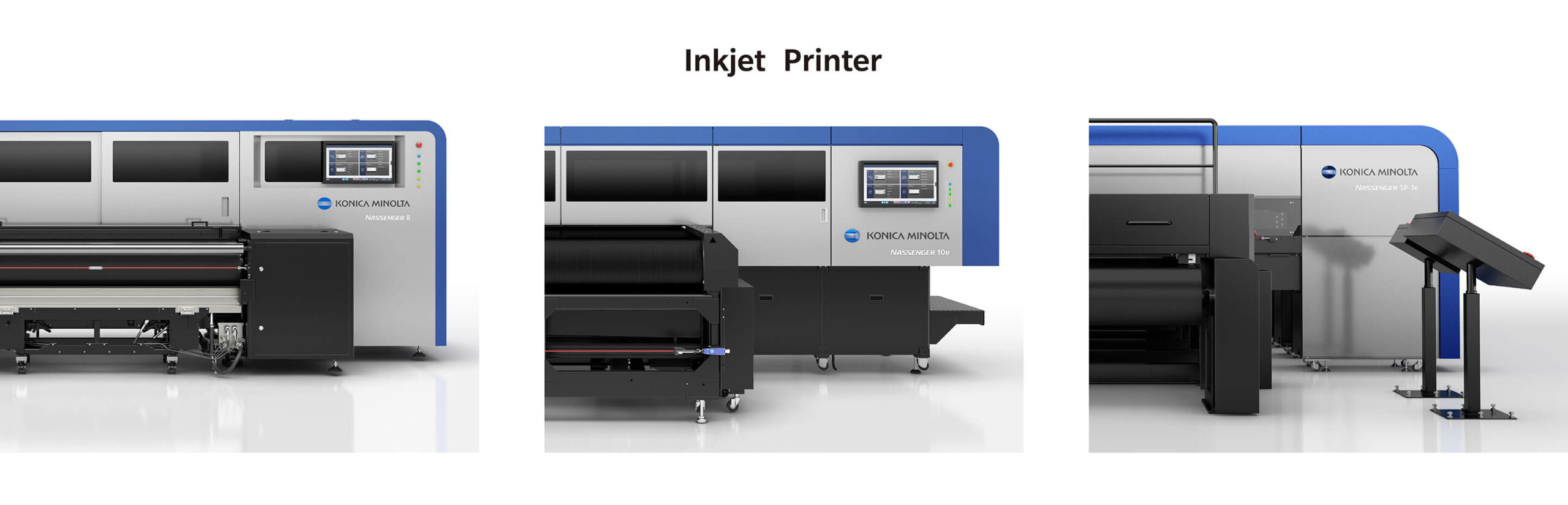
The global textile printing machine market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for sustainable, high-speed, and digital printing technologies across the fashion, home textiles, and technical fabrics sectors. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 2.56 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.8% from 2024 to 2029. This expansion is further supported by Grand View Research, which highlights increasing adoption of digital textile printing due to its lower water consumption, reduced waste, and ability to support on-demand manufacturing models. As brands prioritize customization and faster time-to-market, leading manufacturers are investing heavily in automation, AI integration, and eco-friendly inks. Against this backdrop, innovation in printing textile machines has become a competitive imperative. The following list highlights the top 10 manufacturers shaping the industry through technological advancement, global reach, and scalable solutions that meet evolving market demands.
Top 10 Printing Textile Machine Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Mimaki Global
Domain Est. 2000
Website: mimaki.com
Key Highlights: Mimaki Engineering Co., Ltd., a global industry leader and manufacturer of wide-format inkjet printers, cutting plotters / vinyl cutters, 3D printers, ……
#2 EFI Reggiani Digital Textile Printers
Domain Est. 1989
Website: efi.com
Key Highlights: Our industry-leading scan and single-pass printers offer cutting-edge technology for a wide range of fabric and paper printing applications….
#3 Inkjet Textile Printer-Products-Industrial Inkjet
Domain Est. 2003
Website: konicaminolta.com
Key Highlights: Konica Minolta is a leading supplier of industrial inkjet printheads, inks and textile printer to commercial printing and industrial manufacturing markets….
#4 ROQ International
Domain Est. 2014
Website: roqinternational.com
Key Highlights: ROQ is a European industrial company producing silkscreen and digital printing, folding and packaging machines for textile and other industries….
#5 Textile printing
Domain Est. 2016
Website: hanglorygroup.com
Key Highlights: Direct to Fabric Printer. Large Format Inkjet Printer. Max. Production: 2100+ m²/hr. Accommodates a maximum 1.8m printing width….
#6 Faster, More Elegant Textile Printing
Domain Est. 2022
Website: corporate.epson
Key Highlights: Fabric printed with an Epson digital direct-to-fabric printer. The colors are strikingly vivid and the softness of the fabric is conveyed. “Epson is, after all, ……
#7 Fabric Printers
Domain Est. 1986
Website: hp.com
Key Highlights: HP textile printers provide vibrancy and color consistency across prints and printers to deliver high quality, professional looking results each and every time….
#8 Monna Lisa ® Direct
Domain Est. 1991
Website: epson.com
Key Highlights: The ML-8000 packs the power and performance of the latest world-class Epson inkjet printing and manufacturing technologies into a single package….
#9 Digital Printing Machines for Textile and Paper
Domain Est. 2004
Website: msitaly.com
Key Highlights: The MS knowledge and experience allow us to develop innovative products for the demanding and ever-changing market of digital textile printing….
#10 SPGPrints
Domain Est. 2007
Website: spgprints.com
Key Highlights: SPGPrints is an authority in textile printing, dedicated to bringing colour to the world. Our unique rotary screen printing concept allowed us to move beyond ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Printing Textile Machine
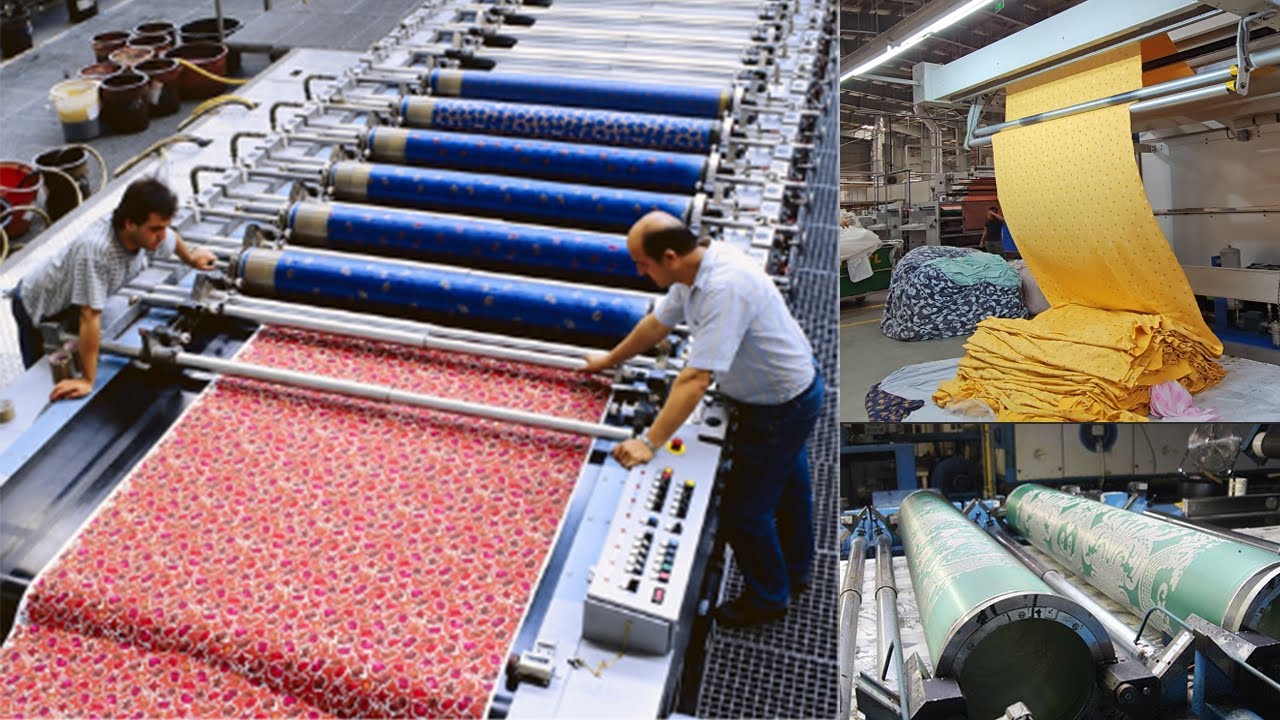

2026 Market Trends for Printing Textile Machines
The global textile printing machinery market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological innovation, sustainability demands, and shifting consumer behaviors. Here are the key trends shaping the industry:
Digital Transformation Accelerates Dominance
Digital textile printing machines are expected to capture an even larger share of the market by 2026. Growth will be fueled by the rising demand for short-run, customizable, and on-demand production, particularly in fast fashion and personalized apparel. Advancements in inkjet technology—such as higher print speeds, improved color consistency, and enhanced fabric compatibility—will make digital printing more competitive with traditional methods like rotary screen printing, even for medium to large volumes.
Sustainability Becomes a Core Competitive Advantage
Environmental regulations and consumer awareness are pushing sustainability to the forefront. Printing machinery manufacturers will increasingly focus on developing waterless printing systems, energy-efficient drying and curing technologies, and machines compatible with eco-friendly inks (e.g., water-based, pigment, and bio-based inks). Closed-loop water recycling systems and reduced chemical usage will be key selling points, especially in regions with strict environmental standards such as the EU and North America.
Integration of Smart Manufacturing and AI
By 2026, Industry 4.0 integration will be standard in high-end textile printing machines. Features such as IoT-enabled monitoring, predictive maintenance, real-time quality control using AI-powered vision systems, and seamless integration with enterprise resource planning (ERP) and product lifecycle management (PLM) software will enhance operational efficiency and reduce downtime. Automation in roll handling, ink loading, and color matching will further streamline production.
Demand for Hybrid and Multi-Substrate Capabilities
Printers are seeking versatile machines that can handle a wide range of fabrics—including natural fibers like cotton and silk, synthetics like polyester, and emerging bio-based textiles. Hybrid printing systems capable of both direct-to-fabric and sublimation printing will gain traction, allowing manufacturers to serve diverse market segments without investing in multiple dedicated machines.
Regional Shifts and Emerging Markets
While Europe and North America remain strong markets due to high adoption of digital printing and sustainability initiatives, Asia-Pacific—particularly India, Vietnam, and Bangladesh—will see robust growth. These regions are investing in modernizing textile infrastructure, driven by rising domestic consumption, export demand, and government incentives. Local manufacturing of printing machines is also expected to increase, reducing costs and lead times.
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Buyers will increasingly evaluate printing machines based on long-term operational efficiency rather than just upfront cost. Factors such as ink consumption efficiency, maintenance requirements, downtime reduction, and energy usage will heavily influence purchasing decisions. Machine suppliers offering comprehensive service packages, remote support, and lifecycle management solutions will gain a competitive edge.
In summary, the 2026 textile printing machine market will be defined by digitalization, sustainability, intelligence, and flexibility. Manufacturers that innovate in these areas will be best positioned to meet evolving industry demands and capture growth opportunities.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Printing Textile Machines (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing printing textile machines from international suppliers, particularly in cost-competitive markets, can present significant challenges related to quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to operational disruptions, financial losses, and legal complications. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Inadequate Quality Verification
Many buyers rely solely on supplier claims or product brochures without conducting independent quality assessments. This can result in receiving machines that fail to meet performance, durability, or safety standards. Machines may have substandard components, poor calibration, or inconsistent print quality, leading to high defect rates and production downtime.
Lack of On-Site Factory Audits
Skipping on-site inspections increases the risk of partnering with unqualified or fraudulent manufacturers. Without verifying the factory’s production capabilities, quality control processes, and working conditions, buyers may end up with unreliable equipment or face supply chain instability.
Insufficient Technical Specifications and Testing Protocols
Vague or incomplete technical documentation can lead to misunderstandings about machine capabilities. Buyers should insist on detailed specifications, performance benchmarks, and sample testing under real-world conditions before finalizing purchases. Failure to do so may result in machines that cannot handle required production volumes or fabric types.
Ignoring After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
High-quality printing machines require regular maintenance and timely access to spare parts. Sourcing from suppliers with limited or no local support can lead to extended machine downtimes. Ensure service agreements, technician training, and spare parts logistics are clearly defined and contractually guaranteed.
Overlooking Intellectual Property Risks
Many low-cost suppliers replicate patented technologies or use counterfeit software without authorization. Purchasing such machines can expose buyers to IP infringement claims, especially when operating in regions with strong IP enforcement (e.g., EU, USA). This may result in legal action, equipment seizure, or reputational damage.
Using Machines with Unauthorized Software or Firmware
Some suppliers install pirated or reverse-engineered control software to cut costs. This not only violates software licenses but also poses cybersecurity risks and limits future upgrades or technical support. Always verify software authenticity and licensing compliance.
Failure to Conduct IP Due Diligence
Buyers should investigate whether the machine design or technology infringes on existing patents. Conducting a patent landscape analysis or working with legal experts can help avoid costly litigation and ensure freedom to operate in target markets.
Absence of IP Clauses in Contracts
Supplier agreements should explicitly address IP ownership, warranty against infringement, and liability in case of IP disputes. Without these protections, buyers may bear the legal and financial burden of third-party claims.
Assuming Compliance with International Standards
Not all machines meet international safety, environmental, or electromagnetic compatibility standards (e.g., CE, UL, ISO). Assuming compliance without verified certifications can lead to import rejections, regulatory fines, or workplace safety issues.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls—through rigorous supplier vetting, independent quality testing, comprehensive contracts, and IP due diligence—buyers can significantly reduce risks and ensure a reliable, legally sound investment in textile printing machinery.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Printing Textile Machines
Overview
Transporting printing textile machines requires careful planning to ensure equipment arrives undamaged and all regulatory requirements are met. These machines are often large, heavy, and sensitive to environmental conditions. This guide outlines essential logistics and compliance steps for domestic and international shipments.
Packaging Requirements
- Use custom wooden crates with cushioning materials (e.g., foam, bubble wrap) to protect delicate components.
- Secure all moving parts and print heads with locking mechanisms or protective caps.
- Include moisture-absorbing desiccants in enclosed packaging to prevent condensation.
- Clearly label packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Do Not Stack” indicators.
- Seal electrical panels and control units with waterproof covers to prevent dust and moisture ingress.
Transportation Modes
- Road: Ideal for regional or domestic delivery. Use enclosed, climate-controlled trucks to protect against weather and debris.
- Sea Freight: Most cost-effective for international shipments. Use 20ft or 40ft containers; secure the machine with bracing and anti-sway straps. Consider container desiccants for long voyages.
- Air Freight: Faster but more expensive; suitable for urgent deliveries. Confirm airline weight and size limits; disassemble large units if needed.
Handling & Installation
- Use forklifts or cranes with soft slings for unloading—never drag or tilt the machine.
- Ensure receiving site has adequate space, power supply (voltage, phase, grounding), and floor strength.
- Retain all packaging until installation is complete in case of return or re-shipping.
- Follow manufacturer’s setup manual; schedule technician support if required.
Regulatory Compliance
- Export Controls: Verify if the machine contains dual-use technology (e.g., precision controllers) subject to export regulations (e.g., EAR in the U.S.).
- Customs Documentation: Prepare commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading/air waybill, and certificate of origin. Include HS code (typically 8443.59 for textile printing machinery).
- Import Duties & Taxes: Research destination country’s tariffs, VAT, and import permits. Some countries require pre-shipment inspection (PSI).
- CE Marking (EU): Ensure machine complies with Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC, EMC Directive, and Low Voltage Directive. Maintain Declaration of Conformity.
- RoHS & REACH (EU): Confirm machine components comply with hazardous substance restrictions.
- Electrical Safety Certifications: Provide local certifications (e.g., UL for U.S., CCC for China) if required.
Environmental & Safety Standards
- Avoid transporting during extreme temperatures or high humidity unless climate-controlled.
- Ensure compliance with local noise and emission standards at the installation site.
- Provide safety data sheets (SDS) for inks, solvents, or cleaning agents shipped with the machine.
Insurance
- Obtain comprehensive cargo insurance covering damage, loss, theft, and delays.
- Specify full replacement value and include coverage during loading, transit, and unloading.
- Verify insurer’s policy on high-value machinery and exclusions (e.g., improper packaging).
Documentation Checklist
- Commercial Invoice
- Packing List
- Bill of Lading / Air Waybill
- Certificate of Origin
- Export/Import Licenses (if applicable)
- CE/UL/CCC Certifications
- Technical Manual & Warranty
- Insurance Certificate
Post-Delivery Actions
- Inspect machine immediately upon arrival for damage; document and report issues to carrier and insurer.
- Retain all shipping records for at least five years for audit and warranty purposes.
- Register equipment with local authorities if required (e.g., for environmental compliance).
By following this guide, businesses can ensure the secure, compliant, and efficient delivery of printing textile machines across global supply chains.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Printing Textile Machine
In conclusion, sourcing a printing textile machine is a strategic decision that requires careful evaluation of various technical, operational, financial, and long-term business factors. The selection process should align with the specific production needs, fabric types, print complexity, volume requirements, and sustainability goals of the business.
After assessing different machine types—such as screen printing, rotary, flatbed, and digital direct-to-textile (DTG or DTF) printers—it becomes evident that digital textile printing machines offer superior flexibility, faster turnaround times, and reduced waste, making them ideal for customization and small to medium production runs. However, high-volume manufacturers may still benefit from traditional rotary or screen printing systems due to their speed and cost-efficiency at scale.
Key considerations such as machine reliability, vendor reputation, after-sales support, training, and spare parts availability are critical to ensuring smooth integration and long-term performance. Additionally, evaluating energy consumption, environmental impact, and compliance with industry standards contributes to a more sustainable and responsible operation.
Ultimately, investing in the right textile printing machine enhances production efficiency, improves product quality, and strengthens competitive advantage in a rapidly evolving market. A well-informed sourcing decision, supported by thorough research and supplier engagement, will lay the foundation for innovation, scalability, and long-term success in the textile printing industry.