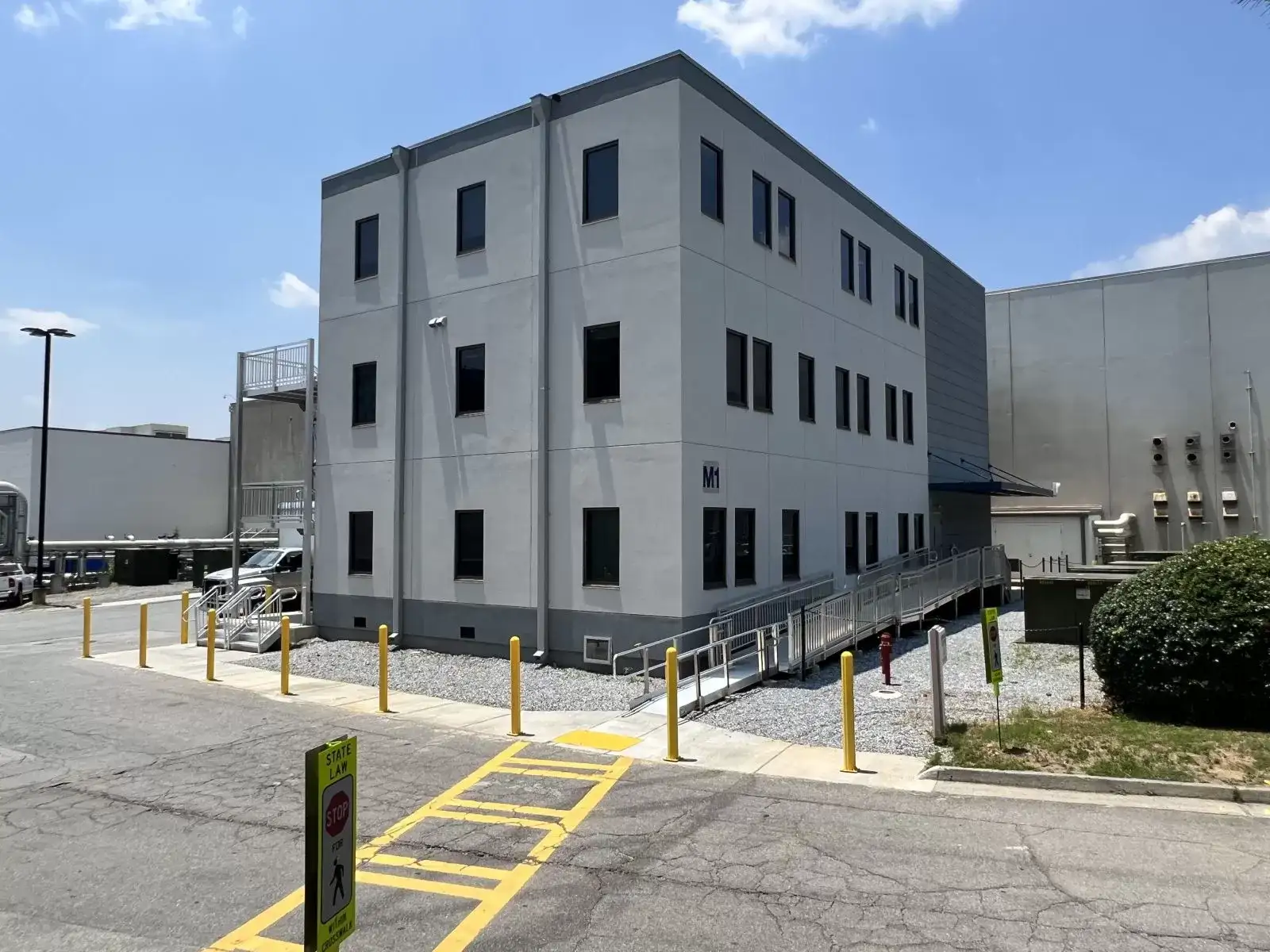
The global prefabricated buildings market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by rising demand for rapid construction, cost efficiency, and sustainable building practices. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the prefabricated building market was valued at USD 127.86 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2024 to 2029. This surge is further supported by urbanization, infrastructure development, and the need for temporary or modular workspaces across industries such as construction, education, healthcare, and energy. Within this growing sector, prefabricated office buildings have emerged as a key solution for businesses seeking scalable, flexible, and eco-friendly work environments. As demand intensifies, a number of manufacturers have distinguished themselves through innovation, quality, and global reach. Based on market presence, production capacity, and customer reviews, the following list highlights the top 10 prefabricated office building manufacturers shaping the future of modular construction.
Top 10 Prefabricated Office Building Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
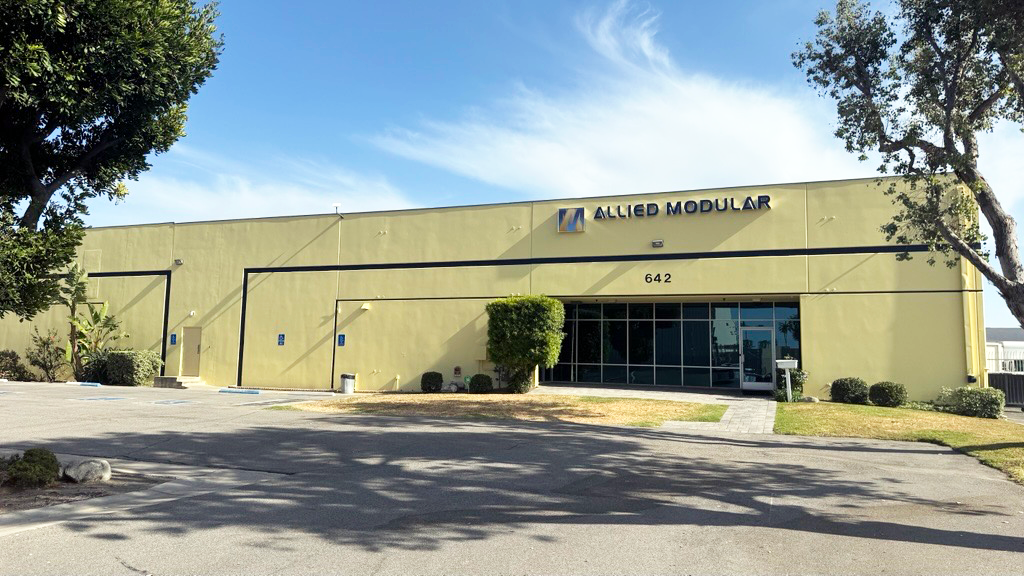
#1 Allied Modular Building Systems
Domain Est. 1997
Website: alliedmodular.com
Key Highlights: Top-rated manufacturer of modular buildings, Modular offices, Guardhouses, Cleanrooms and other types of prefab Buildings….
#2 Prefab Offices
Domain Est. 2004
Website: panelbuilt.com
Key Highlights: Panel Built’s prefab offices provide a fast and efficient solution for expanding workspace in industrial, commercial, and warehouse environments….
#3 Modular Building Systems & Complexes
Domain Est. 1995
Website: willscot.com
Key Highlights: When your business needs a larger modular office space, look to our Modular Spaces or Redi-Plex offering to solve your space needs….
#4 Modular Offices and Inplant Buildings
Domain Est. 1995
Website: portaking.com
Key Highlights: Porta-King’s modular office buildings offer an effective solution for creating space inside all types of manufacturing, distribution and warehouse facilities….
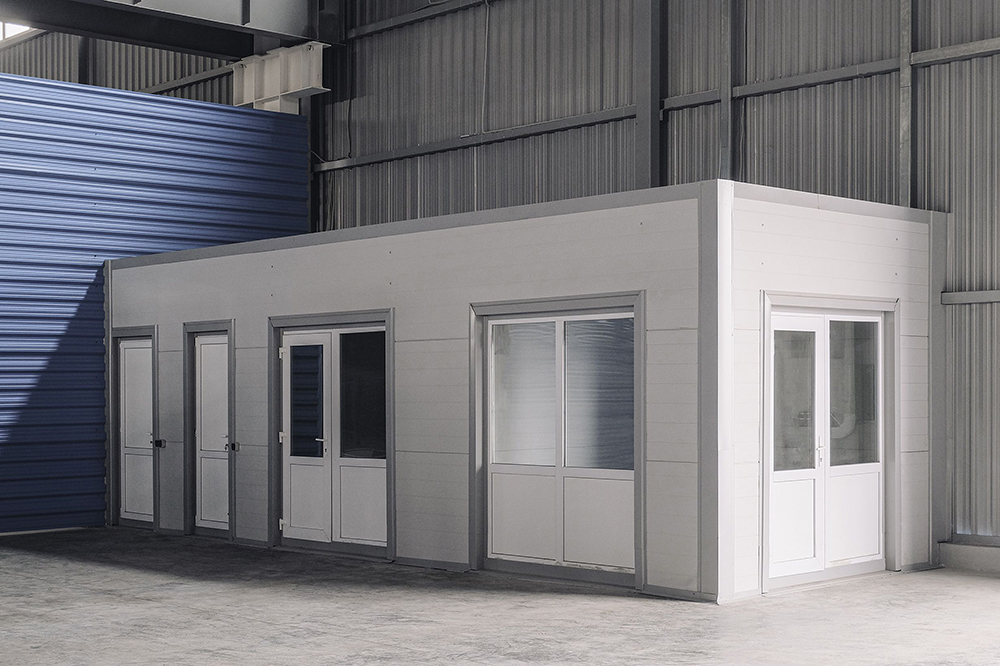
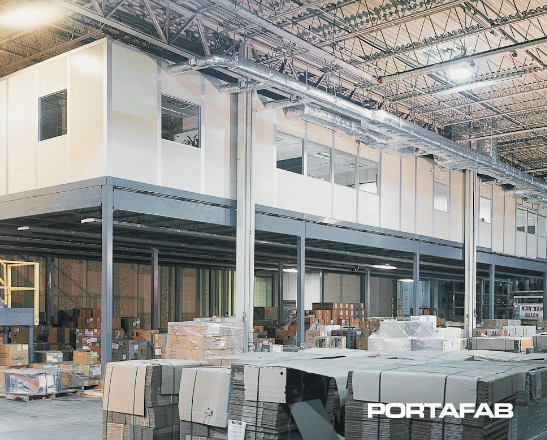
#5 PortaFab
Domain Est. 1997
Website: portafab.com
Key Highlights: PortaFab offers modular building products that are easy to customize, along with expert engineering support and local installation teams….
#6 Modular Office Buildings for Flexible Workspaces
Domain Est. 1997
Website: mobilemodular.com
Key Highlights: Rating 4.8 (319) Discover cost-effective modular office buildings. From single-wide to multi-unit complexes, find the perfect solution for your business needs….
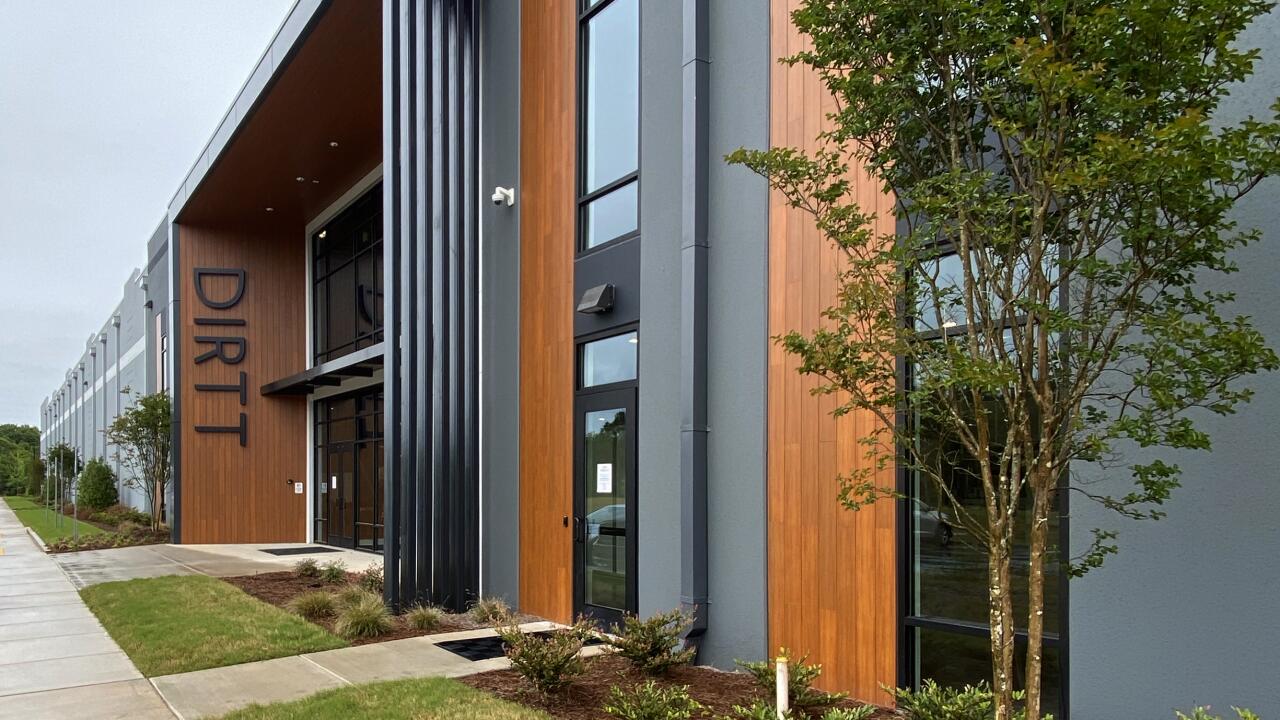
#7 DIRTT Construction Systems
Domain Est. 2003
Website: dirtt.com
Key Highlights: Speed up construction by up to 30% with DIRTT’s modular construction systems. Get accurate, real-time pricing and adaptable solutions for any project….
#8 Triumph Modular
Domain Est. 2005
Website: triumphmodular.com
Key Highlights: Triumph Modular delivers durable, prefabricated buildings for schools, contractors, and businesses. With over 40 years of experience, we provide fast, ……
#9 Modular Genius
Domain Est. 2005
Website: modulargenius.com
Key Highlights: Offering Permanent modular construction and relocatable modular buildings. Modular Genius specializes in both permanent and temporary modular buildings, ……
#10 About BOXX Modular
Domain Est. 2005
Website: boxxmodular.com
Key Highlights: BOXX Modular rents, leases, and sells temporary and permanent modular buildings, including standard buildings ready for immediate delivery and custom-designed ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Prefabricated Office Building

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Prefabricated Office Buildings
The global market for prefabricated office buildings is poised for substantial transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in construction technology, rising demand for sustainable infrastructure, and shifting workplace dynamics. This analysis explores key trends expected to shape the prefabricated office building sector in 2026 under the H2 (second half) outlook.
-
Accelerated Adoption Due to Sustainability Mandates
Environmental regulations and corporate ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals will significantly influence the construction sector in 2026. Prefabricated office buildings, with their reduced material waste, lower carbon footprint, and energy-efficient designs, are increasingly favored. Governments in regions like the EU and North America are expected to enforce stricter sustainability standards, making modular construction a strategic choice for commercial developers. -
Growth in Hybrid and Flexible Work Models
The post-pandemic shift toward hybrid work has redefined office space needs. Companies are opting for smaller, decentralized workspaces or satellite offices—ideal applications for prefabricated buildings. By 2026, modular offices will be increasingly deployed as temporary or scalable solutions in urban peripheries, industrial parks, and remote locations, providing cost-effective and rapidly deployable workspaces. -
Technological Integration and Smart Building Features
Prefabricated office units in 2026 will increasingly integrate IoT (Internet of Things), AI-driven climate control, and energy management systems. Off-site manufacturing allows for seamless embedding of smart technologies during production, ensuring higher precision and compatibility. This trend will enhance operational efficiency and user experience, making modular offices competitive with traditional constructions. -
Expansion in Emerging Markets
While North America and Europe lead in modular construction adoption, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa will see accelerated growth by 2026. Rapid urbanization, infrastructure deficits, and the need for quick deployment in developing business hubs are driving demand. Countries like India, Indonesia, and Nigeria are expected to invest heavily in prefabricated office solutions for industrial zones and tech parks. -
Supply Chain Optimization and Cost Efficiency
By H2 2026, manufacturers will leverage digital twins, BIM (Building Information Modeling), and AI-powered logistics to streamline production and delivery. These advancements will reduce lead times and improve cost predictability. With inflationary pressures still affecting traditional construction, the cost stability of off-site manufacturing will be a key market differentiator. -
Increased Investment and Market Consolidation
The prefabricated office building sector is expected to witness greater involvement from institutional investors and real estate developers. Mergers and acquisitions among modular construction firms will rise as companies scale to meet global demand. This consolidation will improve standardization, quality assurance, and access to capital. -
Regulatory Support and Standardization
Regulatory bodies will introduce clearer codes and certifications for modular construction by 2026, enhancing investor and client confidence. Standardized modules will facilitate easier approvals, insurance, and financing—key enablers for market expansion.
In conclusion, the H2 2026 outlook for prefabricated office buildings is highly positive. Fueled by sustainability, digital innovation, and evolving workplace needs, the sector is transitioning from a niche alternative to a mainstream construction solution. Stakeholders who embrace scalability, smart technology, and green building practices will be best positioned to capitalize on this growth.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Prefabricated Office Buildings: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing prefabricated office buildings offers speed and cost benefits, but buyers must navigate several critical pitfalls—particularly concerning quality control and intellectual property (IP)—to ensure long-term value and legal compliance.
Inconsistent or Substandard Quality
One of the most frequent issues in sourcing prefabricated buildings is inconsistent quality across modules or batches. Since manufacturing occurs off-site, often by third-party fabricators, variations in materials, workmanship, and adherence to specifications can occur. Buyers may receive components that do not meet structural, insulation, or finish standards, leading to on-site delays, rework, or safety concerns.
Lack of Independent Quality Verification
Many suppliers conduct only internal quality checks, which may not be objective or comprehensive. Without third-party inspections or certifications at key production stages (e.g., pre-shipment or during assembly), hidden defects—such as poor welding, inadequate waterproofing, or non-compliant electrical installations—can go unnoticed until after delivery or installation.
Misalignment with Local Building Codes and Standards
Prefabricated units designed in one country may not comply with the building codes, seismic requirements, or energy efficiency standards of the destination market. Suppliers may claim compliance without proper documentation or testing, leading to regulatory rejection, costly modifications, or project delays.
Poor Integration of Building Systems
Electrical, plumbing, HVAC, and data systems must be seamlessly integrated within and between modules. Poor coordination during design or manufacturing can result in mismatched connections, inefficient energy use, or system failures. This is especially problematic when multiple subcontractors are involved without a unified oversight process.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Using design templates or modular systems from suppliers without clear IP ownership can expose buyers to legal risks. Some vendors may reuse or resell designs without proper licensing, or incorporate patented technologies (e.g., connection systems, energy solutions) without authorization. Buyers may unknowingly become liable for IP violations.
Ambiguous Design Ownership and Usage Rights
Contracts often fail to specify who owns the design after customization. Buyers may invest in tailored layouts or branding elements only to discover they cannot reuse, modify, or replicate the design without permission or additional fees. This limits flexibility for future expansions or relocations.
Inadequate Documentation and As-Built Records
Missing or inaccurate technical documentation—such as schematics, material certifications, or maintenance manuals—complicates operations, compliance audits, and future modifications. Without proper as-built records, verifying IP usage or ensuring warranty coverage becomes difficult.
Overreliance on Supplier Representations
Buyers often accept quality claims or IP assurances at face value without independent verification. Due diligence, including site audits, design reviews, and legal checks on IP rights, is essential to mitigate risks but is frequently overlooked in favor of faster procurement timelines.
Addressing these pitfalls requires thorough vetting of suppliers, clear contractual terms on quality benchmarks and IP rights, and engagement of independent experts during design and manufacturing phases.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Prefabricated Office Building
Planning and Site Preparation
Ensure the delivery site is accessible and prepared before shipment. Confirm road dimensions, turning radii, weight limits, and overhead clearance for transport vehicles. Prepare a level, stable foundation or base according to engineering specifications. Coordinate with local authorities for site access permits and temporary laydown areas if required.
Transportation and Delivery
Schedule deliveries during off-peak hours to minimize traffic disruption. Use specialized flatbed or low-boy trailers designed for oversized loads. Secure modules with proper bracing, straps, and corner protectors to prevent shifting or damage. Provide detailed delivery schedules and module sequencing to align with on-site assembly plans.
Import/Export Compliance (if applicable)
Verify customs requirements for cross-border shipments. Prepare accurate documentation, including commercial invoices, packing lists, bill of lading, and certificates of origin. Ensure compliance with international trade regulations (e.g., INCOTERMS). Confirm that modular components meet destination country standards for construction materials and safety.
Building Code and Regulatory Compliance
Design and fabricate modules in accordance with local building codes (e.g., IBC, NFPA, or regional equivalents). Obtain necessary third-party certifications for structural integrity, fire resistance, and energy efficiency. Submit stamped engineering drawings and compliance documentation to local authorities for permitting.
Safety and Handling Protocols
Train personnel in safe lifting and rigging procedures using cranes or forklifts. Use personal protective equipment (PPE) during unloading and assembly. Follow manufacturer guidelines for stacking, storage, and handling to avoid structural deformation or damage to finishes.
Environmental and Sustainability Compliance
Adhere to environmental regulations for material sourcing, emissions, and waste management during fabrication. Ensure insulation, adhesives, and finishes meet VOC (volatile organic compound) standards. Document use of recycled or sustainable materials for green building certification (e.g., LEED, BREEAM).
On-Site Assembly and Integration
Follow the approved assembly sequence and torque specifications. Verify alignment, leveling, and sealing between modules to maintain weatherproofing and structural continuity. Connect utilities (electrical, plumbing, HVAC) per local codes and manufacturer instructions.
Inspections and Occupancy
Schedule required inspections during and after installation (e.g., structural, electrical, fire safety). Address any non-compliance issues promptly. Obtain a Certificate of Occupancy (CO) or equivalent before use. Maintain a complete compliance file including inspection reports, as-built drawings, and operation manuals.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Prefabricated Office Building
Sourcing a prefabricated office building offers a compelling solution for organizations seeking speed, cost-efficiency, sustainability, and flexibility in their workspace development. The off-site construction method significantly reduces construction timelines, minimizes on-site disruptions, and ensures higher quality control through factory-based manufacturing processes. Additionally, prefabricated offices often come with customizable design options, allowing businesses to tailor the space to their specific operational and aesthetic requirements.
From a financial perspective, lower overall project costs, reduced labor expenses, and potential savings in foundation and utility work contribute to a strong return on investment. Moreover, the modular nature of prefabricated buildings supports future scalability—modules can be expanded, reconfigured, or relocated as business needs evolve.
Environmental benefits further enhance the appeal, as many prefab solutions utilize sustainable materials and generate less construction waste. With growing emphasis on green building practices and carbon footprint reduction, prefabricated offices align well with corporate sustainability goals.
In conclusion, sourcing a prefabricated office building is a strategic, forward-thinking choice that balances efficiency, affordability, and adaptability. As technology and design capabilities continue to advance, prefabrication is increasingly becoming the preferred method for modern commercial construction, offering a practical and innovative alternative to traditional building approaches.