The global precision measuring instruments market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for accuracy and quality control across industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and manufacturing. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 8.47 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 11.35 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of approximately 5.0% during the forecast period. This expansion is fueled by technological advancements in digital measurement systems, rising automation in production processes, and stringent regulatory standards requiring high-precision inspections. As manufacturers increasingly adopt smart metrology solutions, including coordinate measuring machines (CMMs), laser scanners, and optical comparators, the role of leading suppliers becomes pivotal in shaping the future of industrial accuracy. In this context, the following nine companies have emerged as key innovators and top manufacturers in the precision measuring instruments sector—setting benchmarks in technology, reliability, and global reach.
Top 9 Precision Measuring Instruments Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Helmut Fischer
Domain Est. 1996
Website: helmut-fischer.com
Key Highlights: High-precision measuring devices for coating thickness measurement, material analysis, nanoindentation and material testing from the technology leader….
#2 Mahr Metrology
Domain Est. 1997
Website: metrology.mahr.com
Key Highlights: As a manufacturer of innovative production metrology, we have been supporting our customers for over 160 years, in the measuring room and in production….
#3 Central Tools Inc.
Domain Est. 1999
Website: centraltools.com
Key Highlights: Central Tools offers automotive mechanics the precision measuring tools including micrometers, indicators, dial gages, calipers, torque products, ……
#4 Innovative measuring instruments
Domain Est. 2014
Website: tesatechnology.com
Key Highlights: TESA MICRO-HITE designed for workshops as well as for laboratories, fill ideally the gap between traditional instruments and sophisticated measuring machines….
#5 Precision instruments
Domain Est. 1995
Website: thk.com
Key Highlights: High-precision LM Guide are used in these devices to provide accuracy, smooth movement and rigidity. Small measuring microscopes. More and more fine machining ……
#6 Mitutoyo America Corporation
Domain Est. 1996
Website: mitutoyo.com
Key Highlights: Mitutoyo America Corporation offers innovative precision measurement solutions with the highest level of quality, precision and expertise….
#7 Precision Measurements and Instruments Corporation
Domain Est. 1997
Website: pmiclab.com
Key Highlights: Precision Measurements and Instruments Corporation is an ISO/IEC 17025 accredited testing laboratory that provides quality test measurements from cryogenic to ……
#8 Starrett Products
Domain Est. 1998
Website: starrett.com
Key Highlights: Discover premium precision measuring tools and cutting solutions including micrometers, calipers, band saw blades and much more. Many American-made since ……
#9 VOGEL GERMANY
Website: vogel-germany.de
Key Highlights: Explore all Vogel Germany precision measuring tools in our main catalogue. Here you will find more than 4,500 articles e.g. for purposes of length measuring and ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Precision Measuring Instruments
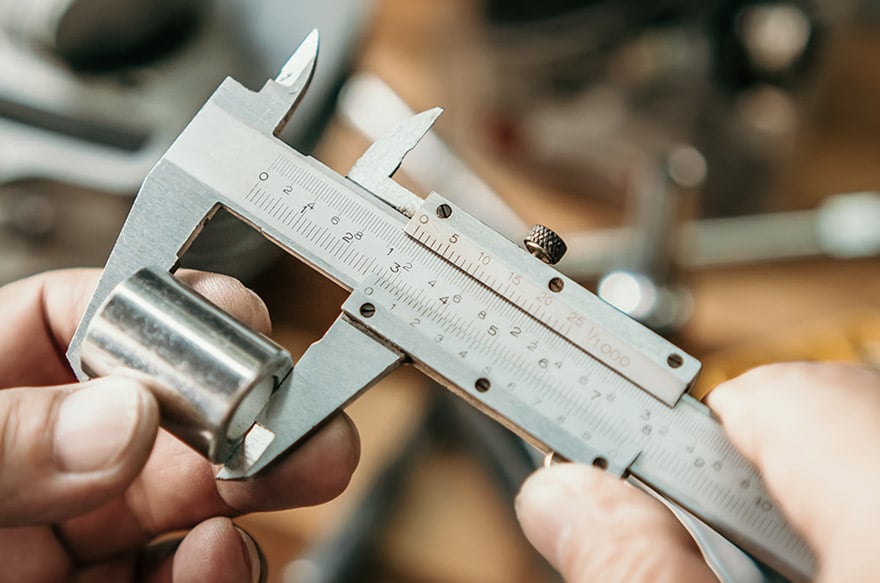

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Precision Measuring Instruments
The global market for precision measuring instruments is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by rapid technological advancements, increasing demand for quality assurance across industries, and evolving manufacturing paradigms. Key trends shaping the market in this period include the integration of smart technologies, expansion in emerging economies, rising automation, and stricter regulatory standards.
1. Integration of Smart and Digital Technologies
By 2026, the adoption of Internet of Things (IoT)-enabled measuring devices is expected to be widespread. Smart sensors, connected metrology tools, and cloud-based data analytics are enhancing real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance in manufacturing processes. Instruments such as coordinate measuring machines (CMMs), laser trackers, and optical comparators are increasingly incorporating AI and machine learning algorithms to improve accuracy and reduce human error.
2. Growth in Automotive and Aerospace Sectors
The automotive and aerospace industries remain major drivers of demand for high-precision instruments. As electric vehicles (EVs) and advanced aerospace components (e.g., turbine blades and composite materials) require tighter tolerances, manufacturers are investing heavily in non-contact measurement systems, 3D scanning, and vision-based inspection technologies.
3. Expansion in Asia-Pacific Markets
Countries such as China, India, and South Korea are witnessing accelerated industrialization and government-backed initiatives in advanced manufacturing (e.g., “Made in China 2025” and “Make in India”). This regional growth is fueling demand for precision instruments, particularly in electronics, semiconductors, and medical device manufacturing.
4. Emphasis on Automation and Industry 4.0
The transition toward Industry 4.0 is compelling manufacturers to integrate automated inspection systems directly into production lines. In 2026, inline metrology solutions—such as robotic-arm-mounted sensors and automated optical inspection (AOI)—are expected to account for a growing share of the market, enabling faster throughput and reduced downtime.
5. Advancements in Portable and Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) Instruments
Portable measurement devices, including handheld 3D scanners and ultrasonic thickness gauges, are gaining traction due to their flexibility and ease of use in field inspections. These tools support quality control in remote or challenging environments, such as oil & gas pipelines and construction sites.
6. Sustainability and Regulatory Compliance
Environmental regulations and quality standards (e.g., ISO 9001, AS9100) are pushing industries to adopt more reliable and traceable measurement practices. Calibration services and instruments with built-in compliance reporting features are becoming essential, particularly in regulated sectors like pharmaceuticals and medical devices.
7. Competitive Landscape and Innovation
Leading players such as Hexagon AB, Mitutoyo Corporation, KEYENCE Corporation, and ZEISS Group are focusing on R&D to launch compact, faster, and more user-friendly instruments. Mergers and partnerships are also on the rise, aimed at expanding product portfolios and geographic reach.
In conclusion, the 2026 precision measuring instruments market will be defined by digitalization, automation, and global industrial growth. Companies that invest in intelligent, scalable, and compliant metrology solutions are likely to gain a competitive edge in this evolving landscape.
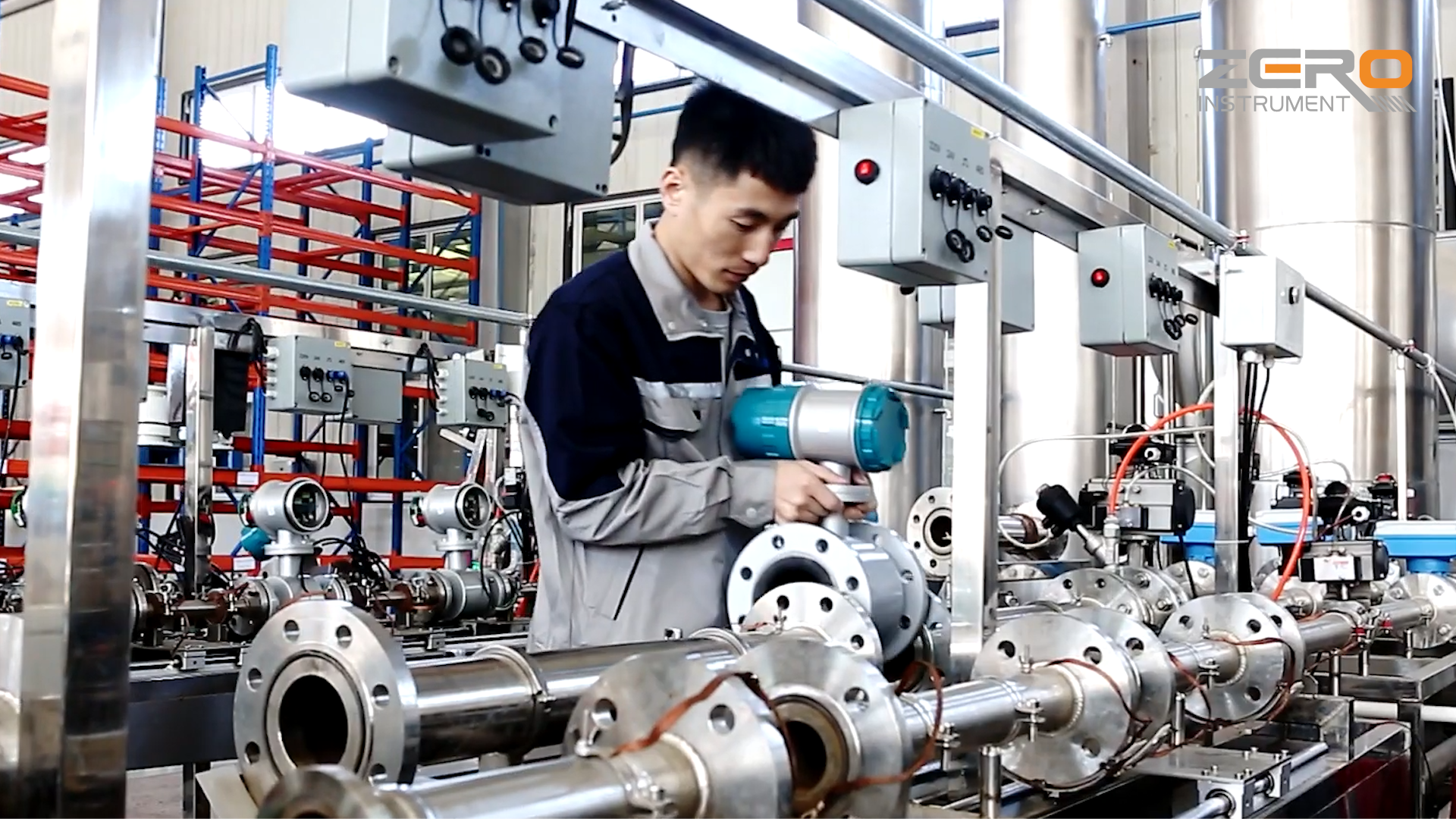

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Precision Measuring Instruments (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing precision measuring instruments demands rigorous attention to detail, as errors can compromise product quality, regulatory compliance, and intellectual property (IP) integrity. Below are key pitfalls to avoid in both quality assurance and IP protection.
Inadequate Supplier Qualification and Due Diligence
Many organizations fail to properly vet suppliers, leading to inconsistent instrument quality. Selecting vendors based solely on price often results in receiving substandard equipment that lacks accuracy, repeatability, or proper calibration documentation. Always verify ISO 17025 accreditation, traceable calibration certificates, and compliance with international standards (e.g., ISO 9001, ANSI, or DIN).
Overlooking Calibration and Traceability
A common quality oversight is neglecting instrument traceability to national or international standards. Without documented, accredited calibration, measurement data cannot be trusted. Instruments lacking proper calibration history may drift over time, producing unreliable results and risking non-compliance during audits or inspections.
Ignoring Long-Term Maintenance and Support
Precision instruments require regular maintenance, recalibration, and technical support. Sourcing from suppliers who don’t offer service agreements or spare parts access can lead to extended downtime and increased total cost of ownership. Ensure service capabilities and response times are clearly defined in procurement contracts.
Compromising on Environmental and Operational Suitability
Instruments must match the environmental conditions (temperature, humidity, vibration) and usage requirements of the application. Selecting a high-precision device unsuited for a factory floor, for example, can lead to premature failure and measurement inaccuracies. Always validate specifications against real-world operating conditions.
Failure to Protect Intellectual Property in Custom Instruments
When sourcing custom-designed or modified measuring systems, companies often neglect IP clauses in contracts. This can result in ambiguous ownership of designs, software, or proprietary algorithms. Always define IP rights explicitly—ensuring your organization retains ownership of custom developments and that suppliers do not reuse designs for competitors.
Risk of Counterfeit or Non-Genuine Equipment
The market includes counterfeit or refurbished instruments misrepresented as new. These pose serious quality and safety risks. Source only from authorized distributors or directly from OEMs, and verify serial numbers and warranty documentation upon delivery.
Insufficient Training and Knowledge Transfer
Even the most accurate instrument is ineffective if operators lack proper training. Overlooking knowledge transfer during procurement can lead to misuse, incorrect data, and accelerated wear. Ensure supplier agreements include comprehensive training and technical documentation.
Poor Documentation and Audit Trail Management
Incomplete or missing documentation—such as calibration reports, user manuals, compliance certificates—undermines quality systems and complicates audits. Require full documentation packages at delivery and maintain secure, accessible records throughout the instrument’s lifecycle.
Avoiding these pitfalls ensures reliable measurements, regulatory compliance, and protection of your organization’s intellectual assets. A strategic sourcing approach combining technical evaluation, legal safeguards, and lifecycle planning is essential for success.
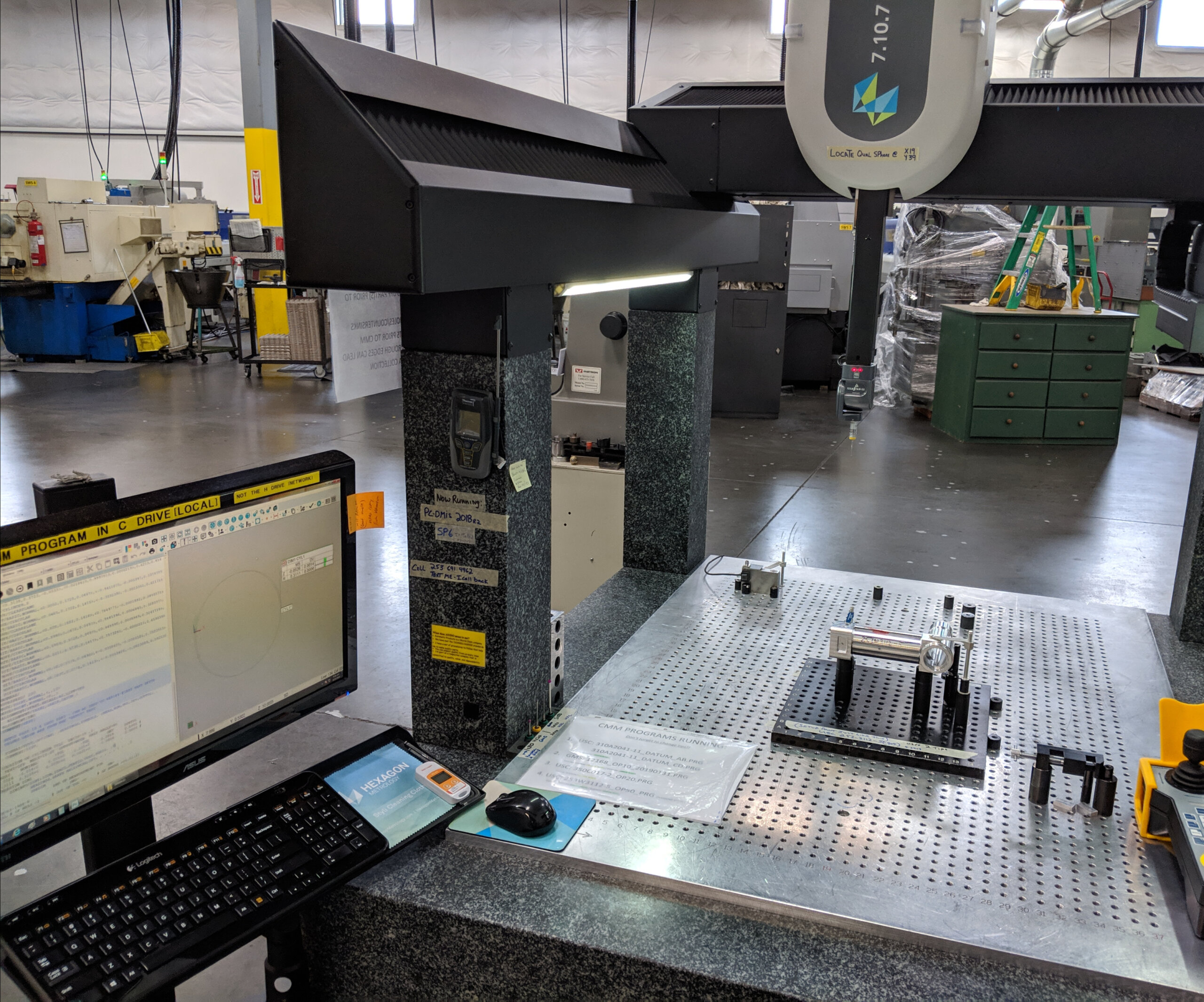

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Precision Measuring Instruments
Overview
Precision Measuring Instruments (PMIs) such as calipers, micrometers, coordinate measuring machines (CMMs), laser interferometers, and optical comparators are critical tools in manufacturing, quality assurance, aerospace, and automotive industries. Due to their high sensitivity, accuracy requirements, and frequent international use, their logistics and compliance management demand special attention. This guide provides structured recommendations for safe handling, transportation, regulatory compliance, and traceability throughout the supply chain.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Proper packaging and handling are essential to preserve the calibration and functionality of PMIs during transit.
– Use manufacturer-recommended packaging with custom foam inserts to prevent movement.
– Include desiccants to control moisture, especially for instruments with glass or metal components.
– Clearly label packages as “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Precision Instrument.”
– Avoid stacking heavy items on PMI shipments.
– Use anti-static materials where applicable to protect electronic components.
Transportation and Shipping Protocols
Selecting the right carrier and shipping method minimizes risk of damage and delays.
– Choose carriers with experience in handling high-value, sensitive equipment.
– Opt for temperature-controlled and shock-monitored shipping solutions when available.
– Use tracked and insured services with real-time GPS monitoring for high-value shipments.
– Maintain stable orientation; avoid frequent tilting or inversion unless specified by the manufacturer.
– Document pre-shipment condition with photos and condition reports.
Calibration and Traceability Management
Maintaining metrological traceability is a compliance and quality imperative.
– Ensure all instruments have a valid calibration certificate traceable to national or international standards (e.g., NIST, ISO/IEC 17025).
– Implement a calibration schedule based on usage, environment, and manufacturer recommendations.
– Maintain a digital or physical calibration log with dates, results, and responsible parties.
– Ship calibrated instruments with updated certificates; update upon receipt if required.
Regulatory Compliance
PMIs may be subject to various regulatory frameworks depending on destination and application.
– Export Controls: Verify if instruments are listed under export control regimes such as the Wassenaar Arrangement, EAR (Export Administration Regulations), or ITAR. High-accuracy CMMs and laser measurement tools may require export licenses.
– Customs Documentation: Provide accurate HS codes (e.g., 9031.41, 9031.80 for measuring instruments), commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin.
– CE Marking and Safety Standards: In the EU, ensure instruments comply with directives such as the Measuring Instruments Directive (MID 2014/32/EU) or EMC/RED as applicable.
– RoHS and REACH Compliance: Confirm that instruments and packaging materials comply with hazardous substance regulations in the EU and other jurisdictions.
Import Considerations
Importing PMIs requires understanding of local technical and customs requirements.
– Check for import duties, VAT, or temporary importation under ATA Carnet for trade shows or short-term use.
– Some countries require pre-shipment inspection or local certification (e.g., INMETRO in Brazil, KC Mark in South Korea).
– Instruments used in regulated industries (e.g., aerospace, medical) may require additional verification by local authorities.
Storage and Inventory Control
Proper storage preserves instrument integrity between uses.
– Store in a clean, dry, temperature-stable environment (typically 20°C ±2°C, 40–60% RH).
– Avoid exposure to dust, vibration, and electromagnetic interference.
– Use dedicated storage cabinets with locking mechanisms to prevent unauthorized handling.
– Implement a first-in, first-out (FIFO) or scheduled rotation system for loaned or shared instruments.
Maintenance and Repair Logistics
Service and repair must not compromise calibration or compliance status.
– Use only authorized service centers or certified technicians.
– Document all maintenance, repairs, and post-repair recalibration.
– For international repairs, ensure the service provider complies with relevant standards and return shipping meets export/import rules.
Data Security and Intellectual Property
Some digital PMIs store sensitive measurement data or proprietary algorithms.
– Encrypt data stored on devices or in cloud-connected systems.
– Disable or wipe internal memory before shipping for repair or disposal.
– Comply with data privacy laws (e.g., GDPR) when transferring measurement data across borders.
Sustainability and End-of-Life Management
Responsible disposal or recycling aligns with environmental regulations.
– Follow WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) guidelines for electronic components.
– Recycle metals, plastics, and hazardous materials through certified e-waste handlers.
– Consider manufacturer take-back or refurbishment programs.
Conclusion
Logistics and compliance for Precision Measuring Instruments require meticulous planning, documentation, and adherence to international standards. By following this guide, organizations can ensure the accuracy, reliability, and regulatory conformity of their measurement tools while minimizing risks during transportation, storage, and operation across global operations. Regular audits and staff training are recommended to maintain compliance and operational excellence.
In conclusion, sourcing precision measuring instruments requires a strategic approach that balances accuracy, reliability, cost-effectiveness, and long-term performance. It is essential to partner with reputable suppliers who adhere to international quality standards such as ISO 9001 and provide certified calibration documentation. Factors such as measurement range, resolution, environmental conditions, and compatibility with existing systems must be carefully evaluated to ensure optimal functionality. Additionally, considering after-sales support, warranty, and available training can significantly enhance instrument longevity and user proficiency. By conducting thorough due diligence and selecting instruments tailored to specific application needs, organizations can ensure consistent quality control, improved productivity, and compliance with industry regulations—ultimately supporting excellence in manufacturing, research, and quality assurance processes.