The global power supply circuit operation market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for energy-efficient electronics, advancements in industrial automation, and increasing adoption of switch-mode power supplies (SMPS) across consumer, automotive, and telecommunications sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global power supply market size was valued at USD 44.5 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects a CAGR of over 6% during the forecast period (2023–2028), fueled by the proliferation of IoT devices, electric vehicles, and data center infrastructure. As demand for reliable, compact, and high-efficiency power conversion solutions intensifies, a select group of manufacturers has emerged as leaders in innovation, scalability, and global market reach. The following list identifies the top 10 power supply circuit operation manufacturers shaping the industry through technological differentiation and strong R&D investment.
Top 10 Power Supply Circuit Operation Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
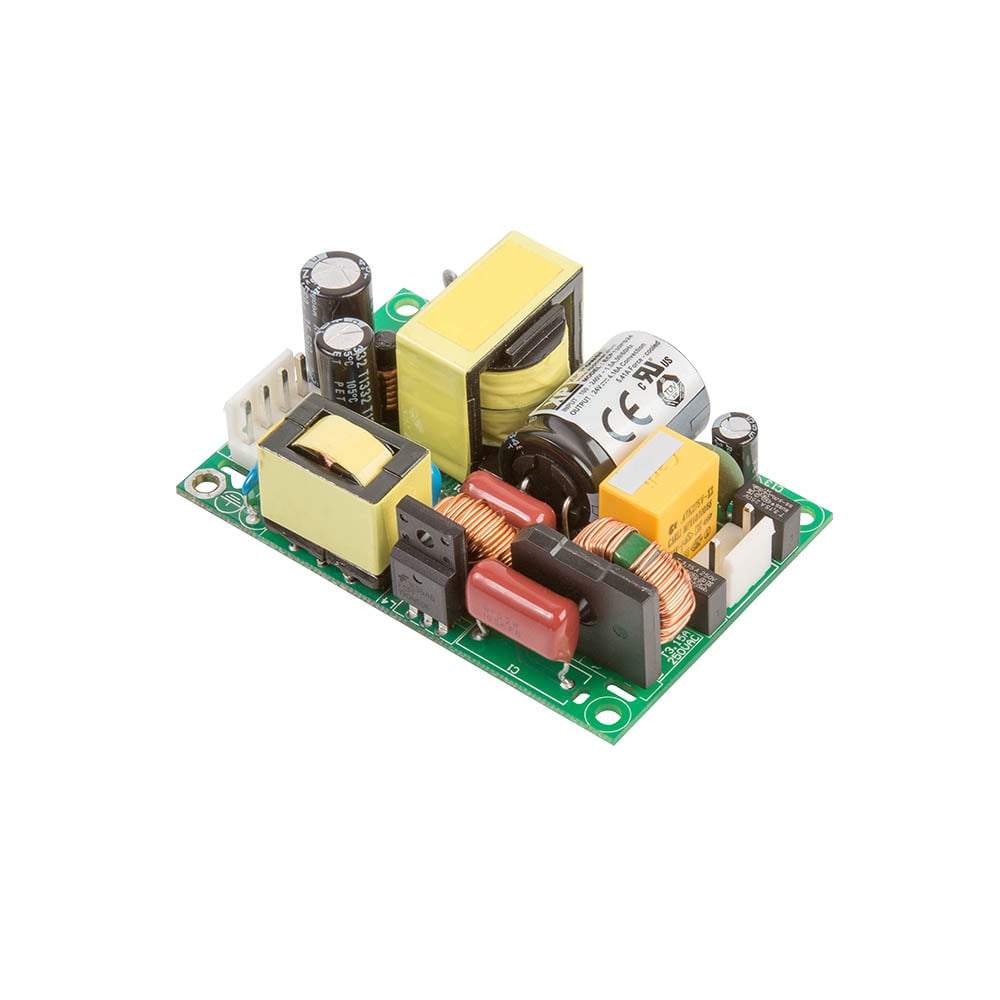
#1 MEAN WELL Switching Power Supply Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1997
Website: meanwell.com
Key Highlights: MEAN WELL is one of the world’s few standard power supply mainly professional manufacturers, covering 0.5 to 25600W products are widely used in industrial …Missing: circuit oper…
#2 PULS
Domain Est. 2000
Website: pulspower.com
Key Highlights: The PULS group is your partner for DIN rail power supplies, decentralised Field Power Supplies & wireless charging technology from Wiferion….
#3 Industrial Switching Power Supply Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2003
Website: mornsun-power.com
Key Highlights: MORNSUN is a professional one-stop power supply manufacturer, providing the best-in-class switching power supply solutions for various industries….
#4 Espey Mfg. & Electronics Corp.
Domain Est. 1996
Website: espey.com
Key Highlights: Espey Mfg. & Electronics Corp. designs, develops, tests and manufactures specialized Military and Rugged Industrial Power Supplies and Transformers….
#5 Eaton: Electrical and Industrial
Domain Est. 1996
Website: eaton.com
Key Highlights: Eaton is an intelligent power management company dedicated to improving the quality of life and protecting the environment for people everywhere. We are guided ……
#6 XP Power
Domain Est. 2000
Website: xppower.com
Key Highlights: Looking for the leading manufacturer of AC-DC power supplies, DC-DC converters, high voltage, RF & custom power products? Discover our extensive range….
#7 RECOM: DC/DC & AC/DC Converter
Domain Est. 2006
Website: recom-power.com
Key Highlights: RECOM Power is a leading manufacturer of AC/DC electronic power supplies and DC/DC converters, with over 30,000 compact standard power supplies alongside ……
#8 Power Supply Products
Domain Est. 1996
Website: coselusa.com
Key Highlights: COSEL USA, now the LITEON Power Master Distributor, offers diverse power supply solutions, latest product releases, tech support, and sample programs….
#9 Power supplies
Domain Est. 1996
Website: phoenixcontact.com
Key Highlights: Find the perfect power supply for your application, whether for the DIN rail, suitable for panel mounting, or in 19′′ format for rack mounting….
#10 Vicor Power Systems
Domain Est. 2001
Website: vicorpower.com
Key Highlights: Vicor high-performance power supplies solve the toughest problems quickly and reliably. Explore turnkey, custom products, solutions and application …Missing: circuit operation…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Power Supply Circuit Operation
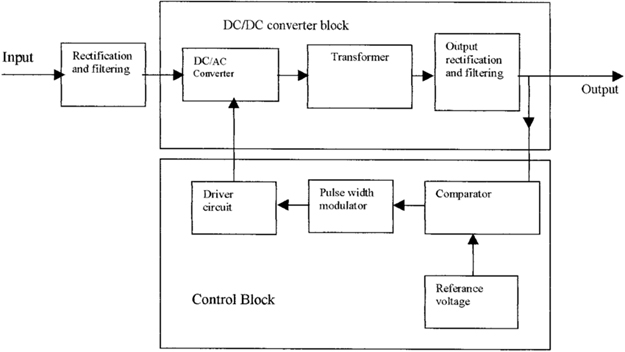
2026 Market Trends for Power Supply Circuit Operation
As the global electronics and energy sectors continue to evolve, power supply circuit operation is poised for significant advancements and shifts by 2026. Driven by increasing demand for energy efficiency, miniaturization, and integration with smart technologies, the market is witnessing transformative trends that will shape the design, functionality, and deployment of power supply circuits across industries.
Advancements in Wide Bandgap Semiconductor Technologies
One of the most influential trends shaping power supply circuit operation by 2026 is the widespread adoption of wide bandgap (WBG) semiconductors such as silicon carbide (SiC) and gallium nitride (GaN). These materials offer superior thermal conductivity, higher breakdown voltages, and faster switching speeds compared to traditional silicon-based components. As manufacturing costs decline and production scales up, GaN and SiC are increasingly being integrated into power supplies for data centers, electric vehicles (EVs), and renewable energy systems. This shift enables smaller, more efficient power supply circuits with reduced energy losses, directly addressing global energy conservation goals.
Rising Demand for High-Efficiency and Compact Designs
With the proliferation of portable electronics, IoT devices, and wearable technology, there is growing pressure to design power supply circuits that are both highly efficient and physically compact. In 2026, the market trend favors power supplies with higher power density, achieved through advanced topologies like resonant converters and multi-level designs. Innovations in passive component miniaturization and embedded power architectures are also contributing to smaller form factors without compromising performance or thermal management.
Integration of Digital Control and Smart Power Management
Digital power management is becoming a standard feature in modern power supply circuits. By 2026, an increasing number of power supplies will incorporate digital signal controllers (DSCs) and microcontrollers to enable real-time monitoring, adaptive voltage scaling, and predictive maintenance. This trend is particularly evident in data centers and telecom infrastructure, where intelligent power systems improve reliability and reduce operational costs through dynamic load management and remote diagnostics.
Growth in Renewable Energy and Energy Storage Applications
The global push toward decarbonization is accelerating the integration of power electronics in renewable energy systems. In 2026, power supply circuits will play a critical role in solar inverters, wind turbine converters, and battery energy storage systems (BESS). These applications demand robust, scalable, and grid-compatible power conversion solutions. Trends include the adoption of modular multilevel converters (MMCs) and advanced control algorithms to ensure stable power delivery under fluctuating input conditions.
Emphasis on Sustainability and Regulatory Compliance
Environmental regulations are becoming stricter, particularly in regions such as the European Union and North America. Energy efficiency standards like ENERGY STAR, the EU’s Ecodesign Directive, and the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Level VI are pushing manufacturers to develop power supply circuits with ultra-low no-load power consumption and higher average efficiency. By 2026, compliance with these standards will be a key differentiator in the market, driving innovation in circuit design, materials, and manufacturing processes.
Expansion of Automotive and EV Charging Infrastructure
The automotive sector, especially electric vehicles, is a major driver of power supply circuit innovation. Onboard chargers (OBCs), DC-DC converters, and traction inverters require highly reliable and efficient power electronics. By 2026, the market will see increased use of integrated power modules and bidirectional power flow capabilities to support vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technologies. Additionally, the expansion of fast-charging networks will demand high-power, thermally efficient supply circuits capable of handling 350 kW and above.
Conclusion
The 2026 market landscape for power supply circuit operation is defined by technological innovation, regulatory pressures, and evolving end-user demands. From the adoption of wide bandgap semiconductors to the integration of digital intelligence and sustainability, these trends are converging to create smarter, smaller, and more efficient power systems. Companies that embrace these developments will be well-positioned to lead in industries ranging from consumer electronics to clean energy and electric mobility.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Power Supply Circuit Operation (Quality, IP)
When sourcing power supply circuit solutions—whether as discrete components, integrated modules, or embedded IP cores—designers and procurement teams often encounter critical challenges related to quality and intellectual property (IP). Overlooking these aspects can lead to product failures, legal disputes, or compromised performance. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Component Quality and Reliability
Sourcing low-quality or counterfeit components is a prevalent risk. Substandard capacitors, inductors, or ICs may fail prematurely under thermal or electrical stress, leading to unstable voltage regulation, overheating, or complete power failure. Always verify supplier credentials, request reliability data (e.g., MTBF, temperature ratings), and conduct incoming inspections.
Inadequate Compliance with Safety and Regulatory Standards
Power supply circuits must meet stringent safety standards (e.g., UL, CE, IEC 62368-1). Sourcing designs or modules without proper certification can result in regulatory non-compliance, recalls, or liability issues. Ensure that all sourced solutions include documented compliance with relevant regional and industry-specific requirements.
Insufficient Thermal and Load Performance Validation
Some sourced power solutions may perform adequately under lab conditions but fail under real-world thermal or dynamic load scenarios. Always validate performance across the full operating temperature range and under expected load transients. Lack of proper derating or thermal management in the design can cause long-term reliability issues.
Lack of Design Documentation and Support
Insufficient technical documentation—such as schematics, BOMs, layout guidelines, or test reports—complicates integration and troubleshooting. Sourcing from vendors with poor technical support or opaque design processes increases development time and risk. Prioritize suppliers who provide comprehensive design resources and engineering assistance.
Unverified or Unclear Intellectual Property Rights
Using third-party power management IP (e.g., in ASICs or FPGAs) without clear licensing agreements can lead to IP infringement. This is especially critical when sourcing reference designs or soft/hard IP cores. Always confirm that the IP is properly licensed for your application and production volume to avoid legal exposure.
Hidden Licensing Fees or Usage Restrictions
Some IP providers impose per-unit royalties or restrict usage to specific markets or volumes. These terms may not be apparent during initial sourcing. Conduct due diligence on licensing models and ensure alignment with your production scale and business model to prevent unexpected costs.
Incompatibility with Existing System Architecture
Sourced power solutions may not integrate seamlessly with the host system due to mismatches in control interfaces, communication protocols (e.g., PMBus), or physical footprint. Verify compatibility with your system’s voltage domains, sequencing requirements, and mechanical constraints early in the design cycle.
Overlooking Long-Term Supply Chain Stability
Component obsolescence or supplier discontinuation can disrupt production. Source power solutions from vendors with strong long-term availability commitments and consider lifecycle management strategies, such as second sourcing or end-of-life notifications.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls, engineering and procurement teams can ensure robust, compliant, and legally sound power supply implementations.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Power Supply Circuit Operation
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the safe, efficient, and legal operation of power supply circuits across various applications, including industrial, commercial, and laboratory environments.
Procurement and Supply Chain Management
Ensure power supply components are sourced from reputable suppliers adhering to international quality standards (e.g., ISO 9001). Maintain accurate records of component specifications, batch numbers, and certifications (such as UL, CE, RoHS) to support traceability and compliance audits. Implement vendor qualification processes and conduct periodic supplier assessments.
Storage and Handling Protocols
Store power supply units (PSUs) and related components in a dry, temperature-controlled environment to prevent moisture damage and thermal degradation. Use anti-static packaging and handling procedures to protect sensitive electronic parts. Clearly label all inventory with handling instructions, expiry dates (if applicable), and compliance markings.
Transportation and Installation Logistics
Use appropriate packaging and shock-absorbing materials when transporting power supply systems to prevent physical damage. During installation, follow manufacturer guidelines and electrical codes (e.g., NEC, IEC 60364) for proper mounting, ventilation, and electrical connections. Ensure qualified personnel perform installations and document all setup procedures.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Adhere to regional and international regulations governing electrical safety, electromagnetic compatibility (EMC), and environmental standards. Key compliance frameworks include:
– Electrical Safety: UL 60950-1 / UL 62368-1 (North America), IEC 62368-1 (International)
– EMC: FCC Part 15 (USA), CISPR 32 (EU)
– Environmental: RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances), REACH, WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment)
Maintain up-to-date compliance documentation, including Declaration of Conformity (DoC) and test reports from accredited laboratories.
Operational Safety and Maintenance
Implement routine inspection and preventive maintenance schedules to ensure reliable operation. Monitor for signs of overheating, abnormal noise, or voltage fluctuations. Use calibrated test equipment for performance verification. Only trained personnel should perform maintenance, following lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures to ensure energy isolation.
Documentation and Record Keeping
Maintain comprehensive records including:
– As-built circuit diagrams and schematics
– Equipment logs (installation, maintenance, repairs)
– Calibration certificates
– Safety inspection reports
– Training records for operating personnel
Ensure documentation is securely stored and accessible for audits or incident investigations.
End-of-Life and Disposal Procedures
Decommission power supply circuits in accordance with environmental regulations. Recycle components through certified e-waste handlers compliant with WEEE or local disposal standards. Remove and properly dispose of hazardous materials such as electrolytic capacitors or lead-containing solder. Document all disposal activities for regulatory compliance.
Training and Personnel Certification
Ensure all personnel involved in the operation, maintenance, or handling of power supply circuits are adequately trained in electrical safety, emergency response, and relevant regulatory requirements. Maintain training certifications and conduct periodic refresher courses to uphold safety and compliance standards.
Risk Assessment and Incident Reporting
Conduct regular risk assessments to identify potential hazards such as electrical shock, fire, or arc flash. Implement mitigation strategies including protective devices (fuses, circuit breakers, surge protectors). Establish a clear incident reporting system for malfunctions, near misses, or safety violations, and perform root cause analysis to prevent recurrence.
In conclusion, the operation of a power supply circuit in a sourcing configuration involves delivering regulated voltage and current from the power source to the load, ensuring stable and reliable performance across varying load conditions. Key aspects such as rectification, filtering, regulation, and protection mechanisms work together to convert raw input power (often AC) into a clean, steady DC output. Effective sourcing power supply design must prioritize efficiency, voltage accuracy, ripple suppression, and thermal management. Additionally, incorporating feedback control and safety features enhances reliability and safeguards connected components. Overall, a well-designed sourcing power supply circuit is fundamental to the proper functioning of electronic systems, providing the necessary energy with precision and consistency.