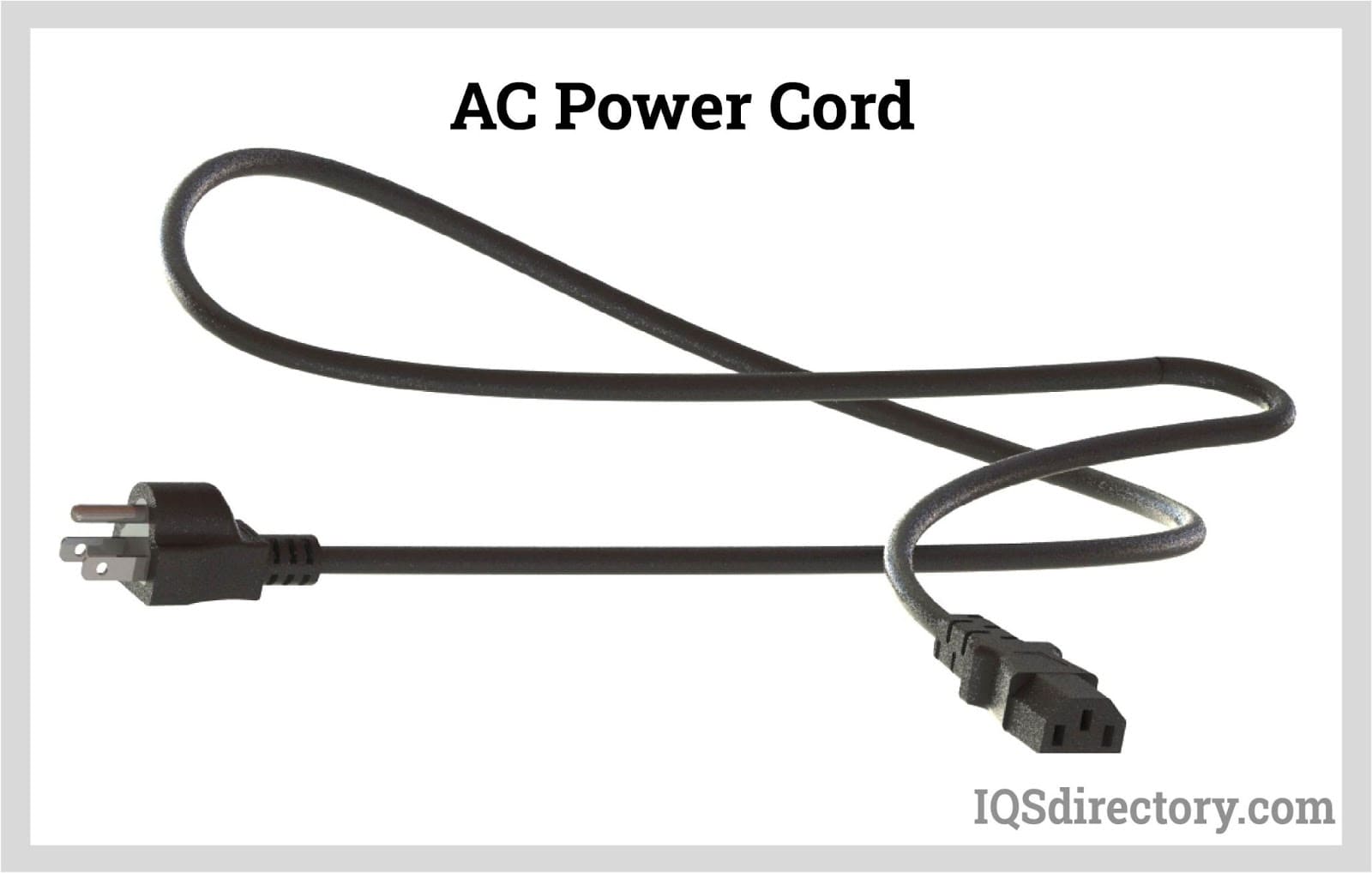
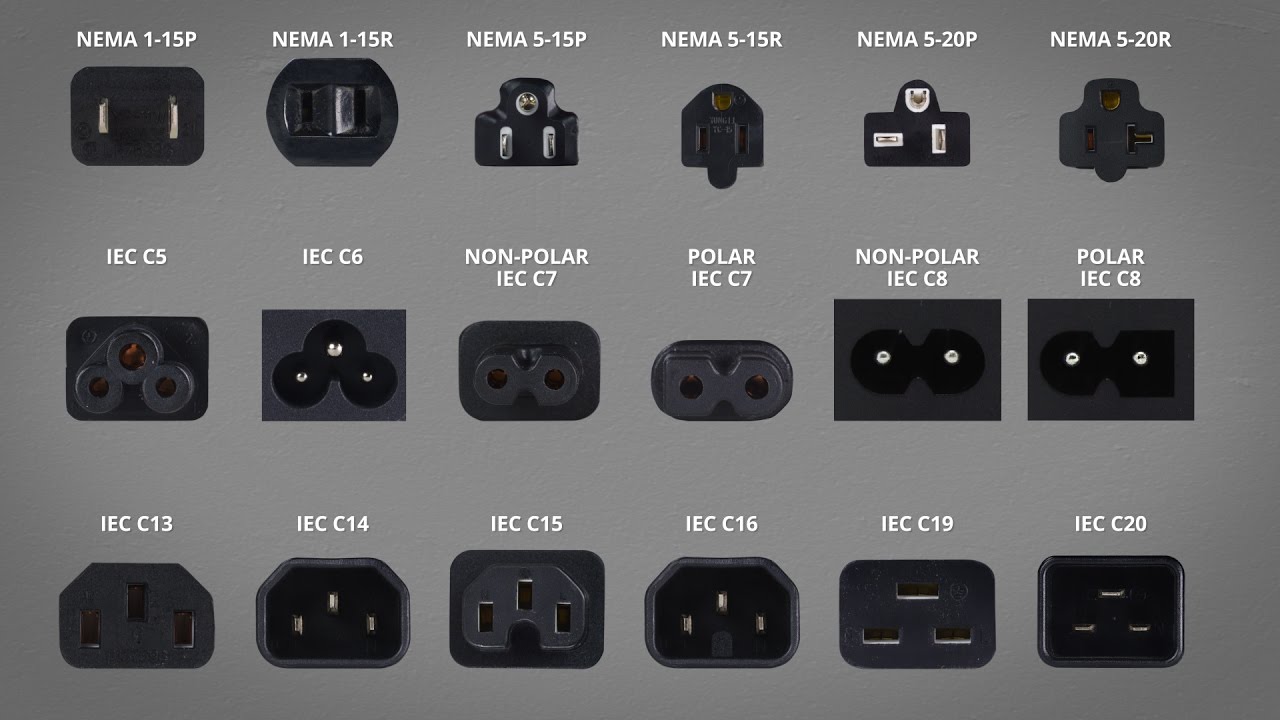
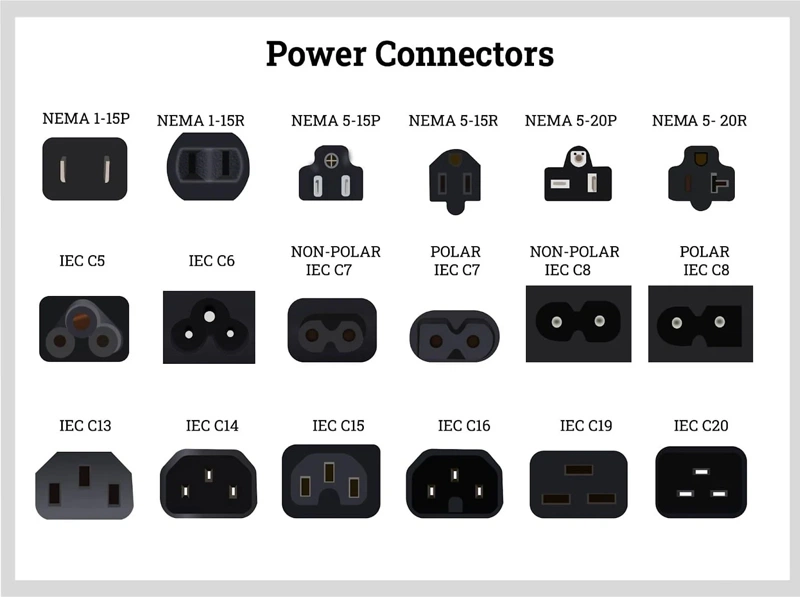
The global power cord connector market is undergoing rapid expansion, driven by rising demand across consumer electronics, industrial equipment, and healthcare sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global power cord market size was valued at USD 23.7 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by increasing electrification, stringent safety standards, and the proliferation of portable devices requiring reliable power delivery. As the backbone of safe and efficient power transmission, connector quality and compliance have become critical differentiators. With Asia Pacific dominating production and consumption due to robust manufacturing ecosystems in China and India, the competitive landscape is shaped by innovation in materials, compact design, and interoperability standards. Against this backdrop, identifying the top manufacturers of power cord connector types—those leading in product range, global certifications, R&D investment, and market reach—offers crucial insight for procurement professionals and design engineers navigating an increasingly complex supply chain.
Top 10 Power Cord Connector Types Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Meltric
Domain Est. 1997
Website: meltric.com
Key Highlights: MELTRIC offers a full line of industrial plugs and receptacles, including our signature brand of UL-listed Switch-Rated devices with DECONTACTOR™ ……
#2 Power Cord Manufacturer • Custom & Standard
Domain Est. 1997
Website: conwire.com
Key Highlights: Consolidated Offers Standard & Custom Power Cords for North American & International Applications. Serving Multiple Industries. Get a Free Quote Today!…
#3 Power Cord & Electrical Cords
Domain Est. 1999
Website: americord.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery 30-day returnsWe offer a wide variety of power cords online, ranging from electronics power cords to cords for industrial machinery and everything in between….
#4 Power Cord Manufacturers
Domain Est. 2001
Website: cordsets.org
Key Highlights: Instantly view the leading power cord manufacturers and suppliers in the United States who offer an assortment of power cords with varying lengths and uses ……
#5 Power Cord Manufacturers
Domain Est. 2019
Website: powercordmanufacturers.com
Key Highlights: Cord sets are electrical cables designed to link an appliance or device to a primary power source, supplying it with electrical energy….
#6 Types of Electrical Connectors and Wire Connectors
Domain Est. 1992
Website: te.com
Key Highlights: From USB connectors and RJ45 connectors to TE’s DEUTSCH connectors and AMP connectors, we design and manufacture the electrical connectors and wire connectors ……
#7 Connectors
Domain Est. 1994
Website: molex.com
Key Highlights: Molex offers a wide variety of wire-to-board connector types that fit applications requiring high-power, microminiature, sealed, rugged, and reliable solutions….
#8 Power Cords and Adapters
Domain Est. 1996
Website: tripplite.eaton.com
Key Highlights: We offer AC power cords, extension cords, splitters and adapters for computers, servers and PDUs. Our cords have innovative features like coiled cords and ……
#9 Power Cables & Connectors
Domain Est. 2021
Website: amphenol-cs.com
Key Highlights: Amphenol offers high-performance power cables and connectors, including AC, high-voltage, and high-current solutions for diverse applications….
#10 World plugs
Website: iec.ch
Key Highlights: The Type C electrical plug (or Europlug) is a two-wire plug that has two round pins. It fits into any socket that accepts 4.0 – 4.8 mm round contacts on 19 mm ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Power Cord Connector Types
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Power Cord Connector Types
The global market for power cord connector types is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological innovation, sustainability mandates, and evolving consumer and industrial demands. As energy efficiency, smart infrastructure, and electrification gain momentum worldwide, power cord connectors are no longer passive components but critical enablers of safe, reliable, and intelligent power delivery across diverse applications. This analysis identifies key trends shaping the power cord connector landscape in 2026.
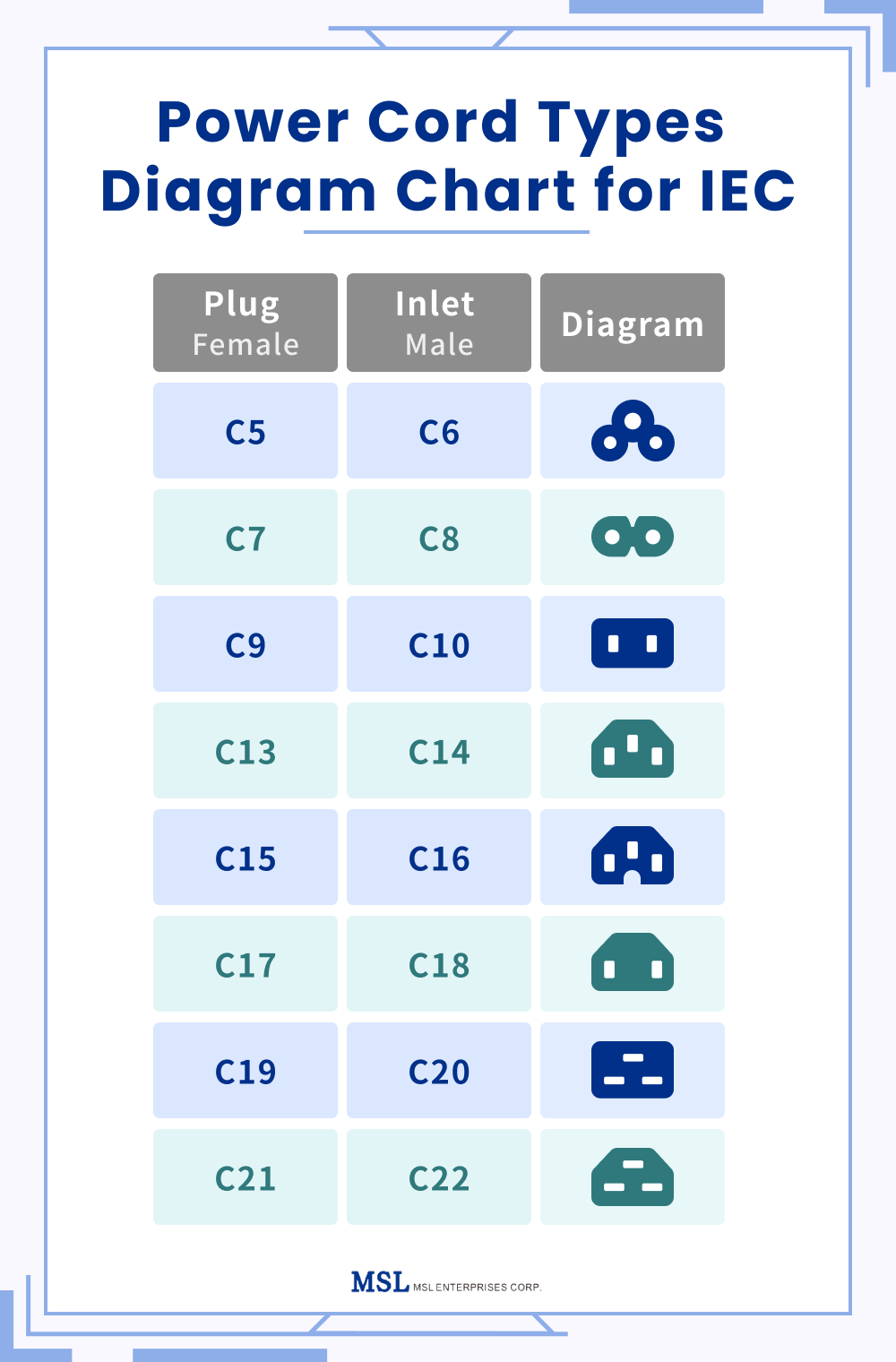
1. Surge in Demand for IEC 60320 Connectors in Consumer and IT Sectors
The IEC 60320 family of connectors, particularly C5, C7, and C13/C14 variants, will continue to dominate the consumer electronics, data centers, and office equipment markets. With the proliferation of compact laptops, gaming consoles, and power-hungry server racks, demand for standardized, interoperable, and thermally efficient connectors remains high. The C13/C14 configuration will remain the de facto standard for desktop computers and enterprise IT infrastructure, supported by global harmonization and low manufacturing costs.
2. Growth of Industrial and High-Power Connectors for EV and Renewable Energy Applications
Connectors such as IEC 60309 (CEE industrial plugs), NEMA L-series, and specialized EV charging connectors (Type 1, Type 2, CCS, and CHAdeMO) are expected to see accelerated adoption. By 2026, the global electric vehicle (EV) fleet will surpass 100 million units, driving massive demand for durable, weather-resistant, and high-current connectors. Type 2 connectors (Mennekes) will dominate in Europe due to EU charging standards, while CCS (Combined Charging System) gains traction in North America. Additionally, solar and wind energy installations will increase the need for high-voltage, low-loss connectors in power distribution systems.
3. Rise of Smart and IoT-Enabled Connectors
Intelligent power connectors with integrated sensors, data communication, and power management capabilities are emerging as a key trend. By 2026, smart connectors featuring built-in current monitoring, temperature sensing, and wireless connectivity (Bluetooth, Zigbee) will be increasingly used in smart homes, industrial IoT, and healthcare devices. These connectors support predictive maintenance, energy optimization, and remote diagnostics, aligning with Industry 4.0 and smart grid development.
4. Emphasis on Miniaturization and High-Density Designs
With the trend toward smaller, more powerful electronics—especially in wearables, medical devices, and portable power tools—there is growing demand for miniaturized connectors. Proprietary and micro-USB/USB-C power connectors will continue to evolve, with USB Type-C becoming a universal power and data interface. By 2026, USB-C PD (Power Delivery) connectors are expected to support up to 240W (USB PD 3.1), enabling them to power laptops, monitors, and even small appliances, reducing the need for multiple connector types.
5. Sustainability and Regulatory Compliance Driving Material Innovation
Environmental regulations such as RoHS, REACH, and the EU’s Ecodesign Directive are pushing manufacturers to adopt halogen-free, recyclable, and flame-retardant materials in connector housings. Bioplastics and recycled thermoplastics are gaining interest as sustainable alternatives. Additionally, modular and repairable connector designs are being promoted to extend product life and reduce e-waste, aligning with circular economy principles.
6. Regional Diversification and Standardization Challenges
While global harmonization efforts continue, regional differences in voltage, frequency, and plug standards persist. North America relies heavily on NEMA 5-15 and 5-20 connectors, while Europe standardizes on Schuko (CEE 7/4) and French (CEE 7/5) types. In Asia, a mix of local standards (e.g., India’s IS 1293, China’s GB 2099) creates complexity for multinational manufacturers. However, by 2026, international standards like IEC 60906-1 may gain broader adoption, especially in emerging markets seeking modernization.
7. Enhanced Safety and Durability Features
Safety remains a top priority, especially in high-power and hazardous environments. Connectors with IP67/IP68 ratings for dust and water resistance, enhanced strain relief, and anti-arcing mechanisms are becoming standard in industrial, outdoor, and medical applications. Locking mechanisms (e.g., in IEC 60309) prevent accidental disconnection, improving reliability in critical systems.
8. Supply Chain Resilience and Localization
Post-pandemic and geopolitical disruptions have prompted a shift toward regional manufacturing and diversified sourcing. By 2026, North America and Europe are expected to increase domestic production of power connectors to reduce dependency on Asian supply chains. This trend supports nearshoring and investment in automation, boosting quality control and responsiveness.
Conclusion
The power cord connector market in 2026 will be defined by a convergence of standardization, electrification, digitalization, and sustainability. While traditional connector types maintain strong market positions, innovation will center on smart functionality, energy efficiency, and environmental responsibility. Stakeholders—from manufacturers to regulators—must adapt to these dynamic trends to ensure compatibility, safety, and scalability in an increasingly electrified world.
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Power Cord Connector Types (Quality, IP)
Sourcing the right power cord connectors requires careful attention to both quality and Ingress Protection (IP) ratings. Overlooking key factors can lead to safety hazards, premature failure, and non-compliance. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Inadequate Quality Assessment
Many sourcing professionals focus solely on price, neglecting essential quality indicators. Low-cost connectors may use substandard materials such as brittle plastics, undersized conductors, or poor-grade metals, leading to overheating, arcing, or mechanical failure. Always verify certifications (e.g., UL, CE, VDE), request material specifications, and conduct supplier audits or sample testing before mass procurement.
Misunderstanding IP Rating Requirements
A frequent mistake is assuming a high IP rating is always better without considering the actual application environment. For example, specifying an IP68-rated connector for a dry indoor device increases cost unnecessarily. Conversely, using an IP20 connector in an outdoor or washdown environment risks water and dust ingress, causing short circuits or corrosion. Accurately assess environmental conditions—moisture, dust, chemicals, and exposure—to match the correct IP rating.
Overlooking Mechanical Durability
Connectors in industrial or high-use settings face repeated mating cycles, vibration, and physical stress. Sourcing connectors without evaluating mechanical lifecycle ratings (e.g., 1,000+ mating cycles) can result in cracked housings or loose contacts. Ensure the chosen connector meets durability requirements for the intended use case.
Ignoring Compliance and Regional Standards
Power connectors must comply with regional safety and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards. Using non-compliant connectors can delay product certification, lead to recalls, or restrict market access. Confirm that sourced connectors meet relevant standards such as IEC, NEMA, or country-specific regulations like CCC (China) or PSE (Japan).
Poor Supply Chain Transparency
Relying on suppliers without traceability or clear documentation increases the risk of counterfeit or inconsistent components. Establish a supply chain with verifiable manufacturing sources, batch traceability, and clear quality control procedures to ensure consistency and reliability.
Mismatched Connector Configuration
Selecting connectors based on appearance or pin count alone, without verifying voltage/current ratings, polarization, or locking mechanisms, can result in unsafe connections or incompatibility. Always cross-reference technical specifications with the end application’s electrical and mechanical needs.
Avoiding these pitfalls ensures reliable performance, regulatory compliance, and long-term cost savings in your power cord connector sourcing strategy.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Power Cord Connector Types
Understanding power cord connector types is essential for global logistics, regulatory compliance, and product safety. This guide outlines key considerations to ensure shipments meet international standards and avoid delays, penalties, or safety risks.
Understanding Regional Connector Standards
Power cord connectors vary significantly by region due to differing voltage, frequency, and safety regulations. Common international standards include:
-
Type A & B (North America, Japan):
Type A (NEMA 1-15) is ungrounded; Type B (NEMA 5-15) includes a grounding pin. Used in the U.S., Canada, Mexico, and parts of Central/South America and Japan. Voltage: 120V, 60Hz. -
Type C (Europlug):
Two-pin, ungrounded plug used across Europe, parts of Asia, Africa, and South America. Voltage: 230V, 50Hz. Not grounded; not suitable for high-power devices. -
Type E & F (Schuko – Europe):
Type E (France, Belgium, Poland) and Type F (Germany, Austria, Netherlands, Spain, etc.) are grounded, rated up to 16A. Must comply with EU Low Voltage Directive and CE marking. -
Type G (UK):
Three rectangular pins; used in the UK, Ireland, Malta, and several former British colonies. Requires compliance with UKCA (UK) or BS 1363 standards. -
Type I (Australia, New Zealand, China):
Slanted pins; used in Australia, New Zealand, Argentina, and China. Must meet AS/NZS 3112 (Australia/NZ) or GB 2099.1-2008 (China). -
Type J (Switzerland):
Distinctive three-pin design with a recessed earth pin. Requires SEV 1011 certification. -
Type M (South Africa):
Similar to Type D but rated for higher currents. Must comply with SANS 164 standards.
Regulatory Compliance and Certification Requirements
Each region mandates specific certifications to ensure safety and compatibility:
-
North America:
UL (Underwriters Laboratories) or CSA (Canadian Standards Association) certification is required. Devices must meet FCC regulations for electromagnetic interference. -
European Union:
CE marking is mandatory. Compliance with the Low Voltage Directive (LVD), Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive, and RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) is required. -
United Kingdom:
UKCA marking replaces CE for goods placed on the UK market (post-Brexit). BS 1363 compliance for plugs and sockets. -
Australia & New Zealand:
SAA (now part of RCM – Regulatory Compliance Mark) certification is required. AS/NZS standards must be met. -
China:
CCC (China Compulsory Certification) is mandatory for power cords sold or used in China. -
Other Regions:
Countries such as South Korea (KC mark), Japan (PSE mark), and Russia (EAC mark) have their own certification systems.
Logistics Considerations
-
Labeling and Packaging:
Clearly label power cords with voltage, frequency, and certification marks. Include multilingual instructions where applicable. -
Inventory Management:
Stock region-specific connectors to avoid shipping non-compliant products. Use SKU differentiation for each connector type. -
Customs Clearance:
Provide technical documentation (test reports, certificates of conformity) to customs authorities. Missing certifications can result in shipment rejection or fines. -
Reverse Logistics:
Non-compliant or incompatible cords returned from international markets incur restocking and shipping costs. Proactive compliance reduces returns.
Safety and Risk Mitigation
-
Use of Adapters vs. Native Cords:
Advise against using plug adapters for high-power devices. Ship region-specific cords instead. -
Voltage Compatibility:
Ensure devices support local voltage (e.g., 110–120V vs. 220–240V). Mismatches can cause equipment damage or fire hazards. -
Field Inspections:
Conduct periodic audits of power cord compliance in warehouses and during fulfillment.
Best Practices
- Pre-Ship Compliance Check: Verify connector type, certification, and labeling before dispatch.
- Partner with Certified Suppliers: Source cords from manufacturers with valid regional certifications.
- Maintain Compliance Documentation: Keep certificates, test reports, and technical files accessible for audits.
- Train Logistics Teams: Ensure staff recognize connector types and compliance requirements.
By adhering to regional standards and maintaining proper certifications, businesses can ensure smooth logistics operations, meet legal obligations, and protect end-user safety.
In conclusion, sourcing the appropriate power cord connector types requires careful consideration of several key factors including regional electrical standards, device voltage and current requirements, safety certifications, environmental conditions, and intended application. Common connector types such as IEC standards (e.g., C13/C14, C5/C6, C7/C8), NEMA plugs (e.g., NEMA 5-15, NEMA 6-15), and country-specific connectors (e.g., BS 1363, Type C, Type F) each serve distinct purposes and must be selected based on compliance and compatibility.
It is essential to work with reputable suppliers and verify compliance with relevant regulations such as UL, CE, RoHS, or CSA to ensure safety and reliability. Additionally, future-proofing through modular or universal designs can enhance flexibility, particularly for global product distribution. Ultimately, a thorough understanding of technical specifications and regional requirements will lead to optimal sourcing decisions, minimizing risks and ensuring efficient, safe, and standardized power connectivity.