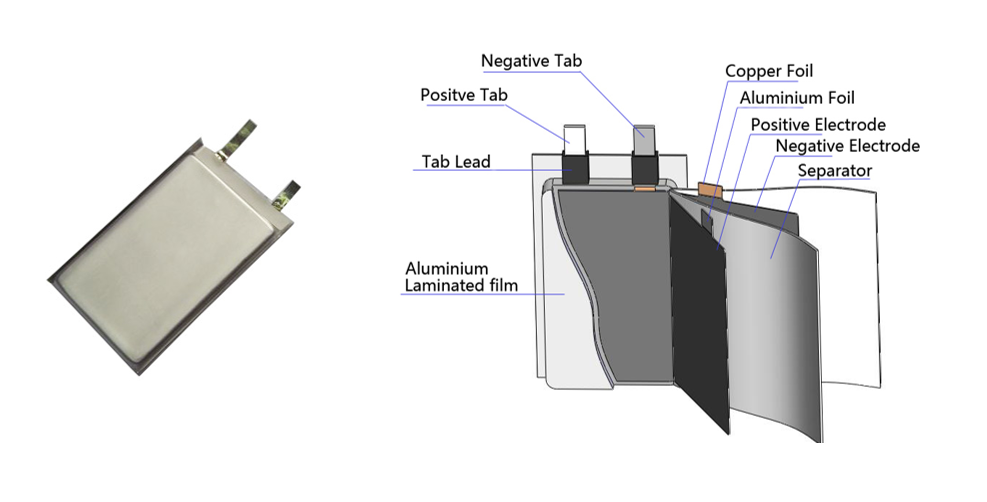
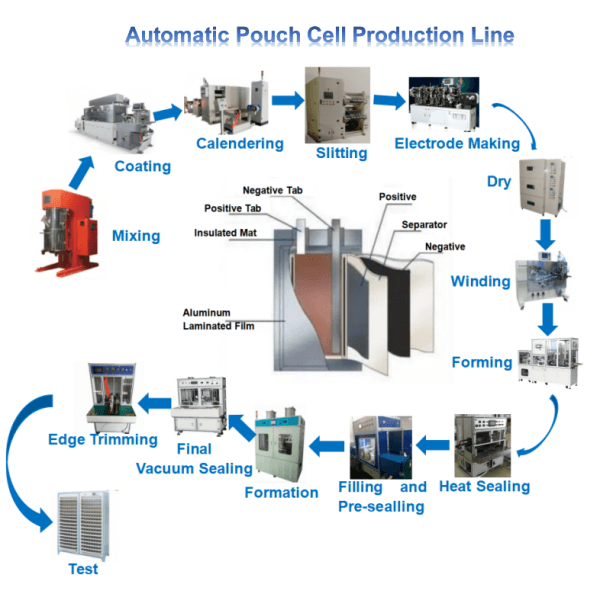
The global lithium-ion battery market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by rising demand for portable electronics, electric vehicles (EVs), and energy storage systems. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 53.7 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.4% through 2028. A key contributor to this growth is the increasing adoption of pouch lithium-ion batteries, favored for their high energy density, lightweight design, and flexible form factor. These attributes make them ideal for applications in smartphones, wearable devices, and next-generation EVs. As innovation accelerates and demand surges, a select group of manufacturers has emerged at the forefront of pouch cell production, shaping the future of energy storage technology.
Top 10 Pouch Lithium Ion Battery Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Amperex Technology Limited
Domain Est. 2000
Website: atlbattery.com
Key Highlights: ATL is the world’s leading producer and innovator of lithium-ion batteries. We are known worldwide for our high-tech, high-volume prowess….
#2 Batteries
Domain Est. 1994
Website: murata.com
Key Highlights: Murata provides various kinds of battery systems and battery products such as storage battery systems, lithium-ion secondary batteries, micro fuel cells, ……
#3 Saft Batteries
Domain Est. 1995
Website: saft.com
Key Highlights: For 100 years Saft has been specializing in advanced-technology battery solutions for industry, on land, at sea, in the air and in space….
#4 Molicel
Domain Est. 2001
Website: molicel.com
Key Highlights: A leading manufacturer of high-performance lithium-ion batteries designed for energy storage, electric vehicles, and advanced applications….
#5 Wanxiang A123 Systems Corp
Domain Est. 2001
Website: a123systems.com
Key Highlights: Wanxiang A123 Systems Corp The company has a global patent for super nano lithium iron phosphate, which is the world’s best technology for high safety, ……
#6 NEI Corporation
Domain Est. 2003
Website: neicorporation.com
Key Highlights: NEI Corporation is a leading manufacturer of protective and functional coatings, lithium-ion and sodium-ion battery materials, and custom specialty ……
#7 ANDRITZ Sovema
Domain Est. 2016
Website: sovemagroup.com
Key Highlights: We are your partner for technology needs in battery manufacturing and testing, providing lithium-ion and lead-acid batteries solutions….
#8 What is pouch cell lithium battery?
Domain Est. 1999
Website: grepow.com
Key Highlights: The pouch cell is a kind of prismatic battery that has a layer of aluminum plastic film on the outer bread of liquid or semi-solid ……
#9 Lithium
Domain Est. 2022
Website: leadintelligent.com
Key Highlights: LEAD is specialized in formation and aging solutions for pouch lithium battery cells, ensuring optimal battery quality and reliability….
#10 Enpower Greentech
Website: enpower-greentech.eu
Key Highlights: Enpower Greentech manufactures advanced batteries to power the green economy and reach net-zero, carbon reduction goals….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Pouch Lithium Ion Battery
H2: Market Trends for Pouch Lithium-Ion Batteries in 2026
By 2026, the global pouch lithium-ion (Li-ion) battery market is projected to experience substantial growth, driven by rising demand across key industries, technological advancements, and supportive regulatory environments. The pouch cell format—known for its lightweight design, high energy density, and flexible form factor—is increasingly favored over traditional cylindrical and prismatic cells, particularly in applications requiring customization and space optimization.
1. Electric Vehicles (EVs) as Primary Growth Driver
The electric vehicle sector remains the most significant contributor to pouch Li-ion battery demand. Automakers such as Hyundai, Kia, and Volvo have heavily adopted pouch cells due to their superior energy-to-weight ratio and thermal performance. By 2026, increasing EV production targets in Europe, North America, and China—supported by government mandates to phase out internal combustion engines—are expected to boost pouch battery adoption. Additionally, the rise of premium EVs and electric SUVs, which prioritize longer range and design flexibility, will further favor pouch cell integration.
2. Advancements in Energy Density and Safety
Manufacturers are investing in next-generation pouch battery chemistries such as nickel-rich NMC (e.g., NMC 811) and emerging solid-state hybrid designs. These innovations are expected to enhance energy density beyond 300 Wh/kg by 2026, extending EV driving ranges and improving performance in consumer electronics. Concurrently, advancements in laminate materials and internal cell design are reducing swelling and puncture risks, addressing long-standing safety concerns associated with pouch cells.
3. Expansion in Consumer Electronics and Wearables
The demand for thinner, lighter, and more flexible devices continues to favor pouch batteries in smartphones, tablets, ultrabooks, and wearable tech. With the proliferation of foldable and rollable displays, pouch cells’ form factor adaptability makes them ideal for next-gen electronics. By 2026, the integration of AI-powered devices and IoT wearables will further accelerate demand for customizable, high-capacity pouch batteries.
4. Growth in Energy Storage Systems (ESS)
While cylindrical and prismatic cells dominate the stationary energy storage market, pouch cells are gaining traction in residential and modular ESS due to their scalability and efficiency. Innovations in battery management systems (BMS) tailored for pouch configurations are improving cycle life and thermal management, making them more viable for long-duration storage applications. Asia-Pacific, particularly South Korea and Japan, is expected to lead in pouch-based ESS deployments.
5. Regional Manufacturing and Supply Chain Shifts
Asia remains the epicenter of pouch Li-ion battery production, with South Korea (LG Energy Solution, Samsung SDI) and China (CALB, CATL) leading in technology and scale. However, by 2026, localized production is expanding in Europe and North America due to geopolitical concerns and incentives like the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) and the EU Battery Regulation. These policies promote domestic manufacturing and sustainable sourcing, encouraging pouch cell producers to establish regional gigafactories.
6. Sustainability and Recycling Initiatives
Environmental regulations are pushing manufacturers toward sustainable practices. By 2026, closed-loop recycling systems for pouch batteries are expected to become more efficient, recovering up to 95% of critical materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel. The use of recyclable aluminum-laminated packaging in pouch cells offers advantages over rigid metal casings, aligning with circular economy goals.
7. Competitive Landscape and Strategic Partnerships
The market is witnessing increased consolidation and joint ventures. Automakers are forming strategic alliances with battery producers to secure pouch cell supply. For example, Stellantis’ partnership with LG Energy Solution for EV battery plants highlights the trend toward vertical integration. These collaborations are expected to drive innovation and reduce costs, making pouch batteries more competitive.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the pouch lithium-ion battery market will be shaped by strong demand from electric mobility, advancements in performance and safety, and a shift toward localized, sustainable manufacturing. While challenges around durability and standardization persist, ongoing R&D and strategic industry alignment position pouch cells as a critical enabler of the global energy transition.
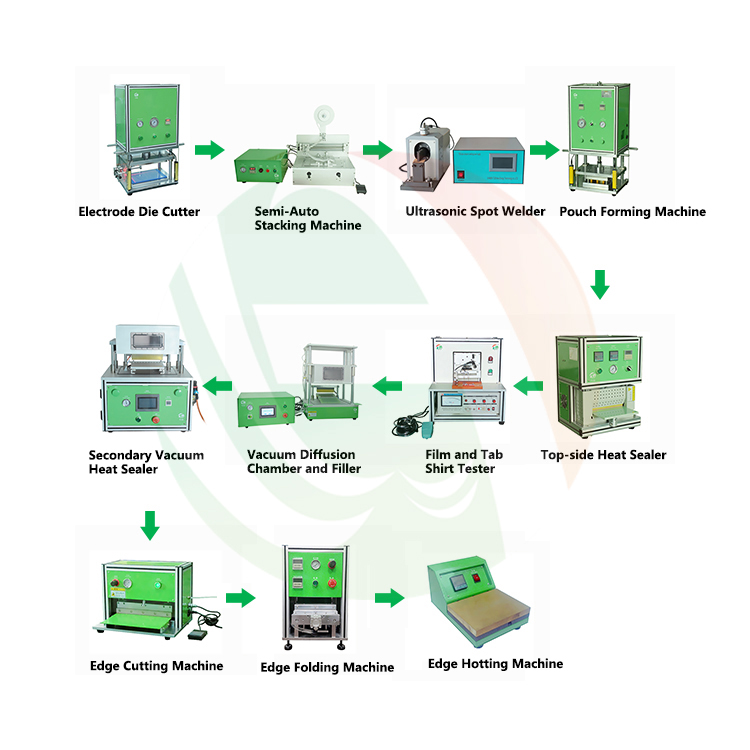

H2: Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Pouch Lithium-Ion Batteries (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing pouch lithium-ion batteries presents unique challenges, particularly concerning quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to product failures, safety hazards, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Below are the most common pitfalls in both domains.
H3: Quality-Related Pitfalls
- Inconsistent Cell Performance and Capacity
- Pitfall: Suppliers may provide cells with significant variations in capacity, internal resistance, and cycle life, even within the same batch.
- Risk: Results in uneven performance in battery packs, reduced lifespan, and potential thermal runaway in multi-cell configurations.
-
Mitigation: Require detailed test reports (e.g., capacity grading, impedance testing), implement incoming quality control (IQC), and conduct third-party validation.
-
Poor Manufacturing Process Control
- Pitfall: Inadequate control over sealing, electrode coating, and electrolyte filling processes leads to defects like delamination, electrolyte leakage, or micro-shorts.
- Risk: High field failure rates, swelling, or fire hazards.
-
Mitigation: Audit supplier manufacturing facilities, request process capability (Cp/Cpk) data, and inspect for consistent pouch sealing quality.
-
Lack of Robust Safety Testing
- Pitfall: Suppliers may skip or underperform critical safety tests (e.g., nail penetration, overcharge, crush, thermal cycling).
- Risk: Increased likelihood of safety incidents, non-compliance with standards (UN 38.3, IEC 62133), and liability exposure.
-
Mitigation: Mandate full safety certification documentation and conduct independent lab testing on sample cells.
-
Use of Substandard or Recycled Materials
- Pitfall: To cut costs, some suppliers use inferior-grade active materials, separators, or electrolytes—or even reconditioned cells.
- Risk: Poor cycle life, elevated self-discharge, instability under load, and safety vulnerabilities.
-
Mitigation: Perform material traceability checks, chemical analysis (e.g., via XRF or ICP-MS), and cycle testing to detect anomalies.
-
Inadequate Aging and Formation Processes
- Pitfall: Skipping proper formation and aging steps results in unstable solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) layers and unpredictable performance.
- Risk: High initial capacity fade and premature failure.
- Mitigation: Require documentation of formation protocols and verify with capacity retention testing over initial cycles.
H3: Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
- Design and Technology Infringement
- Pitfall: Sourcing from manufacturers that replicate patented cell designs, electrode formulations, or manufacturing techniques without licensing.
- Risk: Legal liability for IP infringement; product recalls, import bans, or litigation initiated by original IP holders.
-
Mitigation: Conduct due diligence on supplier’s IP compliance, request proof of licenses, and include IP indemnification clauses in contracts.
-
Reverse Engineering and Design Copying
- Pitfall: Suppliers may reverse engineer your custom battery pack or BMS design and sell identical products to competitors.
- Risk: Loss of competitive advantage and market share.
-
Mitigation: Use NDAs, limit technical disclosure, apply for design patents, and select suppliers with strong IP ethics.
-
Unprotected Custom Specifications
- Pitfall: Sharing custom form factors, performance specs, or integration details without proper safeguards allows suppliers to commoditize your innovation.
- Risk: Your differentiated product becomes a generic offering.
-
Mitigation: File provisional patents or utility models before engagement; use tiered information sharing.
-
Weak Contractual IP Clauses
- Pitfall: Vague or absent IP ownership terms in supply agreements may result in shared or lost rights to jointly developed technologies.
- Risk: Disputes over ownership, inability to exclusively use or license the technology.
-
Mitigation: Clearly define IP ownership in contracts; specify that all custom designs remain the buyer’s sole property.
-
Geopolitical IP Risks
- Pitfall: Sourcing from regions with lax IP enforcement increases the risk of unauthorized replication and export of your battery designs.
- Risk: Grey market products, counterfeit cells, and erosion of brand trust.
- Mitigation: Prefer suppliers in jurisdictions with strong IP frameworks; use trusted logistics and anti-counterfeit measures.
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers must adopt a proactive sourcing strategy that combines rigorous technical evaluation, supplier audits, third-party testing, and robust legal safeguards. Prioritizing quality and IP protection not only mitigates risk but also ensures long-term product reliability and market competitiveness.
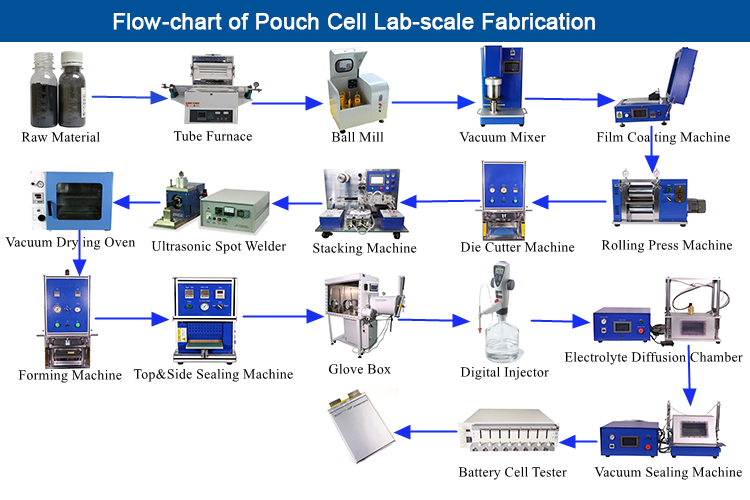
H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Pouch Lithium-Ion Batteries
Pouch lithium-ion batteries (Li-ion), known for their lightweight, flexible design, and high energy density, are widely used in consumer electronics, medical devices, and electric vehicles. Their transport, however, is strictly regulated due to fire and safety risks. This guide outlines key logistics and compliance requirements for safely and legally shipping pouch Li-ion batteries globally.
H2: Regulatory Framework
Pouch Li-ion batteries are classified as dangerous goods under international regulations due to their potential to overheat, ignite, or explode under certain conditions (e.g., short circuit, mechanical damage, overcharging).
Key regulatory bodies and standards include:
- UN Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods (Model Regulations): Provides the global foundation for classifying and transporting dangerous goods.
- IMDG Code (International Maritime Dangerous Goods): Governs sea transport.
- IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations (DGR): Governs air transport; most stringent and frequently updated.
- ADR (European Agreement concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road): Governs road transport in Europe.
- 49 CFR (Code of Federal Regulations, USA): Governs domestic and international transport in the United States.
- UN Manual of Tests and Criteria, Part III, Subsection 38.3: Mandatory testing required for all Li-ion batteries prior to transport.
H2: Classification and UN Numbers
Pouch Li-ion batteries are typically assigned the following classifications:
- UN 3480: Lithium ion batteries (including pouch cells, modules, and battery packs) – when shipped alone (not installed in equipment).
- UN 3481: Lithium ion batteries contained in equipment or packed with equipment.
- Proper Shipping Name (PSN): “Lithium ion batteries” or “Lithium ion batteries contained in equipment”.
Note: Pouch batteries are not exempt from regulation based on form factor; compliance depends on watt-hour (Wh) rating and packaging configuration.
H2: Pre-Transport Requirements
- UN 38.3 Testing Certification:
- All pouch Li-ion batteries must pass UN 38.3 tests (simulated transport conditions: altitude, thermal, vibration, shock, etc.).
-
A valid test summary must be available and may be requested by carriers or authorities.
-
State of Charge (SoC):
- For air transport (IATA DGR): Batteries must not exceed 30% state of charge when shipped alone (UN 3480).
-
This does not apply to batteries packed with or in equipment (UN 3481).
-
Design and Construction:
- Batteries must include protection circuits to prevent overcharge, short circuit, and excessive discharge.
- Pouch cells must be protected from puncture, compression, and contact with conductive materials.
H2: Packaging Requirements
Proper packaging is critical to prevent short circuits, physical damage, and thermal runaway.
- Individual Protection:
- Each pouch cell or battery must be electrically insulated (e.g., individually wrapped in non-conductive material or placed in non-conductive sleeves).
-
Terminals must be protected from contact with other batteries, metal objects, or conductive surfaces.
-
Rigid Outer Packaging:
- Use strong, UN-certified packaging capable of withstanding normal handling.
-
Inner packaging must prevent movement and protect terminals.
-
Separation and Cushioning:
-
Use non-conductive, non-combustible cushioning (e.g., foam inserts, bubble wrap) to separate batteries and absorb shocks.
-
No Mixed Loads:
- Li-ion batteries must not be packed with incompatible dangerous goods (e.g., oxidizers, flammables).
H2: Marking and Labeling
All packages containing pouch Li-ion batteries must be correctly marked and labeled:
- Proper Shipping Name and UN Number:
-
e.g., “UN 3480, LITHIUM ION BATTERIES” or “UN 3481, LITHIUM ION BATTERIES CONTAINED IN EQUIPMENT”.
-
Class 9 Miscellaneous Dangerous Goods Label:
-
Diamond-shaped label with “9” and “MISC.”; required for all Li-ion battery shipments.
-
Lithium Battery Handling Label:
- Required for all packages containing lithium batteries (IATA DGR Section 7.1.5).
-
Includes telephone number for emergency response information.
-
Shipper’s Declaration for Dangerous Goods (if required):
- Mandatory for air shipments of UN 3480 (batteries alone).
- Not required for small quantities under IATA’s “excepted” provisions (e.g., batteries under 100 Wh, limited to 2 kg per package).
H2: Quantity Limits and Exceptions
- Excepted Quantities (EQ):
- Small batteries (≤ 20 Wh for cells, ≤ 100 Wh for batteries) may qualify for reduced regulations under IATA and IMDG if shipped in limited numbers and properly packaged.
-
Mark with “LITHIUM ION BATTERIES—EXEMPT” and use Excepted Quantity mark.
-
Passenger vs. Cargo Aircraft:
- Shipments of loose Li-ion batteries (UN 3480) are generally prohibited on passenger aircraft under IATA DGR.
- Allowed only on cargo aircraft, subject to approval and quantity limits.
H2: Documentation and Training
- Shipping Papers:
- Include UN number, proper shipping name, hazard class, packing group (PG II), quantity, and emergency contact information.
-
For air shipments: Fully completed Shipper’s Declaration (when required).
-
Training:
- Personnel involved in preparing, offering, or handling Li-ion battery shipments must receive dangerous goods training compliant with IATA, IMDG, or 49 CFR as applicable.
- Training must be refreshed every 1–2 years.
H2: Carrier and Country-Specific Requirements
- Carrier Variations:
- Airlines and freight forwarders may impose additional restrictions (e.g., banning certain battery types, requiring pre-approval).
-
Always consult carrier-specific dangerous goods manuals.
-
Import/Export Compliance:
- Some countries require import permits, battery registration, or compliance with local safety standards (e.g., CE, UKCA, KC, PSE).
- Check destination country regulations before shipping.
H2: Emergency Response
- Emergency Contacts:
-
Provide 24-hour emergency response phone number on shipping documents.
-
Incident Reporting:
-
Report any incidents involving battery leakage, overheating, or fire to relevant authorities (e.g., FAA, national transport agency).
-
Spill Kits and Fire Suppression:
- Train staff in handling thermal runaway events (use Class D fire extinguishers or large amounts of water; never use water on metal fires unless trained).
Conclusion: Transporting pouch lithium-ion batteries requires strict adherence to international dangerous goods regulations. Proper classification, packaging, documentation, and training are essential to ensure safety and compliance. Always consult the latest edition of IATA DGR, IMDG Code, or 49 CFR before shipping, and work with certified dangerous goods consultants when in doubt.
Conclusion for Sourcing Pouch Lithium-Ion Batteries
Sourcing pouch lithium-ion batteries requires a strategic approach that balances performance, safety, cost, and reliability. These batteries offer compelling advantages such as lightweight design, high energy density, and flexible form factors, making them ideal for applications in consumer electronics, electric vehicles, and portable energy storage systems. However, their sensitivity to mechanical stress, swelling, and thermal conditions demands careful evaluation of suppliers and rigorous quality control.
Successful sourcing involves selecting reputable manufacturers with proven experience in pouch cell production, adherence to international safety standards (such as UL, IEC, and UN38.3), and strong R&D capabilities. It is critical to assess supply chain transparency, scalability, and compliance with environmental and ethical sourcing practices. Additionally, engaging with suppliers who offer technical support and customization options can enhance product integration and performance.
In conclusion, while pouch lithium-ion batteries present unique challenges, a well-structured sourcing strategy focused on quality, safety, and long-term partnership can unlock their full potential, ensuring reliable and efficient power solutions for innovative applications. Continuous monitoring of technological advancements and market trends will further support sustainable and competitive battery procurement.