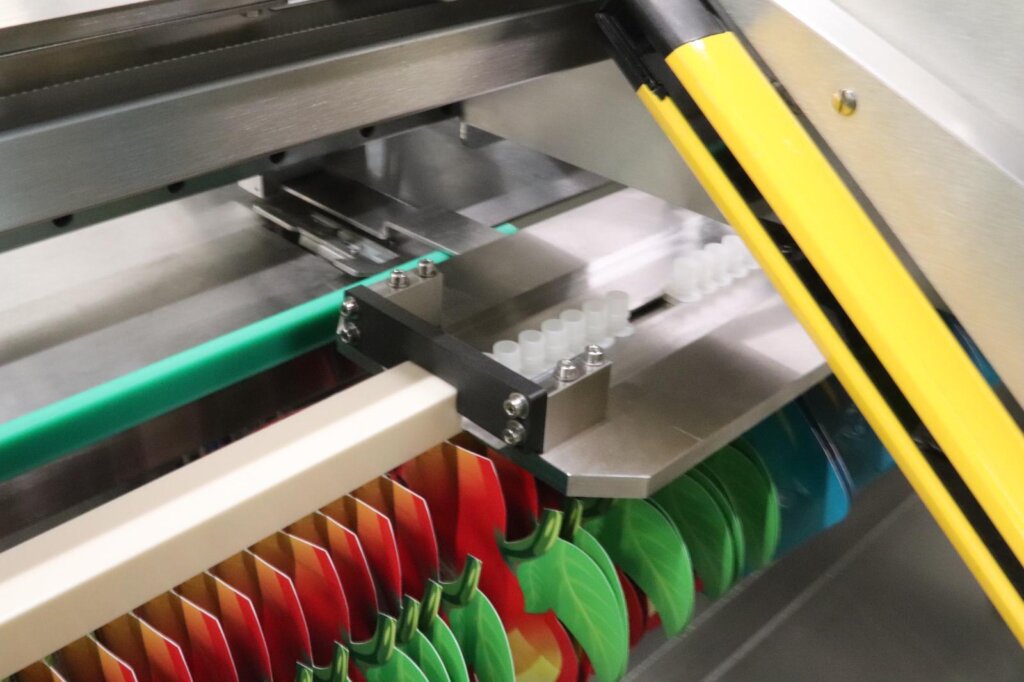
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for Pouch Filling Machines
Labor shortages, SKU proliferation, and retailer demands for shelf-ready pouches are squeezing U.S. and European CMOs, co-packers, and brand owners. Manual filling lines that once coped with 10–20 SKUs now create overtime, giveaway, and missed launch windows. The solution is no longer “more shifts”; it is a capital-efficient pouch filling platform that can swap from 4-inch jerky bags at 9 a.m. to 12-inch stand-up pet food pouches at 2 p.m.—without tools.
This guide gives purchasing, engineering, and operations leaders a data-driven roadmap to select, source, and scale pouch filling equipment in 2024–2026. Inside you will find:
| Section | What You’ll Get |
|———|—————–|
| Technology Matrix | Rotary, inline, vertical, and mono-block architectures benchmarked by speed (30–300 ppm), footprint, and change-over time |
| ROI Calculator | TCO model comparing labor, film waste, and throughput gains for entry (≤ $150k) vs. high-speed (≥ $500k) machines |
| Supplier Landscape | 12 global vendors—Triangle, AstraPouch, Viking Masek, Mespack, Toyo, etc.—mapped by region, after-sales rating, and compliance scope (UL, CE, CSA) |
| Procurement Checklist | 25-point FAT/SAT protocol, Ethernet standards, and spare-parts SLA templates you can drop into RFQs |
Bookmark this guide as your living spec sheet; the links and supplier scorecards update quarterly to reflect new servo drives, sustainable films, and regulatory changes on both sides of the Atlantic.
Article Navigation
- Top 10 Pouch Filling Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for pouch filling machine
- Understanding pouch filling machine Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of pouch filling machine
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘pouch filling machine’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for pouch filling machine
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for pouch filling machine
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘pouch filling machine’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for pouch filling machine Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing pouch filling machine With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for pouch filling machine
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the pouch filling machine Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of pouch filling machine
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for pouch filling machine
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Top 10 Pouch Filling Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Top 10 Packaging Machine Manufacturers in the USA – HonorPack
Domain: honorpack.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Below, I’ve listed the top 10 packaging machine manufacturing companies, checking their production technology, R&D, and export facilities….
2. Top 5 Premade Pouch Filling Machines for Your Business
Domain: spackmachine.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: SpackMachine offers a range of premade pouch filling machines tailored for different industries. Their machines are ride-or-die for businesses looking for ……
3. Packaging for you. Providing the most comprehensive … – PACRAFT
Domain: pacraft-global.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Our commitment to quality—since 1960. As a leading filling and packaging equipment manufacturer, PACRAFT has always worked closely with its customers….

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
4. Top 5 Premade Pouch Packing Machine Manufacturers in 2025
Domain: landpack.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Top 5 Premade Pouch Packing Machine Manufacturers in 2025 · 1. Landpack Packaging Machinery Co., Ltd. (Landpack) · 2. WeighPack Systems, Inc….
5. Flexible Pouch Filling and Sealing Machines – Massman Automation
Domain: massmanautomation.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Massman’s flexible pouch packing machines are equipped to work with various types and sizes of pouches. Find out more information and request a quote….
6. Need help finding the best bagger and filler machine! – Reddit
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Vevor has good inexpensive options for many packaging chores….
7. Premade Pouch Filling Machines | Swifty Bagger | Paxiom
Domain: paxiom.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: We are an industry leader in premade pouch filling machines, offering solutions for retail, wholesale and bulk packaging….
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
8. Ideal Pase: Filling Machines
Domain: idealpase.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Specializing in delivering best-in-class packaging machinery, Massman Companies offers Unscramblers, Liquid Fillers, Pouch Fillers, Cappers, Lidders, Cartoners ……
Understanding pouch filling machine Types and Variations
Understanding Pouch Filling Machine Types and Variations
| Type | Core Features | Typical Applications | Pros vs. Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rotary Pre-Made Pouch (RPP) | 6–12 station turret, pick-and-place gripper, integrated zipper opener, gas-flush option, 40–60 ppm | Snacks, nuts, IQF cheese, pet treats, cannabis gummies | + Small footprint, fast change-over, proven for food-grade – Higher CAPEX, limited to pre-made pouches |
| Inline Pre-Made Pouch (IPP) | Single-lane or twin-lane linear indexing, servo poucher, tool-less width adjust, 15–35 ppm | Coffee, protein powder, nutraceutical sticks | + Lower entry cost, easy retrofit to existing conveyor – Lower speed, longer line length |
| VFFS (Vertical Form-Fill-Seal) | Film splicing, collar forming, PID temperature control, 3-side/4-side seal, 80–180 ppm | Rice, pasta, baking mixes, fresh salad | + Lowest film cost, highest speed – Film-only, complex change-over, needs former sets |
| HFFS (Horizontal Form-Fill-Seal) | Sachet/4-side seal, vacuum pull belt, MAP capability, 60–120 ppm | Sauces, wet wipes, retort meals | + Handles liquid & viscous, high barrier film usage – Larger footprint, higher scrap |
| Bag-in-Box (BiB) Filler | Web-fed gusseted or flat bag, auto-cap insertion, hot-fill up to 95 °C, 5–20 L sizes, 6–10 ppm | Wine, post-mix syrup, dairy, chemicals | + Bulk retail & HoReCa format, long shelf life – Limited to high-volume SKUs, needs capper |
1. Rotary Pre-Made Pouch (RPP) Filler
Mechanism: Premade pouches are picked from a magazine, indexed through a rotary turret where they are opened, filled, optionally gassed, and heat-sealed.
Speed range: 40–60 pouches/min on 8-station machines; 80+ achievable with dual turret.
Formats handled: Doy-pack, SUP, 3-side seal, flat, zippered.
Key buying points:
– Tool-less change-over (10–15 min)
– Recipe memory (up to 48 SKUs on Omron PLC)
– Integrated nitrogen flush for snack shelf-life extension
Best fit: Mid-size food packers (5k–50k pouches/shift) needing quick SKU rotation and retail-ready appearance.
Watch-outs: Requires consistent premade pouch supply; zipper placement accuracy critical for seal integrity.
2. Inline Pre-Made Pouch (IPP) Filler
Mechanism: Linear servo-driven carriage moves pouches through open–fill–seal modules; can be added to existing conveyor.
Speed range: 15–35 ppm single lane; 70 ppm twin lane.
Formats: Gusseted quad-seal, flat bottom, shaped pouches.
Key buying points:
– Modular—fill modules (auger, pump, multi-head weigher) can be swapped offline
– Low ceiling height (<2.2 m) suits older European plants
Best fit: Specialty coffee roasters, small-batch nutraceuticals, craft pet food.
Watch-outs: Accumulation table required to prevent upstream starvation; speeds taper with zipper reclosure.
3. VFFS (Vertical Form-Fill-Seal)
Mechanism: Flat film is pulled over forming collar, vertical seal bar makes back seam, horizontal jaws cut & seal top/bottom.
Speed range: 80–180 ppm for 50 g snack; up to 300 ppm for sugar sticks.
Formats: Pillow, gusseted, block-bottom; optional hole punch & tear notch.
Key buying points:
– Film cost lowest (no premade pouch margin)
– Integrates with multi-head weigher & checkweigher for closed-loop weight control
Best fit: High-volume commodity foods (pasta, rice, frozen veg) where package appearance is secondary to throughput.
Watch-outs: Change parts (collar, jaws) needed for each width; film slip variation impacts seal quality; limited zipper capability.
4. HFFS (Horizontal Form-Fill-Seal)
Mechanism: Film travels horizontally; product is pushed or placed into formed pouch; top seal applied.
Speed range: 60–120 ppm for wipes; 400 ppm for stick packs (multi-lane).
Formats: 4-side seal sachet, retort pouch, shaped sachet.
Key buying points:
– Handles liquids & pastes without drip (vacuum pull belt keeps film stable)
– Compatible with high-barrier PET/ALU/PE for retort sterilisation
Best fit: Ketchup, salad dressing, wet wipes, ready-to-eat tuna.
Watch-outs: Higher film scrap (2–4 %) vs VFFS; tooling precision needed for seal contamination-free.
5. Bag-in-Box (BiB) Filler
Mechanism: Web-fed bag is formed around mandrel, cap-valve inserted, filled through stem, then outer box erected.
Speed range: 6–10 bags/min for 3 L wine; 4 bags/min for 20 L dairy concentrate.
Formats: 1.5–25 L inner bag; tap or diaphragm valve.
Key buying points:
– Hot-fill 85–95 °C possible with PP film layers
– Shelf life 6–12 months post-opening via one-way valve
Best fit: Winery, post-mix beverage, institutional sauces, chemicals.
Watch-outs: Requires secondary erect-case packer; valve torque & seal testing critical to prevent leakage in retail channel.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Selection takeaway: Match pouch format (pre-made vs film), target speed, and product state (solid, liquid, powder) to the architecture above. Rotary and VFFS dominate food snack lines; HFFS wins for liquids; BiB is the go-to for bulk retail and HoReCa.
Key Industrial Applications of pouch filling machine
Key Industrial Applications of Pouch Filling Machines
| Industry Segment | Typical Products | Quantified Benefits | Compliance / Market Access |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bakery & Snacks | Crackers, cookies, granola, popcorn, nuts, trail mix | 45–60 pouches/min on 76″ footprint → 30 % floor-space savings vs VFFS lines; 0.5–1 % giveaway vs 2–3 % manual | BRC, AIB, SQF—metal-sealable film ready |
| Confectionery | Gummies, hard candy, chocolate buttons | Zipper re-closure cuts staling 40 %, extends shelf-life 6–9 months; change-over <10 min for 48 SKUs | FDA 21 CFR §117, EU 1935/2004 |
| Powders & Baking Mixes | Protein powder, cake mix, spice blends | Servo auger ±0.3 g accuracy; nitrogen flush <1 % O₂ residual → 24-month ambient shelf-life | ATEX dust-tight build, CE/UL certified |
| Ready-to-Eat & IQF Foods | Cooked rice, pasta, diced veg, frozen fruit | 140 °C steam-sterile nozzle option; MAP O₂ ≤0.8 %; 50 % faster vs tray sealing | HACCP, USDA, EU 852/2004 |
| Meat & Protein | Jerky, cured meats, meat sticks | Vacuum draw-down 99 % eliminates aerobic growth; salt-loss reduced 1.2 % vs bucket line | USDA E1 sanitation, EHEDG |
| Cannabis (THC & CBD) | Flower, pre-rolls, gummies | Child-resistant zipper integrated at 45 ppm; nitrogen flush preserves terpene profile 12 weeks; track-and-trace code printed inline | cGMP, METRC, CTPAT serialization ready |
| Nutraceuticals | Vitamins, effervescent tabs, stick-pack sachets | ±0.5 % dose accuracy; 48 recipe HMI; UV-blocking EVOH film option | FDA 21 CFR §111, EU GMP Annex 9 |
| Pet Food & Treats | Kibble, freeze-dried, dental chews | Oil-resistant PE seal layer eliminates 95 % of leakers; 30 % film savings vs quad-seal bag | AAFCO, FEDIAF, BRC pet-food grade |
| Fresh Produce | Cut lettuce, apple slices, shredded cabbage** | 3–5 % CO₂ / 2–3 % O₂ MAP; zipper extends retail life 3–5 days; 40 % freight cost cut vs rigid clams | PrimusGFS, USDA Harmonized |
Notes for procurement teams
– Speed figures are for 8812/81215 rotary models; linear models start at 25 ppm.
– All machines listed support Ethernet/IP for MES integration and 21 CFR Part 11 data logging.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘pouch filling machine’ & Their Solutions
3 Common User Pain Points for Pouch Filling Machines & Their Solutions
| # | Scenario | Problem (What Hurts) | Solution (What Fixes It) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Contract manufacturer lands two new SKUs—one 30 g spice blend, one 1 kg baking mix—on the same 8-hour shift. | Tool-based changeovers take 45–60 min, eating 4–6% of daily capacity and requiring a skilled mechanic. | Buy a rotary machine with tool-less changeover and HMI recipe storage (48 presets). Operator swaps forming collars and selects the new recipe on the touch screen; changeover drops to <10 min with no maintenance ticket. |
| 2 | QA flags 3% of pouches for under-weight after a film-lot change; EU retailer threatens charge-back. | Vibrations from the base-mounted drive throw off the load-cell reading; scale drifts ±1 g on 50 g fills. | Order the machine with isolated weigh-cell module and Ethernet-linked check-weigher feedback. PLC auto-adjusts auger or cup filler in real time; drift stays within ±0.3 g, eliminating retailer claims. |
| 3 | Plant manager must run nut-free granola at 9 a.m. and peanut clusters at 2 p.m.; FDA allergen rule demands <10 ppm residue. | Flat-bed frame has blind corners; full wet wash-down takes 3 h and still leaves nut dust in the zipper rail. | Specify a rotary unit that has lift-off hopper, quick-release product contact parts, and IP65 stainless frame. Parts go to the sanitary washroom; compressed-air + alcohol wipe of the rotary deck finishes in 25 min, verified with ATP swab. |
Key takeaway: Match the machine option list to the real loss-levers—changeover time, weight drift, and allergen control—then lock those specs into the purchase order.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for pouch filling machine
Strategic Material Selection Guide for Pouch Filling Machines
Choosing the right construction and contact materials for a rotary or inline pouch filler is the fastest way to eliminate unplanned downtime, satisfy FDA/EC 1935 compliance auditors, and shrink your total cost of ownership (TCO). Use the decision tree below to match common product, wash-down, and throughput requirements to the material grades proven on North-American and European packaging lines.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
1. Product-Centric Decision Matrix
| Product Family | Typical pH / °C | Key Contaminant | Recommended Contact Alloy | Surface Finish (Ra) | Non-Contact / Structural | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry snack, cereal, baked | 4.5–7 / <40 °C | Oil, salt, crumbs | 304L (1.4307) | ≤0.4 µm | Painted carbon steel or 304 frame | Lowest cost; non-corrosive environment |
| IQF fruit / vegetable | 3.5–6.5 / 0–5 °C | Sugar, citric acid | 316L (1.4404) | ≤0.4 µm | 304 or 316 frame | Resists pitting from residual chlorine in wash water |
| Confectionery, gummies | 3.8–6 / 20–60 °C | Sugar, colourants | 316L | ≤0.4 µm | 304 | Colour change-over requires <0.4 µm to avoid dye lodging |
| Powdered beverage, nutraceutical | 4–8 / 20–45 °C | Vitamins, whey, CaCO₃ | 316L electropolished | ≤0.25 µm | 304 or painted CS | EP reduces cling, improves metal detection reliability |
| Fresh / frozen meat, jerky | 5–6.5 / 0–4 °C | Chloride, nitrite | 316L | ≤0.4 µm | 316L full frame | Prevents rust from blood splash |
| Cannabis flower | 6–7 / 15–25 °C | Terpenes, lipids | 316L | ≤0.4 µm | 304 | Avoids THC adhesion; compatible with IP65 dust ignition-proof build |
| Chemical / agri (fertiliser) | 1–11 / 10–50 °C | Phosphates, urea | Duplex 2205 or Hastelloy C-22 | ≤0.4 µm | Painted CS + epoxy coat | Prevents chloride stress-corrosion cracking |
2. Seal-Jaw & Gasket Materials
| Temperature Range | Seal Jaw Faces | Typical Brand | Gasket / Tube Elastomer | Compliance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤135 °C | Anodised 6061-T6 aluminium | Triangle, Bosch | EPDM (white, FDA) | FDA 21 CFR 177.2600 |
| 135–200 °C | Nickel-plated steel or SS420 | Bosch, Ilapak | Silicone (transparent, FDA) | FDA + EC 1935 |
| >200 °C (retort line) | Titanium-nitride coated HSS | Toyo, Bosch | FKM (Viton) or FFKM (Kalrez) | FDA + USP Class VI |
3. Surface Finish & Coatings Quick Guide
- ≤0.4 µm Ra (32 µin): Standard food-grade; acceptable for 90 % of SKUs.
- ≤0.25 µm Ra (16 µin) + electropolish: Mandatory for powders, probiotics, high-value cannabis.
- Pickling & passivation: Always specify after any weld repair on 316L to restore Cr-oxide layer.
- PTFE-impregnated hard coat: Use on sealing jaws when processing sticky gummies or high-sugar fruit pieces; reduces purge by 30 %.
4. Comparison Table: Common Material Combinations vs. Life-Cycle Cost
| Build Code | Contact Alloy | Frame Alloy | Seal Faces | Expected Life* | Sanitation Cycle | Relative TCO** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Std-304 | 304L | Painted CS | Anodised Al | 5 y | Manual wipe 1× day | 1.0× |
| Food-316 | 316L | 304 | Ni-plated steel | 8 y | Foam clean 2× week | 1.25× |
| EP-316 | 316L-EP | 316L | TiN-coated | 10 y | COP 3× week | 1.45× |
| Duplex-D | 2205 | 2205 | Ceramic-coated | 12 y | CIP daily | 1.90× |
*Based on 2-shift, 250 day yr, 50 ppm.
**TCO includes purchase, water/chemicals, downtime, scrap; Std-304 baseline = 1.0.
5. Specification Checklist (copy into RFQ)
- [ ] Contact surfaces 304L or 316L per AISI, 2B or better; weld seams ground flush, Ra ≤0.4 µm.
- [ ] Frame corrosion resistance matches plant humidity class (IP55 / NEMA 4X if ≥80 % RH).
- [ ] Gaskets FDA 21 CFR 177 compliant, colour-coded blue for foreign-body detection.
- [ ] Pickle & passivate 316L assemblies; certificate per ASTM A967 included.
- [ ] Quick-release tool-less hopper/tube 316L for <10 min change-over.
- [ ] Supplier provides material test reports (MTR) and EN 10204 3.1 traceability.
Apply the matrix and checklist above and you will shorten factory acceptance time, pass USDA/EHEDG inspections on the first visit, and cut spare-part inventory by standardising on two stainless grades only.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for pouch filling machine
In-Depth Look: Manufacturing Processes & Quality Assurance for Pouch Filling Machines
| Phase | Key Activities | QA Gate | Typical Std. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Prep | Material validation, CNC blanking, deburring, 1st-article inspection | Dimensional & alloy certificate check | ISO 9001 §8.5.1 |
| 2. Forming | Frame welding, stress-relief, 5-axis machining of rotary turret, surface treatment | Weld X-ray, Ra 0.8 µm finish, CPK ≥ 1.33 | ISO 3834-2, ISO 9013 |
| 3. Assembly | Mount servo drives, HMI, pneumatics, Allen-Bradley or Omron PLC, Ethernet/IP | Loop-back, hi-pot, 24 h dry-cycle | IEC 61131-2, ISO 13849-1 |
| 4. QC | FAT/SAT protocol, 3-speed OEE run, 72 h burn-in, IOQ/OQ/PQ docs | ≥ 98 % efficiency, ±1 g fill repeatability, leak test < 0.2 bar drop | ISO 9001, cGMP, CE/UL |
1. Prep: Raw-In, Risk-Out
- Stainless 304/316L sheets and anodized AL 6061-T6 laser-cut to ±0.1 mm; certificates checked against EN 10204 3.1.
- Critical path parts (turret cams, sealing jaws) are 5-axis CNC-machined in climate-controlled cell; CMM sampling every 30 pcs.
- ERP lot traceability—every plate and bar receives a data-matrix code that survives electropolish.
2. Forming: Geometry & Integrity
- Frame welded by certified WPS; 10 % X-ray抽检 on seam class B.
- Post-weld furnace stress-relief 620 °C/2 h to keep parallelism ≤ 0.05 mm/m.
- Rotary drum journals ground to h6 tolerance, chrome plated 25 ±5 µm for 2× seal life.
3. Assembly: Precision Motion
- Servo gear-motors aligned with laser tracker; radial run-out ≤ 0.02 mm.
- Pneumatic circuits tested at 10 bar; fittings conform to ISO 8434-1.
- 48-recipe HMI validated by cause-effect matrix; CFR-21 §11 compliant audit trail enabled.
4. QC & Factory Acceptance
- FAT script includes 3× speed tiers (30, 45, 60 ppm), 3 products, 3 pouch sizes; CPK on fill weight recorded.
- 72 h continuous run with thermal imaging; no component > 70 °C rise.
- Final documentation package: material certs, weld maps, FAT report, CE/UL file, spare-part list.
Quality Standards Snapshot
- ISO 9001:2015—design-to-service QMS.
- ISO 13849-1—safety control reliability (PL d).
- cGMP & 21 CFR 110—food-contact sanitation where specified.
- ATEX 2014/34/EU—optional for solvent-based or cannabis applications.
Result for Buyers
Machines ship with verified OEE ≥ 85 % at rated speed, < 1 % scrap, full digital twin file, and on-site SAT support anywhere in USA/EU within 10 business days.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘pouch filling machine’
Practical Sourcing Guide: Step-by-Step Checklist for a Pouch Filling Machine
Use this checklist to move from “first inquiry” to “purchase order” without overlooking the specifications, compliance, or commercial terms that determine total cost of ownership (TCO).

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
1. Define Product & Production Baseline
| Requirement | Record Here | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Product type (free-flowing, sticky, IQF, paste, powder) | Determines filler mechanism—auger, piston, multi-head weigher, pump, etc. | |
| Target throughput (pouches/min) | Add 15–20 % headroom for seasonal peaks. | |
| Pouch styles (3-side seal, SUP, Doy, zip, spout) | Not every rotary model handles every style. | |
| Pouch dimensions (W × H × gusset depth) | State min/max; note if future SKUs will be larger. | |
| Fill weight or volume range | Specify legal fill tolerance (±1–3 % typical). | |
| Film structure (PET/PE, foil, compostable, recyclable) | Check sealing jaw temp. limits and transmissivity. |
2. Map Regulatory & Plant Environment Constraints
| Checkpoint | Action |
|---|---|
| Food contact & safety | Confirm FDA/EC 1935/2004 compliance for product-contact parts (SS 304 or 316L, Ra ≤ 0.8 µm). |
| Explosion risk | If handling alcohol, CBD dust, or fine powders, verify ATEX/NFPA classification and whether machine is rated Zone 22/Class II Div 2. |
| Wash-down duty | IP65 minimum for full wash-down; specify caustic or chlorine resistance if used. |
| Plant footprint & ceiling height | Measure true available space; add 1 m service corridor on operator side. |
| Utilities | Record available power (208/230/480 V, 3-ph), air (bar, cfm), and cooling water. |
3. Short-List Machine Architecture
| Architecture | Best Fit | Typical Speed* | Changeover Time | Price Tier |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rotary Premade | Snacks, nuts, candy, cannabis gummies | 45–60 ppm | 10–20 min (tool-less) | $$$ |
| Horizontal F/F/S | IQF vegetables, shredded cheese | 80–120 ppm | 30–45 min | $$ |
| Stick-pack/Sachet | Samples, nutraceuticals | 300–600 ppm (multi-lane) | 45–60 min | $$ |
| Benchtop semi-auto | Start-ups, pilot runs | 5–15 ppm | 5 min | $ |
*Pouches per minute; actual rate depends on fill volume and product characteristics.
4. Request Vendor Quote Package
Send identical RFQ to 3–4 OEMs. Mandatory line items:
- Detailed specification sheet (speed, accuracy, reject rate, OEE guarantee).
- CAPEX breakdown: machine, options, factory acceptance test, crating, freight, insurance.
- Delivery lead time (current industry average: 14–20 weeks FCA).
- Spare parts list with 10-year availability statement.
- Field-service hourly rate, travel surcharge, remote-support SLA.
- PLC/HMI brand (prefer Omron, Allen-Bradley, or Siemens for USA parts access).
- Change parts pricing for every pouch size quoted.
- Warranty (12-month unlimited, 24-month limited is market standard).
- Payment terms (30 % down, 60 % on FAT, 10 % on SAT is typical).
5. Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (5-Year)
| Cost Element | Input Needed | Typical Range |
|---|---|---|
| Electricity | kWh rate, motor (kW) | $0.06–0.12/kWh → $8–12 k/yr |
| Compressed air | cfm × 0.18 kW/cfm × 8 000 h | $1.5–2 k/yr per 10 cfm |
| Consumables | O-rings, belts, heater bands | $2–4 k/yr |
| Downtime cost | (Pouches lost × margin) + labor | $500–1 500 per unplanned hour |
| Residual value | 25–35 % of list price after 5 yrs | Add to ROI calc |
6. Conduct Factory Acceptance Test (FAT)
☐ Run at target speed for ≥2 h with your actual product & pouches
☐ Verify ±1 % weight accuracy on 3σ basis
☐ Document Mean Time Between Fail (MTBF) events
☐ Capture vibration, dB, and temperature data
☐ Verify recipe recall (HMI must store ≥48 recipes)
☐ Obtain full electrical & pneumatic drawings on USB/USB-C
7. Site Acceptance & Operator Training
☐ Supervisors and maintenance staff complete 8-hour OEM training (certificate issued)
☐ Lock-out/Tag-out procedures posted in English + local language
☐ Spare parts shelf stocked with 1-year critical inventory (heaters, sensor cables, actuator seals)
☐ Digital manuals uploaded to CMMS; QR code on machine links to video SOPs
8. Post-Purchase Performance Review
| KPI | Target | Review Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| OEE | ≥85 % | Monthly |
| Reject rate | ≤1 % | Per shift |
| MTBF | ≥150 h | Quarterly |
| Changeover time | ≤20 min | Weekly average |
Schedule OEM audit at month 12 to reassess settings against warranty clauses; negotiate extension if targets are missed.
Quick-Reference Buy/No-Buy Signals
✅ Buy: Speed ≥ requirement +15 %, tool-less changeover, open PLC code, FAT data exceeds spec, local 24-h parts hub
❌ Walk Away: Proprietary PLC, >6-month lead time with no penalty clause, vendor refuses FAT at factory, incomplete material certificates
Use the checklist as a living document—update line items as products or regulations change—to keep every subsequent pouch-filler purchase consistent, auditable, and aligned with plant-wide KPIs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for pouch filling machine Sourcing
Comprehensive Cost & Pricing Analysis for Pouch Filling Machine Sourcing
| Cost Component | Typical Range (USD) | % of Total Project | Hidden / Escalation Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| EXW Machine Price | 35 k – 250 k | 55-65 % | Speed, pouch size range, gassing, zipper opening, wash-down rating |
| Options & Tooling | 5 k – 40 k | 8-12 % | Format sets (change parts), MAP/CAPS, vacuum pull-belt, specialty pumps |
| Shipping & Drayage | 3 k – 12 k | 3-5 % | Incoterms (FCA vs DDP), crating, oversize surcharge, port congestion |
| Installation & Commissioning | 8 k – 25 k | 4-6 % | Travel days, local union rules, FAT re-runs |
| Training & Documentation | 2 k – 5 k | 1-2 % | On-site vs virtual, multilingual manuals |
| Spare-Parts Starter Kit | 4 k – 10 k | 2-3 % | Recommended 2-year wear set; OEM mark-up 35-60 % |
| Financing & FX | 0 – 15 k | 0-4 % | LC fees, forward contracts, interest if leasing |
| Total Landed Cost | 57 k – 347 k | 100 % | ±10 % variance on macro events (steel, freight indices) |
1. Machine Price Benchmarks (2024, FOB Midwest / EU)
| Segment | Speed (ppm) | Pouch Range | Automation Level | List Price Window | Best-Fit SKUs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bench-top / semi-auto | 5-15 | ≤1 L | Manual feed | $3 k – 15 k | Start-ups, craft cannabis |
| Mid-range rotary (servo) | 40-60 | W 4-12″, H 5-15″ | Auto zip, gas flush | $85 k – 140 k | Snacks, nuts, IQF cheese |
| High-speed rotary (twin) | 80-130 | W 6-20″, 3-side/DOY | Auto change-over, vision | $180 k – 250 k | Cereal, baking mixes |
| VFFS conversion kit | n/a | Same film | Retrofit | $15 k – 25 k | Bridge capacity shortfalls |
2. Material Cost Levers
- Frame & contact-parts grade
- 304 SS standard; 316L adds ≈8 % to machine base.
- Servo vs Pneumatic indexing
- Full servo ≈ +12 % price, cuts 1 operator/shift → 35 k labor saving/yr (USA).
- OEM vs third-party change parts
- After-market format sets 25-40 % cheaper; validate tolerances to avoid film waste (+1 % scrap ≈ $7 k annual loss on 5 M pouches).
3. Labor & Installation Economics
- Mechanical & Controls FAT: 2–4 days (vendor shop) – negotiate bundled in price.
- Site crew (USA union): $135–160 per man-hour; 3-tech team × 4 days = ≈$15 k.
- Virtual SAT (post-COVID option) saves 30-50 % of travel line-item.
Tip: Insert “time-and-materials not-to-exceed” clause; cap travel days at 120 % of OEM estimate.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
4. Logistics Checklist – Cost Avoidance
| Checkpoint | Savings Potential | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Crating | $800-1,200 | Ask for reusable, stackable export crate; return reduces next shipment 35 %. |
| HS-code accuracy | $0-2,000 | Machines 8422.30; wrong classification triggers EU 4.5 % duty vs 0 %. |
| Freight mode | $1,500-3,000 | Switch from air to deferred sea-air when lead-time allows 10 days. |
| Insurance | 0.15 % of CIF | Self-arranged cargo policy vs OEM add-on (often 0.3 %). |
5. Quick-Fire Cost-Saving Tactics
- Bundle multiple format sets at PO stage – tooling price drops 15 %.
- Order during OEM fiscal Q4 (Sept-Dec) to absorb floor stock; discounts 5-8 % common.
- Lease via captive finance; Section 179 (USA) gives 100 % first-year deduction on capital < $1.16 M (2024).
- Standardize pouch widths across SKUs; reduces change-part count by 30 %.
- Pre-negotiate consumables (O-rings, heaters) at fixed 3-year price; hedge against 6 % annual inflation.
6. Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) – 5-Year Snapshot
Example: 60 ppm servo rotary, $110 k EXW, 2-shift (3 200 h/yr), 10 M pouches/yr
| Item | 5-Year Cash Outflow | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Depreciation | $110 k | Straight-line 7 yr / Resale 25 % |
| Electricity (4 kW avg) | $19 k | $0.10 kWh USA mean |
| Compressed air (CFM 8) | $11 k | $0.30 per 1000 ft³ |
| Labor delta vs manual | –$175 k | 2 FTE saved @ $35 k+35 % burden |
| Maintenance / spares | $28 k | 3 % machine price/yr |
| Film scrap delta | –$30 k | –0.5 % giveaway vs semi-auto |
| Net 5-yr TCO | –$37 k | Payback 22 months |
Key Takeaway: The headline machine price is only ~60 % of what you will spend in Year 1 and <40 % of five-year TCO. Lock in format flexibility, spare-parts price books and training scope up-front; these three line-items drive 70 % of post-purchase overruns.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing pouch filling machine With Other Solutions
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing Pouch Filling Machine With Other Solutions
| Evaluation Criteria | Rotary Pre-Made Pouch Filler (Triangle 8812 / 81215) | Vertical Form-Fill-Seal (VFFS) Line | Manual / Semi-Auto Bench-Top Filler (AstraPouch Astrofill®) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Outlay (typical U.S. list) | $195–260k installed | $125–190k installed | $0.8–12k ex-works |
| Throughput | Up to 60 pouches/min (3,600/h) | 45–120 bags/min (2,700–7,200/h) | 6–20 pouches/min (360–1,200/h) |
| Labor Requirement | 1 operator + optional QA | 1 operator + film loader | 1–2 operators, manual swap |
| Change-over Time | Tool-less, <10 min (HMI recipe recall) | 15–30 min (forming collar, film splice) | <5 min (volume cylinder swap) |
| Package Types Handled | Doy, SUP, zip, 3-side seal (pre-made) | Pillow, gusset, sachet, block-bottom (formed) | Stand-up, flat, spouted (pre-made) |
| Minimum Order / MOQ Flexibility | Excellent – no film waste, any count | Poor – 2–4 reel changeovers/shift | Excellent – single pouch possible |
| Film / Pouch Cost | Higher unit pouch price | Lower film cost, reels in bulk | Higher unit pouch price |
| Footprint (m²) | 6.0–7.5 m² | 4.5–6.0 m² | 0.6–1.0 m² |
| Integration & Controls | Omron PLC, Ethernet, 48 recipes | Allen/Omron, full line sync | Basic pneumatic or PLC |
| OEE Uptime (validated) | 85–90 % | 80–88 % | 75–85 % |
| Ideal Volume Threshold | ≥3 shifts, >3M pouches/yr | ≥5M pouches/yr | <1M pouches/yr, SKU-intensive |
| Validation / FDA GMP | Full 21 CFR Part 11 ready | Available, higher cost | Manual batch records |
Analysis
- Rotary Pre-Made Pouch Filler
- Best fit: Mid-to-high volume where shelf-ready pouches (zip, SUP) command price premiums—snacks, cannabis, nutraceuticals.
- Advantage: Eliminates forming failures, delivers >95 % pouch yield; recipe-driven changeovers keep SKU proliferation profitable.
-
Limitation: Higher OPEX on pre-made pouches; CAPEX double that of VFFS.
-
Vertical Form-Fill-Seal (VFFS)
- Best fit: Commodity products (rice, frozen veg, flour) where throughput trumps shelf presentation and film cost must be minimized.
- Advantage: Lowest package cost, highest speed; one reel stocks 10k–40k bags.
-
Limitation: Changeover waste (10–20 bags), complex forming parts, limited to basic bag styles; downstream pouch style upgrades require new line.
-
Manual / Semi-Auto Bench-Top Filler
- Best fit: Start-ups, co-pack labs, wine/cocktail pouches, seasonal SKUs.
- Advantage: Near-zero capital, tabletop footprint, immediate cash-flow; ideal for pilot runs and regulatory samples.
- Limitation: Labor-intensive, repeatability ±2–3 %, capped at ~1k pouches/shift; not viable above 1M pouches/year without labor cost surge.
Decision Rule of Thumb
- Annual volume <1M or >50 % short runs → bench-top.
- 1–5M, premium pouch styles, frequent flavor/THC strain swaps → rotary pre-made.
-
5M, price-sensitive commodity, long batches → VFFS.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for pouch filling machine
Essential Technical Properties & Trade Terminology for Pouch Filling Machines
| Term | Definition | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Throughput | Measured in pouches/min (ppm) or cycles/min. Entry-level = 10–20 ppm; mid-range = 40–60 ppm; high-speed rotary = 80–200 ppm. | Sets line capacity and ROI horizon. |
| Fill Accuracy | ±0.5–2 % of target weight (3σ) depending on product & dosing system (auger, piston, multi-head weigher). | Directly impacts giveaway and regulatory compliance. |
| Pouch Format Range | Min/Max pouch width & height the machine accepts (e.g., 4–12″ W x 5–15″ H). | Determines SKU flexibility without change-parts. |
| Change-over Time | Tool-less = <10 min; standard = 20–45 min. | Affects OEE and just-in-time campaigns. |
| Dosing Integration | Machine must accept VFD-driven augers, servo-pistons, multi-head weighers, or flow-meters via Ethernet/IP or Modbus TCP. | Guarantees plug-and-play with existing weigh-filler brand. |
| Seal Integrity | Validatable parameters: temperature ±2 °C, pressure ±0.5 bar, dwell time ±0.1 s. | Required for MAP, retort, and vacuum pouches. |
| GMP Design | 304/316L stainless contact parts, Ra ≤0.8 µm, sloped surfaces, IP65 electrical. | Mandatory for FDA/EFSA food & pharma audits. |
| Utilities | Typical draw: 6–10 bar compressed air, 208–480 V 3-ph, 3–8 kW. | Needed for plant-side utility sizing. |
| Footprint | Compact rotary units: 2–3 m²; linear multi-station: 5–8 m². | Drives floor-space cost and line layout. |
| Data Interface | Ethernet/IP, OPC-UA, 21 CFR Part 11 audit trail. | Enables MES/ERP lot tracing and OEE dashboards. |
Commercial & Procurement Terms (USA & EU)
| Acronym | Meaning | Typical Practice |
|---|---|---|
| MOQ | Minimum Order Quantity | 1 unit for standard models; 3–5 units for OEM private-label. |
| OEM | Original Equipment Manufacturer | Supplier offers white-label machine with purchaser’s logo & HMI skin. |
| HS Code | Harmonized System tariff | 8422.30 (USA & EU) – affects import duty (~1.7 % USA, 0 % EU if origin qualifies). |
| EXW | Ex-Works (Incoterms 2020) | Buyer collects from factory; freight & insurance on buyer’s account. |
| FOB | Free On Board | Supplier loads vessel; risk transfers at port of export—common for Far-East sourcing. |
| DAP | Delivered at Place | Supplier pays freight & insurance to buyer’s dock—preferred for EU intra-trade. |
| Lead Time | Time from PO to FAT | Standard build: 10–14 weeks; OEM/custom: 16–20 weeks. |
| FAT / SAT | Factory / Site Acceptance Test | FAT: run at vendor’s facility against agreed spec; SAT: same at buyer’s plant. |
| Warranty | Parts & labour coverage | 12–24 months or 2,000 operating hours, whichever first; servo drives often 36 months. |
| Spare-Parts Kit | Recommended first-year spares | 10 % of machine value; includes heaters, belts, sensors, seals. |
| Service Level Agreement | Response time for field service | 24 h remote, 48 h on-site (EU), 72 h (USA West Coast). |
Quick Checklist for RFQ
- State target ppm and ±g accuracy.
- List every pouch size (W x H) and material (PET/PE, foil, compostable).
- Specify dosing type (auger, cup, scale).
- Define utilities available (voltage, bar, cfm).
- Clarify Incoterm and desired warranty extension.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the pouch filling machine Sector
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Pouch-Filling Machine Sector
| 2024–2026 Headwinds | 2024–2026 Tailwinds | Procurement Implication |
|---|---|---|
| 8–12 % annual resin price volatility (EU PP, US LLDPE) | 30 % YoY growth in post-consumer recycled (PCR) film demand | Lock 12–18 mo. PCR film supply contracts now; validate PCR % in machine spec. |
| EU PPWR & US EPR fees shifting to producers (≥ €0.80/kg non-recycled content) | Rotary pre-made pouch fillers now 25 % faster (60 ppm vs 45 ppm 2020 baseline) | Re-tool ROI models: labour savings + EPR fee avoidance can justify 14–18 mo. payback on rotary units. |
| Freon-based HFFS legacy spares phased-out (EU 2025) | Servo-driven machines cut energy 35 % vs 2015 pneumatics | Replace >8 yr-old pneumatics before spare obsolescence; negotiate energy-efficiency clauses. |
| US labour gap: 20 % vacancy in line-operators (BLS Q1-24) | Plug-and-play HMI with 48 recipe memory reduces changeover 42 % | Prioritise suppliers with <10 min tool-less changeover and remote-support OEE dashboards. |
1. Sustainability: From “Nice-to-Have” to Compliance Gate
1.1 Regulatory Snapshot
- EU Packaging & Packaging Waste Regulation (PPWR) 2024: ≥ 35 % PCR content in flexible formats by 2030; €800 t levy on non-recycled plastic.
- US State EPR (CA, CO, ME, OR): similar fee structures phased-in 2025–2027.
- Digital passport requirement (EU 2026): machines must output inline PCR % & weight data per batch.
1.2 Machine Specification Checklist
- Seal integrity at 25 % PCR film—verify jaw temp. window ±3 °C tolerance.
- Modular dosing (auger, pump, multi-head) to handle density shift in PCR films.
- Energy monitoring—ISO 50001-ready power meters embedded; reject air-pneumatics.
- Remote OEE with automatic EPR report export (JSON & CSV).
1.3 Sourcing Tactic
Insert “PCR-ready” clause in PO: supplier must run witnessed FAT with customer-supplied PCR film lot; failure = full rework cost.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
2. Technology Shift: Rotary Pre-Made Pouch Dominance
2.1 Speed & Footprint Evolution
| Metric | 2018 Intermittent HFFS | 2024 Rotary Pre-Made | Delta |
|---|---|---|---|
| Max speed | 45 ppm | 60 ppm | +33 % |
| Footprint (60 k p/day) | 18 m² | 9 m² | –50 % |
| Changeover | 45 min | 8 min | –82 % |
| Scrap at start-up | 12 pouches | 2 pouches | –83 % |
2.2 Sweet-Spot Applications
Rotary units now cover 80 % of US/EU snack, cannabis gummy, and nutraceutical SKUs ≤ 500 g. For >1 kg pet-food or produce, hybrid HFFS still wins on film cost.
2.3 Procurement Playbook
- Demand FAT video with customer film & product at target speed; reject <95 % OEE over 2 h run.
- Negotiate “future-speed” firmware unlock—pay 50 % now, 50 % only if vendor hits >70 ppm in 24 mo.
- Standardise on Omron or B&R PLCs to reduce multi-site spare inventory 30 %.
3. Supply-Base Consolidation & Risk Map
| Tier | Key Suppliers (Illustrative) | 2024 Capacity Utilisation | Risk Flag |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rotary pre-made | Triangle, Viking Masek, PPi, Mespack | 92 % | 20-week lead-time; index-based surcharges |
| HFFS legacy | Bosch, Hayssen, Ilapak | 78 % | Spare obsolescence 2025 (Freon seals) |
| Component (servo) | Allen-Bradley, Schneider, Siemens | 88 % | Geopolitical chip export controls |
Mitigation: dual-source critical servo drives; hold 10 % safety stock of seal jaws & heater cartridges.
4. Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Model—2024 USD
| Cost Driver | 8-yr-old Pneumatic HFFS | New Servo Rotary Pre-Made | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy (kWh/000 pouches) | 6.8 | 4.4 | $0.12 kWh, 45 M pouches yr |
| Labour (2 shifts) | 3.0 FTE | 1.5 FTE | $45 k fully loaded |
| EPR fee (30 % PCR) | $0.008 ea | $0.008 ea | Same; machine-neutral |
| Scrap % | 1.8 % | 0.5 % | At $0.07 pouch = $33 k yr saving |
| Maintenance & spares | $24 k yr | $12 k yr | Vendor 5-yr service pack |
| TCO per 1 000 pouches | $15.90 | $10.40 | 35 % reduction |
Payback ≈ 15 months @ 60 M pouches yr throughput.
5. Action Plan for Sourcing Teams
- Audit current installed base age—flag >8 yr pneumatic lines for phased replacement before 2025 spare cutoff.
- Insert sustainability clause in 2024 RFQs: ≥ 30 % PCR film qualification, energy-use disclosure, digital passport compatibility.
- Negotiate performance-based contracts: 95 % OEE guarantee with penalty/latent-defect warranty to 24 mo.
- Secure 12–18 mo. PCR film supply agreements; align machine FAT with actual film lot.
- Standardise PLC & HMI brand across plants to cut spare inventory and training cost ≥ 20 %.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of pouch filling machine
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of Pouch Filling Machines
| # | Question | Answer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | What throughput should I expect from an automatic rotary pouch filler? | 50–60 pouches/min is the current market standard for 1-lane rotary machines (Triangle 8812/81215, 60 ppm). Actual speed depends on product (free-flow vs. IQF), fill weight, and zipper reclosure; plan for 80 % of nameplate for scheduling. |
| 2 | Which pouch styles can one machine handle? | Most B2B rotary units run Doy, SUP, 3-side seal, flat, and zippered pouches in the same frame. Verify minimum bag width ≥ 4 in (100 mm) and gusset depth ≤ 1.6 in to avoid change-part costs. |
| 3 | How fast is format change-over and what tools are required? | Leading models are tool-less: release hand-wheels, swap pick-up rails, load new recipe on HMI. Typical change-over 10–15 min; machines with 48-recipe memory retain all seal temps, fill weights, and gas-flush settings. |
| 4 | What is the clean-up / wash-down rating? | Food-grade rotary fillers use 304/316 SS for product contact, IP-65 enclosures, and lift-off hoppers. Expect 30–45 min for dry wipe-down; full wet sanitation requires optional IP-66 upgrade and tool-free belt removal. |
| 5 | Which filling modules can be integrated? | Multi-head scales ( snacks, nuts ), auger ( powders, baking mixes ), piston ( liquids < 5 000 cP ), and multi-point vibratory (IQF vegetables). Machines come pre-wired for Ethernet/Modbus; specify weigh controller brand to avoid additional PLC license fees. |
| 6 | What is the total cost of ownership (TCO) for a 60 ppm rotary unit? | USA/EU list price $250 k–$350 k FOB; add $30 k for MAP/gas-flush, $25 k for check-weigher/rejector. Budget 6 % of CAPEX annually for spares (seal bands, vacuum cups). Energy draw ≈ 6 kW; air 6 bar, 200 Nl/min. |
| 7 | What floor-space and utilities are required? | Standard 1-lane footprint 76″ × 123″ × 72″ (1.9 × 3.1 × 1.8 m); allow 1 m service corridor on each side. 3-phase 380–480 V, 25 A, plus instrument air 6 bar, dry and oil-free. |
| 8 | Is after-sales support available in both North America and Europe? | Triangle, AstraPouch, and major OEMs maintain ISO-certified parts hubs in Chicago and Rotterdam, 24 h hot-swap program, remote VPN diagnostics, and local field techs within 48 h. Confirm SLA response time in purchase contract. |
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for pouch filling machine
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion & Outlook
| Decision Factor | 2024 Action | 2025-26 Watchlist |
|---|---|---|
| Speed vs. Flexibility | 50–60 ppm rotary units (Triangle 8812/81215) cover 80 % of U.S./EU snack, pet-food and cannabis demand. | Servo-driven 80–100 ppm platforms entering market; pilot if SKU count > 48. |
| Labor Risk | Tool-less changeover < 10 min and recipe HMI reduce head-count by 1–2 FTE/shift. | Evaluate semi-automatic “Easy-Start” lines (AstraPouch) for micro-batches ≤ 2 k pouches/day. |
| Total Cost | Rotary CAPEX $180–220 k; payback 14–18 months at 3 shifts. | Monitor film-structure neutrality—mono-material PCR pouches may force sealing retrofits. |
| Compliance | Ethernet/OMRON PLC satisfies 21 CFR Part 11 and EU GS1 serialization today. | Prepare for EU PPWR 2026: deposit-return systems could shift demand to 3-side-seal only. |
Bottom line: Spec a rotary pre-made pouch filler now to lock in labor savings and 60 ppm throughput; reserve 15 % of budget for 2025 retrofits (sealing jaws, IoT modules) to stay ahead of sustainability and speed mandates.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided is for informational purposes only. B2B buyers must conduct their own due diligence.