The global portable cleanroom market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by increasing demand for contamination-controlled environments across pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, semiconductor manufacturing, and healthcare sectors. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 4.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.4% from 2023 to 2028, reaching an estimated USD 6.6 billion. This growth is fueled by rising regulatory scrutiny, the need for modular and flexible cleanroom solutions, and the proliferation of advanced manufacturing technologies. As industries prioritize operational efficiency and compliance with ISO and GMP standards, portable cleanrooms have emerged as cost-effective, rapidly deployable alternatives to traditional fixed facilities. In this evolving landscape, leading manufacturers are leveraging innovation in filtration systems, modular design, and smart monitoring to meet diverse client requirements. Below is a data-driven analysis of the top 10 portable cleanroom manufacturers shaping this dynamic market.
Top 10 Portable Cleanroom Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Modular Cleanrooms & Custom Cleanroom Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1997
Website: portafab.com
Key Highlights: PortaFab is a modular cleanroom manufacturer with over 40 years of experience in designing, engineering, and manufacturing cleanroom systems….
#2 Custom and Standard Modular Cleanrooms for Industrial Use
Domain Est. 1998
Website: cleanairproducts.com
Key Highlights: Order modular cleanrooms & cleanroom products for industrial & medical applications. Get customizable solutions, ISO compliance, & high-performance designs….
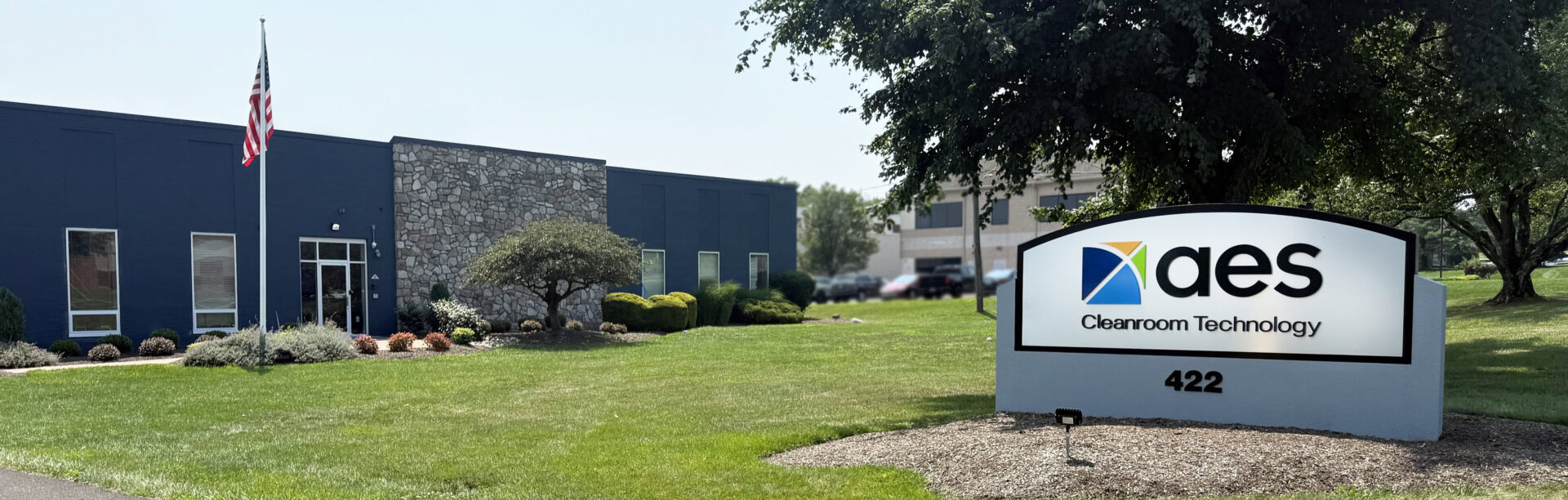
#3 AES Clean Technology: Industry
Domain Est. 2000
Website: aesclean.com
Key Highlights: Based in the USA, AES Clean Technology performs design, manufacture, & install of cGMP modular cleanrooms. See what makes AES the standard in cleanrooms ……
#4 Labworks International: Climate
Domain Est. 2005
Website: labworksinternational.com
Key Highlights: Labworks designs and manufactures environmental test chambers for healthcare, research, pharmaceutical, and industrial use across Canada….
#5 G
Domain Est. 2009
Website: gconbio.com
Key Highlights: As a trusted cleanroom manufacturer, G-CON specializes in innovative cleanroom manufacturing solutions that accelerate pharmaceutical and biotech facility ……
#6 Clean Room Manufacturers
Domain Est. 2015
Website: clean-rooms.org
Key Highlights: Cleanrooms By United is the industry’s premier manufacturer of modular clean room systems. We design, manufacture and install our clean rooms to meet our ……
#7 Germfree: World
Domain Est. 1996
Website: germfree.com
Key Highlights: Germfree is a pioneering laboratory & cleanroom manufacturing company. We build world-class mobile & modular cleanrooms, labs & equipment….
#8 Cleanrooms, ISO 8 Cleanroom, ISO Class 7 Cleanroom, ISO 5, ISO …
Domain Est. 1998
Website: cleanairtechnology.com
Key Highlights: We specialize in the Turnkey Design, Engineering, Fabrication, Installation, Startup, and Testing of ISO Class 1 to ISO Class 9 Modular Cleanrooms….
#9 Terra Universal
Domain Est. 1999
Website: terrauniversal.com
Key Highlights: Terra Universal designs, manufactures, and stocks comprehensive lines of cleanrooms, air filtration systems, pass-through chambers, desiccator cabinets, ……
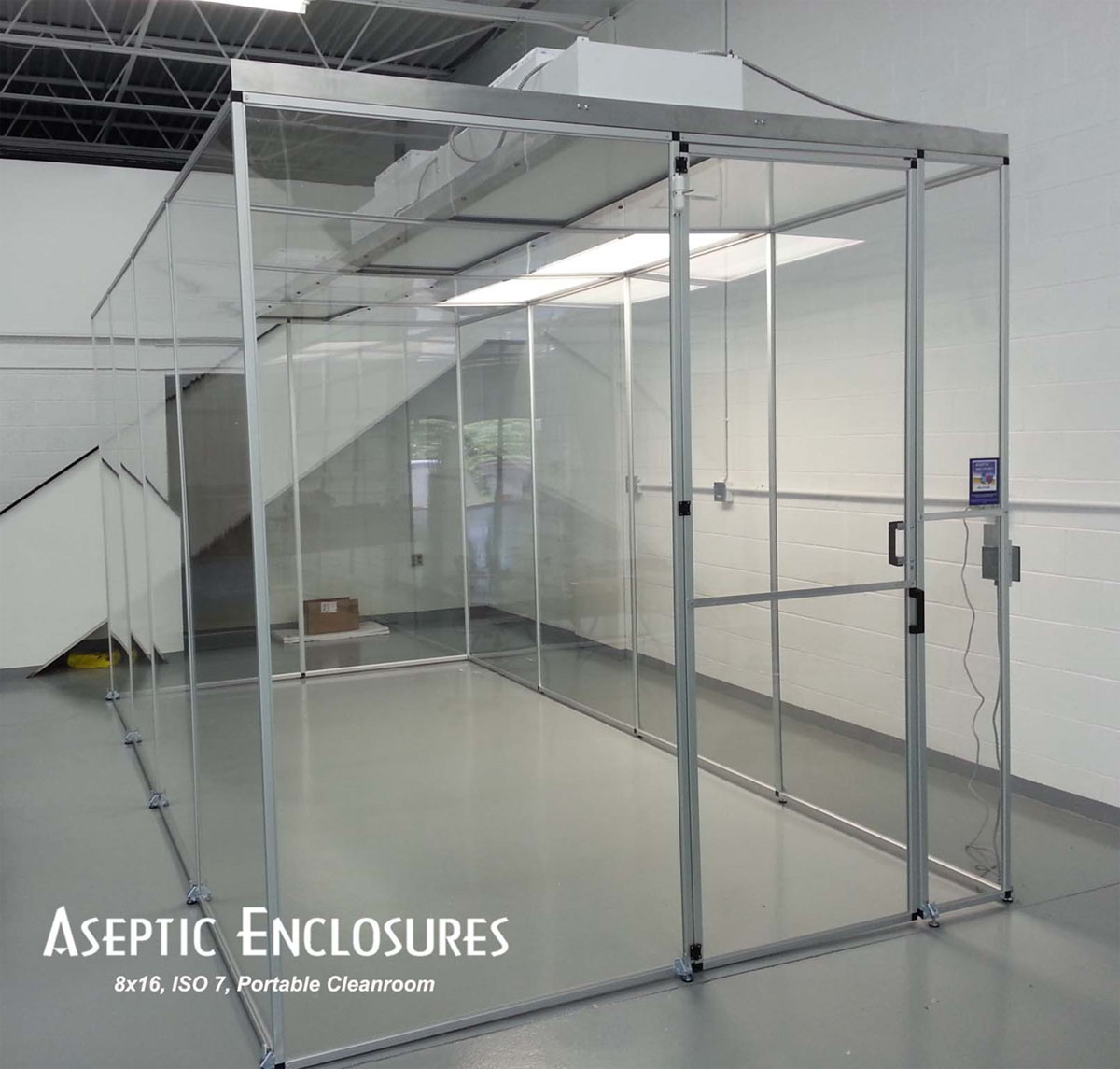
#10 Design Build Portable Cleanrooms
Domain Est. 2006
Website: asepticenclosures.com
Key Highlights: Design Build Portable Cleanrooms – Built on casters for mobility. They can be produced in a variety of sizes to accommodate your work….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Portable Cleanroom

H2: Projected Market Trends for Portable Cleanrooms in 2026
The global portable cleanroom market is poised for significant growth and transformation by 2026, driven by increasing demand across life sciences, pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and electronics manufacturing sectors. Key trends shaping the market include technological innovation, regulatory evolution, expansion into emerging markets, and a growing emphasis on flexibility and cost-efficiency in controlled environments.
1. Rising Demand in Life Sciences and Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
The continued focus on biopharmaceutical development, personalized medicine, and rapid vaccine production has intensified the need for modular and flexible cleanroom solutions. Portable cleanrooms offer scalable, compliant environments for research, pilot production, and clinical trials, making them ideal for fast-paced R&D settings. By 2026, this segment is expected to dominate market demand, particularly with the expansion of contract development and manufacturing organizations (CDMOs).
2. Advancements in Modular and Smart Cleanroom Technology
Innovation in prefabricated, reconfigurable cleanroom units with integrated IoT sensors, real-time environmental monitoring, and automated controls will be a major trend in 2026. These “smart” portable cleanrooms improve contamination control, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency. Enhanced filtration systems (e.g., HEPA/ULPA), energy-efficient designs, and compatibility with GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) standards are driving adoption in regulated industries.
3. Growth in Emerging Economies
Developing regions such as Asia-Pacific (particularly India, China, and Southeast Asia), Latin America, and parts of Africa are witnessing increased investments in healthcare infrastructure and pharmaceutical manufacturing. Portable cleanrooms offer a cost-effective and rapidly deployable solution for these markets, reducing installation time and capital expenditure compared to traditional cleanrooms. This trend is expected to accelerate market expansion through 2026.
4. Regulatory and Sustainability Pressures
Stricter global regulatory standards for contamination control—especially in pharmaceuticals and medical devices—are pushing companies to adopt compliant, auditable cleanroom solutions. Additionally, sustainability concerns are influencing design trends, with manufacturers focusing on energy-efficient HVAC systems, recyclable materials, and reduced carbon footprints in portable cleanroom construction.
5. Impact of Pandemic Preparedness and Decentralized Manufacturing
Lessons learned from the COVID-19 pandemic continue to influence infrastructure planning. Governments and private institutions are investing in mobile and portable cleanrooms for rapid response to public health emergencies, including vaccine and diagnostic production. Decentralized manufacturing models, particularly in rural or underserved areas, are also promoting the use of portable units for local production capabilities.
6. Competitive Landscape and Market Consolidation
The portable cleanroom market is becoming increasingly competitive, with both established players and niche innovators introducing differentiated products. Strategic partnerships, mergers, and acquisitions are expected to rise by 2026 as companies seek to expand geographic reach, integrate advanced technologies, and offer end-to-end cleanroom solutions.
In conclusion, the 2026 portable cleanroom market will be characterized by technological sophistication, broader industry adoption, and geographic diversification. Companies that prioritize flexibility, compliance, and sustainability will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities in this dynamic sector.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Portable Cleanrooms: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
When sourcing portable cleanrooms, organizations often focus heavily on cost and lead time while overlooking critical quality and intellectual property (IP) concerns. These oversights can result in compromised performance, regulatory non-compliance, and potential legal exposure. Below are key pitfalls to avoid in both quality assurance and IP protection.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Certification and Compliance Verification
Many suppliers may claim ISO or other cleanroom standards compliance without providing verifiable documentation. Relying on unverified certifications can lead to cleanrooms that fail to meet required air quality, particle count, or environmental control specifications, jeopardizing product integrity and regulatory approval.
Poor Material and Component Quality
Low-cost vendors may use substandard materials—such as non-HEPA-grade filters, non-compliant sealants, or off-gassing plastics—that degrade performance and contaminate sensitive environments. Inadequate structural materials can also compromise the integrity of the cleanroom over time, especially in high-usage or sterile applications.
Insufficient Testing and Validation Support
Some portable cleanrooms are delivered without proper factory acceptance testing (FAT) or installation qualification (IQ)/operational qualification (OQ) documentation. This places the burden of validation on the buyer and increases project timelines and costs, especially in regulated industries like pharmaceuticals or medical devices.
Lack of Traceability and Documentation
Reputable suppliers provide full traceability of critical components (e.g., filter batch numbers, material certifications). Sourcing from vendors who do not maintain detailed component records makes troubleshooting, audits, and regulatory submissions significantly more difficult.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
Using Generic or Copycat Designs
Some manufacturers produce portable cleanrooms that mimic patented designs from leading brands. Purchasing these units, even unknowingly, can expose the buyer to IP infringement claims, particularly if the cleanroom is used in a commercial or regulated setting where design patents are actively enforced.
Absence of IP Indemnification in Contracts
Many procurement agreements fail to include IP indemnification clauses. If a third party later asserts that the cleanroom design or components infringe their patents, the buyer may be held liable for damages or forced to replace the unit at significant cost—unless the supplier agrees to assume legal responsibility.
Customization Without IP Clarity
When working with suppliers to develop custom configurations, unclear ownership of design modifications can lead to disputes. Without a written agreement specifying that IP rights for custom features belong to the buyer (or are appropriately licensed), the supplier may reuse or resell the design, undermining competitive advantage.
Unauthorized Use of Proprietary Technology
Certain cleanroom systems incorporate proprietary airflow management, monitoring software, or modular connection systems protected by patents or trade secrets. Sourcing from unauthorized resellers or gray-market suppliers risks integrating counterfeit or reverse-engineered components that may malfunction or expose the user to legal action.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should:
– Require third-party certification reports and conduct on-site or remote audits of supplier facilities.
– Specify material and component standards in procurement contracts.
– Insist on full FAT, IQ/OQ support, and comprehensive documentation.
– Conduct IP due diligence, including patent landscape reviews for critical design features.
– Include strong IP indemnification and ownership clauses in supplier agreements.
– Source only from reputable, authorized manufacturers or distributors.
By proactively addressing both quality and IP risks, organizations can ensure their portable cleanroom investment supports long-term operational success and regulatory compliance.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Portable Cleanroom
Overview
Portable cleanrooms are self-contained, relocatable environments designed to maintain controlled levels of contamination, temperature, humidity, and pressure for sensitive operations. Proper logistics planning and regulatory compliance are essential for safe transport, installation, operation, and ongoing use. This guide outlines key considerations for managing a portable cleanroom across its lifecycle.
Transportation & Handling
- Pre-Transport Inspection: Ensure all internal components (HEPA filters, lighting, control systems) are secured and protected. Disconnect utilities and seal openings to prevent debris ingress.
- Packaging & Crating: Use manufacturer-recommended crating or protective covers. Clearly label fragile components and indicate lifting points.
- Load Securing: Secure the unit to transport vehicles using straps or chains at designated anchor points. Prevent shifting during transit.
- Route Planning: Verify route clearance (height, width, weight) and avoid rough terrain. Coordinate with site personnel for delivery access.
- Environmental Protection: Shield the unit from extreme weather, moisture, and direct sunlight during transit and temporary storage.
Site Preparation & Installation
- Foundation Requirements: Ensure the installation site has a level, stable, and clean surface capable of supporting the cleanroom’s weight. Verify load-bearing capacity with structural engineers if needed.
- Utility Access: Confirm availability and compatibility of power (voltage, phase, frequency), compressed air, exhaust connections, and data lines per manufacturer specifications.
- Clearance & Access: Maintain adequate space around the unit for servicing, airflow, and compliance with fire codes. Include access for filter replacement and maintenance.
- Environmental Controls: Assess ambient conditions (temperature, humidity, particulate levels) to ensure they fall within the cleanroom’s operational tolerance.
Regulatory & Industry Compliance
- Cleanroom Classification: Adhere to ISO 14644-1 standards for airborne particulate cleanliness. Validate classification through particle counting and certification.
- Electrical Safety: Comply with local electrical codes (e.g., NEC in the U.S., IEC internationally) and ensure grounding, circuit protection, and labeling are up to standard.
- Fire Safety: Install smoke detectors, fire suppression systems (if required), and ensure materials meet fire-resistance ratings (e.g., UL 94, FM approvals).
- Occupational Health & Safety: Follow OSHA (or equivalent) guidelines for workplace safety, including ventilation, emergency exits, and hazardous material handling.
- Pharmaceutical & Biotech Applications: Comply with cGMP (21 CFR Part 211), FDA, EMA, or other relevant regulatory frameworks for sterile manufacturing or testing.
- Environmental Regulations: Ensure compliance with EPA or local regulations for HVAC emissions, refrigerants, and waste disposal.
Operational Compliance & Maintenance
- Routine Monitoring: Implement continuous monitoring of particle counts, differential pressure, temperature, and humidity. Maintain electronic or paper logs as required.
- Scheduled Maintenance: Follow the manufacturer’s maintenance plan for HEPA/ULPA filter replacement, motor servicing, and calibration of sensors and controls.
- Cleaning Procedures: Use approved cleaning agents and methods to avoid contamination or damage to surfaces. Document cleaning activities.
- Personnel Training: Train staff on cleanroom protocols, gowning procedures, contamination control, and emergency response.
- Change Control: Document and approve any modifications to the cleanroom structure, airflow, or process to maintain compliance.
Documentation & Validation
- Installation Qualification (IQ): Document delivery, installation, and utility connections per manufacturer and regulatory standards.
- Operational Qualification (OQ): Verify all systems operate within specified parameters under no-load conditions.
- Performance Qualification (PQ): Demonstrate the cleanroom maintains required conditions during simulated or actual operation.
- Certification Reports: Retain valid cleanroom certification reports from accredited third-party testing agencies.
- Audit Readiness: Maintain logs, maintenance records, training documents, and validation reports for regulatory inspections.
Decommissioning & Relocation
- Decontamination: Thoroughly clean and decontaminate the interior before disassembly or relocation, especially if used with hazardous materials.
- Component Removal: Carefully disassemble modular panels, seal utilities, and label components for reassembly.
- Transportation Plan: Repeat pre-transport checks and secure packaging as in initial delivery.
- Re-Validation: After relocation, conduct full IQ/OQ/PQ and re-certification before resuming operations.
Conclusion
Successful deployment of a portable cleanroom depends on meticulous planning, adherence to regulatory standards, and disciplined operational practices. By following this logistics and compliance guide, organizations can ensure the integrity, safety, and performance of their portable cleanroom environment across its entire lifecycle.
In conclusion, sourcing a portable cleanroom requires careful evaluation of your specific application needs, regulatory requirements, and environmental controls. Key factors such as classification standards (e.g., ISO 14644), build quality, ease of installation and mobility, material durability, and filter efficiency must be thoroughly assessed. Additionally, considerations around supplier reputation, technical support, customization options, and total cost of ownership—including maintenance and energy consumption—play a critical role in ensuring long-term performance and compliance.
By aligning the portable cleanroom’s specifications with your operational goals and validating suppliers through due diligence, you can secure a reliable, scalable, and efficient solution that enhances contamination control, supports product quality, and improves workflow flexibility. Ultimately, a well-sourced portable cleanroom serves as a strategic investment in maintaining controlled environments across industries such as pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, electronics, and healthcare.