The global pop rivet market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand across automotive, aerospace, construction, and electronics industries. According to Grand View Research, the global rivets market size was valued at USD 5.6 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% from 2023 to 2030. A key factor shaping this growth is the increasing preference for lightweight materials, particularly aluminum, in manufacturing—especially in transportation sectors aiming to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. At the same time, stainless steel rivets remain critical in high-corrosion environments and applications requiring superior tensile and shear strength. With material selection directly impacting performance and longevity, understanding the strengths and trade-offs between stainless steel and aluminum pop rivets has become essential for engineers and procurement specialists. This analysis evaluates the top 8 manufacturers excelling in strength, durability, and innovation across both material categories, offering data-driven insights into their product performance, market presence, and technological advancements.
Top 8 Pop Rivet Strength Stailness Vs. Aluminum Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Stainless vs. Aluminum Pop Rivets Question
Domain Est. 2004
Website: sailingforums.com
Key Highlights: The rated shear strength for these is 260 pounds, and tensile strength is 320 pounds, for a single rivet. More than adequate for a sunfish …Missing: stailness manufacturer…
#2 The Blind Rivets : technical datas
Domain Est. 1998
Website: degometal.com
Key Highlights: The two mechanical properties that are essential for a blind rivet are tensile and shear strength. Tensile strength is the capacity of a rivet to resist forces ……
#3 Strength of Aluminum vs Stainless Steel Rivets
Domain Est. 2003
Website: marshfasteners.com
Key Highlights: Aluminum rivets are lighter than stainless, which means they’re easier to install. When it comes to strength, aluminum has the best strength-to-weight ratio….
#4 POP®
Domain Est. 2012
Website: stanleyengineeredfastening.com
Key Highlights: The POP rivet range includes a wide variety of high-quality fasteners that will meet the needs of your demanding manufacturing assembly process….
#5 Aluminum Rivets vs Stainless Steel Rivets
Domain Est. 2020
Website: kenenghardware.com
Key Highlights: Stainless steel rivets are more suitable for workpieces with high fastening strength, while aluminum rivets are mainly used for civilian workpieces….
#6 Difference between stainless steel rivets and aluminum rivets
Domain Est. 2020
Website: rivets-factory.com
Key Highlights: The hardness of stainless steel is much higher than that of aluminum, so the tensile and shear resistance of stainless steel is relatively large ……
#7 Aluminium Rivets in Steel
Website: dafra.com.au
Key Highlights: Explore the advantages and challenges of using aluminium rivets in steel and stainless steel, with tips for preventing galvanic corrosion….
#8 Rivets: which material is best for you?
Domain Est. 2012
Website: essentracomponents.com
Key Highlights: For example, steel rivets are stronger than aluminium rivets, but aluminium rivets (and stainless-steel solid rivets) are more corrosion ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Pop Rivet Strength Stailness Vs. Aluminum
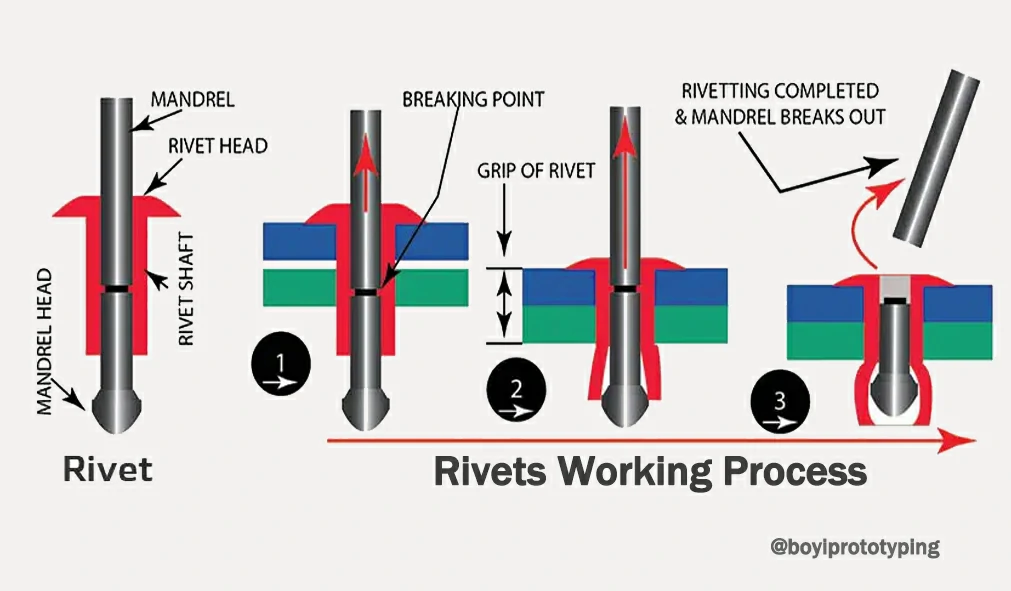
H2: 2026 Market Trends – Pop Rivet Strength: Stainless Steel vs. Aluminum
As the global fastener market evolves toward higher performance, sustainability, and cost efficiency, the competition between stainless steel and aluminum pop rivets is expected to intensify by 2026. Key market trends indicate a growing divergence in application-specific demand, driven by material properties, industry shifts, and regional economic factors.
1. Strength and Durability Demand Favors Stainless Steel
Stainless steel pop rivets continue to dominate in applications requiring high tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and longevity. By 2026, sectors such as aerospace, marine, construction, and heavy industrial manufacturing are projected to increase their preference for stainless steel rivets due to stringent safety and durability standards. Stainless steel’s superior strength—particularly grades like 304 and 316—ensures reliability in high-stress and corrosive environments, supporting long-term infrastructure projects and sustainable building initiatives.
2. Lightweight and Cost Efficiency Drive Aluminum Adoption
Aluminum pop rivets maintain a strong foothold in industries where weight reduction and cost-effectiveness are critical. The automotive and transportation sectors—especially in electric vehicle (EV) production—are expected to see rising demand for aluminum rivets by 2026. Their lighter weight contributes to improved fuel efficiency and battery range, aligning with global emissions regulations. Additionally, aluminum’s lower raw material and processing costs make it attractive for high-volume manufacturing, particularly in emerging markets.
3. Sustainability and Recycling Influence Material Choice
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals will play a pivotal role in material selection. Both stainless steel and aluminum are highly recyclable, but aluminum holds an edge in energy efficiency during recycling—requiring up to 95% less energy than primary production. This advantage may boost aluminum’s market share in eco-conscious industries. However, stainless steel’s longer service life reduces replacement frequency, contributing to lifecycle sustainability, especially in permanent installations.
4. Regional Market Dynamics and Supply Chain Shifts
By 2026, Asia-Pacific—led by China and India—is expected to be the fastest-growing market for both rivet types, driven by infrastructure expansion and industrialization. However, supply chain localization and trade policies may influence material availability and pricing. Stainless steel production is more energy-intensive and may face cost pressures due to carbon taxation in Europe and North America, potentially increasing the competitiveness of aluminum in these regions.
5. Technological Innovations and Hybrid Solutions
Advancements in coating technologies and hybrid rivet designs (e.g., aluminum rivets with stainless steel mandrels) are blurring traditional performance gaps. These innovations allow manufacturers to optimize strength-to-weight ratios, expanding application versatility. By 2026, such hybrid solutions may capture niche markets, though stainless steel will likely retain dominance in pure strength-critical applications.
Conclusion
While aluminum pop rivets are poised for growth in lightweight and cost-sensitive sectors, stainless steel will remain the material of choice where strength, durability, and corrosion resistance are paramount. The 2026 market landscape will reflect a segmented but complementary relationship between the two materials, shaped by technological progress, regulatory environments, and evolving industry needs.
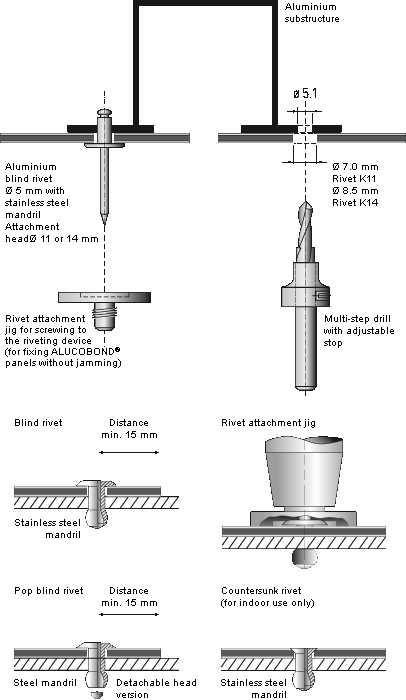
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Pop Rivets: Stainless Steel vs. Aluminum (Quality and IP Considerations)
Sourcing pop rivets, particularly when choosing between stainless steel and aluminum, involves critical decisions that impact performance, longevity, and compliance. Overlooking key quality and Ingress Protection (IP) factors can lead to product failure and increased costs. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Overlooking Material Strength Requirements
A frequent mistake is selecting rivets based solely on cost or weight without evaluating the mechanical demands of the application. Stainless steel rivets offer higher tensile and shear strength compared to aluminum, making them suitable for structural or high-stress environments. Choosing aluminum in such cases can result in joint failure, especially under vibration or load. Conversely, using stainless steel in low-stress, weight-sensitive applications may add unnecessary cost and complexity.
Neglecting Corrosion Resistance and Environmental Exposure
While stainless steel provides superior corrosion resistance—especially in humid, marine, or chemically aggressive environments—some assume all “stainless” grades perform equally. Sourcing low-quality stainless steel (e.g., non-austenitic grades or counterfeit materials) can lead to premature rusting. Aluminum naturally forms an oxide layer, but in salty or acidic conditions, galvanic corrosion can occur when aluminum rivets are used with dissimilar metals. Failing to consider the full environmental profile and material compatibility is a major quality risk.
Ignoring Ingress Protection (IP) Ratings in Sealed Applications
Pop rivets are often used in enclosures requiring specific IP ratings (e.g., IP65, IP67) for dust and water resistance. Standard open-tail rivets can compromise sealing, allowing moisture and contaminants to enter. A common pitfall is using basic aluminum or stainless rivets without specifying sealed or blind rivets with rubber grommets or plugging features. Even with corrosion-resistant materials, improper sealing undermines the intended IP performance, leading to equipment damage.
Accepting Substandard Manufacturing Quality
Low-cost suppliers may offer rivets with inconsistent diameters, improper mandrel break points, or poor head formation. This is especially prevalent with imported aluminum rivets, where dimensional tolerances affect installation reliability and clamping force. For stainless steel, poor cold-working during manufacturing can reduce ductility and lead to cracking during installation. Always verify supplier certifications (e.g., ISO 9001) and request material test reports (MTRs) to ensure quality.
Failing to Match Rivet Type to Installation Tools and Techniques
Using high-strength stainless steel rivets with underpowered hand tools can result in incomplete setting or tool damage. Aluminum rivets, being softer, may deform incorrectly with excessive force. Mismatched tooling leads to inconsistent joint quality and reduced fatigue life. Additionally, some sealed or structural rivets require specific nosepieces or installation procedures that are often overlooked during sourcing.
Underestimating Total Cost of Ownership
While aluminum rivets are cheaper upfront, their lower durability in harsh environments may necessitate more frequent maintenance or replacement. Stainless steel, though costlier initially, often provides longer service life and reduced lifecycle costs in demanding applications. Focusing only on initial price per unit without evaluating long-term performance is a strategic error.
By addressing these pitfalls—through rigorous material selection, attention to environmental and IP requirements, quality verification, and lifecycle cost analysis—sourcing professionals can ensure reliable, compliant, and cost-effective fastening solutions.
Logistics & Compliance Guide: Pop Rivet Strength – Stainless Steel vs. Aluminum
Material Properties and Strength Comparison
When selecting pop rivets for industrial or construction applications, understanding the mechanical properties of stainless steel and aluminum is crucial. Stainless steel pop rivets typically offer higher tensile and shear strength compared to aluminum. For example, 304 or 316 stainless steel rivets can have tensile strengths exceeding 70,000 psi, while aluminum rivets (such as 5056 alloy) generally range between 30,000 and 40,000 psi. This makes stainless steel ideal for high-stress environments, whereas aluminum is better suited for lightweight assemblies where strength demands are moderate.
Corrosion Resistance and Environmental Suitability
Stainless steel rivets, especially those made from grade 316, provide superior corrosion resistance, making them ideal for marine, outdoor, or high-humidity environments. Aluminum rivets also resist corrosion well due to their natural oxide layer but are more prone to galvanic corrosion when used with dissimilar metals, particularly steel or copper. Proper material compatibility planning is essential during design and installation to avoid premature joint failure.
Weight Considerations and Handling
Aluminum pop rivets are significantly lighter than their stainless steel counterparts—typically about one-third the density. This makes aluminum ideal for aerospace, automotive, and other weight-sensitive applications. The reduced weight also simplifies logistics, lowering shipping costs and improving ease of handling during high-volume installations. However, this weight advantage comes at the expense of lower mechanical strength.
Regulatory Compliance and Industry Standards
Both stainless steel and aluminum pop rivets must comply with relevant industry standards to ensure safety and performance. Common standards include:
– ASTM F468: Standard specification for stainless steel blind rivets.
– ASTM F1301: Standard specification for aluminum alloy blind rivets.
– NASM13392 / MS20426: Aerospace-grade rivet specifications.
Ensure rivets are certified and traceable, particularly in regulated industries like aerospace, defense, and medical equipment, where material traceability (e.g., mill test reports) and RoHS/REACH compliance may be required.
Shipping and Storage Requirements
Stainless steel and aluminum rivets have similar shipping profiles, typically packaged in moisture-resistant containers to prevent corrosion. However, aluminum rivets should be stored away from steel materials to avoid galvanic reactions. Both materials are non-hazardous under DOT, IATA, and IMDG regulations, allowing standard transportation methods. Use clearly labeled packaging indicating material type, alloy grade, diameter, and length to support inventory accuracy and traceability.
Handling and Installation Tools
Installation tools (rivet guns) must be compatible with the rivet material. Stainless steel rivets require higher pulling forces due to their strength, often necessitating heavy-duty rivet tools or hydraulic systems. Aluminum rivets, being softer and weaker, can be installed with standard hand tools. Using the correct mandrel and nose piece is essential to prevent tool wear and ensure proper blind-side formation.
End-of-Life and Sustainability
Both materials are highly recyclable, aligning with sustainability goals. Aluminum has a lower melting point and requires less energy to recycle than stainless steel, offering environmental advantages in closed-loop systems. Proper segregation during disposal is necessary to maintain recyclability. Compliance with WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives may apply depending on the application sector.
Selection Guidelines Summary
Choose stainless steel pop rivets for:
– High-strength requirements
– Corrosive or outdoor environments
– Long-term durability where maintenance is limited
Choose aluminum pop rivets for:
– Lightweight applications
– Non-structural or moderate-load joints
– Cost and shipping efficiency in high-volume use
Always verify compliance with project-specific codes, environmental regulations, and material compatibility to ensure safe and reliable performance.
Conclusion: Sourcing Pop Rivet Strength – Stainless Steel vs. Aluminum
When selecting pop rivets for a specific application, the choice between stainless steel and aluminum involves a careful balance of strength, weight, corrosion resistance, and cost. Stainless steel pop rivets offer superior tensile and shear strength compared to aluminum, making them ideal for high-stress environments and structural applications where durability is critical. They also provide excellent resistance to corrosion, UV exposure, and extreme temperatures, ensuring long-term performance in harsh conditions such as marine, industrial, or outdoor settings.
In contrast, aluminum pop rivets are significantly lighter and more cost-effective, making them suitable for applications where weight savings are essential, such as in aerospace or automotive body panels. While aluminum rivets offer good corrosion resistance in many environments, they are generally less strong than stainless steel and may not perform as well under heavy loads or in aggressive chemical environments.
Ultimately, the decision should be guided by the specific requirements of the application. For maximum strength and durability, especially in demanding environments, stainless steel pop rivets are the preferred choice. However, where weight reduction and cost efficiency are priorities—and loads are moderate—aluminum pop rivets provide a practical and effective solution. Proper sourcing should therefore consider both material properties and operational demands to ensure optimal performance and longevity.