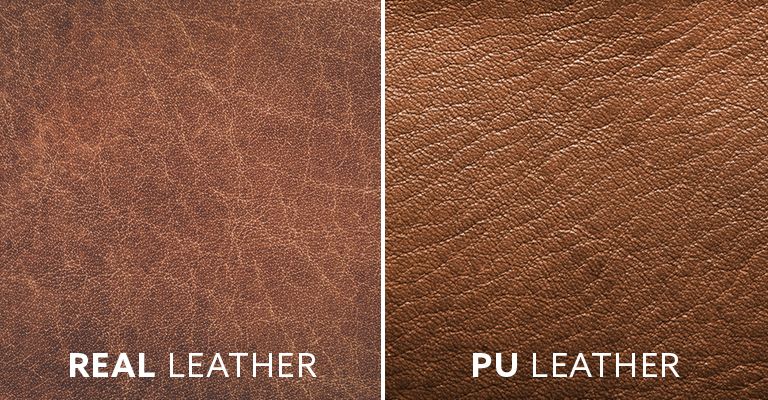
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for Polyurethane Upholstery
Procurement teams in the USA and Europe face a dual mandate: specify upholstery that looks and feels like premium leather while protecting budgets, timelines, and compliance. Polyurethane (PU) and semi-urethane upholstery deliver a supple, leather-like hand at a lower cost than genuine leather, yet buyers still encounter quality variability, inconsistent chemistry, and regulatory differences across regions.
What you’ll learn:
– Market landscape: why PU matters; USA vs. Europe differences
– Product basics: PU vs. semi-urethane vs. PVC; how formulations, backing, and finishes impact hand, durability, and care
– Supplier strategy: supplier selection, certifications, minimums, lead time, and risk management
– Price and terms: CFR/FOB/CIF, currency, payment, and commercial clauses
– Quality and compliance: standards, material safety (REACH, Prop 65), VOCs, and testing
– Logistics: packaging, roll vs. roll/yardage, sampling, QC plan, and customs
– Negotiation levers: total landed cost, schedule flexibility, and vendor development
Quick comparison to orient decisions:
| Material | Hand Feel | Typical Applications | Indicative Price Band (USD/yd) | Compliance Focus |
|———|———–|———————-|——————————-|——————|
| PU/Semi-urethane | Soft, leather-like | Contract seating, hospitality, marine | ~$6.97–$20.95 | Verify regional standards (e.g., EN 1021; TB 117-2013) |
| Traditional PVC vinyl | Firmer, stiffer | General upholstery, partitions | Varies | DMF usage and REACH implications (country-dependent) |
How to use this guide: start with material basics to match your end-use, then apply supplier, pricing, compliance, and logistics frameworks to select, negotiate, and manage a resilient vendor portfolio.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Article Navigation
- Top 10 Polyurethane Upholstery Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for polyurethane upholstery
- Understanding polyurethane upholstery Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of polyurethane upholstery
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘polyurethane upholstery’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for polyurethane upholstery
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for polyurethane upholstery
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘polyurethane upholstery’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for polyurethane upholstery Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing polyurethane upholstery With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for polyurethane upholstery
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the polyurethane upholstery Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of polyurethane upholstery
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for polyurethane upholstery
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Top 10 Polyurethane Upholstery Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. 6 Best Foam Suppliers – Redesign Upholstery
Domain: redesignupholstery.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: 1. Pomona Quality Foam · 2. Adams Foam · 3. Hibco Foam Plastics · 4. New England Foam Products · 5. Merryweather Foam · 6. Custom Foam Products, Inc….
2. Stanley Foam Co. – Polyurethane Foam | Wallington, NJ
Domain: stanleyfoam.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: In business since 1965. FREE problem solving advice. Upholstery products. Polyurethane foam. Foam rubber, supplies, tools and more. Call 973-778-1660….
3. Polyurethane Companies – Top Company List – Mordor Intelligence
Domain: mordorintelligence.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Top 5 Polyurethane Companies ; Huntsman International LLC ; Engages in the development of specialty chemicals, particularly for flexible and rigid polyurethanes….
4. Upholstery – Arc|Com
Domain: arc-com.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: The Arc-Com Design Team creates, develops and introduces innovative and high performance textile products for the corporate, hospitality, healthcare and ……

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
5. All Upholstery | Carnegie Fabrics
Domain: carnegiefabrics.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: From bleach cleanable and finish-free textiles to coated fabrics, our upholstery solutions come in an array of designs, colors and patterns….
6. Furniture & Comfort – Pearl Polyurethane
Domain: pearlpolyurethane.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Comfortable and functional upholstered furniture often use polyurethane foams as the core with products ranging from office chairs to beds….
7. Grand Rapids Foam Technologies – Custom Foam Solutions
Domain: grft.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Discover top-notch polyurethane foam manufacturing. With 75 years of excellence, we offer personalized solutions for diverse industries. Contact us!…
Understanding polyurethane upholstery Types and Variations
Understanding Polyurethane Upholstery Types and Variations
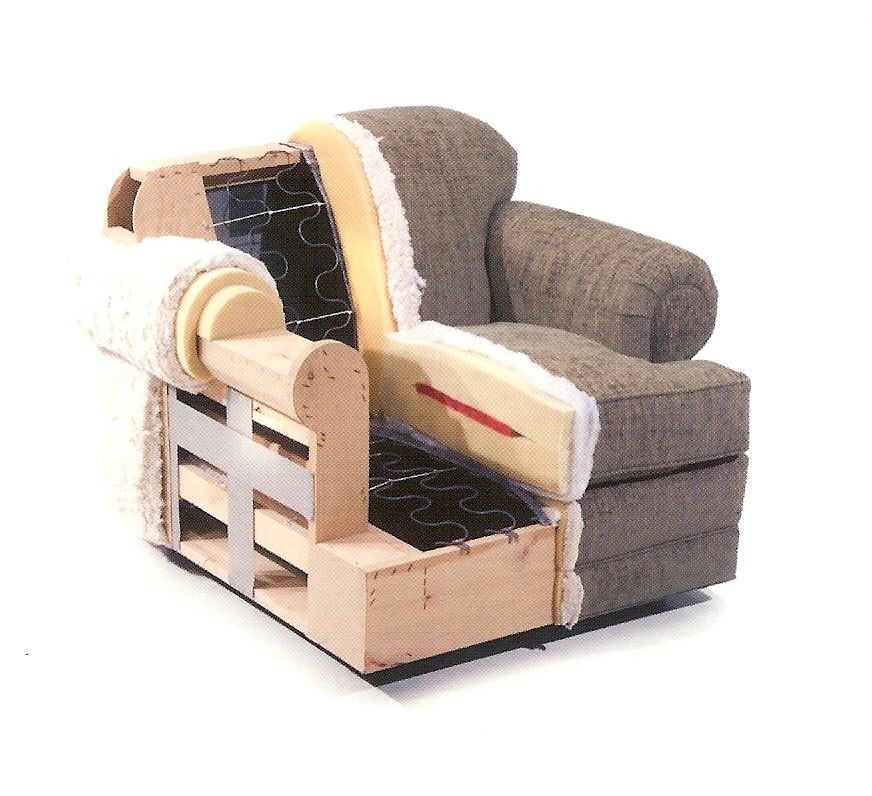
Choosing the right polyurethane (PU) upholstery requires clarity on chemistry, construction, and finish—each affecting hand feel, durability, cleanability, and regulatory fit. The following overview distinguishes core PU types and the most impactful variations for B2B decision-making.
Core Types and Variations (Quick Comparison)
| Type | Features | Applications | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100% PU (solventborne) | 100% PU polymer; high flex-crack resistance; leather-like hand; typically 0.7–1.2 mm; breathable microporous structure | Seating in hospitality, healthcare waiting areas, contract furniture, automotive interiors | Supple hand; good abrasion and flex performance; stable colors | Higher VOC potential; formulation/finish dependent; can be sensitive to harsh cleaners |
| 100% PU (waterborne) | 100% PU latex dispersed in water; lower VOC; similar hand and durability to solventborne; PFAS-free topcoats common | High-compliance interiors; commercial healthcare/office seating; education facilities | Lower VOC; strong abrasion and flex; good chemical/cleaner resistance when properly finished | Slightly higher cost; cure/drying climate sensitive |
| Semi-PU (PU/PVC blend) | Composite face (PU over PVC) with foam or knit backing; softer than typical vinyl; leather-like hand at lower price | Hospitality lounge chairs, headboards, wall panels, contract decor | Cost-effective; leather-like feel; broad colorways | Can show seam tracking; less breathable; lower heat resistance vs premium PU |
| Backed PU (with knit/woven/polyester backing) | PU face over knit/polyester scrim; improved seam strength and dimensional stability; tailored stretch | Tight-back sofas, curved frames, high-wear contract seating | Strength and stability; reduces seam slippage; good conformability | Heavier; may need specific sewing methods; potential seam visibility |
| Finished PU (silicone or fluorocarbon topcoats) | Treated PU topcoat for stain release and cleanability; graffiti/ink resistance common | Healthcare, hospitality, education, transport | Excellent cleanability; stain/oil resistance; consistent aesthetics | Finish life varies; re-treatment may be needed; formulation-specific performance |
100% PU Upholstery (Solventborne and Waterborne)
- What it is: True PU leather—a 100% polyurethane polymer surface engineered for supple, leather-like hand, flex-crack resistance, and abrasion durability.
- Construction: Microporous structure with breathable cells, usually supplied 0.7–1.2 mm thick; may include knit or polyester backings for stability.
- Finish/topcoat: Silicone or fluorocarbon treatments are common to improve stain release and resistance to inks and oils. Waterborne systems are increasingly PFAS-free.
- Applications: Hospitality seating, healthcare waiting areas, contract furniture, and automotive interiors where aesthetics and durability must balance.
- Key attributes: Supple hand, strong flex performance, consistent colorfastness, good abrasion scores when properly formulated.
- Considerations: Solventborne variants carry higher VOC potential; waterborne variants support stricter environmental requirements but may be costlier and require controlled drying.
Semi-PU (PU/PVC Blend) Upholstery
- What it is: A composite face combining PU over PVC, typically supported by a foam or knit backing to achieve a softer hand at a lower price point.
- Construction: PU top layer provides leather-like feel; underlying PVC adds structure; backing adds cushioning and stability.
- Applications: Headboards, wall panels, contract lounge seating, decorative frames—where budget and aesthetic softness matter but maximum durability is less critical.
- Key attributes: Leather-like hand softer than typical vinyls; broad colorway availability.
- Considerations: Can exhibit seam tracking or delamination under stress; less breathable and lower heat resistance versus premium PU.
Backed PU Upholstery (Knit/Woven/Polyester Backings)
- What it is: PU face layer adhered to knit, woven, or polyester scrim/backing to enhance seam strength, dimensional stability, and conformability.
- Construction: Backings range from lightweight knits to robust polyester scrims; selection influences stretch, seam performance, and upholstery handling.
- Applications: Tight-back sofas, curved frames, high-wear contract seating requiring strong seam integrity and controlled stretch.
- Key attributes: Improved seam slippage resistance; better dimensional stability; consistent handling during fabrication.
- Considerations: Heavier constructions may require specialized sewing methods; slight trade-offs in hand vs. heavier weight.
Finished PU Upholstery (Silicone/Fluorocarbon Topcoats)
- What it is: PU upholstery with enhanced surface treatments—often silicone or fluorocarbon—optimized for stain release and cleanability.
- Performance: Graffiti and marker resistance, oil and ink repellency, and easier maintenance, particularly valuable in healthcare, hospitality, and transport.
- Applications: High-traffic, high-cleanability environments; public seating and walls subject to frequent sanitation.
- Key attributes: Superior cleanability; consistent aesthetics; reduced maintenance overhead.
- Considerations: Finish durability depends on formulation and use intensity; re-treatment may be required over time to maintain performance.
Selection Notes for USA and Europe
- Regulatory alignment: Waterborne PU typically simplifies VOC compliance; confirm local requirements (US EPA/CARB, EU REACH).
- Finish choice: For demanding environments, select PU with robust stain-release topcoats; for budget-sensitive projects, semi-PU can deliver leather-like hand at lower cost.
- Backing impact: Knit or polyester backings improve seam performance and dimensional stability; match backing to frame geometry and upholstery technique.
This framework enables sourcing teams, designers, and specifiers to map PU types to performance, compliance, and application requirements efficiently.
Key Industrial Applications of polyurethane upholstery
Key Industrial Applications of Polyurethane Upholstery
Why PU matters in commercial environments
PU and semi-PU upholstery (often labeled “PU leather”) deliver a supple, leather-like hand at accessible price points, with diverse textures and colors that suit design-forward and heavy-wear settings. Compared with typical vinyls and faux leathers, PU is lighter, often more breathable, and easier to shape, while still enabling robust service-life performance when matched to the right specification.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Applications by industry (USA & Europe)
| Industry/Segment | Typical Use-Cases | PU/Upholstery Types | Key Benefits | Compliance/Considerations | Reference Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contract Office & Corporate Seating | Task, guest, lounge, and modular seating; breakroom and lobby furniture | 100% PU and semi-PU (cast/laminated/coated), embossed grain finishes | Supple hand with high tear/abrasion resistance; wide colorways and patterns; cost-efficient vs genuine leather; reduced plasticizer migration vs PVC | Confirm FR behavior and low VOC performance for the specific grade (e.g., CAL TB 117-2013; CA Prop 65 in CA). Note that FR performance varies by formulation; verify for your grade | PU is softer than typical vinyls and offers diverse textures/colors |
| Hospitality (Hotels, Restaurants, Bars, Nightclubs) | Headboards, banquettes, booths, lounge seating, lobby pieces | 100% PU or semi-PU topcoats on warp-knits/nonwovens; high-traffic finishes | Resilient to scuffing; stain-resistant topcoats; cohesive leather aesthetic across colorways; consistent yardage availability | Seek stain-resistant/topcoat options; verify FR for upholstery in sleeping rooms and public spaces per local codes | Catalog patterns emphasize varied textures/colors for design continuity |
| Healthcare (Clinics, Assisted Living, Patient Rooms) | Patient seating, visitor chairs, lounge pieces, procedure-room seating | High-cleanability PU with stain- and chemical-resistant finishes | Cleanable surfaces with disinfectant-compatible finishes; reduced tackiness; lighter weight than leather | Confirm chemical resistance to expected disinfectants and cleaners; check FR and low-emission claims for the exact grade | Soft hand can increase patient comfort; verify topcoat chemistry |
| Education (Universities, Schools, Libraries) | Lecture hall seating, student lounges, library stacks, dining | 100% PU or semi-PU with abrasion-focused backings | Durability for frequent use; aesthetic cohesion across campus projects | Verify FR requirements for educational occupancies; request low-VOC emissions data where applicable | Textures/patterns support brand and wayfinding themes |
| Entertainment & Leisure (Theaters, Museums, Lounges) | Auditorium seating, lounge seating, VIP boxes, ticketing counters | 100% PU with high-abrasion backings; embossed grain | Comfort, wear resistance, and cleanability for public seating | Confirm FR and flammability requirements for assembly spaces | Supple feel enhances guest experience |
| Transportation Interiors (Transit Buses/Rail, Aviation, Marine) | Seating, headrests, armrests, wall panels | PU and semi-PU composites; soft-hand laminates | Lighter than leather; good tear strength; design flexibility across interiors | Compliance to transport-specific FR, smoke/toxicity, and low-emission standards is grade-dependent | SUPA (e.g., Duratouch) names are relevant to public-transit, with finish names referenced |
| Retail & Pop-Up Stores | Feature walls, fixtures, shop-in-shop seating | 100% PU; printed/coated embossed grains | High style with lower cost; consistent color matching; quick turnover for pop-ups | Ensure FR for display fixtures as required | Rich textures help create brand statements |
| Senior Living | Lounge seating, dining chairs, bedroom seating | Soft-hand PU with cleanability topcoats | Comfortable touch; cleanable for care environments; cost-effective refresh cycles | Validate disinfectant compatibility and FR for sleeping/lounge areas | Softer hand improves perceived quality and resident comfort |
| Cruise Lines & Marine | Public-area seating, daybeds, cabin furniture | PU/semi-PU with marine-suited finishes | Soft hand in humid environments; easier to reupholster than leather | Confirm UV and moisture resistance in product data for your grade | Avoids leather upkeep while achieving upscale aesthetics |
What PU brings across applications
- Design and hand
- Leather-like drape and soft hand; broad grain/texture palette; consistent color runs and patterns.
- Performance
- High tear and abrasion resistance; good cold crack performance; breathable feel compared with vinyls; typically lighter than leather.
- Maintainability
- Cleanable with appropriate topcoats; stain-resistant options; easier patch-and-repair during refurbishment cycles.
- Cost and sustainability
- Lower cost vs genuine leather; material efficiency and potential for thinner gauges; can support refurbishment and extended service life.
- Flexibility for procurement
- Available across budget and premium collections (e.g., semi-PU topcoats vs full PU); readily sourced in US/EU with closeout/standard programs.
Specification notes (USA & Europe)
- FR compliance: Requirements vary by end use and jurisdiction (e.g., hospitality rooms, transport, public assembly). Always confirm the specific grade’s FR certification(s) and test standards with the supplier.
- Low-VOC/emissions: Ask for VOC data and certifications for projects where indoor air quality is a priority.
- Cleanability and disinfection: Verify topcoat chemistries and recommended cleaners; confirm compatibility with facility disinfectants to avoid surface damage.
- UV/weathering: For marine and exterior-adjacent applications, confirm UV and moisture performance; grade-dependent.
- Thickness and backing: Match thickness and backing to stress points (seat pans, arms) to optimize durability.
- Sustainability: Where relevant, request recycled content, chemical restrictions, and end-of-life guidance; validate against your internal targets and regional regulations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘polyurethane upholstery’ & Their Solutions
3 Common User Pain Points for Polyurethane Upholstery & Their Solutions
Pain Point 1 — Softer “hand” vs. durability trade-offs
- Scenario
- A product team selects PU or semi-PU upholstery for its leather-like softness, then discovers the initial rub performance and seam strength vary by line and construction.
- Problem
- Variability in formulation and backings can lead to mixed results on abrasion, seam slippage, and touch—making it harder to standardize feel with durability across SKUs and batches.
- Solution
- Treat PU/semi-PU as a family of performance levels. Define and document minimums at specification stage, validate with lot-specific QC, and avoid closeouts for mission-critical runs.
| Selection & Validation Checklist | What to do | Why it matters |
|---|---|---|
| Define use and touch target | State the desired hand feel and application severity (e.g., accent vs. high-contact) | Aligns material choice to real use conditions |
| Spec the fabric family | Separate PU vs. semi-PU; note backing type, thickness, and finish | Different constructions perform differently |
| Set minimum QC thresholds | Require: seam slippage resistance; flex/fold cracking checks; Martindale or similar abrasion (light/duty as appropriate) | Ensures repeatable performance and prevents early wear |
| Request certification/data | Ask supplier for backing type, finish chemistry, and applicable test reports | Confirms construction claims and reduces surprises |
| Evaluate pre-production samples | Run mock-ups, seams, and folds across colorways | Identifies performance variation before mass production |
| Avoid closeouts for critical runs | Use closeouts for non-critical accents or sample-only use | Closeouts can include end-of-line variability and limited reworkability |
Notes based on source materials
– PU and semi-PU differ from typical faux vinyl in suppleness and hand feel; performance can vary by line and pattern.
– Inventory states (e.g., “Closeout”) and stock yardage should be matched to application risk.
Pain Point 2 — Color lot matching and visible inconsistencies
- Scenario
- Designer selects a colorway (e.g., JUBILEE, LARA, ARIES) based on a sample; subsequent rolls arrive with noticeable color drift or gloss differences.
- Problem
- Even small shifts are visible on large, continuous surfaces and accent pieces, causing rework, rejections, or brand mismatches.
- Solution
- Implement color and finish lot management across the full BOM, not just the primary fabric.
| Color & Finish Lot Control | Action | What it prevents |
|---|---|---|
| Lock master swatch | Approve a sealed swatch per colorway from the chosen lot | Establishes a color baseline |
| Match full specification | Confirm color, finish level, and gloss together | Finish changes can look like color shifts |
| Document lot/batch IDs | Record roll/lot on cut tickets and trim spec sheets | Traceability for future replenishment |
| Sample from each lot | Pull and approve side-by-side swatches from every incoming lot | Detects drift before sewing |
| Test lightfastness | Compare exposure on master vs. new lot | Predicts long-term consistency |
| Align trim | Specify and purchase matching dye lots for threads, edges, and labels | Avoids trim “off” color when the fabric is on target |
| Set tolerances | Define acceptable ΔE and finish uniformity for acceptance | Clear go/no-go criteria |
| Separate critical vs. non-critical | Use closeouts only on less visible areas or mock-ups | Limits visibility of unavoidable variation |
Notes based on source materials
– Multiple colorways are available across patterns (e.g., JUBILEE, LARA, DURATOUCH, ARIES). Each colorway may have distinct lot histories.
– Closeout inventory and yardage availability vary; plan replenishment early.
Pain Point 3 — Cleaning and maintenance compatibility
- Scenario
- A hospitality client applies a standard vinyl cleaner and notices tackiness, surface haze, or “gumming,” especially on high-touch areas.
- Problem
- Many cleaners and conditioners intended for PVC/vinyl or traditional leather can negatively affect PU/semi-PU topcoats, changing feel and appearance.
- Solution
- Adopt a PU-specific care regimen and communicate it to facility teams and end customers.
| PU Upholstery Care Protocol | Do | Don’t |
|---|---|---|
| Daily | Wipe with a soft, lint-free cloth; remove spills promptly | Use abrasive pads or aggressive scrubbing |
| Routine cleaning | Use mild, PU-safe cleaner per supplier guidance; test in an inconspicuous area | Use acetone, alcohol, solvents, or PVC/vinyl cleaners/conditioners |
| Stains | Blot, don’t rub; follow supplier’s spot-clean guidance | Over-wet the surface or use heat to “set” stains |
| Disinfection | Verify disinfectant compatibility for PU; avoid harsh quats/alcohol if not cleared | Assume all hospital-grade wipes are safe for PU |
| Testing | Run a touch/look check after each clean to catch early changes | Clean large areas without a pre-test |
| Training | Provide a one-page care sheet to housekeeping/facilities | Rely on generic vinyl or leather procedures |
Why this works
– PU and semi-PU are softer than many faux vinyls and can be more sensitive to solvent-type cleaners. Maintaining a PU-specific protocol preserves hand feel and finish integrity.
Implementation tip
– Tie the care protocol to SKU-level material families and lot tracking so cleaning guidance follows the exact finish deployed on site.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Strategic Material Selection Guide for polyurethane upholstery
Strategic Material Selection Guide for Polyurethane Upholstery
Purpose: align product choice to price tier, stock needs, and application fit while maintaining a leather-like hand and budget control.
- Definition and differentiators
- PU and semi-urethane upholstery faux leather offer a softer, more supple “hand” compared with typical vinyl, closer to genuine leather.
-
Price, texture, and colorway variety differ by brand and collection; selection should be driven by availability, price per yard, and intended use.
-
Price tiers as decision anchors
- Economy: $6.97–$10.12/yard. Use for low-traffic staging, contract spec hold-outs, and budget prototypes.
- Mid: $13.29–$18.99/yard. Use for everyday contract seating, waiting areas, and hospitality where durability expectations are higher.
-
Premium: $20.95/yard. Use for statement pieces, high-visibility reception, and projects where perceived quality is critical.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Stock planning
-
Check current inventory and “More yardage available” flags. Where continuity over time is required, favor lines showing additional yardage.
-
Procurement best practice
- Confirm colorway availability and lot-to-lot matching.
-
Request updated swatches and technical data prior to specification.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Compliance and region
- Validate FR, chemical, and emissions requirements with each supplier for USA and Europe (e.g., REACH, Prop 65 as applicable).
-
Note: specific standards and certifications are not provided in the source; do not assume compliance.
-
Application notes
-
Choose texture and colorway to match use. For higher wear environments, move up a price tier within the same project where possible to reduce lifecycle risk.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Comparison table: representative PU upholstery SKUs and attributes
| SKU | Brand | Product Name | Price ($/yd) | Stock (yd) | More Yardage? | Colorways | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6157813 | — | ARIES IVORY | 6.97 | 5 | No | — | Economy; soft hand |
| 6158115 | — | LARA WHITE | 10.12 | 19 | No | More available | Economy; multiple colorways |
| 6158113 | — | LARA IVORY | 10.12 | 13 | No | More available | Economy; multiple colorways |
| 6158112 | — | LARA BRONZE | 10.12 | 11 | No | More available | Economy; multiple colorways |
| 445782 | Omnova Boltaflex | DURATOUCH 445782 FOREST | 13.97 | 27 | No | More available | Mid; curated colorway |
| 445787 | Omnova Boltaflex | DURATOUCH 445787 ROSE | 13.97 | 26 | No | More available | Mid; curated colorway |
| 445781 | Omnova Boltaflex | DURATOUCH 445781 MOSS | 13.97 | 20 | No | More available | Mid; curated colorway |
| 445776 | Omnova Boltaflex | DURATOUCH 445776 SQUASH | 13.97 | 7 | No | More available | Mid; curated colorway |
| 7115211 | — | JESSE TERRACOTTA | 18.99 | 37 | Yes | More available | Mid; higher price tier |
| 7115213 | — | JESSE BLACK | 18.99 | 23 | Yes | More available | Mid; higher price tier |
| 7115212 | — | JESSE ARMY GREEN | 13.29 | 5 | No | More available | Closeout; verify availability |
| 7084612 | — | JUBILEE PEARL | 20.95 | 27 | Yes | More available | Premium tier |
| 7084617 | — | JUBILEE SPA | 20.95 | 27 | Yes | More available | Premium tier |
Notes:
– “More yardage available” indicates greater continuity potential for larger runs.
– Availability, yardage, and colorways are dynamic; confirm current values before specification.
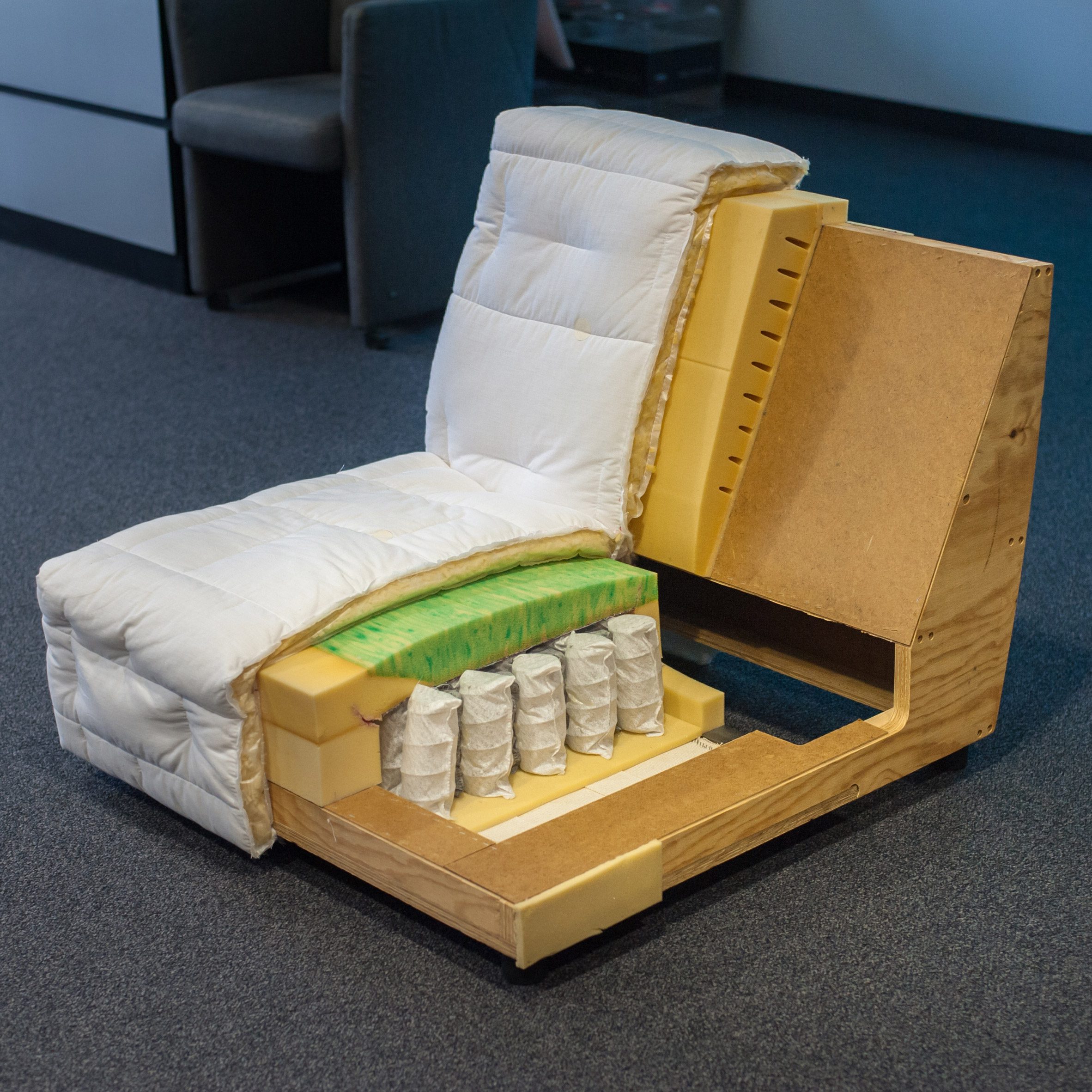
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for polyurethane upholstery
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for Polyurethane Upholstery
Purpose: Clarify how polyurethane (PU) and semi-urethan faux leathers are made for upholstery, and how consistent quality is achieved from substrates through final shipment. This overview is oriented to U.S. and European buyers and covers process control, key quality tests, and compliance.
Manufacturing Steps
| Step | What happens | Why it matters | Typical parameters (qualitative) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Substrate preparation | Clean, back-coat (if needed), and heat-set knitted or woven polyester/poly-cotton blends; optionally apply a scrim or reinforcement for dimensional stability. | A stable, clean substrate ensures uniform resin take-up and seam performance. | Uniform coating weight; tension control; moisture content managed to prevent defects. |
| 2. Resin formulation & system selection | Choose either solventborne PU or aqueous PU dispersion systems; add pigments, UV absorbers, slip and leveling agents; prepare crosslinker (isocyanate) for wet-on-wet/online cure. | System choice influences hand feel, breathability, abrasion, hydrolysis resistance, and emissions. | Viscosity tuned to application method; solids content optimized per line speed. |
| 3. Direct or transfer coating | Apply a base PU resin layer onto the prepared substrate (direct) or onto a release paper (transfer), then dry/cure. | Builds the base film/microporous structure and adhesion. | Controlled air temperature zones; line speed matched to gel/curing time. |
| 4. Microporous layer (optional) | For soft-hand, breathable PU: generate open-cell microporous structure by controlled moisture diffusion/coagulation during drying, followed by washing and drying. | Delivers supple hand and moisture transport; improves leather-like feel. | Precise humidity/temperature profiles to control pore size and distribution. |
| 5. Grain embossing | Use heated engraved rollers to emboss realistic grain while the PU is still plastic; set precise temperature/pressure/dwell. | Controls visual grain depth and tactile feel; reduces surface gloss variations. | Temperature ramp matched to resin heat-deflection; nip pressure tuned for uniform definition. |
| 6. Surface finishing | Apply topcoats (clear PU/polyacrylate) with stain- and scratch-resistant chemistry; optional anti-microbial and flame-retardant finishes. | Enhances durability, cleanability, and maintains color fastness. | Film weight tuned for hand; post-cure to achieve crosslinking. |
| 7. Cooling and roll-up | Cool under tension and spool; inspect via web inspection systems for pinholes, streaks, or defects. | Prevents back-coat transfer and warping; early detection of line issues. | Controlled tension; ambient cooling time before winding. |
| 8. Cutting and packaging | Slit or sheet to width, cut to specified lengths, roll with protective films/boards, label, and package. | Protects finish during transport; maintains traceability. | Clean cuts to avoid tearing; edge protection on rolls. |
| 9. Upholstery assembly (as applicable) | Bond with compatible PU adhesives; handle with low-tension tools to prevent abrasion and seam stress; conduct fit-up checks before shipment. | Protects hand-feel and appearance; prevents seam slippage. | Use recommended cleaners; avoid high heat in finishing procedures. |
Notes on system choices:
– Solventborne systems generally yield superior hand and depth, but require stricter emissions controls and crosslinker hygiene.
– Aqueous systems minimize solvent emissions; require robust drying capacity for consistent film formation.
– Semi-urethan variants typically use lighter-weight or fewer topcoats, trading some durability for a softer hand; ensure performance validation if specifying semi-urethan.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Quality Assurance (QA) and Testing
QA follows ISO 9001 principles (process control, nonconformance, corrective actions, and traceability) and relies on accredited labs operating per ISO 17025.
Common U.S./EU tests and acceptance considerations:
| Category | Test / standard | Purpose / notes | Typical acceptance range (buyer-defined) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abrasion resistance | ASTM D4157 (Wyzenbeek), ASTM D4966 (Martindale), ASTM D3884 (Taber) | Predicts wear life. Higher cycles for heavy commercial use. | 50,000–200,000 cycles (project-specific; specify direction and weight). |
| Tear strength | ASTM D1424 (Trapezoid), ASTM D2261 (Tongue), ISO 4674-1 | Prevents tears at seams and cuts. | Meets or exceeds minimum values per end-use. |
| Seam slippage | ASTM D4034 | Ensures seams stay tight under stress. | No separation under specified loads. |
| Breaking strength | ASTM D5034 (Grab) | Confirms tensile capacity. | Meets project minimums. |
| Pilling resistance | ASTM D3511 (Martindale) | Reduces fuzz balls on surfaces. | Specified rating target (e.g., 4–5). |
| Colorfastness – crocking | AATCC 8 (dry) and AATCC 165 (wet) | Prevents dye transfer. | Meets specified ratings. |
| Colorfastness – light | ISO 105-B02 (Xenon) or AATCC 16 | Ensures UV resistance; critical for light colors. | Blue-scale rating target per application. |
| Colorfastness – water | ISO 105-E01 | Prevents staining from water exposure. | Rating target per specification. |
| Waterborne vs solventborne behavior | ISO 2418, ISO 2417 | Provides baseline characterization of coated textiles. | Reference values; used for supplier validation. |
| Volatile organic compounds (VOC) | ISO 16000 series (for finished products) | Validates low emissions from finishes. | Project limits; commonly required in contract/commercial settings. |
| Flammability (if required) | USA: California Technical Bulletin 117-2013; EU: ISO 3795 | Confirms ignition/flame spread behavior. | Pass per local regulation and contract. |
| Hydrolysis/UV aging | ISO 4589/ASTM G155 or internal accelerated aging | Validates long-term resistance; essential for warm-humid climates. | Meets project endurance targets. |
| Dimensional stability | ISO 7770; seam shrinkage tests | Prevents warping and seam movement. | Meets project tolerances. |
| Cleanability/stain resistance | AATCC 130; supplier-specific protocols | Ensures stain removal without surface damage. | Stain clearing rating per spec. |
| Adhesion | ASTM D4541 (Pull-off); supplier cross-cut test | Confirms coating adhesion to substrate. | Meets minimum values. |
| Microporosity/breathability | ISO 9237 (air permeability) | Ensures intended hand and comfort. | Project-defined air-perm ranges. |
Sampling and variability controls:
– Use statistically valid sampling plans (e.g., Lot AQL if applicable; supplier-defined) with traceability to roll and batch codes.
– Maintain reference swatches for visual comparators.
– Document any finishing changes (e.g., topcoat chemistries) to isolate impacts on colorfastness and hand.
Compliance and Sustainability Considerations
- Product safety: Verify compliance with regional regulations. For finished upholstery in commercial environments, buyers typically require low-VOC finishes and may request Proposition 65 compliance in California. If required, ask for supplier declarations.
- PFAS and stain repellents: If specifying oil/water repellency, confirm the chemistry used and any regional PFAS-related requirements.
- REACH and SVHC: For EU buyers, request REACH compliance statements from suppliers (especially for colorants/additives).
- Lab accreditation: Rely on ISO 17025–accredited testing or validated internal methods; maintain accredited test reports on file.
- Eco-label support (optional): If pursuing certifications such as GREENGUARD/GREENGUARD Gold or Cradle to Cradle, confirm with suppliers that material formulations and process conditions align with their certification paths.
Quick Procurement Notes
- Distinguish PU vs. semi-urethan in the specification: semi-urethan often has softer hand with lighter topcoats—ensure abrasion, crocking, and stain tests cover the intended use.
- Clarify whether solventborne or aqueous systems are used if indoor emissions are critical.
- Require roll-to-roll test data covering abrasion, tear, seam slippage, colorfastness (crocking and light), and water resistance. Include baseline ISO 2418/2417 characterization.
- Keep grain, embossing, and topcoat parameters on the PO for reproducible feel and appearance.
- For global programs, standardize on ISO test methods where possible and align U.S. acceptance bands with your contract requirements.
If you need a supplier QA plan template aligned to ISO 9001 and test matrices mapped to contract risk levels, I can provide one next.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘polyurethane upholstery’
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for Polyurethane Upholstery
1) Define end-use and compliance
- Map product use-case (seating, headboards, ottomans, panels, contract vs. hospitality, or retail).
- Confirm regional fire/compliance requirements:
- USA: TB 117-2013 (California; check updated 116/117) and local codes (e.g., NFPA 701 for drapery; municipal codes for contract seating).
- EU/UK: Construction Products Regulation (reaction to fire), UK Furniture & Furnishings Fire Safety Regulations (BS 5852 or EN 1021), EN 13501 series as applicable.
- Health/environment (as applicable): Confirm REACH/SVHC status for EU; Prop 65 for California; FR chemistry disclosures; PVC/halogen-free preferences.
2) Choose material architecture
- PU (polyurethane) leather:
- Softer hand, leather-like drape; typically solvent-based topcoats; higher scuff/abrasion risk vs. semi-PU.
- Ideal for residential-like comfort, accent pieces, fashion-forward builds.
- Semi-PU (hybrid):
- Co-continuous PU/PVC structure; firmer hand; higher scuff resistance and cost-effectiveness; often better abrasion per dollar.
- Ideal for high-wear contract seating, hospitality, or kids’ furniture.
- Vinyl/faux leather:
- Firmest hand; strongest scuff/wipe-clean performance; lowest cost per yard; heavier duty cleanability.
- Ideal for healthcare, cafeteria, and heavy-use contract environments.
- Select backing if relevant (knit, woven, or nonwoven) to match stretching/seam stability and tufting requirements.
3) Specify performance attributes (complete “job pack” below)
- Abrasion (Wyzenbeek or Martindale), tear/tensile strength.
- Cold crack (important for cold climates/transport).
- Hydrolysis resistance and anti-fungal treatment.
- UV/colorfastness (UVA/UVB xenon-arc hours).
- Stain/soiling and cleanability; antimicrobial if required.
- Seam slippage and pilling propensity.
- Weight (gsm/oz) and thickness.
- Flame-retardant options and FR chemistry.
- Roll width, repeat (if printed/grained), and grain direction.
4) Color and finish
- Specify base color and grain/texture (embossed grain, smooth, pebble).
- Batch-to-batch consistency policy; shade-lot control (ΔE tolerance).
- Edge contrast vs. body; dye-lot tracking.
- Topcoat finish: matte vs. semi-gloss; anti-fingerprint/touch-up requirements.
5) Sampling and lab testing
- Request A, B, C samples (baseline grain variants and two colorways).
- Validate physicals via certified lab reports; confirm FR status.
- Conduct in-house wear and cleanability tests on prototype.
- Require signed-off LABDIP or bulk-match swatches before PO.
6) Build the RFQ (include these fields)
- Product code, colorway, grain/texture name.
- End-use category and target compliance (by region).
- Target specs: abrasion, tear, tensile, hydro/cold crack, UV hours, FR requirement.
- Roll width, thickness, weight, backing type, repeat.
- Quantity (yards), lead time, ship method, Incoterms (EXW/FOB/CIF/DDP), delivery windows.
- Warranty (delamination/peeling, hydrolytic failure), anti-microbial guarantee (if required).
- QA and dye-lot controls; shade variance tolerance.
- Certification requirements (REACH/SVHC, TB 117, EN 1021/BS 5852).
- Packaging, labeling, traceability, batch retention.
7) Evaluate offers: spec vs. cost
- Price bands vary by construction and performance. Example market references (USA/EU):
- Budget: Aries Ivory (PU; ~200–300 gsm; ~$6.97/yd; typical 54–55″ width; limited stock/closeout).
- Mid: Lara Ivory/White (PU; ~250–300 gsm; ~$10.12/yd; many colors; standard widths).
- Value/high-grade: Jesse Black (PU; ~350–400 gsm; ~$18.99/yd; thicker/softer hand; decent stock).
- Contract/textured: Jubilee Pearl (PU; ~300–350 gsm; ~$20.95/yd; fashion textures; stock available).
- Semi-PU/textured: Omnova Duratouch (e.g., Moss/Rose/Forest; ~300–350 gsm; ~$13.97/yd; firm hand; wide colorways; frequent closeouts).
- Normalize per square yard for apples-to-apples:
- $/yd ÷ (width in inches ÷ 36) = $/sq yd.
- Request:
- Abrasion and cold-crack data per lot; hydro warranty length; batch tracking; MOQ.
- Lead time by color; reorder lead; freight terms; stocking options (domestic vs. overseas).
8) Supplier due diligence
- MOQ and pack size; lot traceability; shade control.
- Production capacity and lead times; peak-season buffers.
- QC: on-roll inspection, sampling plan, defect allowances.
- Claims/warranty terms; RMA policy and time limits.
- ESG and compliance docs (REACH, RoHS, Prop 65 as applicable).
- Payment, currency, FX risk, and deposit terms.
9) Order with tight controls
- Attach spec sheet, LABDIPs, batch test reports, packaging/label specs.
- Line-item QC: width, thickness, weight, rolls/lot IDs.
- Pre-shipment inspection for shade, defects, and packaging.
- Confirm FR compliance documentation prior to freight release.
10) Logistics and delivery
- Ship method (LTL/TL or courier for samples); freight class and density.
- Incoterms and customs clearance (EU: EORI; US: ISF/ACE; duties as applicable).
- Inspection on arrival; roll/yardage count verification; re-wrap where needed.
11) Risk & alternatives
- PU disadvantages: scuffing, hydrolytic sensitivity in humid climates; mitigate with topcoat/top finishes and hydro warranties.
- If PU fails hydro or abrasion targets, step up to semi-PU or vinyl; verify FR availability.
- Maintain an alternate supplier and comparable grain/colorway for continuity.
Spec checklist to include in your RFQ/Purchase Order
| Category | Field to specify | Why it matters |
|---|---|---|
| Product | Product code; colorway; grain/texture; batch/dye lot tracking | Ensures exact match and shade continuity across POs |
| Material | PU / Semi-PU / Vinyl; backing type (knit/woven/nonwoven) | Controls hand, durability, and process compatibility |
| Physicals | Abrasion (Wyzenbeek or Martindale); tear/tensile; hydro resistance; cold crack; UV colorfastness | Matches wear/cleaning/lifecycle requirements |
| Fire | Target codes (TB 117; EN 1021/BS 5852); FR chemistry and treatment level | Regional compliance, hospital/hospitality readiness |
| Construction | Roll width; thickness; weight; repeat (if printed); grain direction | Fit-to-cut, seam performance, and yield planning |
| Cleanability | Stain/soiling classes; cleanability protocol; anti-microbial (if required) | Reduces lifetime care cost and complaints |
| QA | Shade variance tolerance (ΔE), sampling plan, batch test reports | Minimizes rework and replacements |
| Commercial | Quantity (yd); MOQ; lead time; freight terms; Incoterms; warranty | Predictable cost and schedule; risk transfer |
| Logistics | Packaging/roll wrap; labeling and traceability; inspection criteria | Efficient receiving and batch control |
This checklist keeps procurement decisions rigorous and comparable, reducing change orders and ensuring the selected polyurethane upholstery meets contract-grade performance in both the USA and Europe.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for polyurethane upholstery Sourcing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for Polyurethane Upholstery Sourcing
1) Cost modeling approach
- Scope: A typical dining chair or lounge chair with ~2 yards of PU leather per unit. You can scale to any seat count using the same structure.
- Cost buckets: Materials (fabric), Labor (cutting, sewing, lamination, finishing), and Logistics (transport, duties, handling). Other buckets (packaging, R&D, scrap, overhead) are optional add-ons.
Table 1. Indicative per-seat cost model (illustrative)
| Region | Materials @ $13.97/yd | Materials @ $18.99/yd | Labor per seat (typical) | Logistics per seat (typical) | Total per seat (range) |
|—|—:|—:|—:|—:|—:|
| USA | ~$28 | ~$38 | $6–$12 | $2–$5 | ~$36–$55 |
| Western/Northern EU | ~$35–$36 | ~$40–$41 | €4–€10 | €3–€6 | ~€42–€57 |
Notes:
– Materials assume 2.0 yards per seat.
– Labor varies by complexity and automation.
– Logistics includes domestic freight, duties, VAT/import fees, and last-mile.
2) Benchmark pricing: PU upholstery prices in the USA (reference range)
Source snapshot (per yard, in stock, U.S. market):
– 6157813 ARIES IVORY – $6.97 (Closeout)
– 6158115/6158113/6158112 LARA (Ivory/White/Bronze) – $10.12 (Closeout)
– 445781–445787 Omnova Boltaflex DURATOUCH (Moss/Rose/Forest/Squash) – $13.97 (Closeout)
– 7115211/7115213 JESSE (Terracotta/Black) – $18.99
– 7084612 JUBILEE (Pearl) – $20.95

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Table 2. Example material benchmarks
| Material | Price per yard (USD) | Character |
|—|—:|—|
| ARIES IVORY (6157813) | $6.97 | Closeout/limited |
| LARA series (615811x) | $10.12 | Closeout/multi-color |
| DURATOUCH series (445xxx) | $13.97 | Brand-backed, closeout |
| JESSE series (711521x) | $18.99 | Regular line |
| JUBILEE (708461x) | $20.95 | Regular line |
Implication: Most PU upholstery fabrics in the U.S. appear to cluster roughly between $7 and $21 per yard, with closeouts and older collections offering lower entry points.
3) Europe-side material pricing view
As EU pricing is not provided in the reference, it typically converges to U.S. list levels plus EU import friction (freight + duties/VAT). Use a practical factor-of-trade lens:
Table 3. Typical EU net landed price view
| U.S. list price (USD/yd) | Duty (EU, example 4%) | Freight & handling (EU, ballpark) | Subtotal | VAT (e.g., 19%) | Net landed EUR/yd (illustrative) |
|—:|—:|—:|—:|—:|—:|
| $13.97 | +$0.56 | +$1.70–$2.30 | ~$16.23–$16.83 | +$3.08–$3.20 | ~$19.31–$20.03 |
| $18.99 | +$0.76 | +$1.70–$2.30 | ~$21.45–$22.05 | +$4.08–$4.19 | ~$25.53–$26.24 |
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Notes:
– VAT rates vary by country (commonly 19–21%). Exchange rate and local handling fees apply.
– Freight is sensitive to volumes and Incoterms.
4) Logistics: Incoterms that shape the landed price
Incoterms determine who pays for what:
– EXW/FCA: Buyer assumes main carriage and all import costs.
– FOB/CIF: Seller covers to vessel port; buyer pays main carriage, duties, and local delivery.
– DDP: Seller handles import duties, VAT, and delivery.
Table 4. Cost inclusion matrix (what the buyer pays)
| Cost element | EXW | FCA | FOB | CIF | DDP |
|—|—|—|—|—|—|
| Local pickup | Buyer | Buyer/Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller |
| Main ocean freight | Buyer | Buyer | Seller | Seller | Seller |
| Insurance | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer | Seller | Seller |
| Customs clearance | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer | Seller |
| Duties/VAT | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer | Seller |
| Domestic delivery | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer | Seller |
Best practices:
– For USA: Many fabric imports land under FOB or CIF; confirm HTS code and fabric composition to validate duty treatment.
– For EU: Verify EUR.1/EUR.1/Form A if you claim preferences; otherwise expect the statutory duty and local VAT on import.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
5) Freight and landed examples (illustrative)
Assumptions:
– 1 x 20′ container (CBM not given here); we show per-container and per-yard conversions using the formula: price_per_yd ÷ 1,000.
Table 5. Example landed conversions
| U.S. list price (USD/yd) | Freight share (per-yard) if freight = $2,500/container | Duty (USA ≈ 8.2% if applicable) | Effective landed USD/yd (example) |
|—:|—:|—:|—:|
| $13.97 | $2.50/yd | +$1.35/yd | ~$17.82/yd |
| $18.99 | $2.50/yd | +$1.76/yd | ~$23.25/yd |
For EU (example 4% duty; freight share shown low/mid/high):
– $13.97 → $17.63–$20.25 net landed (excl. VAT); with 19% VAT ≈ $20.98–$24.10/yd
– $18.99 → $23.16–$26.05 net landed (excl. VAT); with 19% VAT ≈ $27.56–$31.00/yd
6) Landed cost calculator (fill-in worksheet)
Use this to translate your own quotes into landed per-yard costs.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
| Input | USA | Western/Northern EU |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier list price (USD/yd) | ||
| Freight cost per container (USD) | ||
| Freight per yard (Freight ÷ 1,000) | ||
| Duty rate (HTS) | 8.2% (example) | 4.0% (example) |
| Duty per yard (Duty% × list) | ||
| Subtotal (list + freight + duty) | ||
| Handling/customs/other | ||
| VAT rate | n/a (collected separately) | |
| VAT amount (Subtotal × VAT%) | ||
| Landed price per yard |
Notes:
– If you have CBM, use: Freight per yard = (Freight ÷ Container_yard_capacity × Container_yards) where Container_yards ≈ 1,000 for textiles in a 20′ container.
– If your supplier is VAT-registered and delivers within the EU under reverse charge, VAT may be deferred by the importer.
7) Labor costs and cycle time (indicative)
- Cutting and sewing complexity drive labor cost per seat more than material price. Complex stitchwork, tufting, or deep-buttoning multiply time.
- Automation (laser cutting, CNC, automated sewing cells) reduces unit time and variance.
Table 6. Typical labor intensity (illustrative)
| Process step | Typical time (min) | Notes |
|—|—:|—|
| Cutting (CNC/laser) | 4–8 | Nesting reduces waste |
| Skiving/lamination | 2–5 | Depends on thickness/adhesive |
| Sewing (upholstery) | 8–25 | Straight seams are faster; complex shapes slower |
| Tacking/finishing | 3–7 | Reinforcement and trimming |
Implications:
– In high-labor markets, savings from a $3–$5/yd material swing are quickly offset if labor efficiency is poor.
– In lower-labor markets, a slightly higher-priced, better-handling PU may deliver higher yields (less rework/scrap).
8) How to translate benchmarks into per-seat pricing
Steps:
1) Choose a benchmark price (e.g., JESSE at $18.99/yd).
2) Compute materials: 2 yds × price per yd.
3) Add freight share if importing (see Table 5).
4) Add duty (if applicable) and VAT (EU).
5) Add labor per seat and logistics to retail DC.
6) Add your margin and overheads.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Example:
– U.S. bench at $18.99/yd:
– Materials for 2 yds: ~$37.98
– Freight share: ~$2.50/yd → $5.00 total
– Duty (if applicable): ~$3.52
– Labor per seat: $6–$12
– Total seat cost: ~$53–$59 (before margin and overhead)
- EU landed (illustrative, 19% VAT):
- Net landed per yd: ~$27.56–$31.00 (Table 5)
- Materials for 2 yds: ~$55.12–$62.00
- Labor: €4–€10
- Total: ~€59–€72 per seat (before margin and overhead)
9) Tips to save cost without sacrificing quality
- Mix-and-match price tiers
- Use closeout or older collections (e.g., ARIES at $6.97/yd, LARA at $10.12/yd, DURATOUCH at $13.97/yd) for back-of-house or SKUs with lower wear. Reserve premium lines (e.g., JESSE at $18.99/yd) for visible/front-of-house.
- Volume and payment terms
- Standard textile packs: ~1,000–3,000 yd commitments. Larger volume improves price and speeds approvals.
- 30–90 days payment terms reduce working capital strain; negotiate early-pay discounts instead of late fees.
- Design for yield
- Improve nesting on roll goods; 54–57″ usable widths. Use CAD/nesting to cut waste from 20–25% to 12–16%.
- Standardize SKUs where possible; reduce dye-lot complexity to enable blanket orders at better pricing.
- Freight and duty optimization
- Ship full containers or consolidate. Compare FOB vs CIF to find total landed savings.
- Confirm duty classification and certificates of origin; in the EU, preferential origin can reduce or eliminate duty.
- Inventory and lead-time planning
- Use closeouts/overstocks for immediate replenishment; build a buffer of standard materials to protect lead times.
- Supplier risk and quality control
- Keep ≥2 qualified sources. Use a standard spec sheet (thickness, tear strength, abrasion, hand-feel, finish) and enforce AQL inspections to reduce rework and claims.
- Automation and process control
- Invest in cutting automation and consistent stitching fixtures to cut labor variance and improve per-unit consistency.
10) Regional price and logistics comparison (executive view)
Table 7. USA vs Western/Northern EU (illustrative)
| Item | USA | Western/Northern EU |
|—|—|—|
| Typical material price bands | ~$7–$21/yd (observed) | ~+15–35% net landed vs USA list, depending on freight/VAT |
| Common duty baseline | ~8.2% (example; confirm HTS) | ~4% (example; confirm HTS) |
| VAT on import | n/a (collected downstream) | ~19–21% (country-specific) |
| Freight mode for volume | Ocean FCL or LCL | Ocean FCL/LCL; some overland for EU distribution |
| Freight sensitivity | High west/east coast differences | High Benelux vs Scandinavia/Southern Europe differences |
| Terms preference | FOB/CIF | FOB/CIF or DDP for turnkey |
| Lead times (door-to-door) | ~30–50 days | ~35–55 days |
11) Action checklist (to operationalize this analysis)
- Fix a per-seat fabric usage target and tolerance.
- Qualify 2–3 materials per price tier (value, mid, premium).
- Build a landed calculator (Table 6) and re-use it for every quote.
- Choose Incoterms that align with your logistics capability; for first-time imports, consider DDP or FCA to simplify.
- Lock payment terms and volume bands; align PO cadence to factory capacity.
- Establish quality thresholds (abrasion, hand-feel, seam slippage) and embed them into inspection protocols.
If you share your monthly volumes, seat design, target price per seat, and preferred Incoterms, I can convert these ranges into a precise landed cost model and pricing guidance.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing polyurethane upholstery With Other Solutions
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing Polyurethane Upholstery With Other Solutions
For contract-grade seating and casegoods, polyurethane (PU) upholstery competes directly with PVC/vinyl and genuine leather. Each material carries distinct trade-offs on cost, comfort, durability, cleanability, sustainability, and regulatory posture.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Comparative overview (contract-grade)
| Criteria | Polyurethane (PU) upholstery | PVC/Vinyl (faux leather) | Genuine leather |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial material cost (per yard) | Low–mid, with stock patterns commonly $6.97–$20.95/yd | Low | High (premium hides + finishing) |
| Hand-feel/comfort | Supple, leather-like | Firmer, plastic-like unless topcoated | Naturally soft and luxurious |
| Abrasion/Martindale durability | Mid–high (grade/construction dependent) | Mid (topcoat quality dependent) | High when premium hides and finishes are used |
| Tear/puncture resistance | Mid–high | Mid | High (with proper weight splits) |
| Cleanability/stain resistance | Strong; alcohol-based cleaners acceptable on most series; avoid harsh solvents | Good; alcohol/bleach typically acceptable; plasticizer migration can cause stickiness | Moderate; must avoid harsh solvents; can stain; needs periodic conditioning |
| Breathability/comfort | Mid–high (open weave backings and finishes improve) | Lower; can feel warm/clammy over long sessions | Mid (varies with finish; hotter than fabric, cooler than vinyl) |
| Flammability (cigarette test) | Generally passes CAL TB 117-2013 (smolder) when properly specified; check FR versions for CAL TB 133/BF1/EN 1021 | Typically passes CAL TB 117-2013; FR variants available | Meets FR in contract use with topical finishes; verify standards |
| UV/lightfastness | Mid–high (quality and finish dependent) | Mid (can yellow/fade; topcoat dependent) | Mid–high (quality of finish; premium hides resist fading) |
| Plasticizer migration/stickiness | Not applicable (no plasticizers) | Risk if low-grade/topcoat; can become tacky over time | Not applicable |
| Odor/VOCs | Lower than PVC; verify supplier certifications | Higher potential off-gassing without low-VOC formulations | Lower VOC profile; tanning agents/flavoraldehyde concerns addressed by reputable tanneries |
| Sustainability posture | Typically solvent-based; water-based and solvent-free topcoats available; verify supplier statements (e.g., heavy metal–free finishes) | PVC carries environmental and chemical concerns; recycling limited | Natural material; tanning/chemistry footprints vary by tannery and certifications |
| Customization/design | Wide texture/color catalog; color matching and embossing common | Wide color options; fewer luxury textures | Natural grain; natural marks; limited consistency |
| Sustainability certifications (examples to seek) | RoHS/REACH compliance; low-VOC certifications; recycled/bio-based content | RoHS/REACH; low-VOC; phthalate-free declarations | Leather Working Group (LWG) tanning; RoHS/REACH; low-VOC claims |
| Typical lifecycle | Mid–high for contract use; 5–10+ years with proper maintenance (grade dependent) | Mid; 3–7 years depending on topcoat/use | High; 8–15+ years for premium hides and maintenance |
| End-of-life/recycling | Limited; some suppliers offer take-back; recycling into new PU limited | Complex due to chlorine/plasticizers; mechanical recycling limited | Can be mechanically recycled in small amounts; downcycling common |
| Price volatility | Stable | Stable | Volatile (hide market, supply cycles) |
Sources used to inform range of stock PU pricing and product examples: ARIES IVORY ($6.97/yd), LARA WHITE/IVORY/BRONZE ($10.12/yd), JESSE TERRACOTTA/BLACK/ARMY GREEN ($13.29–$18.99/yd), Omnova Boltaflex DURATOUCH series ($13.97/yd), JUBILEE PEARL/SPA ($20.95/yd). Actual pricing varies by supplier, collection, order volume, dye-lot, and finish.
Practical implications (USA & Europe)
- Select PU when you need:
- A leather-like hand at a lower cost and faster lead time.
- Strong cleanability for healthcare, hospitality, and corporate environments.
-
Mid–high durability with lighter-weight constructions and robust finish chemistries.
-
Select PVC/Vinyl when you need:
- Ultra-cost sensitivity with broad color availability.
-
High chemical tolerance and FR performance across many stock collections.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Select genuine leather when you need:
- Premium tactile quality and long service life in executive/ambassador seating.
- Natural grain and patina with strong brand signaling.
- Balanced breathability and comfort for lounging applications.
Key decisions by application
- Hospitality & healthcare: Prioritize cleanability and FR compliance. Many PU collections meet smolder standards (CAL TB 117-2013); for CAL TB 133/BF1/EN 1021, specify FR versions. Verify disinfectant compatibility and cleaning protocols before purchase.
- Corporate & education: Balance hand-feel and durability. PU often provides the best cost/comfort trade-off. Request Martindale scores and topcoat specifications.
- Luxury hospitality and executive: Leather remains the prestige choice, but premium PU can approximate look/feel at lower TCO when lifecycle management is strong.
- Outdoor/marine: PVC/Vinyl with UV-stabilized topcoats often outperforms PU in prolonged sun exposure; confirm warranty terms for fading/staining.
Notes for specification (USA & Europe)
- Verify FR certifications applicable to your jurisdiction (e.g., CAL TB 117-2013, CAL TB 133, BF1, EN 1021).
- Request REACH (EU) and RoHS compliance statements; confirm low-VOC/phthalate-free declarations for PVC.
- For leather, confirm LWG or equivalent tanning certifications and chemical restrictions.
- Ask for detailed finish chemistry (e.g., water-based vs. solvent-based topcoats), abrasion performance (Martindale), seam slippage, tear strength, and cleaning/disinfection compatibility.
Bottom line: Polyurethane upholstery offers a compelling balance of leather-like feel, cleanability, and cost for contract interiors. PVC/Vinyl remains the cost leader with robust chemical resistance but sacrifices tactile comfort and has sustainability/chemical concerns. Genuine leather wins on premium perception and longevity but comes with higher cost and lifecycle variability.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for polyurethane upholstery
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for Polyurethane Upholstery
What matters technically
- Grade/composition: solvent-based polyurethane (PU), water-based PU, or semi-urethane (PU + PVC surface on backing).
- Thickness and weight: typically 0.9–1.4 mm and ~10–16 oz/yd² (≈340–540 gsm) for seating; thickness affects hand-feel and tear strength.
- Backing knit/woven: often polyester circular knit or nonwoven; stretch can be one- or two-way.
- Physical performance: abrasion (Wyzenbeek double rubs; Martindale cycles), tear and tensile strength, seam slippage, bursting strength.
- Surface and colorfastness: grain definition and emboss pattern, lightfastness (AATCC 16.3, ≥3–4 recommended for indoor seating), dry/wet rub.
- Flammability: can be engineered to meet FR requirements; verify specific tests (e.g., UFAC, CA TB 117-2013 sections, NFPA 701 depending on end-use).
- Environmental/regulatory: REACH (EU), RoHS (EU), Prop 65 (CA), low VOC; recycled/bio-based content (when stated) should include a valid % and standard.
- Acoustics and comfort: breathable/open-cell backing vs. non-breathable; “hand” (suppleness/softness) varies by formulation.
Typical performance expectations (validate with supplier test reports)
– Abrasion: 25,000–100,000 Wyzenbeek double rubs; 20,000–100,000 Martindale cycles for seating.
– Tear strength: 15–40 lbf (65–175 N) transverse and longitudinal.
– Tensile: 50–100 lbf/in (8.7–17.5 kN/m).
– Seam slippage: <6.35 mm at specified load (e.g., 40 lbf/180 N, EN ISO 13936-2).
– Lightfastness: 3–4 (AATCC 16.3) or ≥4 (ISO 105-B02).
PU vs Semi-PU vs PVC Vinyl (quick comparison)
| Property | Polyurethane (PU) | Semi-Urethane (PU+PVC) | PVC Vinyl |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hand (softness) | Supple, leather-like | Moderately supple | Firm, plastic hand |
| Breathability | Better (can be micro-perforated) | Moderate | Lower |
| Tear strength | Medium–high | Medium | Medium–high |
| Abrasion (typical seating ranges) | Solid within stated ranges | Solid within stated ranges | Solid within stated ranges |
| Cold crack | Good (varies by formulation) | Good | Can be lower at low temps |
| Solvent/cleaning | Avoid strong solvents; test cleaners | Same | Solvent-sensitive; avoid ketones/aromatics |
| Price band | Mid–upper mid | Lower mid | Broad (low–mid) |
| Regulatory sensitivity (REACH, Prop 65) | Manageable with compliant formulations | Manageable | Requires plasticizers and stabilizers management |
| Use cases | Furniture, hospitality, healthcare seating with appropriate FR | Budget-conscious seating, accent pieces | High-traffic, easy-clean surfaces; heavy-duty contract |
Values are typical ranges; specific performance is formulation-dependent.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Physical tests commonly referenced
- Abrasion resistance: Wyzenbeek (ASTM D4157) double rubs; Martindale (ASTM D4966) cycles.
- Tear strength: ASTM D1424 (Trapezoid), ASTM D2261 (Tongue).
- Tensile strength: ASTM D5034 (Grab) or ASTM D5035 (Strip).
- Seam slippage: ASTM D4034; EN ISO 13936-2.
- Bursting strength: ASTM D3786 (Mullen).
- Colorfastness: Light ISO 105-B02/AATCC 16.3; Crocking ISO 105-X12/AATCC 8.
- Flammability: UFAC; NFPA 701 (drapery/window treatments); CA TB 117-2013 sections; ASTM E84 for wallcovering (by product type).
Environmental and regulatory notes
- REACH (EU): substances listed as SVHC must be below threshold; obtain supplier DoC with product-level testing.
- RoHS (EU): restricted substances in electrical/electronic components (rare for upholstery unless with electronics).
- Prop 65 (CA): verify declarable substances compliance; labeling may be required.
- Recycled/bio-based content: request third-party verification (e.g., GRS, ASTM D6866 for bio-based content).
- VOC: specify acceptance criteria or test method (e.g., ANSI/BIFMA M7.1 for emission testing of furniture systems).
Glossary
- Hand: tactile feel (softness, drape) of the material.
- Grain: surface texture; can be corrected grain, embossed pattern, or natural-like grain.
- Finish/topcoat: protective layer (e.g., polyurethane or fluorocarbon) influencing cleanability, abrasion, and hand.
- Bi-cast/pigmented split: corrected or split leather with PU or PVC topcoats; not relevant to non-leather PU but a legitimate term in leather categories.
- Breathability: ability to pass vapor; micro-perforation improves comfort.
- FR (flame retardant): refers to performance meeting specific tests; not an inherent property of PU alone.
Trade terminology and commercial norms
| Term | Meaning | Typical units/notes |
|---|---|---|
| MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity) | Smallest production run per SKU/color | Often 150–1,000 yards/meters or full roll; confirm per colorway |
| Lead time | Time from PO to shipment | Stock 1–7 days; custom colors 4–8 weeks; prints 6–10 weeks |
| OEM/ODM | Original Equipment Manufacturer/Design | Custom color, emboss, thickness; specify tolerances (e.g., ±0.05 mm thickness) |
| Incoterms | Delivery terms | FOB, CIF, DAP, DDP; USA/EU buyers commonly use FOB or DDP |
| Packing | How goods are shipped | Rolls on tubes, boxed; standard roll lengths ~30–50 m; film wrap |
| Width | Fabric width | Typically 54 in (137 cm); verify usable width vs. usable “trim” width |
| Sampling | Small quantities for approval | Strike-offs/swatches; typical fee negotiable with purchase |
| Price unit | Pricing basis | US: $/yard; EU: €/meter; volume discounts for full rolls |
| Care labeling | Cleaning/maintenance | Avoid solvent/alkali cleaners; test mild soap; do not machine-wash upholstery |
| CMT | Cut-Make-Trim | Cutting and assembly by buyer or vendor; define packaging and labeling |
| Compliance docs | Regulatory paperwork | REACH statement, RoHS (if applicable), Prop 65, FR certificates |
| Warranty | Performance guarantee | 1–3 years common; specify conditions and exclusions |
| Defect allowance | Acceptance criteria | AQL sampling; 1–2% allowance typical for bulk; define prior to PO |
| Color consistency | Lot-to-lot matching | Provide master swatch; confirm delta-E thresholds (ΔE) |
| FR options | Flame-retardant versions | Confirm test methods to be met by SKU; non-FR default unless specified |
| Back-coating/lamination | Enhancements | Can improve seam stability, sound absorption, or tear; document adhesion standards |
| Embossing/dye-sub | Decorative processes | Custom emboss requires tooling; dye-sub requires print strike-offs |
| Backing type | Substrate construction | Knit, nonwoven, or composite; affects stretch and seam slippage |
Specification checklist (copy/paste)
- Composition: PU or Semi-PU (state % polymers and backing fibers).
- Thickness: ___ mm (tolerance ±0.05 mm typical).
- Weight: ___ oz/yd² (___ gsm).
- Width: ___ in (usable ___ in); EU: ___ cm (usable ___ cm).
- Abrasion: Wyzenbeek ___ double rubs; Martindale ___ cycles (state test method).
- Tear strength: ___ lbf (transverse) / ___ lbf (longitudinal).
- Seam slippage: ___ mm at ___ lbf (state method).
- Lightfastness: ≥4 (ISO 105-B02) or ≥3–4 (AATCC 16.3).
- Flammability: ___ (UFAC, CA TB 117-2013, NFPA 701, etc.).
- Finish/topcoat: ___, cleanability claims (with test method).
- Backing: knit/nonwoven type; stretch properties.
- Environmental/regulatory: REACH statement, Prop 65 compliance, VOC requirement.
- Packaging: roll length , core size , protective wrap, labeling.
- MOQ: , lead time: , Incoterms: ___.
- Sample approval: swatch/strike-off required; master swatch stored.
- Warranty: ___ years; exclusions for misuse or improper care.
- Change control: revision level and date on test reports and specs.
Practical notes
- Always request independent test reports per SKU and lot; do not assume values from marketing pages.
- For seating, prioritize abrasion, seam strength, and FR compliance for your region.
- Confirm usable width and trimming allowance in your cutting plan to avoid waste.
- For hospitality/healthcare, specify cleanability protocol and disinfectants tested (avoid ketones/aromatics on PU).
- If ordering custom colors, require strike-offs and lock in ΔE tolerances prior to bulk production.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the polyurethane upholstery Sector
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Polyurethane Upholstery Sector
Polyurethane (PU) upholstery—often marketed as PU leather or semi-urethane—continues to gain share because it delivers a softer, more supple hand than many PVC or vinyl alternatives at a competitive price point. Across USA and Europe, buyers face shifting input costs, evolving compliance requirements, and a faster product cycle driven by fashion and specification changes. This section outlines the practical drivers to watch and how to structure sourcing for reliability, performance, and sustainability.
What’s shifting in the market
- Demand mix: Hospitality, contract, and consumer seating are leaning toward PU and semi-urethane for cost control and aesthetics. The softer hand and broad range of textures and color-ways enable rapid refresh cycles without the premium of genuine leather.
- Input cost volatility: PU chemistry is tied to polyurethane precursors and petrochemical feedstocks. Spikes in feedstock and solvent prices periodically push quotes and require flexible contracts or indexed pricing to protect margins.
- Regulatory pressure: In the EU, REACH and other material restrictions shape formulation choices. In the USA, California Proposition 65 and local VOC regulations influence finishes and chemicals of concern. Buyers are requesting full disclosure and low-emitting systems.
- Speed-to-market: Shorter development cycles favor suppliers with depth in color-ways and textures and the ability to replenish quickly. Closeouts and opportunistic buys supplement planned spend but must be balanced against continuity needs.
- Sustainability expectations: Waterborne systems, reduced solvent use, and improved recycling or end-of-life pathways are increasingly specified. The absence of animal products is a positive signal but needs to be paired with verifiable material health and circularity plans.
Drivers and impacts to track
| Driver | What’s changing | Buyer impact |
|---|---|---|
| Feedstock pricing (isocyanates, polyols, solvents) | Periodic swings influence PU and semi-urethane costs | Use indexed pricing, dual-source critical SKUs |
| Compliance (REACH, Prop 65, VOC limits) | Tightening restrictions on specific chemicals | Require full formulation disclosure and low-emitting certifications |
| Fashion/spec cycles | Faster refresh of textures and colors | Build agile assortments with vendor-managed inventory |
| Supply chain resilience | Regionalization and multi-tier risk | Qualify back-up mills, track resin and additive availability |
| Sustainability goals | Shift toward waterborne finishes and recycling | Align specs to low-solvent systems and end-of-life plans |
How to source PU upholstery effectively
- Match product to use-case: PU leather typically offers a softer, leather-like hand compared to PVC/vinyl, with semi-urethane positioned as a hybrid. Choose based on abrasion needs, breathability, cleaning requirements, and flame-retardant performance.
- Supplier evaluation: Prioritize mills with scale, finish depth, and documented compliance. Verify quality control on tactile feel, color consistency, and substrate bonding. Request samples across color-ways to test hand-feel and appearance in various lighting.
- Specification essentials: Capture fabric weight (gsm or oz), thickness (mm), tear and tensile strength, Martindale or Wyzenbeek abrasion, UV resistance, flame-retardant compliance, VOC emissions, and care instructions. Keep a baseline spec for each product family to prevent drift.
- Sourcing and lead times: For standard items, lead times can be moderate. High-demand colors and textures extend timelines. Align production slots with your release calendar and negotiate min-order quantities to match consumption without overstocking.
- Inventory strategy: Combine core textures with seasonal color-ways. Use closeouts strategically but maintain continuity SKUs to protect availability for large projects.
USA vs. Europe: practical considerations
| Topic | USA | Europe |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical compliance | Proposition 65 disclosure; low-VOC preferred; supplier may offer Prop 65-compliant or no-warning labels | REACH heavily shapes formulations; demand for low-solvent or waterborne systems |
| Flammability norms | Reference TB 117-2013 for component compliance (smolder and char), local codes vary | EN 1021 and other European standards commonly specified; FR treatments assessed per end-use |
| Sourcing footprint | Diverse domestic and imported supply; lead times depend on import cycles | Regional production is robust; import routes (Asia) add variability |
| Speed-to-market | Seasonal refresh common; VMI and smaller MOQs improve agility | Stable assortments; mid-length refresh; strong documentation expectations |
| Sustainability preference | Recyclability and low-emissions prioritized by many brands | Strong pressure on waterborne finishes and disclosure; circularity and chemical safety valued |
| Price bands (indicative) | $6.97–$20.95 per yard in provided listings; quality-driven | Similar tiers exist; pricing often reflects EU compliance and formulation choices |
| Risk management | Dual-source textures; secure resin contracts | Tighten due diligence on compliance; maintain EU-origin alternatives |
Quality cues in product pages and specs
Many suppliers highlight:
- A “softer hand” and leather-like texture relative to PVC/vinyl
- Extensive texture and pattern libraries across color-ways
- Price tiers that reflect finish quality, abrasion performance, and brand positioning
- Inventory availability by color, with “more colors available” and “more yardage” flags for replenishment
Use these signals to assess fit-for-purpose performance and replenishment risk.
Sustainability and material health
- Prefer waterborne or low-solvent systems to reduce VOC emissions and workplace exposure.
- Request full chemical disclosure and evidence of compliance alignment (e.g., Prop 65 “no-warning” statements or REACH-compliant formulations).
- Consider circularity: explore programs for take-back or recycling, and validate claims with verifiable partners. For semi-urethane and PU layers, document separability if relevant to end-of-life processing.
- Benchmark abrasion and durability to extend product life, which reduces replacement frequency and waste.
Procurement playbook
- Map demand by end-use and environment (hospitality vs. contract vs. residential), then select textures and finishes that meet tactile, cleaning, and durability needs.
- Maintain two qualified suppliers for core textures; secure quarterly price reviews with indexation to manage volatility.
- Set specification gates: require lab testing for abrasion, tear, VOC, and flame-retardant performance; track lot-level consistency.
- Build a staged assortment: core textures in neutrals and a defined palette of rotating colors. Use closeouts for non-critical projects.
- Define sustainability requirements in the RFP: waterborne finishes, low-VOC thresholds, chemical disclosure, and any circularity commitments.
By aligning specification choices with market drivers and regional compliance realities, USA and Europe buyers can secure reliable supply, manage cost variability, and meet rising expectations for material health and sustainability in PU and semi-urethane upholstery.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of polyurethane upholstery
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of Polyurethane Upholstery
1) What is polyurethane upholstery and how does it differ from PVC/vinyl and real leather?
- PU (polyurethane) upholstery is a synthetic leather made with a PU topcoat applied to a textile backing. It is designed to mimic the supple hand of genuine leather without the cost or livestock inputs.
- Compared with PVC (vinyl): PU is more breathable and softer (“hand”) with better drape; PVC is firmer, more plasticky, and typically has higher VOC emissions and odor due to plasticizers.
- Compared with real leather: PU is more consistent in color/pattern, easier to clean, and typically more cost-effective; leather offers natural grain, unique patina, and perceived prestige.
2) What performance properties are typical, and how do they vary by construction?
Key properties and how they change by grade/construction:
– Abrasion resistance: Generally strong; higher-end PU can meet contract-grade cycles. Use Martindale abrasion (ASTM D4966 or EN 14465) to confirm for your end-use.
– Tensile and tear strength: Moderate to good; confirm seam slippage (ASTM D4034 or ISO 13936-2) if the product will undergo frequent stress.
– Water resistance and ease of cleaning: Good surface repellency; water-based stains are easy to wipe. Long-term water exposure can lead to hydrolysis; check the grade’s hydrolytic stability.
– Breathability: Higher than PVC. Moisture vapor transmission varies by formulation.
– UV/lightfastness: Better than many synthetics, but colorfastness can vary. Request ASTM G154 (UV) or ISO 105-B02 (xenon) results if exposed to sunlight.
– Flame performance: Typical upholstery constructions pass California TB 117-2013 (open-flame not required). For stricter codes (marine, transit), specify FR versions and relevant testing.
– Odor/VOC: Lower than PVC in many cases; verify GREENGUARD or similar certifications when low emissions are required.
3) What standards and certifications are commonly required for commercial interiors in the US and EU?
Common tests and compliance (select based on application):
– US
– Flammability: California TB 117-2013 for contract upholstery.
– Durability: ASTM D4966 (abrasion), ASTM D4034 (seam slippage), ASTM D3511 (pilling).
– Colorfastness: AATCC 8 (wet/crocking), AATCC 16 (light).
– Environmental: GREENGUARD Gold for low VOC; recycled content (e.g., SCS Recycled Content).
– EU
– Flammability: EN 1021-1/-2 (cigarette/match) or EN 13773 (for certain building applications).
– Durability: EN ISO 12947-2/-3/-4 (abrasion), EN ISO 13936-2 (seam slippage), EN 388 (not for upholstery), EN 530 (abrasion).
– Lightfastness: EN ISO 105-B02.
– Environmental: REACH compliance for chemical substances; VOC/emission assessments (e.g., German ABG/blue angel) when specified.
Note: Always consult your local building code and project specifications to select the right tests.
4) What grades or thicknesses do you offer, and how do I select the right one?
Typical PU upholstery grades:
– Standard contract PU (topcoat ~0.5–1.0 mm): General seating in hospitality, healthcare waiting areas, corporate, and education where moderate duty is expected.
– Soft-hand premium PU (0.7–1.3 mm topcoat): Lounges, executive seating, luxury hospitality—prioritizes comfort and aesthetics.
– Heavy-duty/performance PU (topcoat ≥1.0 mm with enhanced finishes): Bars, cafes, theaters—seeks better abrasion and stain/soiling resistance; often specified with higher abrasion cycles and stronger backing.
Selection tips:
– Verify actual thickness and backing type (knit vs. woven vs. non-woven) based on seam performance and stretch requirements.
– Match abrasion and colorfastness to traffic level and maintenance plan.
– For high-sun areas, ask for UV-resistant topcoat and confirm xenon/UV test data.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
5) What backing and adhesives work best with PU upholstery?
- Backing: Most PU upholstery has a knit or woven polyester backing; non-wovens are less common. Knit offers flexibility; woven adds stability. Confirm seam slippage results for your chosen backing.
- Adhesives: Water-based and solvent-based polyurethane adhesives are commonly used with PU. Avoid toluene-based or other solvent systems that can degrade the PU topcoat or cause staining/bleed-through.
- Surface prep: Clean the substrate; ensure dust-free and appropriately primed for best adhesion. Consider using seam tapes or edge finishing to prevent fraying and ensure clean seams on curved profiles.
6) How should PU upholstery be specified to avoid mislabeling and greenwashing?
- Claim accuracy: Label as “polyurethane” or “PU” faux leather—not leather or “genuine leather.” Comply with FTC (US) and relevant EU guidelines on leather labeling.
- Emissions and chemicals: Request REACH compliance for EU projects and low-VOC certifications (e.g., GREENGUARD Gold) where relevant.
- Environmental messaging: Avoid indefinite claims like “eco-friendly.” If you claim recycled content, provide the percentage and certification details.
7) What care and cleaning procedures keep PU upholstery looking new?
Recommended care:
– Daily: Remove loose dust with a lint-free microfiber cloth.
– Weekly: Wipe with mild soap and water (pH-neutral), then dry with a clean cloth.
– Stain care: For spills, blot promptly; spot-clean with mild detergent and water. Avoid harsh solvents (acetone, lacquer thinner, strong acids/alkalis).
– Disinfection (healthcare/hospitality): Follow manufacturer-approved disinfectant list; verify compatibility to avoid topcoat damage and embrittlement.
– Protection: Use protective finishes or topcoats in high-wear areas as specified by the manufacturer.
– Avoid: Prolonged heat, direct sunlight without UV-rated products, and petroleum-based oils/greases that can stain.
8) What are the typical lead times, MOQs, warranties, and options for custom colors/brands?
- Lead time: In-stock SKUs: typically 2–5 business days. Made-to-order/custom colors: 6–12 weeks depending on dye-lot and finish requirements.
- MOQ: Varies by collection; common starts at 10–50 yards per color/pattern.
- Warranty: Typically 2–5 years for normal wear, dependent on abrasion thresholds and application. Review exclusions (e.g., sunlight exposure, misuse, spills).
- Customization: Private labeling, brand backprinting, embossing, and protective finishes are available. Large color matching may require minimums.
- Logistics: Freight options include LTL and FTL. Standard roll widths are 54 inches (≈137 cm); confirm net widths and yardage yields with your pattern or cut requirements.
Need help selecting the right PU upholstery?
– Share your performance requirements (traffic level, flame codes, certifications, colorfastness).
– Confirm dimensions and backing needs.
– Request samples and technical data sheets (TDS).
– Include project timeline and logistics (delivery date, destination, dock requirements).
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for polyurethane upholstery
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook
Polyurethane (PU) upholstery delivers leather-like aesthetics, a soft hand, and design freedom at a compelling total cost—making it a defensible, scalable choice across USA and Europe markets.
Value at a glance
| Value driver | Why it matters | Typical data points | Impact on ROI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | Favorable $/sq.yd. with frequent closeouts | ~$6.97–$20.95 per yard (USA supplier listings) | Lowers BOM while maintaining perceived premium |
| Aesthetics & hand | Supple, leather-like feel and varied textures | Multiple textures and colorways | Elevates brand feel with fewer quality trade-offs |
| Availability | Wide stocked SKUs and restocks | 5–37+ yards on listed items | Reduces lead times; supports agile launches |
| Performance control | Specify abrasion, tear, flex, UV/fade | Use spec sheets and samples | Enables fit-for-use choice and predictable durability |
| Compliance & quality | Verify chemical limits and FR where applicable | Request documentation (USA/EU) | Manages regulatory risk and warranty clarity |
Short term: Buyers should lock in multi-supplier samples, confirm performance and compliance, and leverage current supply stability for better pricing. Mid term: Expect continued supply resilience and wider design options; maintain a “compliance-first” sourcing checklist and monitor fabric/chemical requirements by region.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided is for informational purposes only. B2B buyers must conduct their own due diligence.