The global fiber optic cable market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for high-speed data transmission, expanding 5G networks, and rising investments in digital infrastructure. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the fiber optic cable market was valued at USD 10.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 9.5% from 2024 to 2029. Similarly, Grand View Research notes that the global fiber optic cable market size reached USD 11.2 billion in 2023 and is expected to expand at a CAGR of 9.7% from 2024 to 2030, fueled by escalating broadband penetration and government-led smart city initiatives. As network reliability becomes a cornerstone of modern telecommunications, manufacturers specializing in PM (Polarization-Maintaining) maintaining cables—critical for applications in precision optics, quantum communication, and high-performance sensing—are emerging as key enablers of next-generation connectivity. In this competitive landscape, six manufacturers stand out due to their technological innovation, product reliability, and strong market presence.
Top 6 Pm Maintining Cables Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 AR
Domain Est. 2017
Website: focc-fiber.com
Key Highlights: Buy the high quality and highly efficient ar-coated pm patch cables with our factory. We are one of the leading manufacturers and suppliers in China, ……
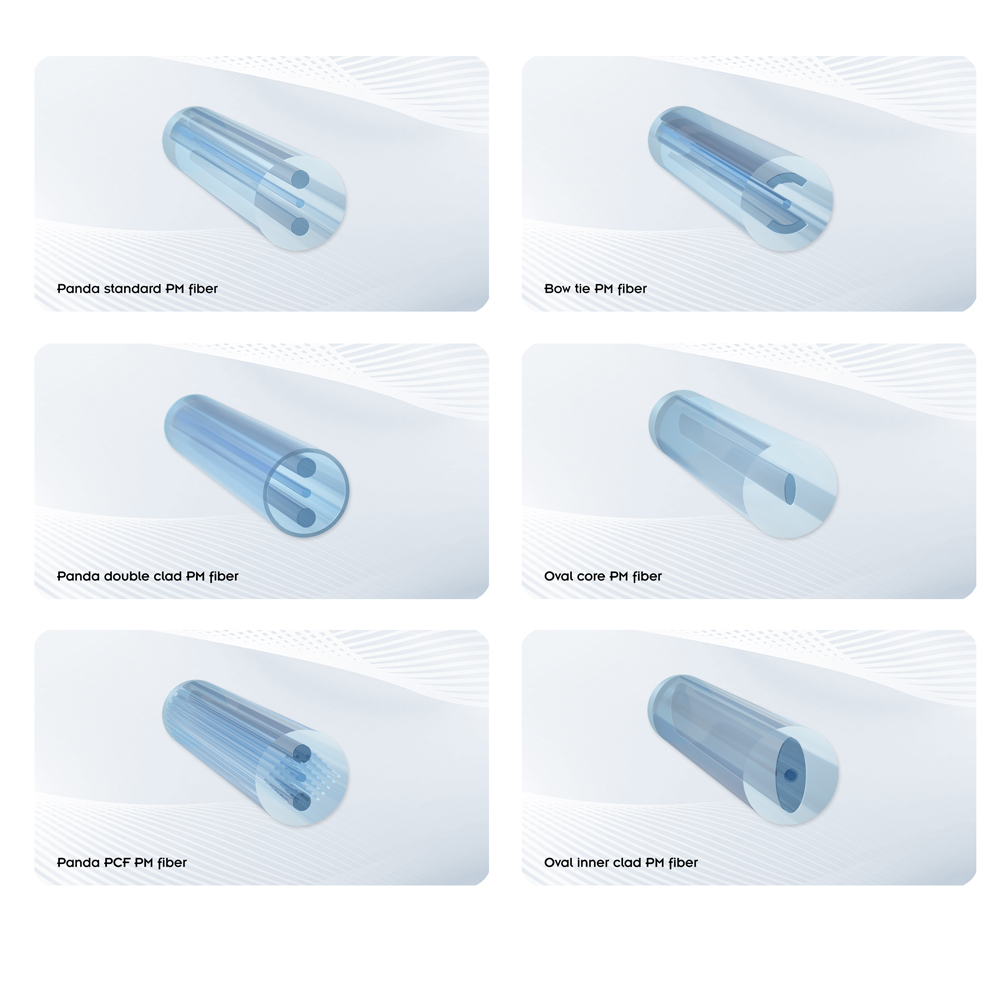
#2 Polarization Maintaining Fiber (PM Fiber)
Domain Est. 1991
Website: corning.com
Key Highlights: PANDA Polarization Maintaining (PM) fibers are designed with high performance properties including excellent birefringence and low attenuation….
#3 Custom Fiber Optic Patch Cables
Domain Est. 1995
Website: thorlabs.com
Key Highlights: Thorlabs stocks the largest selection of single mode and multimode optical fibers in the photonics industry. If our selection of stocked patch cables does not ……
#4 Diamond SA: Fiber Optic Solutions for High
Domain Est. 1997
Website: diamond-fo.com
Key Highlights: Discover DIAMOND’s innovative fiber optic solutions built with 40+ years of expertise. Swiss precision for high-performance applications. Explore now!…
#5 Polarization
Domain Est. 2004
Website: sukhamburg.com
Key Highlights: Schäfter+Kirchhoff’s polarization maintaining fiber cables (PM fiber cables) come with gaussian intensity distribution and low-stress fiber connectors….
#6 Fibermart
Domain Est. 2015
Expert Sourcing Insights for Pm Maintining Cables

H2: Projected Market Trends for PM Maintaining Cables in 2026
The global market for preventive maintenance (PM) maintaining cables—critical components in industrial, energy, telecommunications, and transportation infrastructure—is poised for significant transformation by 2026. Driven by technological innovation, sustainability mandates, and increasing demand for system reliability, several key trends are expected to shape this niche but vital sector.
1. Increased Adoption of Smart Cable Technologies
By 2026, PM maintaining cables are increasingly integrating smart sensors and Internet of Things (IoT) capabilities. These intelligent cables enable real-time monitoring of temperature, load, insulation degradation, and environmental stress. This shift supports predictive maintenance models, reducing unplanned downtime and extending cable lifespan. The integration of AI-driven analytics with sensor data is expected to be a key differentiator for cable manufacturers and maintenance service providers.
2. Growth in Renewable Energy Infrastructure
The rapid expansion of solar, wind, and offshore energy projects is a primary driver for PM cable demand. These installations require robust, long-lasting cabling systems that can endure harsh environments and require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. Preventive maintenance protocols for cables in renewable energy grids are becoming standardized, fueling demand for specialized cables designed for resilience and easy diagnostics.
3. Regulatory Push for Safety and Efficiency
Stricter global regulations regarding electrical safety, fire resistance, and energy efficiency are influencing cable design and maintenance practices. In regions like the EU and North America, standards such as IEC 60332 and NEC Article 725 are prompting upgrades to existing infrastructure. This regulatory environment increases the frequency and rigor of PM routines, boosting demand for high-performance, low-maintenance cables.
4. Rise in Condition-Based Maintenance (CBM)
By 2026, the shift from time-based to condition-based maintenance is accelerating in sectors such as manufacturing, data centers, and rail transportation. PM maintaining cables are being engineered to support CBM workflows, incorporating built-in diagnostics and compatibility with digital twin platforms. This enables operators to perform maintenance only when necessary, reducing costs and improving asset utilization.
5. Sustainability and Circular Economy Practices
Environmental concerns are driving innovation in cable materials and lifecycle management. Manufacturers are developing recyclable, halogen-free, and low-smoke zero-halogen (LSZH) cables that meet PM requirements while reducing environmental impact. Additionally, cable refurbishment and reuse programs are gaining traction, supported by improved diagnostics that validate cable integrity post-deployment.
6. Supply Chain Localization and Resilience
Geopolitical uncertainties and supply chain disruptions have led to a trend toward regional production of PM maintaining cables. By 2026, companies are investing in localized manufacturing and inventory strategies to ensure continuity of supply for critical maintenance operations, especially in strategic industries like healthcare, defense, and utilities.
Conclusion
The 2026 landscape for PM maintaining cables is defined by digitalization, sustainability, and heightened reliability demands. As industries prioritize uptime and efficiency, the role of advanced, maintainable cabling systems will become increasingly central. Companies that innovate in smart materials, integrated monitoring, and lifecycle management will lead the market, positioning PM maintaining cables as a cornerstone of resilient infrastructure.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing PM Maintaining Cables (Quality, IP)
Sourcing power maintenance (PM) cables requires careful attention to both quality and Ingress Protection (IP) ratings to ensure safety, reliability, and compliance. Overlooking key factors can lead to premature failure, safety hazards, or non-compliance with industry standards. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Inadequate Quality Control and Material Selection
One of the most frequent issues is selecting cables based on price alone, leading to substandard materials such as low-grade copper or poor-quality insulation. Inferior conductors increase resistance, causing overheating and energy loss, while weak sheathing reduces durability and fire resistance. Always verify manufacturer certifications (e.g., UL, CE, RoHS) and request material test reports to confirm compliance with required electrical and mechanical standards.
Misunderstanding or Misapplying IP Ratings
The IP rating defines a cable’s protection against solid objects and liquids (e.g., IP67, IP68). A common mistake is assuming a higher IP rating automatically means better performance in all environments. For instance, a cable rated IP68 may be suitable for submersion but lack UV or chemical resistance needed outdoors. Ensure the IP rating matches the exact environmental conditions—such as dust, moisture, or submersion—and confirm whether the rating applies to the cable alone or only when properly terminated.
Overlooking Cable Construction and Flexibility Needs
PM maintaining cables often operate in dynamic or high-vibration environments. Using rigid or inflexible cables in such applications leads to cracking, conductor fatigue, and failure. Avoid generic cables not designed for continuous flexing or mechanical stress. Instead, opt for cables with stranded conductors, robust jacketing, and appropriate fillers to maintain integrity under movement.
Ignoring Temperature and Environmental Suitability
Cables rated for ambient temperatures may degrade rapidly in extreme heat or cold. Similarly, exposure to oils, solvents, or UV radiation can compromise insulation if not specifically designed for such conditions. Always review the cable’s temperature range and environmental resistance properties to ensure long-term reliability in the intended operating environment.
Failing to Verify Full System Compatibility
A cable may meet individual specs but fail when integrated into a system due to incompatible connectors, mismatched voltage ratings, or grounding issues. Ensure the cable is compatible with connected equipment, terminations, and existing infrastructure. Poor terminations, even with high-IP-rated cables, can void protection and create weak points.
Skipping Third-Party Testing and Certification
Relying solely on supplier claims without independent verification is risky. Always request test reports from accredited labs and confirm certifications are valid and up to date. This is especially critical for applications involving safety, explosion hazards, or regulated industries.
Avoiding these pitfalls ensures that sourced PM maintaining cables deliver reliable performance, meet safety standards, and provide long-term value. Prioritize quality documentation, environmental suitability, and system integration during procurement.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for PM Maintaining Cables
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for preventive maintenance (PM) of cables across industrial, commercial, and infrastructure environments. Adhering to these guidelines ensures operational reliability, safety, and regulatory adherence.
Equipment and Material Management
Ensure all required tools, testing equipment (e.g., multimeters, insulation resistance testers), spare cables, connectors, and protective materials (e.g., conduit, cable ties, heat shrink tubing) are inventoried and readily available. Implement a just-in-time (JIT) restocking system to minimize downtime while avoiding overstocking. Use barcode or RFID tags for efficient tracking of cable inventory and PM components.
Maintenance Scheduling and Planning
Develop a detailed PM schedule based on manufacturer specifications, environmental conditions, and usage patterns. Align cable inspections with broader facility maintenance plans to minimize disruptions. Use a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) to assign tasks, track completion, and generate work orders. Schedule PM during low-activity periods to reduce operational impact.
Personnel Training and Certification
Only qualified and certified personnel should perform cable maintenance. Ensure technicians are trained in electrical safety standards (e.g., OSHA 29 CFR 1910 Subpart S, NFPA 70E), lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures, and proper handling of high-voltage systems. Maintain up-to-date training records and conduct annual refresher courses.
Safety and Risk Mitigation
Conduct a job hazard analysis (JHA) prior to each PM activity. Implement LOTO procedures to de-energize circuits before work begins. Provide personnel with appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including insulated gloves, arc flash suits, and safety glasses. Ensure work areas are clearly marked and restricted to authorized personnel.
Regulatory Compliance
All cable maintenance activities must comply with applicable regulations and standards, including:
– National Electrical Code (NEC / NFPA 70) – For installation and maintenance standards.
– OSHA Regulations – For workplace safety and electrical practices.
– IEEE Standards – Such as IEEE 400 for cable testing and diagnostics.
– Local Jurisdictional Codes – Verify and adhere to regional requirements.
Maintain documentation proving compliance during audits.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Keep comprehensive records of all PM activities, including:
– Date and time of inspection
– Technician name and credentials
– Equipment serial numbers and cable specifications
– Test results (e.g., continuity, insulation resistance)
– Repairs or replacements performed
– Photographic evidence (if applicable)
Store records digitally with backup protocols to ensure data integrity and accessibility.
Environmental and Disposal Compliance
Dispose of damaged or obsolete cables in accordance with environmental regulations (e.g., EPA, RoHS, WEEE). Recycle copper and other materials through certified e-waste handlers. Prevent hazardous substances (e.g., lead, PVC byproducts) from entering landfills. Document all disposal activities with certified recycling manifests.
Audit and Continuous Improvement
Conduct internal audits at least annually to evaluate the effectiveness of the PM program. Use findings to refine procedures, update training, and enhance compliance. Benchmark performance against industry standards and incorporate feedback from field technicians to improve logistics efficiency and safety outcomes.
Conclusion: Sourcing and Maintaining PM (Preventive Maintenance) Cables
In conclusion, the effective sourcing and maintenance of preventive maintenance (PM) cables are critical components in ensuring the reliability, safety, and longevity of electrical and mechanical systems. Proper sourcing involves selecting high-quality, application-specific cables from reputable suppliers, taking into account environmental conditions, load requirements, and regulatory standards. Establishing strong vendor relationships, implementing quality assurance checks, and maintaining accurate inventory records further support a resilient supply chain.
Equally important is a structured PM cable maintenance program that includes regular inspections, testing for wear and tear, proper labeling, and timely replacement of aging or damaged cables. Proactive maintenance minimizes unplanned downtime, reduces safety hazards, and enhances overall system efficiency.
By integrating strategic sourcing practices with a disciplined maintenance routine, organizations can optimize performance, reduce lifecycle costs, and ensure continuous operational reliability. Investing in the proper management of PM cables is not just a technical necessity but a strategic imperative for sustainable operations.