The global plug connector market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand across industries such as automotive, consumer electronics, industrial automation, and renewable energy. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 85.6 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2028, reaching an estimated USD 127.4 billion by 2028. This expansion is fueled by increasing electrification, the proliferation of IoT-enabled devices, and the global push toward electric vehicles (EVs) and smart infrastructure. Additionally, Grand View Research highlights the growing adoption of high-performance connectors in harsh environments and data centers as key demand drivers. As the need for reliable, efficient, and compact electrical connections intensifies, manufacturers are innovating to meet evolving performance and miniaturization requirements. In this competitive landscape, a select group of leading plug connector manufacturers are emerging through technological leadership, global supply chain strength, and strategic R&D investments—setting the benchmark for quality and innovation. The following list identifies the top 10 manufacturers shaping the future of connectivity.
Top 10 Plug Connector Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 ITT Cannon
Domain Est. 1995
Website: ittcannon.com
Key Highlights: ITT Cannon is a leading global manufacturer of connector products serving customers in aerospace, defense, medical, industrial and transportation markets….
#2 Meltric
Domain Est. 1997
Website: meltric.com
Key Highlights: MELTRIC offers a full line of industrial plugs and receptacles, including our signature brand of UL-listed Switch-Rated devices with DECONTACTOR™ ……
#3 Types of Electrical Connectors and Wire Connectors
Domain Est. 1992
Website: te.com
Key Highlights: From USB connectors and RJ45 connectors to TE’s DEUTSCH connectors and AMP connectors, we design and manufacture the electrical connectors and wire connectors ……
#4 Connectors
Domain Est. 1994
Website: molex.com
Key Highlights: Molex offers a wide variety of Board-to-Board Connectors for microminiature, high-speed, high-density, and high-power applications….
#5 Connectors
Domain Est. 1996
Website: amphenol.com
Key Highlights: Amphenol has been designing and manufacturing electrical and electronic connectors since the company’s inception in 1932….
#6 Electrical and Electronic Connectors
Domain Est. 1996
Website: hirose.com
Key Highlights: Connector Selector Categories, Applications, Customer Support, Partners, Locations, Contact Us, Privacy Policy | Terms of Use | Membership Agreement…
#7 Plug
Domain Est. 1996
Website: weidmuller.com
Key Highlights: Plug-in connectors – The right connection solutions for transmitting power, signals, and data between the field level and the control cabinet ✓ Connect now!…
#8 JST Sales America: Cutting
Domain Est. 1998
Website: jst.com
Key Highlights: Discover how our product line of over 100000 electrical connectors provides our customers with the tools they need for endless innovation….
#9 LEMO – The Original Push-Pull Connector
Domain Est. 1998
Website: lemo.com
Key Highlights: LEMO offers complete connectivity services for high-performance solutions such as cable assembly, customised solutions and signal integrity services….
#10 Winchester Interconnect
Domain Est. 2016
Website: winconn.com
Key Highlights: Winchester Interconnect is a global leader in connectors, RF & microwave, hermetic, fiber optic & cable assemblies. Trusted interconnect solutions for ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Plug Connector

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Plug Connectors
The plug connector market is poised for dynamic transformation by 2026, driven by technological innovation, evolving industry demands, and global sustainability goals. Here’s an analysis of key trends shaping the sector:
1. Electrification & EV Expansion
- EV Charging Infrastructure Boom: With global EV adoption accelerating, demand for high-power, durable plug connectors (e.g., CCS, CHAdeMO, and emerging NACS standards) will surge. By 2026, ultra-fast charging (350kW+) will require next-gen connectors with advanced thermal management and liquid cooling.
- Standardization Push: North America’s shift toward Tesla’s NACS (now SAE J3400) will unify connector design across automakers, boosting manufacturing scale and reducing costs. This could influence global standards.
2. Industrial & Automation Growth
- Industry 4.0 Integration: Smart factories demand robust, data-enabled plug connectors supporting IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things). Connectors with integrated sensors for monitoring temperature, vibration, and connection integrity will gain traction.
- Miniaturization & High-Density: Automation and robotics require compact, high-pin-count connectors to save space and support complex signal transmission in confined environments.
3. Renewable Energy Integration
- Solar & Wind Infrastructure: Growth in renewable energy installations will drive demand for specialized DC connectors (e.g., MC4 types) with enhanced durability, UV resistance, and IP68+ ratings for harsh environments.
- Energy Storage Systems (ESS): As grid-scale and residential battery storage expands, high-current DC connectors for battery interconnects will be critical, with a focus on safety and ease of maintenance.
4. Sustainability & Circular Economy
- Eco-Design Regulations: Stricter environmental regulations (e.g., EU’s Ecodesign Directive) will push manufacturers toward recyclable materials, reduced hazardous substances, and longer product lifespans.
- Modular & Repairable Connectors: Design for disassembly and reusability will grow in importance, supporting circular economy models and reducing electronic waste.
5. Advancements in Materials & Design
- High-Performance Materials: Increased use of PPS, LCP, and thermoset plastics to withstand higher temperatures, improve fire resistance, and reduce weight.
- Hybrid Connectors: Integration of power, signal, and data (e.g., Ethernet, USB) into single units will streamline installations in automotive and industrial applications.
6. Supply Chain Resilience & Regionalization
- Nearshoring & Diversification: Geopolitical tensions and past disruptions will push companies to regionalize production. Expect growth in connector manufacturing hubs in North America, India, and Southeast Asia to complement traditional centers in China.
- Vertical Integration: Leading players may acquire component suppliers to secure critical materials (e.g., copper, rare earths) and ensure supply stability.
7. Connectivity & Smart Features
- Plug-and-Play Intelligence: Connectors with embedded microchips for authentication, fault detection, and plug-in history tracking will become common, especially in EV and medical sectors.
- Wireless Alternatives as Complement: While wireless power grows in niche applications (e.g., consumer electronics), physical plug connectors will remain dominant for high-power and mission-critical uses.
Conclusion
By 2026, the plug connector market will be defined by performance, intelligence, and sustainability. Success will depend on adaptability to evolving standards (especially in EVs), investment in R&D for smart and durable designs, and alignment with global decarbonization goals. Companies that innovate in connectivity solutions while ensuring supply chain resilience will lead the market.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Plug Connectors (Quality, IP)
When sourcing plug connectors—especially for industrial, automotive, or outdoor applications—focusing solely on cost or availability can lead to significant issues. Two critical areas where problems often arise are quality and Ingress Protection (IP) rating. Overlooking these aspects can result in product failure, safety hazards, and increased long-term costs. Below are common pitfalls to avoid in both categories.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Prioritizing Cost Over Material Integrity
Choosing the cheapest available option often means sacrificing durable materials such as high-grade thermoplastics or corrosion-resistant metals. Low-quality connectors may use recycled or substandard plastics that degrade under heat, UV exposure, or mechanical stress, leading to premature failure.
2. Inconsistent Manufacturing Standards
Suppliers without certified quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001) may produce inconsistent batches. This can result in dimensional inaccuracies, poor contact alignment, or weak locking mechanisms, increasing the risk of intermittent connections or disconnections.
3. Poor Contact Plating and Conductivity
Inferior plating (e.g., thin or non-uniform gold, tin, or nickel layers) increases contact resistance and reduces current-carrying capacity. This leads to overheating, voltage drops, and potential fire hazards—especially in high-power applications.
4. Lack of Testing and Certification
Many low-cost connectors lack third-party testing (e.g., UL, CE, VDE). Without proper certification, there’s no assurance of electrical safety, flame resistance, or performance under rated load conditions.
IP Rating-Related Pitfalls
1. Misunderstanding IP Ratings
A common mistake is assuming a higher IP number (e.g., IP67) automatically means universal protection. However, IP ratings are specific:
– First digit: Solid particle protection (e.g., dust)
– Second digit: Liquid ingress protection (e.g., water jets)
Using an IP54 connector in a submersion scenario (requiring IP67 or IP68) will result in water ingress and failure.
2. Incomplete or False IP Claims
Some suppliers exaggerate or self-certify IP ratings without proper testing. Always request test reports or certification from accredited labs (e.g., TÜV, SGS) to verify claims.
3. Overlooking Environmental Factors
Even with a high IP rating, factors like temperature cycling, UV exposure, or chemical contact can degrade seals and gaskets. For example, an IP67 connector may fail in a saltwater environment if the materials aren’t corrosion-resistant.
4. Improper Installation Compromising IP Integrity
The IP rating assumes correct installation. Using mismatched cable glands, over-tightening, or improper cable strain relief can damage seals and void protection, regardless of the connector’s rated IP.
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, always verify material specifications, demand certified test reports, and match IP ratings to actual environmental conditions. Partnering with reputable suppliers and conducting sample testing before mass procurement can save significant cost and risk in the long run.
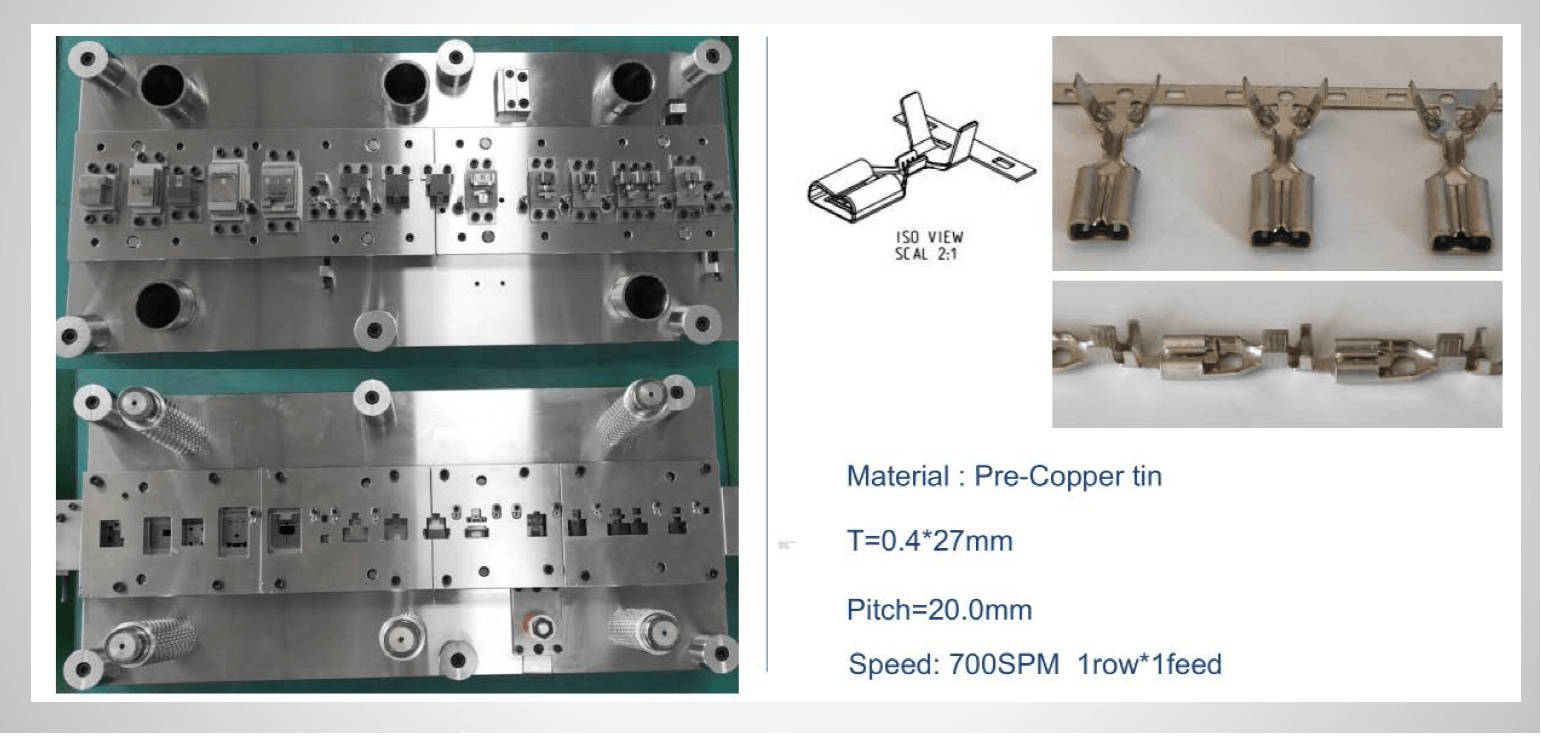
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Plug Connector
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the safe, efficient, and lawful handling, transportation, and distribution of plug connectors. Adherence to these guidelines ensures product integrity, regulatory compliance, and customer safety.
Product Classification and Documentation
Identify the plug connector type (e.g., IEC 60320, NEMA, Schuko) and its electrical specifications (voltage, current, temperature rating). Ensure accurate product classification under relevant international trade codes (e.g., HS Code 8536.90 for electrical connectors). Maintain comprehensive technical documentation, including datasheets, compliance certificates, and user manuals in required languages.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Plug connectors must meet regional and international safety and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards. Key certifications include:
– CE Marking (EU): Compliance with Low Voltage Directive (LVD) and EMC Directive.
– UKCA Marking (UK): Required for products placed on the UK market post-Brexit.
– UL/CSA Certification (USA/Canada): Required for safety compliance in North America.
– PSE Mark (Japan): Mandatory for certain electrical products in Japan.
– CCC Mark (China): Required for products sold in China.
Ensure all certifications are current and documentation is available for customs and market surveillance authorities.
Packaging and Labeling Standards
Use packaging that prevents physical damage and environmental exposure (moisture, dust) during transit. Clearly label each package with:
– Product identification and part number
– Quantity and weight
– Handling symbols (e.g., fragile, do not stack)
– Compliance marks (CE, UL, etc.)
– Manufacturer/importer contact details
– RoHS and REACH compliance symbols where applicable
Labels must be durable and legible throughout the supply chain.
Transportation and Handling
Ship plug connectors via appropriate freight modes (air, sea, road) depending on urgency and volume. Follow IATA, IMDG, or ADR regulations if applicable (though plug connectors typically do not classify as dangerous goods). Protect against electrostatic discharge (ESD) where sensitive components are involved. Train logistics personnel in proper handling procedures to avoid mechanical stress or contamination.
Import/Export Controls
Verify export licensing requirements, especially for shipments to restricted regions. Complete accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. Screen all parties against denied persons lists. Be aware of import duties, VAT, and customs clearance procedures in destination countries.
Environmental and Substance Compliance
Ensure compliance with RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) regulations in the EU. Confirm that materials used (e.g., plastics, metals) do not contain restricted substances such as lead, cadmium, or phthalates above permitted levels. Maintain a Declaration of Conformity and material disclosure reports.
Quality Assurance and Traceability
Implement a traceability system (e.g., batch/lot numbering) to support recalls if necessary. Conduct periodic audits of manufacturing and logistics partners to ensure ongoing compliance. Retain records of compliance testing, shipment details, and quality inspections for a minimum of 10 years, as required by many regulations.
End-of-Life and Recycling
Design plug connectors with recyclability in mind. Provide information on proper disposal methods in accordance with WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) Directive requirements in applicable markets. Partner with certified e-waste recyclers to support responsible end-of-life management.
Conclusion for Sourcing Plug Connectors:
In conclusion, the successful sourcing of plug connectors requires a comprehensive evaluation of technical specifications, quality standards, cost-efficiency, and supplier reliability. Ensuring compatibility with existing systems, adherence to industry regulations (such as IP ratings, voltage/current requirements, and environmental resistance), and long-term durability are critical factors in selecting the right components. Additionally, establishing partnerships with reputable suppliers who offer consistent quality, timely delivery, and responsive support contributes significantly to supply chain stability and product performance. By balancing these elements, organizations can secure plug connectors that meet both technical demands and cost objectives, ultimately supporting reliable and efficient operations across electrical and electronic applications.