The global plastic pelletizing equipment market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for recycled plastics, advancements in polymer processing technologies, and increasing industrial automation. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the plastic recycling market—which directly drives demand for pelletizing solutions—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.5% from 2023 to 2028. Complementing this, Grand View Research estimates that the global plastic processing machinery market, inclusive of pelletizing systems, was valued at USD 38.6 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a CAGR of 5.2% through 2030. This sustained growth is fueled by stricter environmental regulations, growing investment in closed-loop recycling, and the expanding use of plastic pellets across packaging, automotive, and consumer goods sectors. As demand intensifies, manufacturers of plastic pelletizing equipment are scaling innovation in throughput efficiency, energy consumption, and system integration. In this evolving landscape, identifying the leading providers becomes critical for recyclers and processors seeking reliable, high-performance solutions. Here are the top 9 plastic pelletizing equipment manufacturers shaping the industry’s future.
Top 9 Plastic Pelletizing Equipment Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
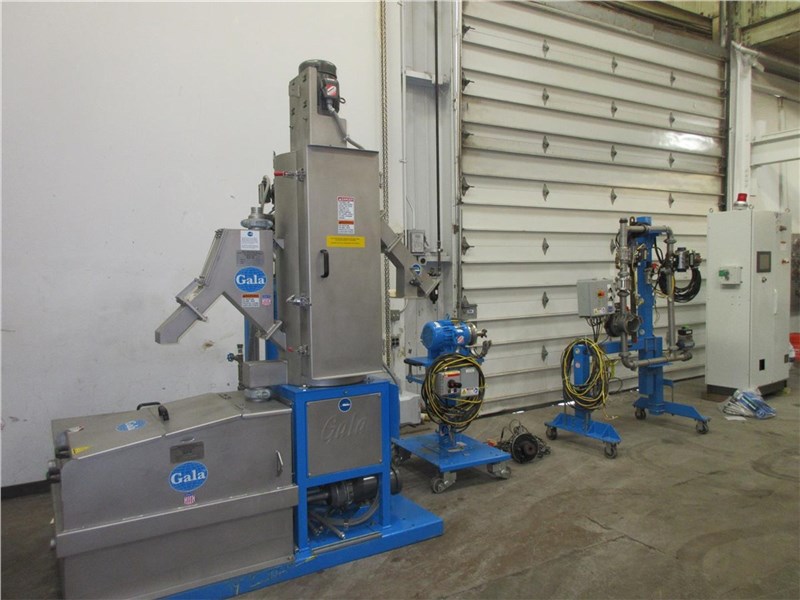
#1 GALA underwater pelletizing systems
Domain Est. 1996
Website: maag.com
Key Highlights: GALA is the global leading manufacturer of underwater pelletizing systems and centrifugal dryers. GALA enjoys an outstanding reputation among national and ……
#2 Pellet Mill & Pelleting Plant Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2012
Website: akahl.com
Key Highlights: PELLET MILL MANUFACTURER: Your expert in the field of flat die pellet mills for feed mills, wood pelleting plants, recycling plants and much more | AMANDUS ……
#3 Pellet Mills
Domain Est. 2013
Website: onecpm.com
Key Highlights: From plastics to industrial products to commercial animal feed, this machine delivers rock-solid performance to meet your pelleting needs day after day….
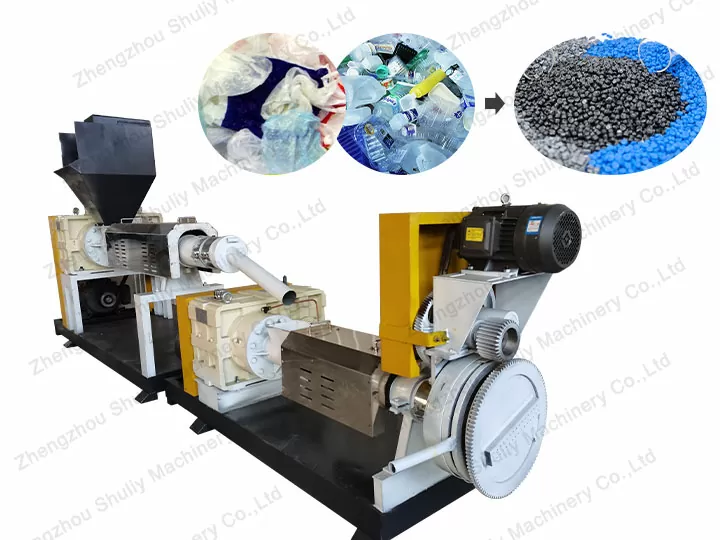
#4 Plastic Pellet Producing Line
Domain Est. 1998
Website: kneader.com.tw
Key Highlights: The plastic pellet producing machine line is fully automatic in weighting, kneading, mixing, extruding, pelletizing, etc., and provides well mixed pellets….
#5 Plastic Recycling Machine
Domain Est. 2011
Website: pureloop.com
Key Highlights: A unique pelletizing machine. The machine is powerful, easy to operate, cost-efficient and delivers more throughput….
#6 Plastic Pelletizers
Domain Est. 2013
Website: plasticrecyclingmachine.net
Key Highlights: Single-Screw Plastic Pelletizing Machines … Our state of the art single screw extruder with Heat Wave Stabilization™ produces high-quality plastic pellets ……
#7 RE
Domain Est. 2016
Website: replast-extruder.com
Key Highlights: A Taiwan company that focus on manufacturing and marketing of plastic pelletizing extruder and other auxiliary equipments for plastic compounding and recycling….
#8 Plastic Pelletizing Machine
Domain Est. 2018
Website: ngr-world.com
Key Highlights: Plastic pellets are the basis for further processing by ♻ recycling machines. ➜ Learn more about the plastic pelletizing machine!…
#9 Rubber and Plastic Pelletizing Machine
Domain Est. 2023
Website: songming-tw.com
Key Highlights: Our specialized plastic pelletizing line is designed to transform waste rubber and plastic efficiently and reliably into valuable pellets, and offering numerous ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Plastic Pelletizing Equipment
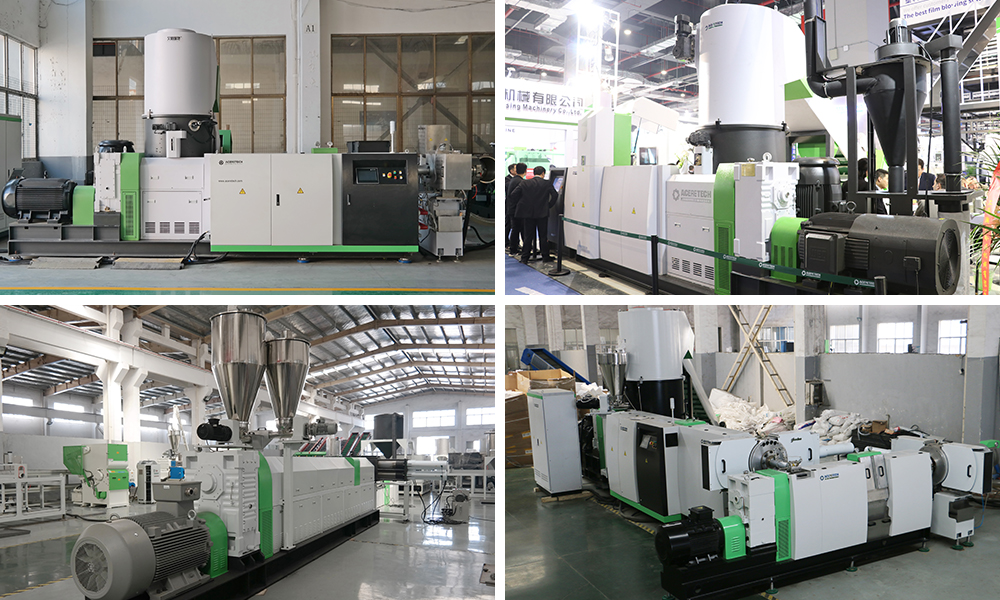

2026 Market Trends for Plastic Pelletizing Equipment
The global plastic pelletizing equipment market is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by sustainability imperatives, technological advancements, and shifting regulatory landscapes. Key trends shaping the industry include:
1. Dominance of Recycling and Circular Economy Drivers
By 2026, the push for a circular economy will be the primary growth engine. Stringent government regulations mandating recycled content in new plastic products (e.g., EU targets, US state laws) are compelling manufacturers to invest heavily in recycling infrastructure. This directly fuels demand for advanced recycling pelletizers, particularly underwater (UW) and strand pelletizers designed for high-throughput, high-purity processing of post-consumer and post-industrial waste. Equipment with superior contaminant removal, precise melt filtration, and consistent pellet quality will be in high demand to meet the stringent quality requirements of food-grade and high-performance recycled resins.
2. Technological Advancements: Automation, AI, and IoT Integration
Pelletizing lines will increasingly feature smart manufacturing technologies. By 2026, expect widespread adoption of:
* Predictive Maintenance: IoT sensors monitoring motor loads, bearing temperatures, and die head pressures will enable predictive maintenance, minimizing unplanned downtime and extending equipment life.
* AI-Driven Process Optimization: Artificial intelligence algorithms will analyze real-time data (throughput, melt viscosity, pellet size) to automatically adjust cutter speeds, water temperature (UW), or strand cooling (strand) for optimal efficiency, energy consumption, and pellet quality consistency.
* Digital Twins: Virtual replicas of pelletizing lines will allow for simulation, optimization, and operator training, reducing commissioning times and improving overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
3. Focus on Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Energy costs and carbon footprint reduction will be critical selection criteria. Equipment manufacturers will compete on:
* Lower Energy Consumption Designs: Innovations in screw and barrel design, high-efficiency motors, and optimized heating/cooling systems will reduce specific energy consumption (kWh/kg).
* Advanced Water Management (UW Pelletizers): Closed-loop water systems with efficient filtration and heat recovery will minimize water usage and thermal energy loss, crucial for both cost savings and environmental compliance.
* Material Efficiency: Equipment minimizing fines generation and startup/stoppage waste will be preferred, contributing to higher yields and lower material costs.
4. Growth in Underwater Pelletizing for High-Performance and Recycling Applications
While strand pelletizing remains dominant for commodity plastics and lower volumes, underwater pelletizing (UW) is expected to see accelerated growth by 2026. Its advantages – producing clean, dust-free, spherical pellets ideal for high-value applications (engineering plastics, food contact, medical) and demanding recycling streams (especially contaminated or mixed post-consumer waste requiring inline melt filtration) – align perfectly with market needs. Investment in larger, more robust UW systems with integrated filtration will be significant.
5. Regional Shifts and Supply Chain Resilience
Geopolitical factors and supply chain disruptions will influence the market:
* Nearshoring/Reshoring: Increased investment in recycling and compounding capacity in North America and Europe, driven by ESG pressures and supply chain security concerns, will boost regional demand for pelletizing equipment.
* Asia-Pacific Growth: China and India will remain major markets, driven by domestic demand, government infrastructure initiatives, and growth in local manufacturing, but with increasing focus on upgrading to more advanced, efficient technology.
* Localization of Service: Equipment suppliers will enhance local service and support networks to meet faster response time demands and reduce operational risks for customers.
6. Demand for Customization and Modular Solutions
The diversity of plastic waste streams and the need for specialized compounds will drive demand for customized and modular pelletizing systems. Manufacturers will seek equipment that can be easily reconfigured for different feedstocks (e.g., films, rigid packaging, mixed waste) or pellet specifications. Modular designs allowing for future upgrades (e.g., adding filtration, changing cutter types) will offer flexibility and protect long-term investments.
In conclusion, the 2026 plastic pelletizing equipment market will be characterized by innovation focused on enabling the circular economy. Success will belong to manufacturers offering intelligent, energy-efficient, and highly reliable solutions—particularly advanced underwater and recycling-optimized systems—supported by strong service and data-driven optimization capabilities, meeting the dual imperatives of sustainability and operational excellence.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Plastic Pelletizing Equipment: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing plastic pelletizing equipment involves significant investment and long-term operational impact. Buyers often encounter challenges related to equipment quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Being aware of these pitfalls helps mitigate risks and ensures a successful procurement process.
Poor Build Quality and Substandard Components
One of the most frequent issues is receiving equipment constructed with inferior materials or lacking precision engineering. Low-cost suppliers may use subpar metals, worn tooling, or outdated control systems, leading to frequent breakdowns, inconsistent pellet quality, and higher maintenance costs. This compromises production efficiency and increases total cost of ownership.
Inadequate Process Validation and Performance Guarantees
Some suppliers fail to provide verified performance data or process validation under real-world conditions. Without clear specifications—such as throughput rates, melt homogeneity, pellet size consistency, or energy consumption—buyers risk acquiring equipment that doesn’t meet production requirements. Lack of performance guarantees makes it difficult to hold suppliers accountable.
Misrepresentation of Technical Capabilities
Suppliers may exaggerate equipment capabilities, such as compatibility with various polymer types (e.g., engineering plastics, biopolymers) or claim advanced automation features that aren’t fully implemented. This misalignment leads to operational bottlenecks, especially when scaling up or processing sensitive materials requiring precise temperature and shear control.
Lack of Intellectual Property Protection
When customizing equipment or sharing proprietary formulations and process parameters, there’s a risk of IP exposure. Unscrupulous suppliers may replicate designs, reverse-engineer processes, or share sensitive information with third parties. Contracts often lack strong IP clauses, leaving buyers vulnerable to theft or unauthorized use of their innovations.
Insufficient Documentation and Know-How Transfer
Incomplete technical documentation, missing schematics, or lack of training can hinder installation, operation, and troubleshooting. Without proper knowledge transfer, operators may struggle to optimize the equipment, increasing downtime and reducing efficiency. This is especially problematic with complex twin-screw extruders or underwater pelletizing systems.
Hidden Costs and After-Sales Support Gaps
Initial quotes may exclude critical components like feeders, dryers, or downstream conveyors. Additionally, suppliers in certain regions may offer limited after-sales support, spare parts availability, or remote diagnostics. This results in prolonged downtimes and increased costs when service is needed.
Non-Compliance with Safety and Regulatory Standards
Equipment that doesn’t adhere to international safety standards (e.g., CE, UL, ISO) poses operational and legal risks. Poorly designed systems may lack essential safety interlocks, proper ventilation, or explosion protection, especially when handling flammable materials or regrind.
Failure to Verify Supplier Credibility and Track Record
Engaging with suppliers who lack a proven history in pelletizing technology increases the likelihood of project failure. Without due diligence—such as site visits, reference checks, or audits—buyers may end up with inexperienced vendors unable to deliver reliable, scalable solutions.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires thorough supplier evaluation, detailed technical specifications, robust contracts with IP protections, and clear performance benchmarks. Engaging third-party engineering consultants can also help validate equipment suitability and safeguard critical business assets.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Plastic Pelletizing Equipment
Overview and Purpose
This guide outlines key logistics considerations and compliance requirements for the transportation, installation, and operation of plastic pelletizing equipment. Whether shipping domestically or internationally, adherence to regulatory standards and proper logistical planning ensures timely delivery, legal compliance, and operational safety.
Equipment Classification and HS Code
Plastic pelletizing equipment typically falls under Harmonized System (HS) code 8477.20, which covers machinery for processing plastics or rubber. Accurate classification is essential for customs clearance, duty assessment, and import/export compliance. Confirm the exact HS code with local customs authorities, as sub-classifications may vary by region and equipment configuration.
International Shipping and Export Documentation
For cross-border shipments, exporters must prepare accurate documentation, including:
– Commercial Invoice
– Packing List
– Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
– Certificate of Origin
– Export Declaration (e.g., AES filing for U.S. exports)
Ensure equipment is properly described with technical specifications (e.g., motor power, dimensions, weight) to avoid customs delays.
Import Regulations and Duties
Importing countries may impose specific duties, taxes, and regulatory requirements. Key considerations include:
– Tariff rates based on the destination country’s trade agreements
– Import permits or product certifications (e.g., CE marking in the EU, CCC in China)
– Compliance with local electrical and mechanical safety standards
Engage a customs broker familiar with industrial machinery imports to streamline clearance.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Pelletizing equipment is often heavy and sensitive to moisture and shock. Use:
– Wooden crates with internal bracing for large components
– Desiccants and moisture barriers in humid climates
– Clearly marked lifting points and “Fragile”/“This Side Up” labels
Document the condition at shipment and upon delivery to support damage claims if needed.
Transportation Mode Selection
Choose transport based on equipment size, urgency, and destination:
– Sea Freight: Cost-effective for large, heavy machinery; use flat-rack or open-top containers if dimensions exceed standard shipping limits
– Air Freight: Faster but expensive; suitable for urgent spare parts or compact units
– Land Transport: Ideal for regional delivery; ensure route feasibility (bridge clearances, road weight limits)
Installation and Site Preparation Compliance
Prior to equipment arrival, verify:
– Facility meets electrical specifications (voltage, phase, grounding)
– Adequate space for operation and maintenance access
– Compliance with local building and fire codes
– Proper ventilation and dust collection systems to meet environmental and OSHA (or equivalent) safety standards
Environmental and Safety Regulations
Plastic pelletizing operations may be subject to environmental controls:
– Spill Prevention: Compliance with regulations such as EPA’s SPCC (Spill Prevention, Control, and Countermeasure) rule if handling large volumes of plastic resin
– Emissions Control: Use of filters and scrubbers to meet air quality standards (e.g., EPA NESHAP, EU Directive 2010/75/EU)
– Noise Levels: Adherence to workplace noise regulations (e.g., OSHA 29 CFR 1910.95)
CE and Other Certification Requirements
For equipment sold in the European Economic Area (EEA), CE marking is mandatory under the Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC). This includes:
– Risk assessment and technical file creation
– Compliance with essential health and safety requirements
– Affixing CE mark and issuing Declaration of Conformity
Other regions may require similar certifications (e.g., UKCA for the UK, EAC for Eurasian Economic Union).
Maintenance and Operational Compliance
To ensure ongoing compliance:
– Follow manufacturer-recommended maintenance schedules
– Train operators on safety procedures and emergency shutdowns
– Keep records of inspections, repairs, and compliance audits
– Update documentation if equipment modifications affect safety or emissions
End-of-Life and Recycling Considerations
When decommissioning equipment:
– Follow WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) Directive guidelines in applicable regions
– Recycle or dispose of components (e.g., motors, circuit boards) through certified e-waste handlers
– Document disposal to meet corporate sustainability goals and regulatory reporting
Conclusion
Successful deployment of plastic pelletizing equipment requires careful attention to logistics and regulatory compliance at every stage—from export to installation and operation. Proactive planning, accurate documentation, and adherence to international and local standards reduce risk, avoid delays, and support safe, efficient production.
In conclusion, sourcing plastic pelletizing equipment requires a careful evaluation of technical specifications, production capacity, energy efficiency, and long-term maintenance requirements. It is essential to partner with reputable suppliers who offer reliable machinery, comprehensive after-sales support, and compatibility with your specific plastic materials and processing needs. Conducting thorough market research, comparing quotes, and considering both initial investment and total cost of ownership will ensure a cost-effective and sustainable solution. Ultimately, selecting the right pelletizing system enhances production efficiency, product quality, and contributes to the overall success of plastic recycling or manufacturing operations.