The global pH meter market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for water quality monitoring across municipal, industrial, and environmental sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global pH meter market size was valued at USD 1.36 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.4% from 2023 to 2030. This expansion is fueled by stringent environmental regulations, rising concerns over water pollution, and the need for real-time monitoring in wastewater treatment and industrial processes. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects steady market growth, citing advancements in sensor technology and the integration of IoT-enabled devices as key drivers. As demand for accurate and reliable water quality assessment tools rises, manufacturers of pH meters are innovating rapidly to meet performance, durability, and connectivity expectations. In this evolving landscape, identifying the top producers of water pH meters is essential for municipalities, labs, and industries seeking precision, compliance, and long-term value.
Top 10 Ph Meter Of Water Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Jenco Instruments
Domain Est. 1998
Website: jencoi.com
Key Highlights: 45-Year OEM/ODM/Jenco-branded manufacturer of water quality meters, including pH meters, ORP meters, conductivity meters, dissolved oxygen meters….
#2 pH Products & Information
Domain Est. 1996
Website: sensorex.com
Key Highlights: 2-day delivery Free 30-day returnsExplore Sensorex’s full range of pH sensors, probes, and electrodes for reliable, accurate measurement in lab, industrial, and environmental appli…
#3 Turbidity Meters, Colorimeters, UV, pH and Conductivity sensors
Domain Est. 1995
Website: optek.com
Key Highlights: optek manufacturers inline turbidity meters, colorimeters, uv absorption and pH and conductivity sensors for all industries for process control….
#4 pH Meters for Water
Domain Est. 1993
Website: mt.com
Key Highlights: Easy-to-use digital pH meters for precise water analysis: Monitor water quality, measure the pH of drinking water, ensure consistency in the lab, and more….
#5 pH Meters
Domain Est. 1995
Website: hach.com
Key Highlights: 3–6 day delivery · 30-day returnsHach provides a wide range of pH meters that deliver precise and reliable results in various settings. These pH meters are crucial for detecting p…
#6 pH Water Monitoring
Domain Est. 1995
Website: badgermeter.com
Key Highlights: pH is the value used to measure the acidity and alkalinity of water. Measure pH in raw water, process water and final water systems….
#7 pH Meters
Domain Est. 1996 | Founded: 1978
Website: hannainst.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $200 · 30-day returnsDiscover reliable pH meters for laboratory and field use. Trusted by professionals since 1978, test confidently with Hanna Instruments and …
#8 Myron L® Company
Domain Est. 1999
Website: myronl.com
Key Highlights: Producing water testing equipment and water quality meters for over 60 years. Hand-held/portable instruments, in-line monitors/controllers, solutions, ……
#9 hmdigital.com
Domain Est. 2003
Website: hmdigital.com
Key Highlights: PH-80 pH HydroTester Series FIND OUT MORE ; HM-100 Monitor Ideal for All Water Quality Testing FIND OUT MORE ; Professional Series FIND OUT MORE Long Type pH/EC/ ……
#10 Milwaukee pH Meters
Domain Est. 2010
Website: milwaukeeinstruments.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $50 14-day returnsOur pH meter range includes everything from affordable pH pens and advanced pH testers to lab grade pH meters, monitors and controllers….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Ph Meter Of Water
H2: 2026 Market Trends for pH Meters in Water Applications
The global market for pH meters used in water quality monitoring is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by increasing environmental regulations, technological advancements, and expanding industrial and municipal water treatment needs. Below is an analysis of key market trends expected to shape the pH meter landscape in water applications by 2026.
1. Rising Demand for Smart and IoT-Enabled pH Meters
By 2026, the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) and cloud-based monitoring systems is expected to dominate the pH meter market. Smart pH meters capable of real-time data transmission, remote calibration, and predictive maintenance are gaining traction across industries such as wastewater treatment, aquaculture, and municipal water supply. These devices enhance operational efficiency and support continuous compliance with water quality standards.
2. Stricter Environmental and Regulatory Standards
Governments worldwide are tightening water quality regulations to combat pollution and ensure safe drinking water. Regulatory bodies like the U.S. EPA and the EU’s Water Framework Directive are mandating continuous monitoring of pH levels in surface, groundwater, and effluent discharges. This regulatory push is accelerating the adoption of high-accuracy, reliable pH meters, especially in emerging markets undergoing industrialization.
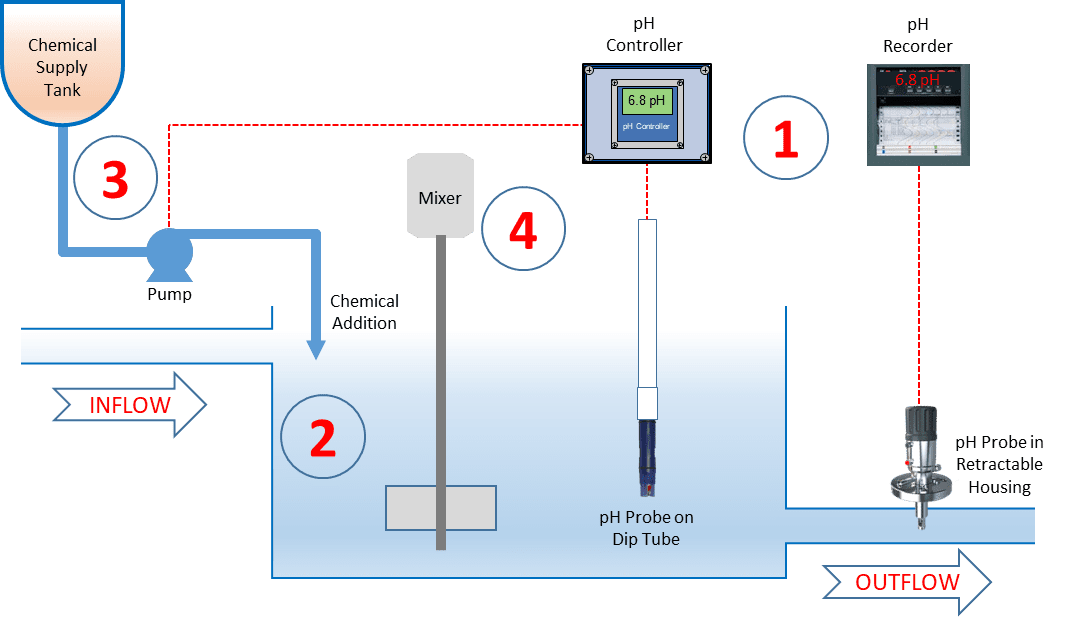
3. Growth in Municipal and Industrial Wastewater Treatment
The expansion of urban infrastructure and industrial activities is increasing wastewater generation. As a result, municipalities and industries are investing in advanced water treatment systems where pH monitoring is critical for effective chemical dosing and process control. The demand for durable, low-maintenance pH meters designed for harsh environments is expected to grow significantly.
4. Advancements in Sensor Technology and Durability
Innovations in electrode materials—such as solid-state sensors, graphene-based electrodes, and self-cleaning probes—are improving the longevity and accuracy of pH meters in challenging water conditions. These advancements reduce calibration frequency and maintenance costs, making them ideal for long-term deployment in remote or automated systems.
5. Expansion in Emerging Economies
Countries in Asia-Pacific (e.g., India, China, and Southeast Asia), Latin America, and Africa are witnessing rapid urbanization and infrastructure development. These regions are investing heavily in water quality monitoring systems, creating a fertile ground for pH meter manufacturers. Local manufacturing and partnerships are expected to rise to meet regional demands and reduce equipment costs.
6. Focus on Sustainability and Green Technologies
Environmental sustainability is becoming a core business priority. Water treatment facilities are adopting energy-efficient and eco-friendly monitoring solutions. pH meters with low power consumption, recyclable components, and minimal chemical usage during calibration are increasingly preferred, aligning with broader ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals.
7. Increased Adoption in Agriculture and Aquaculture
Precision farming and sustainable aquaculture practices are driving demand for portable and handheld pH meters. Farmers and fish farmers rely on accurate pH monitoring to optimize water conditions for crop irrigation and aquatic life. By 2026, this segment is expected to see robust growth, supported by government subsidies and digital farming initiatives.
8. Competitive Landscape and Market Consolidation
The pH meter market is becoming increasingly competitive, with key players such as Hach, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Mettler Toledo, and Hanna Instruments focusing on product innovation and strategic acquisitions. Smaller companies are leveraging niche technologies to capture specific market segments, leading to both innovation and consolidation.
Conclusion
By 2026, the pH meter market for water applications will be characterized by digital transformation, regulatory compliance, and technological innovation. The convergence of smart sensing, environmental awareness, and infrastructure development will drive sustained demand across municipal, industrial, agricultural, and environmental sectors. Companies that prioritize accuracy, connectivity, and sustainability will be best positioned to capitalize on these emerging opportunities.

H2: Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a pH Meter for Water Quality (IP)
Sourcing a pH meter for water quality applications, especially with Ingress Protection (IP) ratings for durability in wet or outdoor environments, requires careful consideration. Overlooking key factors can lead to inaccurate measurements, premature failure, and increased costs. Here are the most common pitfalls to avoid:
H3: 1. Ignoring the Specific Water Matrix
- Pitfall: Assuming a single pH meter fits all water types (e.g., using a sensor calibrated for clean lab water on highly alkaline wastewater or seawater).
- Consequence: Drift, slow response, inaccurate readings, and shortened sensor life due to chemical attack or clogging.
- Solution: Match the electrode design (glass formulation, reference junction type – e.g., double junction for dirty/suspended solids, gel electrolyte for low maintenance) and calibration buffers to your specific water’s pH range, ionic strength, temperature, and contaminants (e.g., oils, sulfides, proteins).
H3: 2. Overlooking Required Accuracy and Resolution
- Pitfall: Selecting a meter based solely on price or features without defining the necessary accuracy (±0.01 pH vs. ±0.1 pH) and resolution (0.01 vs. 0.1) for the application.
- Consequence: Inadequate precision for critical processes (e.g., chemical dosing, regulatory compliance) or unnecessary overspending on high-accuracy features for rough screening.
- Solution: Define the required measurement tolerance upfront. High-precision lab analysis demands higher accuracy than basic field screening.
H3: 3. Underestimating Environmental Conditions & IP Rating Needs
- Pitfall: Choosing an IP67 meter assuming it’s suitable for constant submersion or harsh industrial spray, or selecting an IP54 meter for outdoor rain exposure.
- Consequence: Water ingress, sensor damage, electrical hazards, and unreliable operation. IP67 allows temporary immersion; IP68 or IP69K is needed for continuous submersion or high-pressure washdown.
- Solution: Rigorously assess the environment: dust, rain, hose-downs, submersion depth/duration, temperature extremes, and chemical exposure. Select the minimum IP rating that exceeds these conditions (e.g., IP68 for continuous submersion in monitoring wells).
H3: 4. Neglecting Calibration and Maintenance Requirements
- Pitfall: Choosing a complex meter without considering the availability of buffers, storage solutions, and user expertise for regular calibration and cleaning.
- Consequence: Rapid sensor drift, poor accuracy, and shortened lifespan. High-maintenance sensors in remote locations become impractical.
- Solution: Prioritize meters with stable sensors, easy calibration procedures (e.g., automatic recognition), and low-maintenance designs (e.g., gel-filled, robust junctions). Ensure consumables (buffers, storage solution) are readily available and affordable.
H3: 5. Disregarding Temperature Compensation
- Pitfall: Using a meter without Automatic Temperature Compensation (ATC) or with an incompatible ATC probe in applications with significant temperature fluctuations.
- Consequence: Significant pH measurement errors, as pH is temperature-dependent. A reading can be off by 0.1 pH or more per 10°C change without compensation.
- Solution: Always use a pH meter with integrated ATC using a temperature probe (preferably combined with the pH electrode). Ensure the ATC range covers your application’s temperature extremes.
H3: 6. Choosing Incompatible Materials
- Pitfall: Selecting a housing or sensor body material (e.g., standard PVC) that degrades when exposed to specific chemicals in the water (e.g., solvents, strong acids/bases, chlorine).
- Consequence: Cracking, leaching, contamination of the sample, and structural failure, especially critical for IP-rated enclosures.
- Solution: Verify material compatibility (e.g., PVDF, PEEK, stainless steel 316) with the water’s chemical constituents, including disinfectants. Ensure O-rings/gaskets are chemically resistant (e.g., Viton, EPDM).
H3: 7. Overlooking Data Management and Connectivity
- Pitfall: Not considering how data will be recorded, stored, or transmitted (e.g., manual logging vs. automated data logging, Bluetooth, 4-20mA output).
- Consequence: Inefficient data handling, potential for transcription errors, inability to perform trend analysis or integrate with SCADA/PLC systems for process control.
- Solution: Define data needs early: Do you need logging? Real-time transmission? Analog/digital outputs? Choose a meter with the necessary interfaces (USB, SD card, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, 4-20mA, Modbus).
H3: 8. Focusing Only on Initial Cost
- Pitfall: Selecting the cheapest option without considering Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
- Consequence: Higher long-term costs due to frequent sensor replacement, downtime, inaccurate measurements leading to process issues, and costly consumables.
- Solution: Evaluate TCO, including purchase price, sensor lifespan, calibration frequency/cost, maintenance needs, and potential cost of measurement errors.
By carefully evaluating these common pitfalls against your specific water quality monitoring needs and environmental conditions (IP), you can select a reliable, accurate, and cost-effective pH meter that delivers trustworthy results.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for pH Meters Used in Water Analysis
This guide outlines the critical logistics and compliance considerations for the procurement, handling, transportation, storage, use, and disposal of pH meters designed for water analysis. Adherence to these protocols ensures instrument integrity, data accuracy, regulatory compliance, and user safety.
H2: 1. Pre-Shipment & Procurement Compliance
- Regulatory Verification:
- Confirm the pH meter model meets relevant performance standards for water analysis (e.g., ISO 10523:2020, ASTM D1293, regional standards like US EPA methods).
- Verify calibration certificates are traceable to NIST (or equivalent national metrology institute) and include uncertainty statements.
- Ensure the device and its packaging comply with RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH regulations.
- Documentation:
- Obtain and retain manufacturer’s Declaration of Conformity (DoC) for applicable directives (e.g., CE marking in Europe, FCC in the US).
- Secure detailed product specifications, user manuals (in required languages), Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS/SDS) for electrodes and calibration buffers.
- Confirm software/firmware versions meet data integrity requirements (e.g., 21 CFR Part 11 if applicable).
- Supplier Qualification: Source from reputable suppliers with established quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001).
H2: 2. Packaging & Labeling for Transportation
- Securing the Instrument:
- Use original manufacturer packaging whenever possible. Ensure the pH probe is securely stored in its protective cap filled with storage solution (typically 3M KCl).
- If repackaging, use rigid containers with ample cushioning (foam inserts, bubble wrap) to protect the meter body, probe, and accessories (cables, caps, calibration cups) from shock and vibration.
- Environmental Protection:
- Use moisture-resistant packaging. Include desiccant packs if shipping to humid environments or for extended periods.
- Protect from extreme temperatures (avoid freezing or >50°C/122°F) during transit. Use insulated packaging or temperature-controlled shipping if necessary.
- Hazardous Materials (Calibration Buffers):
- Critical: Most pH buffer solutions (pH 4.0, 7.0, 10.0) are classified as hazardous goods for transport due to corrosivity (pH 4, pH 10) or other hazards.
- Labeling: Packages containing buffers must display appropriate UN number (e.g., UN1760, UN3265), Proper Shipping Name (e.g., “CORROSIVE LIQUID, ACIDIC, INORGANIC N.O.S.”), hazard class (Class 8 – Corrosive), and GHS pictograms.
- Packaging: Use UN-certified packaging designed for liquids, with leak-proof primary containers and sufficient absorbent material.
- Documentation: Prepare a Dangerous Goods Declaration (Shipper’s Declaration) if required by volume/concentration and transport mode (IATA for air, IMDG for sea, ADR for road in Europe, 49 CFR for US).
- General Labeling: Clearly label packages as “FRAGILE,” “THIS SIDE UP,” and “PROTECT FROM MOISTURE” and “PROTECT FROM EXTREME TEMPERATURES.” Include “pH METER FOR WATER ANALYSIS” and consignee details.
H2: 3. Import/Export Regulations
- Customs Documentation: Prepare accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. Clearly describe goods (e.g., “Electronic pH Meter for Water Quality Testing”).
- Import Restrictions: Research destination country regulations:
- CE Marking/UKCA Marking: Required for sale/use in the EEA/UK.
- Other Certifications: Potential requirements for PRC-CC, KC Mark (Korea), INMETRO (Brazil), etc.
- Licensing: Check if specific import licenses are needed for scientific instruments or electronics.
- Hazardous Goods Import: Ensure the destination country accepts the shipped buffer solutions under the declared UN number and packaging. Be aware of specific import restrictions on chemicals.
- Duties & Taxes: Calculate and prepare for applicable import duties, VAT, or GST.
H2: 4. Storage (Upon Receipt & Long-Term)
- Location: Store in a clean, dry, temperature-controlled environment (typically 5°C to 40°C / 41°F to 104°F). Avoid direct sunlight, dust, and corrosive fumes.
- Probe Storage: The electrode is the most critical component.
- NEVER store the glass electrode dry. Always keep the sensing bulb and junction immersed in the recommended storage solution (usually 3M KCl or a specific storage solution provided by the manufacturer).
- Use the protective cap filled with storage solution.
- Avoid storing in distilled or deionized water, as it leaches ions from the glass membrane, damaging it.
- Meter Body: Store in its protective case. Remove batteries if storing for extended periods (>1 month) to prevent corrosion from leakage.
- Buffers & Solutions: Store calibration and storage solutions according to manufacturer instructions (often cool, dark place). Check expiration dates. Store hazardous buffers securely, segregated from incompatible materials.
H2: 5. On-Site Use & Operational Compliance
- Calibration:
- Calibrate frequently (daily or before each use batch) using fresh, traceable NIST standard buffers appropriate for the expected sample pH range (typically pH 4.0, 7.0, and 10.0).
- Document calibration (date, time, buffer values used, slope, offset, temperature, technician) in a logbook or electronic system.
- Follow a documented Standard Operating Procedure (SOP).
- Measurement:
- Rinse the electrode thoroughly with clean water (preferably deionized) between samples and after calibration.
- Gently blot (do not wipe) the electrode tip with lint-free tissue.
- Ensure proper sample temperature compensation (ATC probe or manual input).
- Allow sufficient stabilization time for the reading.
- Record measurements with date, time, location, sample ID, pH value, temperature, and operator.
- Data Integrity: Comply with relevant data governance regulations (e.g., 21 CFR Part 11 for FDA-regulated environments, ISO 17025 for testing labs). Ensure secure, auditable data storage (electronic records with audit trails, controlled paper logs).
- Maintenance: Follow manufacturer’s schedule for cleaning (specific solutions for contaminants), inspection (cracks, contamination), and replacement (electrode lifespan, typically 1-2 years with proper care).
H2: 6. Maintenance, Repair & Disposal
- Maintenance/Repair:
- Use only manufacturer-approved parts and calibration standards.
- Document all maintenance and repairs.
- Ensure repairs are performed by qualified personnel; recalibrate thoroughly afterward.
- End-of-Life Disposal:
- Electrodes: Contain glass, metal (Ag/AgCl), and hazardous electrolyte (KCl, often with AgNO3). DO NOT dispose of in regular trash.
- Treat as hazardous electronic waste (e-waste) and/or hazardous chemical waste.
- Follow local, state/provincial, and national regulations for disposal of chemical-electronic mixtures. Use licensed hazardous waste disposal contractors.
- Check for specific take-back programs offered by the manufacturer or supplier.
- Meter Body: Dispose of as electronic waste (e-waste) through certified e-waste recyclers. Do not landfill.
- Batteries: Remove and recycle separately according to local battery recycling regulations.
- Calibration Buffers: Dispose of unused or expired buffers as hazardous chemical waste according to local regulations and SDS instructions. Neutralization may be required before disposal; consult environmental/safety officer.
- Electrodes: Contain glass, metal (Ag/AgCl), and hazardous electrolyte (KCl, often with AgNO3). DO NOT dispose of in regular trash.
Key Compliance Standards & Regulations:
- Performance: ISO 10523, ASTM D1293, EPA Methods (e.g., 150.1, 150.2)
- Quality Management: ISO 9001, ISO/IEC 17025 (for testing labs)
- Safety & Environment: RoHS, REACH, GHS (Globally Harmonized System)
- Data Integrity: 21 CFR Part 11 (US FDA), EU Annex 11
- Transportation: IATA DGR, IMDG Code, ADR, 49 CFR (Hazardous Materials Regulations)
- Waste: RCRA (US), WEEE Directive (EU), local hazardous waste regulations.
Always consult the specific manufacturer’s instructions and your organization’s Environmental, Health, and Safety (EHS) and Quality Assurance/Quality Control (QA/QC) departments for detailed, site-specific procedures.
Conclusion for Sourcing a pH Meter for Water Testing
In conclusion, selecting the right pH meter for water testing is crucial for ensuring accurate, reliable, and consistent measurements, whether for environmental monitoring, industrial processes, or laboratory analysis. When sourcing a pH meter, key factors such as measurement accuracy, ease of calibration, durability, portability, and resistance to environmental conditions should be carefully evaluated. Additionally, features like automatic temperature compensation (ATC), data logging, and waterproof design can significantly enhance usability and performance.
For routine or field applications, portable and rugged pH meters are ideal, while benchtop models offer higher precision for laboratory environments. It is also essential to consider maintenance requirements, availability of replacement parts (such as electrodes), and vendor support. Investing in a high-quality pH meter from a reputable supplier ensures long-term reliability and compliance with regulatory standards.
Ultimately, the right choice depends on the specific application, budget, and required features. Proper sourcing not only enhances measurement integrity but also contributes to effective water quality management and decision-making.