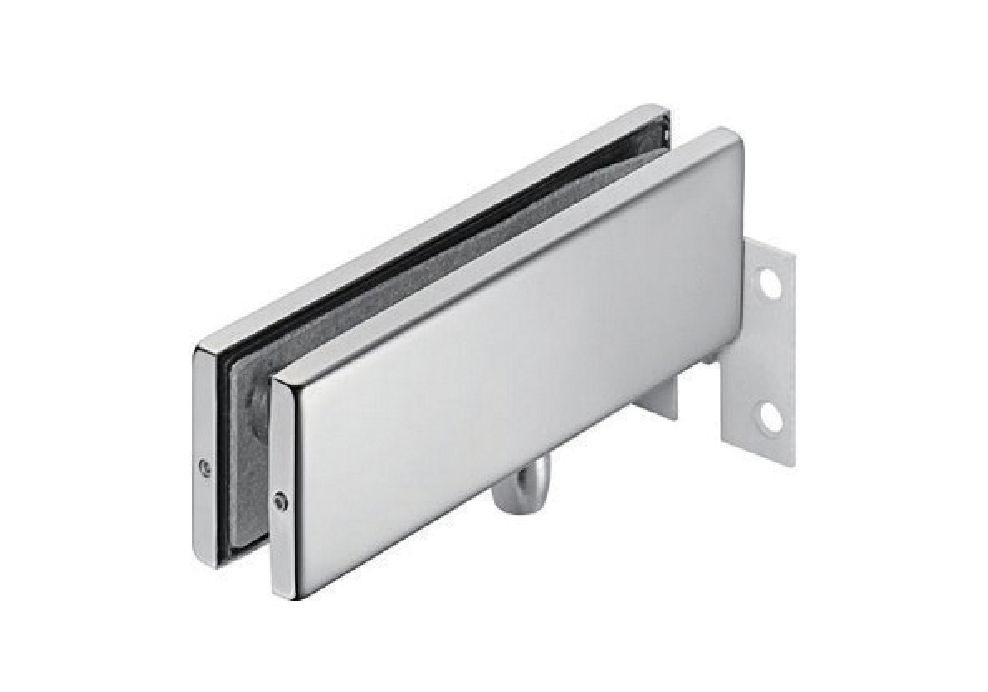
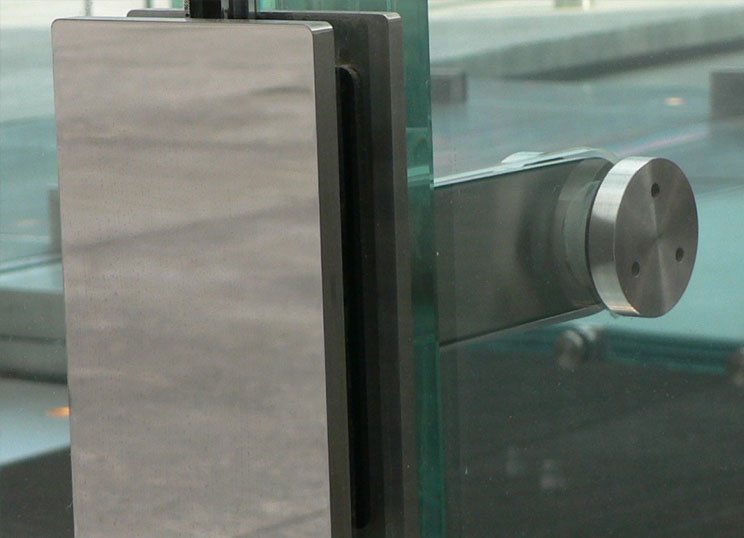
The global patch fitting market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand across industries such as plumbing, HVAC, fire protection, and semiconductor manufacturing. According to Grand View Research, the global pipe and tube fitting market size was valued at USD 34.2 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by rising infrastructure development, stricter safety regulations, and the need for leak-proof, high-performance connections in critical applications. Patch fittings—known for their reliability in repair and maintenance scenarios—are gaining traction as cost-effective, time-saving solutions in both residential and industrial settings. With the Asia Pacific region leading in infrastructure expansion and industrialization, manufacturers are scaling production and innovation to meet evolving quality and performance standards. In this competitive landscape, identifying top-tier patch fitting manufacturers becomes essential for sourcing reliable components that ensure system integrity and operational efficiency.
Top 9 Patch Fitting Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
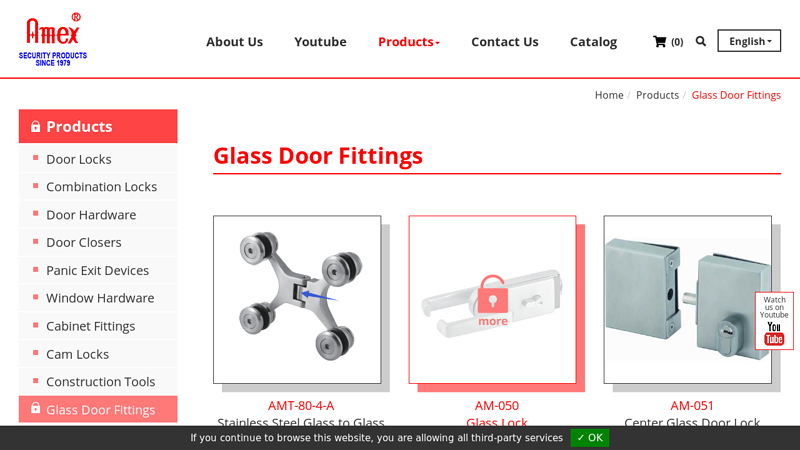
#1 Glass Door Fittings
Domain Est. 2007
Website: amexlock.com
Key Highlights: Glass door lock manufacturer AM-051 Center Glass Door Lock Inquiry Detail Bottom Patch Fitting supplier AM-301 Bottom Patch Fitting Inquiry Detail…
#2 patch fitting
Domain Est. 2002
Website: dnd.com.tw
Key Highlights: A premier Taiwanese manufacturer, specializes in high-quality hardware solutions, including patch fitting, door closers, exit devices, glass hardware, door ……
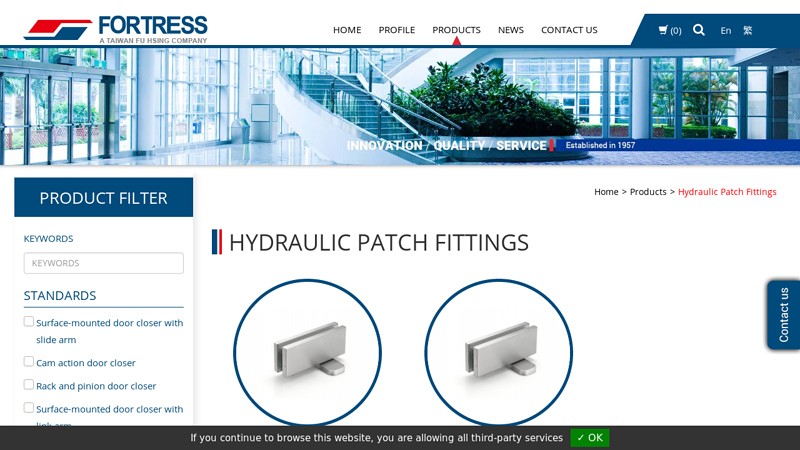
#3 Hydraulic Patch Fitting Manufacturers
Domain Est. 2012
Website: fortress-hardware.com
Key Highlights: Best hydraulic patch manufacturer in Taiwan. Fortress hydraulic patch fittings could be installed without cutting or digging the floor, our patch fittings ……
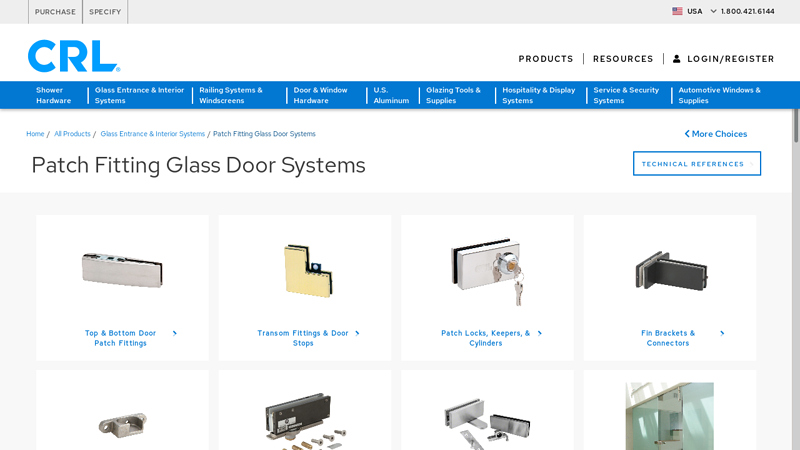
#4 Patch Fitting Glass Door Systems
Domain Est. 1995
Website: crlaurence.com
Key Highlights: Explore our patch-fitting glass door hardware, including sleek fittings, bifold door pivot repairs, and top-notch interior pivot hardware. Shop CRL today….
#5 Patch Fittings
Domain Est. 1996
Website: assaabloy.com
Key Highlights: ASSA ABLOY provides patch fittings for doors, sidelites and transoms, offering designers and architects a complete selection of products for most of the ……
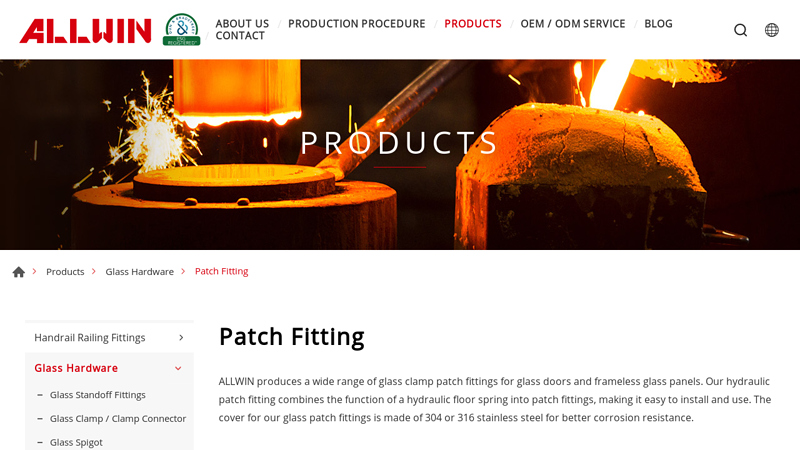
#6 Patch Fitting
Domain Est. 2006
Website: allwinhardware.com
Key Highlights: ALLWIN produces a wide range of glass clamp patch fittings for glass doors and frameless glass panels. Our hydraulic patch fitting combines the function of ……
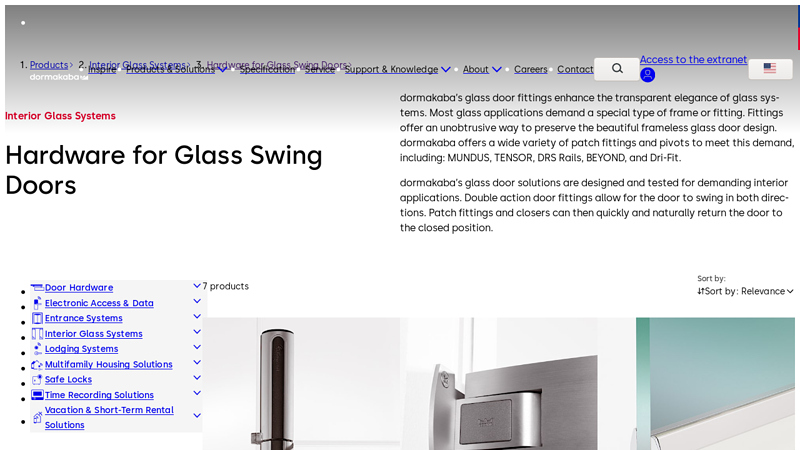
#7 Hardware for Glass Swing Doors
Domain Est. 2015
Website: dormakaba.com
Key Highlights: dormakaba offers a wide variety of patch fittings and pivots to meet this demand, including: MUNDUS, TENSOR, DRS Rails, BEYOND, and Dri-Fit….
#8 Glass Patch Fittings
Domain Est. 2016
Website: assaabloyglass.us
Key Highlights: ROCKWOOD provides glass door patch fittings for doors, sidelites, and transoms, offering designers and architects a complete selection of products….
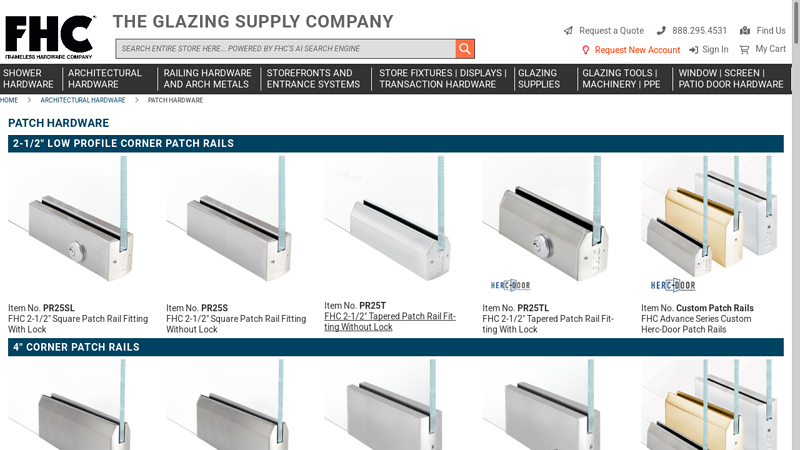
#9 FHC
Domain Est. 2019
Website: fhc-usa.com
Key Highlights: The Frameless Hardware Company is a supplier to the glass, glazing, and fenestration industries. Shop FHC for tools, supplies and hardware solutions for ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Patch Fitting

H2 2026 Market Trends for Patch Fittings
The patch fitting market is poised for dynamic shifts in H2 2026, driven by technological advancements, evolving industry demands, and sustainability imperatives. Here’s a comprehensive analysis of the key trends shaping the sector:
1. Accelerated Adoption of Smart and IoT-Enabled Patch Fittings
By H2 2026, smart patch fittings embedded with sensors and IoT connectivity will move from niche to mainstream, particularly in industrial automation, smart buildings, and critical infrastructure. These fittings enable real-time monitoring of pressure, temperature, and flow rates, supporting predictive maintenance and reducing downtime. Major manufacturers are integrating wireless protocols (e.g., LoRaWAN, NB-IoT) directly into fittings, facilitating seamless integration with digital twin platforms and facility management systems.
2. Growth in Sustainable and Recyclable Materials
Environmental regulations and corporate ESG goals are driving demand for eco-friendly patch fittings. In H2 2026, manufacturers are increasingly shifting from traditional brass and stainless steel to high-performance polymers (e.g., PPS, PEEK) and recycled alloys. Biodegradable sealants and coatings are also gaining traction, especially in water and wastewater applications, reducing long-term environmental impact.
3. Expansion in Renewable Energy and Hydrogen Infrastructure
The global push toward decarbonization is fueling infrastructure investments in hydrogen transport and storage, offshore wind, and geothermal systems. Patch fittings designed for high-pressure hydrogen compatibility (e.g., ISO 19880-certified) are seeing sharp demand growth. Specialized fittings with enhanced leak-tightness and resistance to embrittlement are critical in these applications, creating new market segments.
4. Increased Demand for Miniaturization and High-Density Configurations
Driven by space constraints in data centers, medical devices, and aerospace systems, the trend toward smaller, high-density patch fittings continues. Micro and nano-sized fittings with improved flow efficiency and reduced dead volume are being adopted. Precision manufacturing via additive techniques (e.g., metal 3D printing) enables complex geometries not feasible with traditional methods.
5. Supply Chain Localization and Resilience
Geopolitical uncertainties and past disruptions have prompted companies to reevaluate supply chains. In H2 2026, regional manufacturing hubs in North America, Europe, and Southeast Asia are expanding production capacity for patch fittings to reduce dependency on single-source suppliers. Nearshoring and on-demand manufacturing via digital inventories are becoming standard practices.
6. Standardization and Interoperability Focus
As modular systems grow in popularity, industry bodies are pushing for greater standardization of thread types, dimensions, and performance metrics (e.g., ISO 8434, SAE J514). H2 2026 sees increased adoption of universal fittings that ensure cross-compatibility between brands, reducing inventory complexity and installation errors.
7. Rise of Digital Procurement and BIM Integration
Digital transformation in construction and industrial projects is accelerating the use of Building Information Modeling (BIM) and digital catalogs. Patch fitting manufacturers are providing BIM-compliant product data, enabling seamless integration into project designs. Online marketplaces and configurator tools allow engineers to select, simulate, and order fittings directly, shortening procurement cycles.
8. Enhanced Focus on Leak Prevention and Safety
With heightened regulatory scrutiny (e.g., EPA methane rules, EU F-Gas regulations), there is a growing emphasis on zero-leak solutions. In H2 2026, self-sealing and double-containment patch fittings are gaining market share, especially in chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and LNG applications. Certification to standards like API 622 and TA-Luft is becoming a competitive differentiator.
Conclusion
H2 2026 represents a pivotal period for the patch fitting industry, characterized by digital integration, sustainability, and performance innovation. Companies that invest in smart technologies, eco-conscious materials, and resilient supply chains will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities in energy transition, advanced manufacturing, and infrastructure modernization.
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Patch Fittings: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing patch fittings—especially for critical applications in industries like aerospace, medical devices, or high-performance fluid systems—exposes buyers to significant risks if due diligence is not performed. Two major areas of concern are product quality inconsistencies and intellectual property (IP) infringement. Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to system failures, safety hazards, regulatory non-compliance, and legal liabilities.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
- Inconsistent Material Specifications: Suppliers may claim compliance with standards (e.g., ASTM, ISO) but deliver fittings made from substandard or non-certified materials, leading to premature corrosion or mechanical failure.
- Poor Dimensional Tolerance and Surface Finish: Low-cost manufacturers may cut corners on machining precision, resulting in leaks, improper seals, or difficulty in assembly.
- Lack of Traceability and Documentation: Reputable patch fittings should come with material test reports (MTRs), lot traceability, and certification (e.g., AS9100, ISO 13485). Absence of these raises red flags about quality control processes.
- Inadequate Testing and Validation: Some suppliers perform minimal or no pressure, burst, or leak testing, increasing the risk of in-field failures.
- Counterfeit or Recycled Components: Especially with high-demand or obsolete fittings, counterfeit parts or those made from recycled materials may enter the supply chain, compromising reliability.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
- Unauthorized Reproduction of Patented Designs: Many patch fittings incorporate patented geometries, locking mechanisms, or sealing technologies. Sourcing from unauthorized manufacturers may result in purchasing IP-infringing products.
- Use of Proprietary Branding or Logos: Some suppliers replicate branded fittings (e.g., Parker, Swagelok) with counterfeit logos, exposing the buyer to trademark liability.
- Reverse-Engineered Components Without Licensing: While some fittings are generic, others are protected by design patents or trade secrets. Using unlicensed copies—even if functionally equivalent—can lead to legal action.
- Lack of IP Warranty from Supplier: Many low-cost suppliers do not provide IP indemnification, leaving the buyer liable in case of infringement claims from original equipment manufacturers (OEMs).
- Gray Market Procurement: Purchasing from unauthorized distributors or third-party marketplaces increases the risk of receiving non-genuine or IP-violating parts.
Mitigating these risks requires rigorous supplier qualification, verification of certifications, thorough documentation review, and legal assessment of IP rights—especially when sourcing from offshore or non-franchised suppliers.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Patch Fitting
This guide outlines the essential logistics procedures and compliance requirements for handling, shipping, and implementing patch fittings across supply chain and installation operations. Adherence ensures safety, regulatory alignment, and operational efficiency.
Product Handling and Storage
Patch fittings—small mechanical connectors used in piping, HVAC, or industrial systems—must be stored in controlled environments. Keep products in original packaging, away from moisture, extreme temperatures, and contaminants. Store on elevated, dry pallets in designated inventory zones to prevent corrosion or deformation. Implement FIFO (First In, First Out) stock rotation to minimize aging and ensure material freshness.
Transportation and Shipping Requirements
When shipping patch fittings, use cushioned, sealed containers to prevent movement and damage during transit. Label all packages with handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “Do Not Stack”). For international shipments, comply with IATA, IMDG, or other relevant transport regulations—even for non-hazardous components—by providing accurate HS codes and commercial invoices. Use carriers experienced in industrial component logistics to reduce risk.
Regulatory Compliance
Ensure all patch fittings meet applicable industry standards such as ASME, ASTM, ANSI, or ISO certifications, depending on application (e.g., plumbing, gas lines, or industrial machinery). Maintain documentation including Certificates of Conformance (CoC), Material Test Reports (MTRs), and RoHS/REACH compliance for shipments to the EU. Verify compliance with local building codes and pressure system safety regulations (e.g., OSHA in the U.S. or PUWER in the UK) prior to installation.
Import and Export Documentation
Prepare complete export documentation for cross-border shipments, including packing lists, commercial invoices, and export declarations. Confirm whether the patch fittings require ECCN (Export Control Classification Number) under EAR (Export Administration Regulations). For high-risk regions, conduct sanctions screening and license verification. Retain records for a minimum of five years for audit and traceability purposes.
Installation and Field Compliance
Only qualified personnel should install patch fittings. Follow manufacturer torque specifications, alignment guidelines, and pressure testing protocols. Document all installations with photos, serial numbers, and test results. Conduct periodic audits to verify adherence to safety and quality standards. Report and investigate any field failures immediately to support continuous improvement and regulatory reporting.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Dispose of packaging and defective fittings in accordance with local environmental regulations. Recycle metal components where possible. Provide Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS/SDS) for any coatings or materials used in patch fittings. Ensure worker safety during handling through proper PPE (e.g., gloves, eye protection) and training on pinch-point hazards.
By following this guide, organizations can ensure efficient logistics operations and full compliance throughout the lifecycle of patch fitting use.
Conclusion for Sourcing Patch Fittings:
In conclusion, the successful sourcing of patch fittings requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, reliability, and lead times. By carefully evaluating suppliers based on certifications, production capabilities, and track record, organizations can ensure consistent product performance and compliance with industry standards. Establishing strong supplier relationships, conducting thorough due diligence, and implementing effective supply chain management practices are critical to minimizing risks and maintaining operational efficiency. Additionally, considering factors such as material compatibility, customization needs, and long-term scalability will support sustainable sourcing outcomes. Ultimately, a well-structured sourcing strategy for patch fittings contributes to improved system reliability, reduced downtime, and overall cost savings across projects and operations.