The global textile and leather machinery market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by rising demand for efficient, high-precision automation in manufacturing processes. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global textile machinery market was valued at approximately USD 30.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.8% through 2029. A key segment within this landscape is passing machines—essential equipment used for evenly applying finishes, coatings, or treatments across fabric and leather surfaces. With increasing emphasis on product consistency, energy efficiency, and reduced waste, manufacturers are investing heavily in advanced passing solutions. As automation and smart manufacturing gain traction, particularly in textile hubs across Asia-Pacific and Europe, innovation in passing machine design and functionality has become a competitive differentiator. This growth trajectory, supported by data from leading market research firms, underscores the importance of identifying the top-tier manufacturers driving technological advancement and operational excellence in this niche yet critical sector.
Top 8 Passing Machine Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
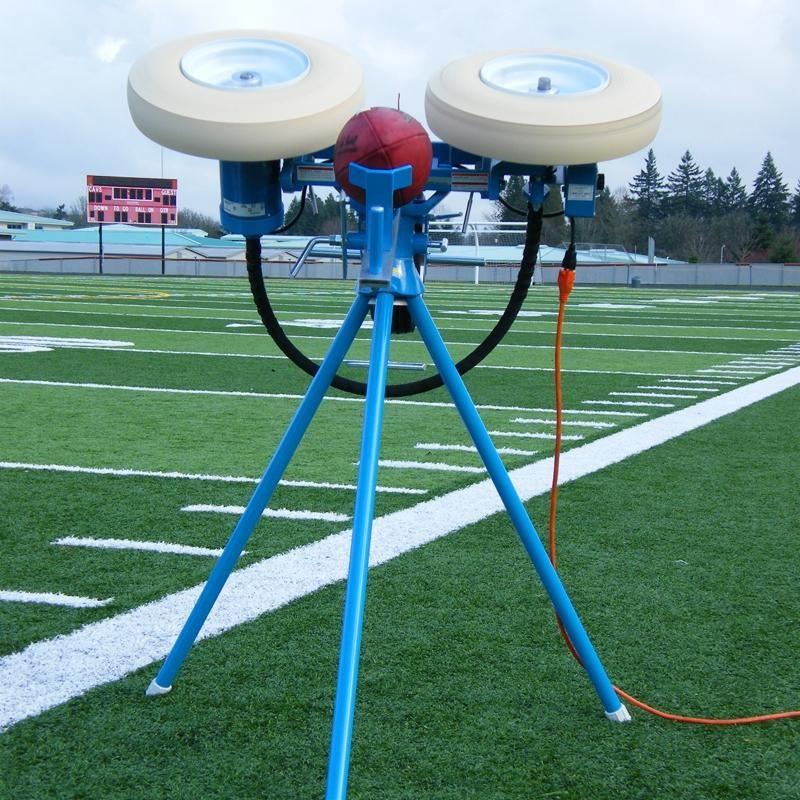
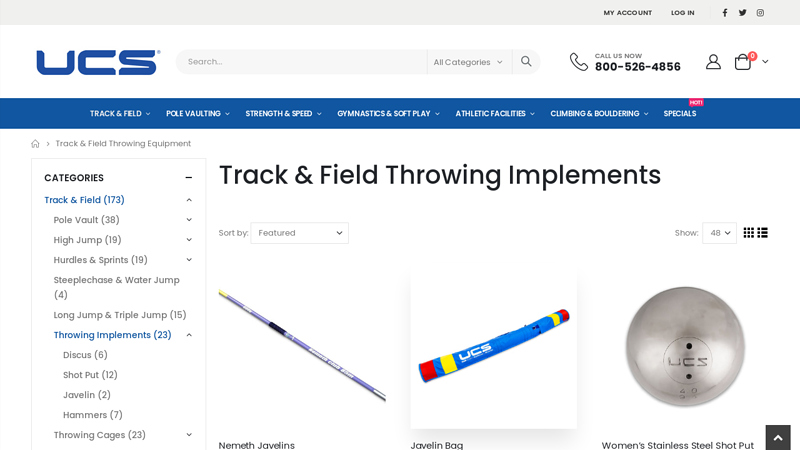
#1 Track & Field Throwing Implements
Domain Est. 1997
Website: ucsspirit.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery 30-day returnsCompetition and training implements engineered for balance, accuracy, and durability. Shop shot puts, discus, javelins, hammers, and accessories today….
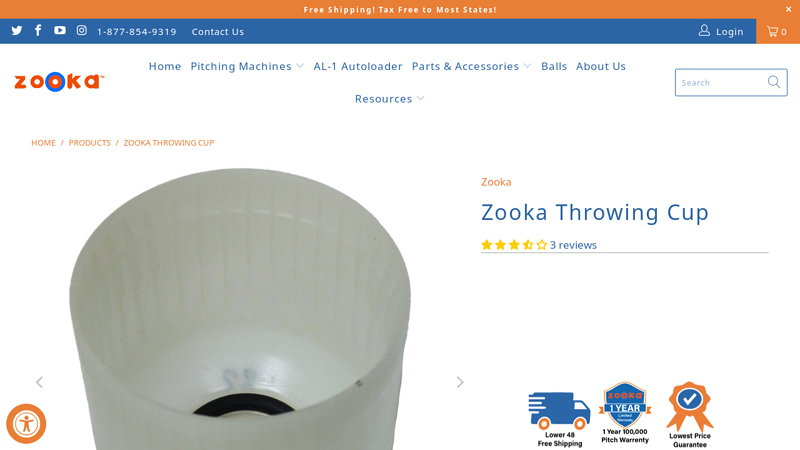
#2 Zooka Throwing Cup
Domain Est. 1999
Website: zooka.com
Key Highlights: In stock Rating 2.5 6 Zooka Barral Throwing Cup. Replacement Throwing Cup for Zooka 720 & Zooka 740 Pitching Machines. What’s Included: Zooka Thowing Cup. Return Policy:….
#3 Baseball Pitching Machines & Softball Pitching Machines
Domain Est. 2001
Website: jugssports.com
Key Highlights: 7–10 day deliveryJUGS Sports baseball pitching machines and softball pitching machines have been trusted by the world’s professional athletes and coaches for over 45 years….
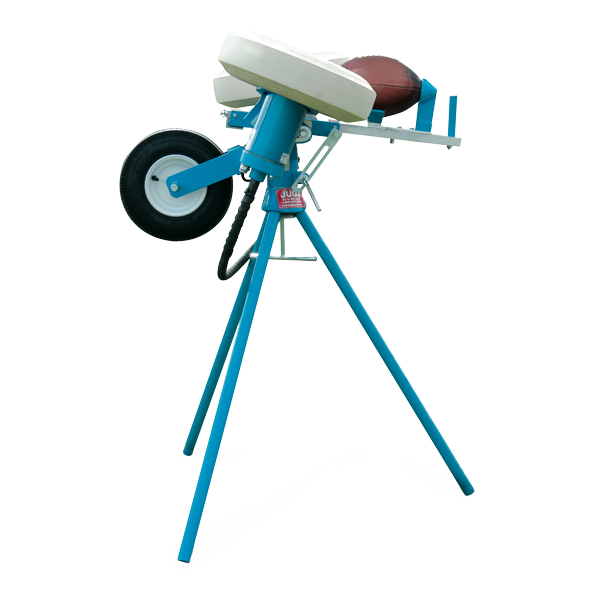
#4 Jugs Football Passing Machine
Domain Est. 2002
#5 Jugs M1700 Football Passing Machine
Domain Est. 2002
Website: anthem-sports.com
Key Highlights: In stock Rating 5.0 3 The Jugs Football passing machine allows you to throw up to 600 passes or “kicks” per hour. This passing machine throws 5 to 80 yard passes….
#6 Monarc Sport
Domain Est. 2015
Website: monarcsport.com
Key Highlights: An intelligent training partner emulating every type of game-like pass, kick, or punt anywhere on the field, the Seeker transforms how athletes train….
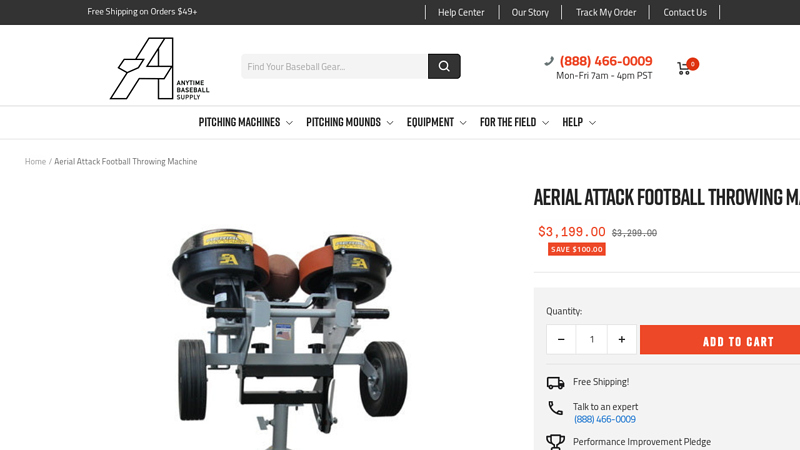
#7 Aerial Attack Football Throwing Machine
Domain Est. 2019
Website: anytimebaseballsupply.com
Key Highlights: In stock Rating 4.8 22 Throw hundreds of passes and run as many drills as you want in your next practice with a football machine because the Aerial Attack can do it all and won’t…
#8 About Us
Domain Est. 2021
Website: footballthrowingmachines.com
Key Highlights: FootballThrowingMachines.com is brought to you by the team at Extra Mile Sports LLC. Our goal is to provide the very best football throwing machines….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Passing Machine

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Passenger Vehicles
While “Passing Machine” appears to be a misunderstanding or typo, the context strongly suggests an analysis of passenger vehicles (commonly referred to as passenger cars or personal automobiles) for the year 2026. Here is an analysis of the key market trends expected to shape the global passenger vehicle market in 2026, under the H2 framework:
H2: Accelerated Electrification and Technological Transformation
By 2026, the global passenger vehicle market will be defined by rapid technological advancement, regulatory pressure, and shifting consumer preferences, with electrification serving as the central driver of change. Automakers will be deep into transformation, pivoting from internal combustion engines (ICE) to electric and connected platforms. Key trends include:
-
Dominance of Electric Vehicles (EVs):
- Mass Market Adoption: Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) and Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) are projected to reach 30-40% of global new car sales by 2026, driven by falling battery costs, expanded model availability, and government mandates (e.g., EU ICE ban from 2035, California’s 2035 target).
- Affordable EVs: The market will see a significant influx of affordable, sub-$30,000 EVs from both legacy automakers (e.g., GM, Ford, VW) and EV-native companies, making electrification accessible to a broader consumer base.
- Charging Infrastructure Expansion: Governments and private companies will invest heavily in charging networks, particularly fast-charging corridors, reducing range anxiety and supporting long-distance travel.
-
Software-Defined Vehicles (SDVs) and Connectivity:
- Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates: Vehicles will increasingly receive software updates for infotainment, driver assistance, and even performance improvements, extending vehicle lifespan and enhancing user experience.
- Enhanced Infotainment & Services: Integration with smartphones, cloud services, and AI-powered assistants will deepen, offering personalized experiences, in-car payments, and seamless connectivity.
- Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X): Early commercial deployment of V2X technology (V2V, V2I) will begin, improving safety and traffic efficiency, laying groundwork for future autonomy.
-
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) Proliferation:
- Mainstreaming of L2+ Automation: Level 2 and enhanced Level 2 (L2+) systems (e.g., hands-off highway driving, automated lane changes) will become standard or common options in mid-to-high tier vehicles.
- Regulatory Push: Safety regulations (e.g., Euro NCAP, IIHS) will increasingly mandate ADAS features like Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB), Lane Keeping Assist (LKA), and Blind Spot Detection, accelerating adoption across all segments.
-
Sustainability and Circular Economy:
- Battery Recycling: Scaling of battery recycling infrastructure will be critical to address raw material supply concerns and environmental impact, becoming a major focus for OEMs and suppliers.
- Sustainable Materials: Use of recycled plastics, bio-based materials, and low-carbon manufacturing processes will increase in vehicle interiors and components.
- Lifecycle Analysis: Consumers and regulators will demand greater transparency on the full lifecycle carbon footprint of vehicles.
-
Shifting Business Models:
- Subscription Services: Beyond connectivity, features like performance boosts, premium audio, or advanced ADAS may be offered via subscription models, creating new revenue streams.
- Mobility as a Service (MaaS): While private ownership remains dominant, integration with ride-hailing, car-sharing, and multimodal platforms within vehicle interfaces will grow.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the passenger vehicle market will be fundamentally reshaped by the H2 of Electrification and Digitalization. Success will depend on automakers’ ability to deliver compelling, affordable, and software-rich electric vehicles while navigating supply chain complexities, regulatory landscapes, and evolving consumer expectations around sustainability and connectivity. The focus will shift from pure hardware to integrated hardware-software-service ecosystems.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Passing Machine (Quality, IP)
Sourcing a passing machine—especially one involving advanced technology or proprietary systems—can present significant challenges related to both quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Failing to address these issues can result in operational inefficiencies, legal disputes, or loss of competitive advantage. Below are key pitfalls to watch for:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Supplier Vetting
One of the most common mistakes is selecting a supplier based solely on cost or delivery timelines without thoroughly evaluating their manufacturing standards, track record, or certifications (e.g., ISO 9001). This can lead to receiving machines with subpar components, inconsistent performance, or shortened lifespans.
Lack of Prototyping and Testing
Skipping or minimizing prototype testing before mass production increases the risk of design flaws, integration issues, or unreliable operation. Without real-world validation, the machine may fail under actual working conditions.
Poorly Defined Specifications
Ambiguous or incomplete technical specifications can result in a machine that doesn’t meet functional requirements. Misunderstandings about precision, throughput, durability, or compatibility with existing systems often emerge only after delivery.
Insufficient After-Sales Support
Choosing a supplier with limited technical support, training, or spare parts availability can severely impact uptime and maintenance. A passing machine that breaks down frequently with no local support leads to costly downtime.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
Unclear Ownership of Design and Software
Failing to establish in writing who owns the machine’s design, firmware, or embedded software can result in disputes. Suppliers may claim ownership, limiting your ability to modify, replicate, or service the machine without permission.
Inadequate IP Protection in Contracts
Contracts that lack robust IP clauses—such as confidentiality agreements, non-disclosure provisions, or explicit assignment of IP rights—leave your innovations vulnerable. This is especially critical if you contributed to the machine’s design or provided proprietary data.
Risk of IP Leakage to Third Parties
When sourcing from overseas manufacturers or contract developers, there’s a heightened risk of design replication or unauthorized use by the supplier or their subcontractors. Without strict controls and audit rights, your technology could be reverse-engineered or sold to competitors.
Use of Infringing Components
Suppliers might unknowingly (or deliberately) incorporate third-party patented technologies into the machine. If the final product infringes on existing IP, your company could face litigation, recalls, or import bans—even if you were unaware of the infringement.
To mitigate these risks, conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, define clear technical and legal terms in contracts, and involve legal and technical experts early in the sourcing process.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Passing Machine
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the transportation, handling, and regulatory adherence related to Passing Machines—automated systems used in manufacturing or quality control to verify product conformity. Proper management ensures operational efficiency, legal compliance, and worker safety.
Transportation and Handling
Ensure that the Passing Machine is securely packaged and transported using appropriate lifting equipment such as forklifts or cranes with rated load capacities exceeding the machine’s weight. Use wooden crates or reinforced pallets to prevent damage during transit. Clearly label the shipment with handling instructions including “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Do Not Stack.” Coordinate with certified freight carriers experienced in handling industrial machinery, and confirm compliance with international shipping standards (e.g., ISTA or ISO 16109) when shipping across borders.
Import/Export Regulations
Verify whether the Passing Machine is subject to export controls under relevant jurisdictions—for example, the U.S. Export Administration Regulations (EAR) or the EU Dual-Use Regulation. Classify the machine using the appropriate Harmonized System (HS) code to determine tariffs, import duties, and documentation requirements. If the machine contains software or technical data, ensure compliance with encryption export rules. Obtain necessary licenses or authorizations prior to shipment, particularly when shipping to restricted destinations.
Safety and Certification Compliance
Ensure the Passing Machine complies with regional safety standards such as CE marking (Europe), UL/CSA certification (North America), or CCC (China). These certifications confirm that the equipment meets health, safety, and environmental protection standards. Maintain records of conformity assessments, test reports, and declarations of performance. Equip the machine with required safety features including emergency stop buttons, protective guards, and warning labels in the local language of the destination country.
Installation and Site Readiness
Before delivery, confirm site readiness by verifying power supply specifications (voltage, phase, frequency), floor load capacity, environmental conditions (temperature, humidity), and available space with required clearances. Conduct a risk assessment to identify potential hazards during installation. Only qualified technicians should perform setup and commissioning, following the manufacturer’s instructions and relevant electrical and mechanical codes (e.g., NEC, IEC 60204-1).
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Maintain a complete compliance dossier including technical files, user manuals, safety data sheets (if applicable), calibration records, and maintenance logs. Keep copies of import/export documentation, customs declarations, and certificates of origin. Retain these records for a minimum of five years or as required by local regulations to facilitate audits and demonstrate due diligence.
Environmental and End-of-Life Compliance
Dispose of or recycle the Passing Machine in accordance with environmental regulations such as the EU WEEE Directive or local e-waste laws. If the machine contains hazardous substances (e.g., lead, mercury), ensure proper handling and reporting under RoHS or equivalent standards. Partner with certified waste management providers to ensure environmentally sound decommissioning and recycling.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Passing Machine
After a thorough evaluation of available options, market suppliers, technical specifications, and cost considerations, sourcing a passing machine is a strategic investment that enhances operational efficiency, accuracy, and productivity. The selected machine meets the required performance standards, integrates seamlessly with existing production processes, and aligns with organizational goals for quality and throughput.
Key factors such as reliability, after-sales support, energy efficiency, and scalability have been carefully assessed to ensure long-term value. By partnering with a reputable supplier and implementing proper training and maintenance protocols, the organization can maximize the return on investment and maintain a competitive edge.
In conclusion, sourcing the appropriate passing machine represents a well-justified decision that supports continuous improvement, reduces manual labor, and ensures consistent product quality. Moving forward, ongoing monitoring and performance reviews will be essential to optimize machine utilization and drive sustained operational excellence.