The global paper folding machines market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand for automated finishing solutions across commercial printing, packaging, and corrugated box manufacturing industries. According to Grand View Research, the global paper processing equipment market—of which folding machines are a key segment—was valued at USD 7.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.6% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence forecasts increasing adoption of high-speed, precision folding systems, particularly in regions with robust printing and packaging sectors like Asia-Pacific and North America. This growth is further fueled by advancements in servo-driven mechanisms, modular designs, and integration with digital print workflows. As automation becomes critical to operational efficiency, leading manufacturers are innovating to deliver smarter, faster, and more reliable folding solutions. In this evolving landscape, nine manufacturers have emerged as industry leaders, consistently delivering technologically advanced and high-performance paper folding machines that meet the dynamic needs of modern print service providers and industrial packaging operations.
Top 9 Paper Folding Machines Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Paper Folding Machine
Domain Est. 2000
Website: prathamtech.com
Key Highlights: Get Advanced industrial Paper Folding Machine Manufacturers in London and Commercial Paper Folding Equipment Suppliers in London….
#2 Folding
Domain Est. 1995
Website: heidelberg.com
Key Highlights: Discover our wide range of folding machines for the commercial sector – now featuring state-of-the-art robot technology….
#3 Baumfolder
Domain Est. 1996
Website: baumfolder.com
Key Highlights: Baumfolder delivers world-class systems for folding, bindery, and automation that streamline post-press, mailing, packaging, and order fulfillment ……
#4 Paper Folding Machines
Domain Est. 1996
Website: formax.com
Key Highlights: Our range of paper folding machines and document folding equipment allows companies to easily fold mailings, documents and letters to give your business in ……
#5 Martin Yale Paper Folders for Offices & Mailrooms
Domain Est. 1996
Website: martinyale.com
Key Highlights: Explore our broad range of Martin Yale paper folders ideally suited for churches, schools, small offices, mailrooms and the quick print industry….
#6 Paper Folder Inserters, Folding Machines, Envelope Stuffers
Domain Est. 2001
Website: paperfolder.com
Key Highlights: PaperFolder Co specializes in folder inserters, envelope stuffing machines and other paper processing machines including paper folders, cutters & shredders….
#7 Martin Yale Machines
Domain Est. 2007
Website: martinyale-machines.com
Key Highlights: $25 delivery 30-day returnsMartin Yale Machines offers top-quality paper-handling equipment to streamline your workflow and maximize productivity. From cutters to laminators, ……
#8 Paper Folding Machines
Domain Est. 2007
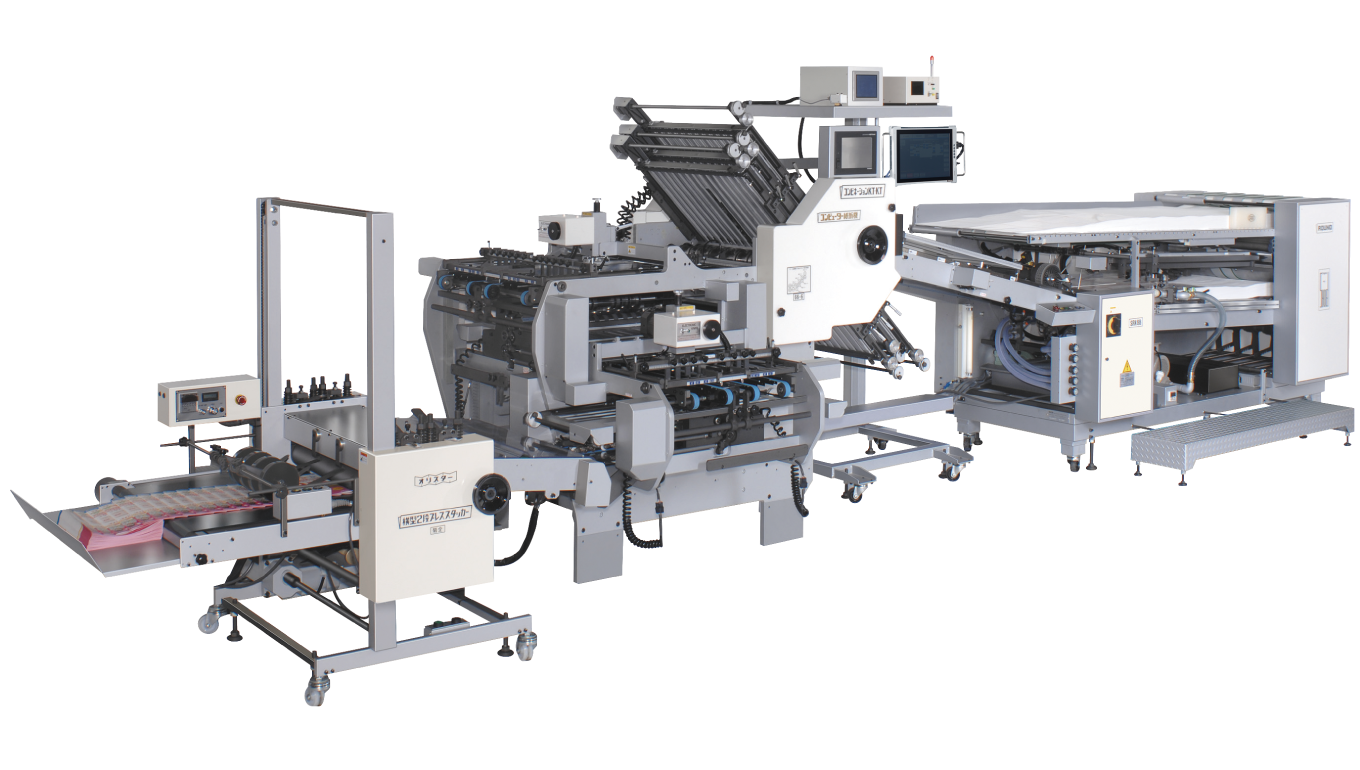
#9 SHOEI MACHINERY MFG.CO.,LTD.
Website: shoei-folder.co.jp
Key Highlights: We are a world-class paper processing machinery maker that keeps on the cutting edge while committing ourselves to our customers….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Paper Folding Machines

H2: Market Trends in Paper Folding Machines (2026 Outlook)
The global paper folding machines market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological innovation, shifting industry demands, and sustainability imperatives. As businesses across print, packaging, and commercial sectors adapt to digital integration and eco-conscious practices, the demand for advanced, efficient, and versatile folding solutions continues to rise. This analysis explores key market trends shaping the paper folding machines landscape in 2026 under the H2 framework—highlighting growth drivers, technological advancements, regional dynamics, and competitive positioning.
1. Increased Automation and Smart Integration
By 2026, automation will be a cornerstone of paper folding machine development. Manufacturers are increasingly incorporating Internet of Things (IoT) capabilities, allowing real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and remote diagnostics. Smart folding systems integrated with digital print workflows—such as those used in on-demand printing and personalized packaging—enable seamless end-to-end production. These intelligent machines reduce labor costs, minimize errors, and improve throughput, making them highly attractive to commercial printers and packaging firms.
2. Demand for High-Speed and Multi-Format Flexibility
As customer expectations for fast turnaround times grow, the demand for high-speed folding machines capable of handling diverse paper weights, sizes, and fold types (e.g., accordion, gate, and roll folds) is rising. By 2026, modular folding systems that can be reconfigured quickly to support short runs and customization will dominate the market. This flexibility is particularly crucial in the packaging and direct-mail industries, where personalization and variable data printing are becoming standard.
3. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Environmental sustainability is a key trend influencing equipment design. By 2026, manufacturers are prioritizing energy-efficient motors, reduced material waste through precision folding, and recyclable machine components. Regulatory pressures and corporate sustainability goals are pushing buyers toward greener machinery. Additionally, machines capable of processing recycled or alternative fiber-based papers without compromising performance are expected to gain market share.
4. Growth in Packaging and E-Commerce Applications
The booming e-commerce sector is fueling demand for efficient folding machines used in corrugated and folding carton production. As brands invest in unique and sustainable packaging for direct-to-consumer models, there is a growing need for compact, high-precision folding solutions that support rapid prototyping and small-batch production. This trend is particularly evident in regions with high e-commerce penetration, such as North America and parts of Asia-Pacific.
5. Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific is expected to lead market growth by 2026, driven by expanding printing and packaging industries in China, India, and Southeast Asia. Rising urbanization, disposable income, and digital printing adoption are accelerating demand for automated folding solutions. In contrast, mature markets like North America and Western Europe will focus on upgrading legacy equipment with smart, energy-efficient models to remain competitive.
6. Competitive Landscape and Strategic Alliances
The market is witnessing increased consolidation, with key players such as Müller Martini, Duplo, and Graphco expanding their portfolios through R&D and strategic partnerships. By 2026, differentiation will hinge on software integration, user-friendly interfaces, and after-sales service. Smaller innovators are also emerging, offering niche solutions for specialty folding applications in medical, luxury goods, and security printing.
In conclusion, the 2026 paper folding machines market will be defined by intelligent automation, sustainability, and adaptability. Companies that invest in smart, flexible, and eco-friendly technologies will be best positioned to capitalize on evolving industry needs and maintain a competitive edge in a rapidly digitizing world.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Paper Folding Machines: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
When sourcing paper folding machines—especially from international suppliers—businesses often encounter significant challenges related to product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these pitfalls can result in operational inefficiencies, financial losses, and legal exposure. Below are key risks to be aware of:
Poor Build Quality and Material Standards
Many low-cost suppliers compromise on materials and manufacturing precision to reduce prices. This can lead to frequent breakdowns, inconsistent folding accuracy, and shorter machine lifespans. Components such as gears, rollers, and motors may be made from substandard materials, increasing maintenance costs and downtime.
Inadequate Quality Control Processes
Suppliers without rigorous quality assurance systems may deliver inconsistent units, even within the same batch. Without third-party inspections or clear quality benchmarks, buyers risk receiving machines that fail to meet performance expectations or safety standards.
Misrepresentation of Technical Specifications
Some suppliers exaggerate machine capabilities—such as folding speed, paper weight capacity, or compatibility with different paper sizes. This misalignment between promised and actual performance can disrupt production workflows and lead to costly retrofits or replacements.
Lack of After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Low-cost machines are often sold without reliable technical support, training, or access to genuine spare parts. This absence of post-purchase service can result in prolonged downtime and force buyers to seek reverse-engineered components, which may affect machine integrity.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Sourcing from manufacturers that replicate patented designs or use counterfeit software/firmware exposes buyers to legal liability. Using a machine that violates IP rights—especially in regulated markets—can lead to seizures, fines, or injunctions, particularly if the buyer is deemed complicit in the infringement.
Use of Unlicensed Software or Control Systems
Some machines incorporate cloned or pirated control software, which not only raises IP concerns but also introduces cybersecurity vulnerabilities and limits software updates or customization options.
Limited Traceability and Transparency
Opaque supply chains make it difficult to verify the origin of components or confirm adherence to ethical manufacturing practices. This lack of traceability increases exposure to IP violations and quality inconsistencies.
To mitigate these risks, buyers should conduct thorough due diligence, including factory audits, IP clearance checks, third-party inspections, and legal review of contracts. Partnering with reputable suppliers and investing in certified, well-supported equipment ultimately ensures long-term reliability and legal compliance.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Paper Folding Machines
Product Classification and HS Codes
Paper folding machines are typically classified under the Harmonized System (HS) code 8441.40, which covers “Other machines for making bags or sacks, or for folding, gumming, or pasting paper or paperboard.” Accurate HS code classification is essential for determining import duties, taxes, and customs clearance requirements in the destination country. Always verify the specific sub-classification based on machine type (e.g., manual, semi-automatic, automatic) and technical specifications.
Import Regulations and Documentation
Importers must provide standard documentation including a commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading (or air waybill), and certificate of origin. Depending on the country, additional documents such as an import license, conformity assessment, or pre-shipment inspection may be required. Ensure all paperwork clearly describes the product as “paper folding machine” and includes technical details like voltage, power rating, and dimensions.
Safety and Electromechanical Compliance
Paper folding machines must comply with regional safety standards governing electrical and mechanical equipment. In the European Union, compliance with the Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC) and the Low Voltage Directive (2014/35/EU) is mandatory, requiring CE marking. In the United States, adherence to OSHA and NFPA 79 standards is recommended, and machines may need UL or ETL certification for commercial use. Always include safety guards, emergency stop functions, and proper labeling.
Packaging and Transport Requirements
To prevent damage during shipping, paper folding machines should be securely packaged in wooden crates or heavy-duty cardboard with internal bracing and protective wrapping. Use moisture-resistant materials to guard against humidity, especially for ocean freight. Clearly label packages with handling instructions such as “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Do Not Stack,” and include the serial number and model for traceability.
Voltage and Plug Compatibility
Verify the machine’s voltage (e.g., 110V, 220V) and frequency (50Hz or 60Hz) compatibility with the destination country’s power supply. Machines shipped to regions with differing standards may require transformers or internal modifications. Include appropriate power cords or specify plug type (e.g., Type B for North America, Type F for Europe) to ensure compliance and safe operation.
Environmental and RoHS Compliance
Ensure the machine complies with environmental regulations such as the EU’s Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive, which limits the use of lead, mercury, cadmium, and other harmful materials in electrical equipment. Provide a RoHS compliance certificate if exporting to Europe or other regions with similar restrictions.
Warranty, After-Sales Support, and Spare Parts
Include documentation outlining warranty terms, service availability, and contact information for technical support. Provide a list of commonly replaced spare parts and their part numbers. For international shipments, consider stocking critical spare parts locally or arranging for quick logistics support to minimize downtime.
End-of-Life and Recycling Compliance
Adhere to waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) regulations where applicable. In the EU, manufacturers must register with national WEEE authorities and provide take-back options for end-of-life equipment. Include recycling instructions in user manuals and label components for proper disposal.
Country-Specific Considerations
Some countries impose additional requirements such as SABER certification (Saudi Arabia), SONCAP (Nigeria), or INMETRO approval (Brazil). Conduct due diligence on destination-specific compliance needs before shipping. Partnering with a local customs broker or compliance consultant can streamline the import process.
Summary and Best Practices
To ensure smooth logistics and compliance:
– Confirm accurate HS code and tariff classification.
– Prepare complete shipping and compliance documentation.
– Certify adherence to safety and environmental standards.
– Package securely for international transport.
– Address electrical compatibility and provide necessary adapters.
– Offer clear after-sales support and comply with end-of-life regulations.
Following this guide minimizes delays, avoids penalties, and supports seamless global distribution of paper folding machines.
Conclusion on Sourcing Paper Folding Machines
Sourcing paper folding machines requires a strategic and thorough approach to ensure that the selected equipment aligns with operational needs, budget constraints, and long-term business goals. After evaluating various models, suppliers, and technological capabilities, it is evident that the ideal machine depends on specific requirements such as production volume, paper types, fold complexity, automation level, and integration with existing workflows.
Key considerations in the sourcing process include machine reliability, ease of use, after-sales support, and total cost of ownership—not just the initial purchase price. Investing in a high-quality paper folding machine from a reputable manufacturer can lead to increased efficiency, reduced downtime, and improved product consistency, ultimately enhancing overall productivity.
Moreover, engaging with multiple suppliers, requesting demonstrations, and reviewing customer feedback helps make an informed decision. Whether opting for semi-automatic or fully automatic models, businesses should prioritize versatility and scalability to accommodate future growth.
In conclusion, a well-researched sourcing strategy ensures the acquisition of a paper folding machine that delivers optimal performance, reliability, and return on investment, supporting streamlined operations and sustained success in print and packaging environments.