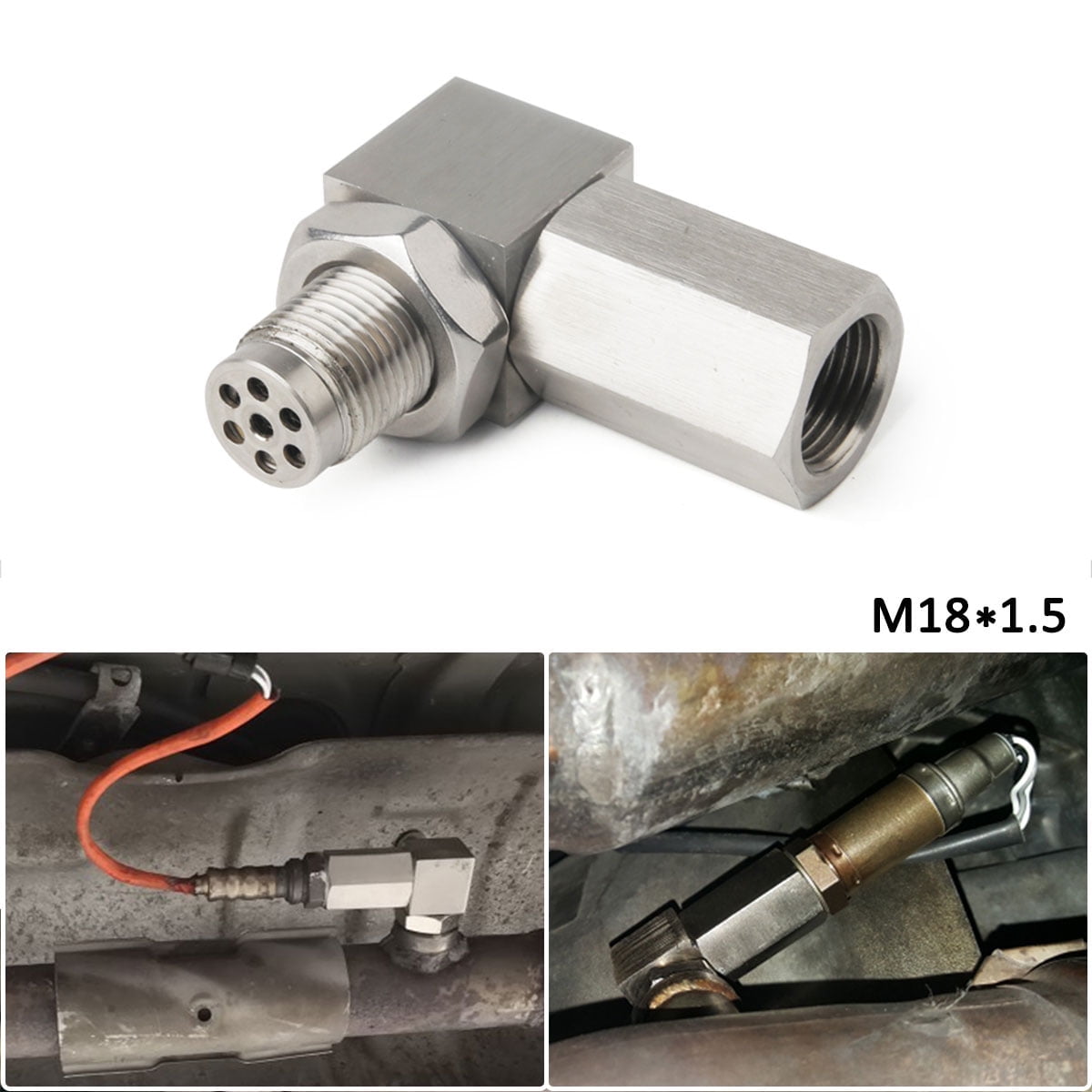
The global oxygen sensor market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasingly stringent emission regulations and rising demand for fuel-efficient vehicles. According to Grand View Research, the market was valued at USD 5.2 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth trajectory underscores the critical role of emissions control components, including oxygen sensor spacers—often used in diesel particulate filter (DPF) delete kits and exhaust system modifications. As demand for aftermarket performance parts rises, particularly in regions with large diesel vehicle fleets, the need for reliable oxygen sensor spacer manufacturers has intensified. Based on production capacity, geographic reach, customer reviews, and compliance with industry standards, we’ve identified the top eight manufacturers leading innovation and quality in this niche yet expanding segment.
Top 8 Oxygen Sensor Spacer Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
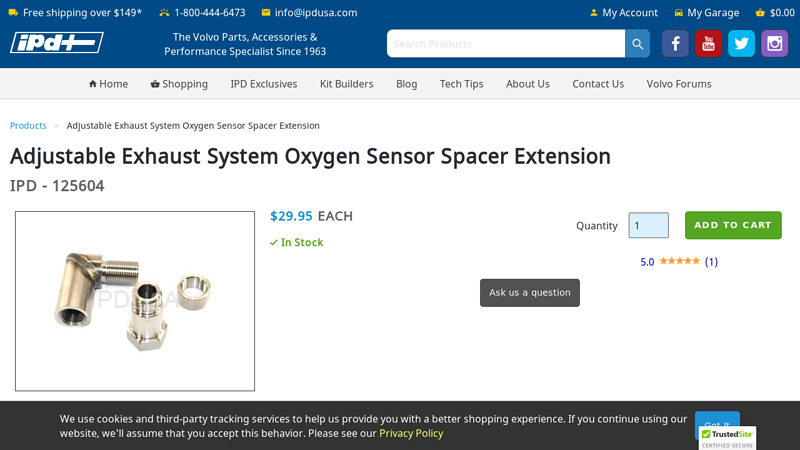
#1 Adjustable Exhaust System Oxygen Sensor Spacer Extension
Domain Est. 1996
Website: ipdusa.com
Key Highlights: In stock Rating 5.0 (1) Reduce the chance of ‘Check Engine’ lights due to use of high flow cats, or race pipes. The multi-piece design means you can assemble it in many variation…
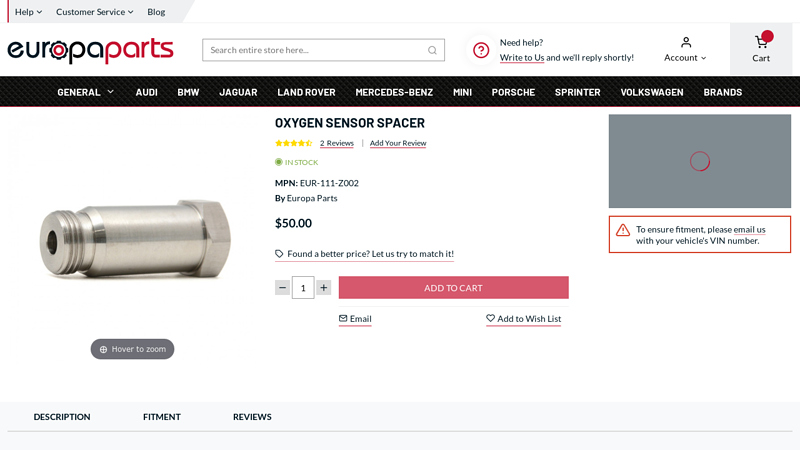
#2 Oxygen Sensor Spacer
Domain Est. 2009
Website: europaparts.com
Key Highlights: In stock Rating 4.5 (2) Professionally manufactured from stainless steel. Works with most O2 sensor designs on the market. Spacer will add approximately 1.7″ to the height of the…
#3 Oxygen O2 Sensor Spacer Adapter Extender Fits Vehicles with …
Domain Est. 2010
#4 Forza O2 Sensor Spacer
Domain Est. 2014
#5 Oxygen Sensor O2 Spacer With Adjustable Inserts
Domain Est. 2017
#6 O2 Oxygen Sensor Angled Extender Spacer 90 Degree 02 Bung …
Domain Est. 2017
Website: eccppautoparts.com
Key Highlights: Out of stockOur Oxygen sensor spacer is universal, It fit most of car. M18X1.5 catalytic converter built inside and will help get rid of that annoying check engine light….
#7 Brace Spacers, Oxygen Sensors Products
#8 90° Universal O2 Sensor Spacer with Mini Catalytic Converter
Website: o2sensorspacer.com
Key Highlights: Our O2 sensor spacer is designed with a built-in mini catalytic converter that slightly shifts the downstream oxygen sensor away from direct exhaust gas flow….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Oxygen Sensor Spacer

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Oxygen Sensor Spacers
The global market for oxygen sensor spacers is poised for measured growth and transformation by 2026, driven by evolving emissions regulations, advancements in automotive technology, and shifting consumer behaviors across key regions. Oxygen sensor spacers—small devices installed between the exhaust system and the oxygen (O2) sensor—are primarily used to manipulate the readings of the sensor, often to accommodate aftermarket modifications such as exhaust system upgrades or removal of catalytic converters. While their use is controversial from a regulatory standpoint, market dynamics indicate continued demand under specific conditions.
1. Regulatory Pressure and Compliance Challenges
By 2026, stringent emissions standards—particularly in North America, the European Union, and China—are expected to intensify. Regulations such as Euro 7, U.S. EPA Tier 4 standards, and China 6b will enforce tighter control over vehicle emissions, making unauthorized modifications like the use of oxygen sensor spacers increasingly illegal. As a result, original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and legitimate aftermarket parts suppliers are distancing themselves from spacer production. However, a robust gray market continues to thrive, especially in regions with lax enforcement.
2. Growth in Aftermarket and Performance Vehicle Modifications
Despite regulatory headwinds, demand for oxygen sensor spacers remains strong in the performance and off-road vehicle sectors. Enthusiasts modifying diesel trucks, SUVs, and off-road vehicles often use spacers to prevent check engine lights (CEL) triggered by changes to exhaust flow after removing catalytic converters or installing cold air intakes. The rise of the DIY automotive culture and online marketplaces (e.g., eBay, Amazon, and specialized forums) facilitates easy access to these components, supporting market resilience.
3. Technological Shifts: Rise of Electric and Hybrid Vehicles
The transition toward electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrids, projected to capture over 30% of global light-duty vehicle sales by 2026, directly impacts the relevance of oxygen sensors—and by extension, spacers. Since EVs do not have internal combustion engines or exhaust systems, the need for O2 sensors and related accessories diminishes. This trend is expected to suppress long-term market expansion, particularly in urban and environmentally regulated markets.
4. Regional Market Variations
– North America: The U.S. remains the largest market for oxygen sensor spacers due to high vehicle customization rates, especially in diesel pickup trucks and off-road vehicles. States with lenient emissions testing (e.g., Texas, Montana) see higher adoption.
– Europe: Strict enforcement and widespread OBD-II (On-Board Diagnostics) testing during vehicle inspections severely limit legal use. However, underground demand persists.
– Asia-Pacific: Emerging markets in Southeast Asia and India show growing interest due to increasing vehicle ownership and aftermarket tuning, though awareness of environmental impact remains low.
5. Innovation and Substitution Trends
By 2026, manufacturers are increasingly offering legal alternatives such as O2 sensor simulators or tuners that reprogram engine control units (ECUs) to accept modified exhaust configurations without triggering error codes. These solutions are more sophisticated and less detectable than physical spacers, signaling a shift away from mechanical fixes toward software-based tuning.
6. Environmental and Legal Risks
The use of oxygen sensor spacers to bypass emissions controls is widely recognized as environmentally harmful. Governments and environmental agencies are increasing penalties for tampering with emissions systems. In the U.S., the Clean Air Act imposes fines of up to $25,000 per violation for manufacturers and modifiers. This growing legal risk is expected to further marginalize the product’s legitimacy.
Conclusion
While the oxygen sensor spacer market will persist through 2026 due to niche demand in vehicle customization and performance tuning, it faces significant headwinds from regulatory crackdowns, the rise of electric mobility, and technological substitution. The market is likely to remain fragmented, operating largely in the informal or gray economy, with long-term decline anticipated as cleaner transportation solutions dominate. Companies involved in this space may need to pivot toward compliant tuning solutions or emissions-friendly performance products to remain viable.

H2: Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Oxygen Sensor Spacers – Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
When sourcing oxygen sensor spacers—components often used to adjust the positioning of oxygen (O2) sensors in exhaust systems for diagnostic or emissions tuning purposes—buyers and manufacturers must navigate several critical pitfalls related to quality and intellectual property (IP). Avoiding these issues is essential to ensure performance, compliance, and legal safety.
1. Compromised Material Quality
Many low-cost oxygen sensor spacers are made from substandard metals such as low-grade stainless steel or even plated brass, which can degrade under high heat and corrosive exhaust environments. This leads to premature failure, inaccurate sensor readings, or exhaust leaks. Buyers may unknowingly receive spacers that do not meet temperature or corrosion resistance specifications, risking engine performance or emissions system integrity.
2. Inconsistent Manufacturing Tolerances
Poorly manufactured spacers often exhibit inconsistent thread pitch, incorrect thickness, or misaligned bores, leading to improper fitment. These dimensional inaccuracies can cause sensor misalignment, exhaust gas leaks, or damage to the O2 sensor threads—potentially resulting in costly repairs.
3. Lack of Certification or Testing Data
Reputable oxygen sensor spacers should undergo thermal and pressure testing to validate durability. However, many suppliers—especially those in unregulated markets—offer products without documentation, test reports, or compliance certifications (e.g., RoHS, ISO). This absence of verifiable quality assurance increases the risk of field failures.
4. Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Some oxygen sensor spacer designs may incorporate patented geometries, thread configurations, or mounting mechanisms protected under existing IP. Sourcing generic copies from third-party manufacturers without due diligence can expose buyers or resellers to legal liability for patent or design infringement, particularly in regulated markets like the U.S. or EU.
5. Misrepresentation of Compatibility and Function
Certain spacers are marketed as “universal fit” or compatible with emissions tuning, but may not meet local emissions regulations (e.g., EPA or CARB standards). Using such components can result in non-compliant vehicle modifications, failed inspections, or violation of anti-tampering laws.
6. Opaque Supply Chains and Counterfeit Products
Global sourcing, particularly from regions with weak IP enforcement, increases the risk of receiving counterfeit or reverse-engineered products. These may mimic branded designs but lack performance validation, posing safety and legal risks.
Recommendations
To mitigate these pitfalls, buyers should:
– Source from suppliers with verifiable quality certifications and material test reports.
– Conduct dimensional and material inspections upon receipt.
– Perform IP due diligence, including patent landscape reviews.
– Avoid products marketed for bypassing emissions controls where legally restricted.
– Establish traceable, transparent supply chains with reliable vendors.
By addressing quality and IP concerns proactively, stakeholders can ensure reliable performance and regulatory compliance when integrating oxygen sensor spacers into automotive systems.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Oxygen Sensor Spacer – Using H2 (Heading Level 2)
H2: Overview of Oxygen Sensor Spacer
An oxygen sensor spacer, also known as an O2 sensor extender or adapter, is a threaded device installed between the oxygen sensor and the exhaust system. It creates a small gap that can delay the sensor’s detection of exhaust gases, potentially affecting the air-fuel ratio readings sent to the engine control unit (ECU). These spacers are commonly used in performance tuning or off-road applications but may impact emissions compliance.
This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations when distributing, installing, or marketing oxygen sensor spacers.
H2: Regulatory Compliance
Emissions Regulations
- U.S. Federal Law (EPA): Modifying or bypassing emissions control systems, including tampering with oxygen sensors, violates the Clean Air Act (42 U.S.C. § 7522). The use of spacers that alter emissions output may be deemed illegal for on-road vehicles.
- California Air Resources Board (CARB): CARB prohibits the sale or installation of parts that reduce the effectiveness of emissions systems. Products must carry a CARB Executive Order (EO) number to be legal for sale in California.
- Other Jurisdictions: Many countries (e.g., EU member states, Canada, Australia) have strict emissions laws. Always verify local regulations before shipping.
Legal Use Cases
- Off-Road / Racing-Only: Spacers may be legal when labeled and sold exclusively for off-road, competition, or racing use. Include clear disclaimers:
“For off-road use only. Not legal for sale or use on public roads in California or other states adopting California emissions standards.” - No Emission Control Function: If the spacer does not alter sensor function but merely provides mechanical spacing (e.g., for clearance), it may fall outside regulatory scope—verify with legal counsel.
H2: Product Labeling & Documentation
- Warning Labels: Affix labels indicating the product is not for street use where emissions regulations apply.
- User Instructions: Provide installation guidelines emphasizing legal restrictions and intended applications.
- Compliance Statements: Include documentation stating whether the product has CARB EO approval or is restricted to off-road use.
- Part Number & Traceability: Maintain clear SKU and batch tracking for recall readiness.
H2: Shipping & Logistics
Packaging
- Use durable packaging to prevent thread damage.
- Include installation hardware (e.g., washers, lock nuts) if applicable.
- Include multilingual compliance labels if shipping internationally.
International Considerations
- EU (CE Marking): While CE marking does not cover emissions, ensure compliance with local environmental and automotive regulations.
- REACH & RoHS: Confirm materials (e.g., stainless steel, brass) comply with chemical safety standards.
- Customs Declarations: Clearly describe product as “Oxygen Sensor Spacer – For Off-Road Use Only” to avoid misclassification as an emissions-tampering device.
Storage & Handling
- Store in dry, non-corrosive environments.
- Avoid contact with contaminants that could affect metal threads.
- Maintain inventory records for traceability.
H2: Risk Mitigation & Best Practices
- Legal Review: Consult environmental and automotive compliance experts before marketing.
- Avoid Misleading Claims: Do not advertise fuel economy or performance benefits that imply emissions system manipulation.
- Retailer Agreements: Require resellers to acknowledge and comply with legal usage restrictions.
- Recall Preparedness: Have a product recall plan in place in case of regulatory action.
H2: Conclusion
Oxygen sensor spacers occupy a gray area in automotive compliance. While useful in specific applications, their potential to interfere with emissions controls demands strict adherence to legal and logistical protocols. By focusing on off-road use, transparent labeling, and regulatory diligence, businesses can minimize risk and ensure responsible distribution.
Always prioritize compliance over performance claims to maintain long-term market access and brand integrity.
Conclusion for Sourcing Oxygen Sensor Spacer:
Sourcing an oxygen sensor spacer can be a practical and cost-effective solution for specific vehicle performance tuning or emission system adjustments. However, it is essential to approach this decision with a clear understanding of both the technical implications and legal considerations. While spacers may help address issues such as sensor fouling or provide temporary solutions for check engine lights related to catalytic converter efficiency codes, they do not resolve underlying engine problems and may mask critical diagnostic information.
Procurement should focus on high-quality, durable materials (such as stainless steel) from reputable suppliers to ensure reliability and longevity. Compatibility with the specific vehicle make, model, and oxygen sensor type must be verified to avoid installation issues or sensor damage. Additionally, users must be aware that modifying or tampering with emissions control systems may violate local laws and regulations, potentially leading to failed inspections or legal penalties.
Ultimately, while oxygen sensor spacers can serve a niche purpose, they should be used judiciously—preferably as a diagnostic aid or temporary measure—rather than a long-term fix. Proper maintenance, accurate diagnostics, and adherence to emissions standards remain the best practices for vehicle performance and environmental responsibility.