The global over molding market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for multi-material plastic components across industries such as automotive, medical devices, consumer electronics, and packaging. According to Grand View Research, the global 2K (two-component) injection molding market, a key enabler of over molding technology, was valued at USD 1.87 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.1% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by rising emphasis on product durability, ergonomic design, and material efficiency. Additionally, advancements in automation and precision molding technologies are enabling manufacturers to meet stringent quality requirements, particularly in highly regulated sectors like healthcare. As demand for complex, integrated plastic components continues to rise, selecting a capable over molding partner has become mission-critical for OEMs seeking to maintain competitive advantage, ensure compliance, and achieve cost-effective production. The following list highlights the top 10 over molding manufacturers recognized for their technological expertise, scalable operations, industry certifications, and consistent performance across high-volume and custom applications.
Top 10 Over Molding Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Overmolding
Domain Est. 2000
Website: teampti.com
Key Highlights: At PTI, we have the experience to guide you through all the critical elements of overmolding from part and mold design to material selection. See us today….
#2 Overmolding
Domain Est. 1995
Website: kaysun.com
Key Highlights: Overmolding is a multi-step injection molding process, overmolding combines two or more materials into one final product….
#3 Medical Silicone Overmolding
Domain Est. 1996
Website: trelleborg.com
Key Highlights: Overmolding is a process in which the finished component of a different material, usually a thermoplastic or metal substrate, is overmolded with LSR….
#4 Davies Molding
Domain Est. 1998
Website: daviesmolding.com
Key Highlights: Experts in plastic molding including thermoset, thermoplastic, compression, and injection processes, delivering custom molded parts and standard parts….
#5 The Rodon Group
Domain Est. 1999 | Founded: 1956
Website: rodongroup.com
Key Highlights: Providing High-Volume, Custom Plastic Injection Molding Solutions Since 1956 · We Offer Solutions to Customers That Need HIGH VOLUME PRECISION MANUFACTURING….
#6 Overmolding Services for Plastic & Silicone
Domain Est. 2002
Website: extrememolding.com
Key Highlights: Extreme Molding provides expert overmolding services for plastic and silicone. Create durable, functional, and aesthetically pleasing parts….
#7 Plastic & Metal Overmolding
Domain Est. 2003
Website: cadrex.com
Key Highlights: Overmolding is the process of molding plastic onto plastic or metal components. The base part is engineered to fit into a steel injection mold….
#8 Plastic Molding Manufacturing
Domain Est. 2008
Website: plasticmoldingmfg.com
Key Highlights: Plastic Molding Manufacturing is a U.S.-based custom plastic injection molding company, providing full-service, single-source solutions for custom molded ……
#9
Domain Est. 2010
Website: deplastics.com
Key Highlights: We specialize in insert molding, over molding, tight tolerance capabilities and two Shot capabilities, to name a few….
#10 Springboard Manufacturing
Domain Est. 2019
Website: springboardmfg.com
Key Highlights: Overmolding is a standard plastic injection process that combines a base layer mold with additional plastic layers that are molded around the part. Overmolding ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Over Molding
H2 2026 Market Trends Analysis for Overmolding
As we approach the second half of 2026, the overmolding market is experiencing significant transformation driven by technological advancements, shifting end-user demands, and sustainability imperatives. Key trends shaping the landscape include:
-
Accelerated Adoption of Multi-Material & Multi-Color Overmolding: Driven by demand for enhanced product functionality, aesthetics, and user experience, manufacturers are increasingly moving beyond simple two-shot processes. Complex overmolding with 3+ materials (e.g., rigid/soft-touch/transparent) and intricate color schemes are becoming standard, particularly in consumer electronics, medical devices, and automotive interiors. This requires more sophisticated molds and tighter process control.
-
Dominance of Sustainable & Bio-Based Materials: Environmental regulations and consumer pressure are forcing a major shift. The use of traditional petroleum-based TPEs and silicones is declining in favor of:
- Bio-based TPEs/TPUs: Derived from renewable sources (e.g., castor oil, corn), offering comparable performance with a lower carbon footprint.
- Recycled Content: Incorporation of post-consumer recycled (PCR) plastics and rubbers in both the substrate and overmold layers is becoming a key differentiator and compliance requirement.
- Enhanced Recyclability: Design for disassembly and material compatibility are paramount. Mono-material overmolding solutions (using compatible polymers) are gaining traction to facilitate end-of-life recycling.
-
Integration of Industry 4.0 & Smart Manufacturing:
- Advanced Process Monitoring & Control: Real-time sensors (pressure, temperature, vision systems) integrated into molds provide immediate feedback, enabling predictive maintenance, automatic parameter adjustments, and significantly reducing scrap rates.
- Digital Twins & Simulation: Extensive use of simulation software for mold filling, cooling, and warpage prediction before tooling is cut, drastically reducing development time and cost. Digital twins of production lines optimize performance.
- Data-Driven Optimization: AI and machine learning analyze production data to identify inefficiencies, predict quality issues, and optimize cycle times and energy consumption.
-
Rise of Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) Overmolding: LSR’s superior biocompatibility, high-temperature resistance, and excellent sealing properties are driving explosive growth in medical devices (e.g., syringe tips, wearable sensors), automotive (e.g., gaskets, seals), and high-end consumer goods. Advances in LSR processing technology are making it more accessible and cost-effective for complex overmolding applications.
-
Miniaturization & Precision Demands (Especially in MedTech & Electronics): The trend towards smaller, more complex devices (e.g., wearables, implantable medical devices, advanced sensors) demands extreme precision in overmolding. This requires:
- Ultra-precision molding machines and molds.
- Handling of micro-thin overmold layers (<0.1mm).
- Exceptional material flow control to prevent defects on tiny substrates.
-
Focus on Enhanced Haptics and Aesthetics: Consumer expectations for premium feel and look are pushing overmolding beyond basic grip. Trends include:
- Textured & Patterned Soft-Touch Finishes: Beyond smooth, incorporating logos, patterns, or specific textures directly into the overmold.
- Translucent & Light-Guiding Overmolds: For integrated lighting effects in electronics, automotive controls, and appliances.
- Metallic & Pearlescent Effects: Achieved through specialized TPEs or additives.
-
Supply Chain Resilience & Regionalization: Geopolitical factors and the desire for shorter lead times are leading to a strategic shift. Companies are:
- Nearshoring/Reshoring: Bringing overmolding production closer to final assembly or key markets (e.g., North America, Europe).
- Diversifying Suppliers: Reducing reliance on single-source material suppliers, particularly for critical TPEs and silicones.
- Investing in Local Tooling: Building regional mold-making capabilities.
-
Growth in High-Performance Polymer Overmolding: Overmolding engineering thermoplastics (e.g., PEEK, PEI, PPS) with high-temp elastomers or other engineering plastics is increasing for demanding applications in aerospace, industrial, and under-the-hood automotive components requiring extreme chemical, thermal, and mechanical resistance.
Conclusion for H2 2026: The overmolding market is characterized by convergence: technological sophistication meets stringent sustainability requirements. Success will depend on manufacturers’ ability to master complex multi-material processes, embrace bio-based and recycled materials, leverage smart manufacturing for efficiency and quality, and cater to the growing demand for miniaturization and premium aesthetics. Companies investing in innovation, sustainability, and digitalization are best positioned to lead in this evolved landscape.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Overmolding: Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
Sourcing overmolding services can offer significant benefits in product design and performance, but it also introduces unique challenges, particularly in the areas of quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Being aware of these common pitfalls is crucial for ensuring successful outcomes and safeguarding your business interests.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Material Bonding
One of the most critical quality issues in overmolding is poor adhesion between the substrate (base part) and the overmolded material. If the materials are incompatible or process parameters (such as temperature, pressure, or surface preparation) are not precisely controlled, delamination or cracking can occur, leading to part failure. Suppliers with limited experience in material science or inadequate process validation may not detect these issues until late in production.
Dimensional Inaccuracy and Warpage
Overmolded parts often involve complex geometries and multiple materials with different shrinkage rates. Inadequate mold design, improper gate location, or inconsistent cooling can result in warpage, sink marks, or dimensional inaccuracies. Without rigorous first-article inspection (FAI) and statistical process control (SPC), these defects may go undetected, especially in high-volume runs.
Hidden Defects in Internal Structures
Many overmolded components encapsulate internal parts such as metal inserts, wires, or electronics. Air entrapment, incomplete filling, or displacement of internal components during the overmolding process can cause latent failures. These defects are often not visible during standard visual inspection and may require X-ray or CT scanning to detect—capabilities not all suppliers possess.
Lack of Process Documentation and Traceability
Reliable quality depends on consistent process control. Some suppliers fail to maintain detailed process records (e.g., mold parameters, material lots, machine settings), making it difficult to trace the root cause of defects or reproduce consistent results across production batches. This lack of traceability can hinder corrective actions and increase risk in regulated industries.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Unprotected Design and Tooling Ownership
Overmolding often requires custom molds and detailed design specifications. If contracts do not explicitly assign ownership of tooling, CAD files, and process know-how to the client, suppliers may claim partial or full rights. This can limit your ability to switch vendors or scale production and expose you to potential IP disputes.
Insufficient Confidentiality Agreements
Overmolding processes may reveal sensitive aspects of your product design, such as material formulations, functional integration, or innovative structural features. Without robust non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) and clear data protection protocols, there’s a risk that your supplier could share or misuse proprietary information with competitors.
Reverse Engineering by Suppliers or Their Subcontractors
Some suppliers outsource part of the overmolding process to third parties without full transparency. If these subcontractors are not bound by the same IP protections, they may reverse engineer your product or use your design to develop competing offerings, especially in regions with weak IP enforcement.
Long-Term Dependency and Vendor Lock-In
When a supplier controls critical tooling or process knowledge and refuses to transfer it, you may become dependent on a single vendor. This lack of control can lead to price increases, reduced flexibility, and vulnerability if the supplier experiences disruptions or goes out of business.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, ensure that:
– Supplier qualifications include proven experience with similar overmolding applications and materials.
– Contracts clearly define IP ownership, confidentiality obligations, and rights to tooling and documentation.
– Quality agreements include acceptance criteria, inspection protocols, and requirements for process validation (e.g., DOE, mold flow analysis).
– Regular audits and sample testing are conducted to verify ongoing compliance and detect early signs of quality drift.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP concerns, companies can reduce risk and build more secure, reliable partnerships when sourcing overmolding services.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Over Molding
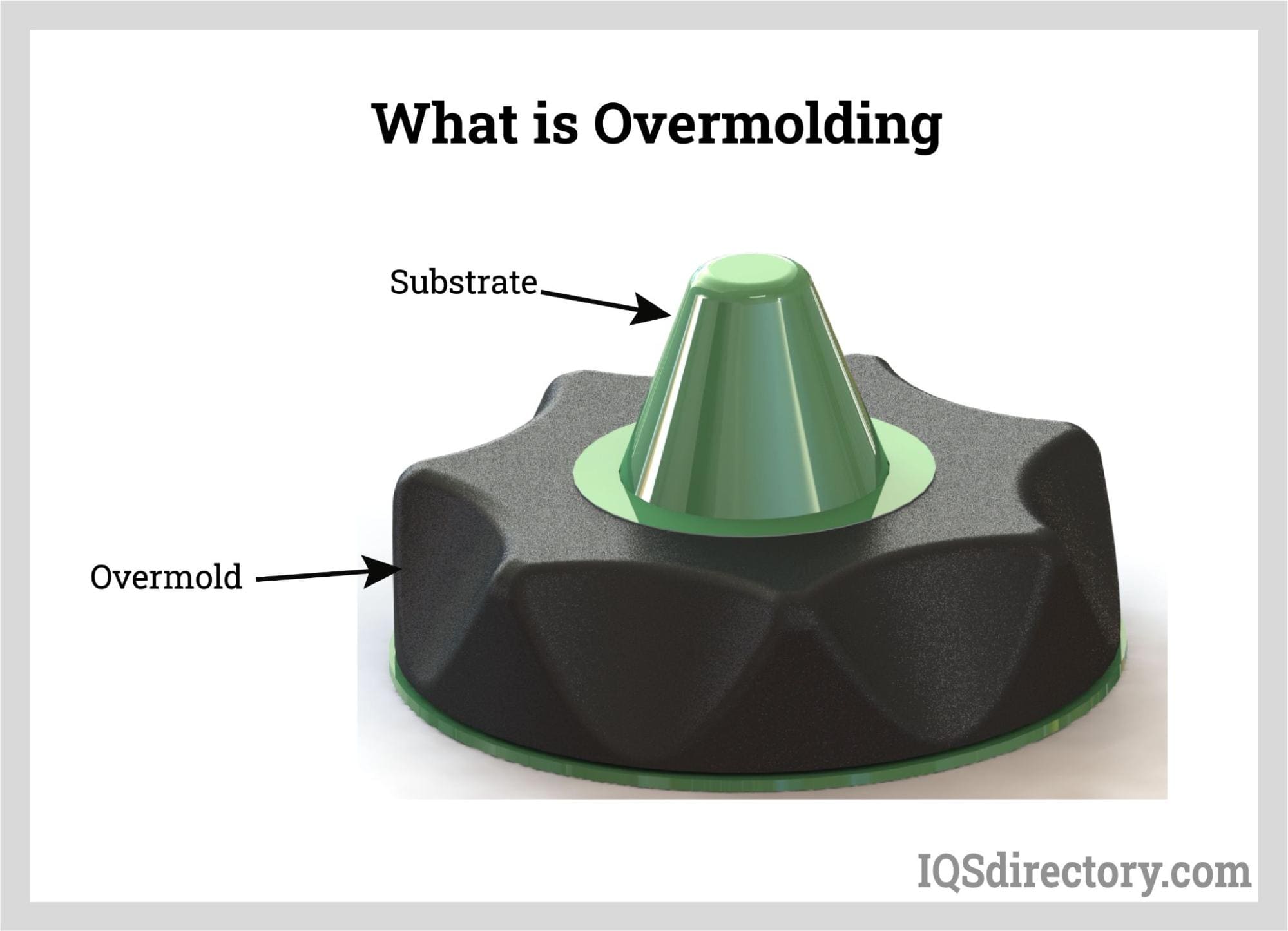
Overview of Over Molding Process
Over molding is a specialized injection molding technique where one material is molded over another, typically combining a rigid substrate with a softer, flexible material. This process is widely used in industries such as automotive, medical devices, consumer electronics, and industrial equipment to enhance product functionality, ergonomics, and durability. Efficient logistics and strict compliance are essential to ensure product quality, regulatory adherence, and timely delivery.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Material Safety and Certifications
All materials used in over molding—base substrate and overmold—must comply with applicable regional and international standards. Key certifications include:
– RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances): Mandatory for electronics in the EU and increasingly adopted globally.
– REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals): Requires full disclosure of chemical substances used.
– FDA Compliance: Critical for over molded parts in food-contact or medical applications (e.g., 21 CFR).
– UL / CSA / CE Marking: Required for electrical safety in consumer and industrial products.
– ISO 10993: For biocompatibility in medical over molded components.
Material data sheets (MDS) and certificates of compliance (CoC) must be maintained and accessible.
Industry-Specific Standards
- Automotive: IATF 16949 quality management system, PPAP (Production Part Approval Process), and IMDS (International Material Data System) reporting.
- Medical: ISO 13485 certification, cleanroom manufacturing (if applicable), and validation of molding processes.
- Consumer Goods: Compliance with CPSIA (Consumer Product Safety Improvement Act) for children’s products.
Supply Chain and Logistics Management
Material Sourcing and Traceability
Ensure dual sourcing for critical materials where feasible to mitigate supply risk. Implement full traceability from raw material to finished product using lot tracking and batch records. Suppliers should provide full material disclosure and undergo regular audits.
Inventory Management
Maintain buffer stock of both substrate and overmold materials to prevent production delays. Use just-in-time (JIT) strategies where stability allows, especially for high-volume production runs. Monitor shelf life of materials, particularly thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) and silicones, which may degrade over time.
Production Flow and Work-in-Process (WIP) Control
Coordinate molding operations to minimize WIP between substrate molding and over molding stages. Use dedicated handling and packaging to prevent contamination or damage to substrate parts prior to over molding.
Packaging, Labeling, and Shipping
Packaging Requirements
Use anti-static, moisture-resistant, and shock-absorbent packaging for sensitive over molded components. For medical or cleanroom applications, packaging must meet ISO 11607 standards for sterile barrier systems.
Labeling and Documentation
Labels must include:
– Part number and revision
– Lot/batch number
– Date of manufacture
– Compliance markings (e.g., RoHS, CE)
– Handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “Keep Dry”)
Accompany shipments with a Certificate of Conformance (CoC), material safety data sheets (MSDS/SDS), and any required regulatory documentation.
Shipping and Transportation
Choose carriers experienced in handling precision plastic components. Control environmental conditions during transit—especially temperature and humidity—for sensitive materials. For international shipments, ensure compliance with import/export regulations, including customs documentation and HTS codes.
Quality Assurance and Process Validation
Process Control
Implement statistical process control (SPC) for critical molding parameters (e.g., melt temperature, injection pressure, cooling time). Conduct first-article inspections (FAI) and regular in-process quality checks.
Testing and Validation
Perform adhesion testing between substrate and overmold layers (e.g., peel, tensile, or shear tests). Conduct environmental stress testing (thermal cycling, UV exposure, chemical resistance) as needed. Validate the process per ASTM or ISO standards relevant to the application.
Environmental, Health, and Safety (EHS) Compliance
Waste Management
Recycle sprues, runners, and rejected parts where possible. Follow local regulations for disposal of non-recyclable polymer waste and contaminated materials.
Workplace Safety
Ensure proper ventilation and personal protective equipment (PPE) for operators handling molten plastics and release agents. Comply with OSHA (or local equivalent) standards for machine guarding and chemical exposure.
Conclusion
Successful over molding operations require robust logistics planning and strict adherence to compliance standards across the supply chain. By integrating regulatory requirements into material selection, production, packaging, and shipping processes, manufacturers can ensure product integrity, reduce risk, and maintain customer trust in competitive markets. Regular audits and continuous improvement are key to sustaining compliance and operational excellence.
Conclusion for Overmolding Sourcing:
Sourcing overmolding components requires a strategic approach that balances technical capability, cost efficiency, quality assurance, and supply chain reliability. As overmolding involves combining multiple materials—typically a rigid substrate with a soft-touch elastomer—supplier selection must prioritize expertise in material compatibility, precision molding techniques, and consistent process control.
Key factors in successful sourcing include choosing partners with proven experience in multi-material injection molding, robust quality management systems (e.g., ISO certification), and the ability to support design for manufacturability (DFM) early in the development process. Geographic location, lead times, scalability, and intellectual property protection also play critical roles, especially for high-volume or global production.
Ultimately, effective overmolding sourcing enhances product performance, improves ergonomics and aesthetics, and can reduce assembly costs through part consolidation. By partnering with qualified and reliable suppliers, companies can ensure durable, high-quality overmolded products that meet both technical requirements and market demands.