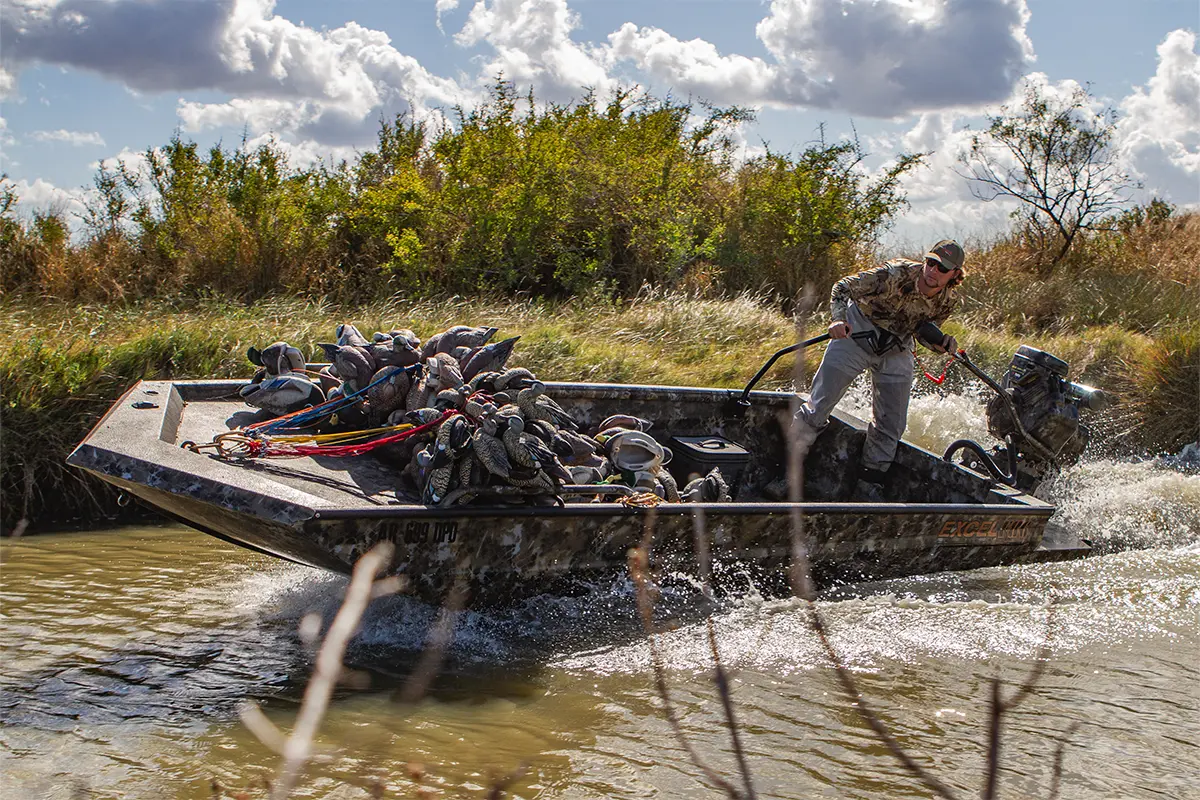
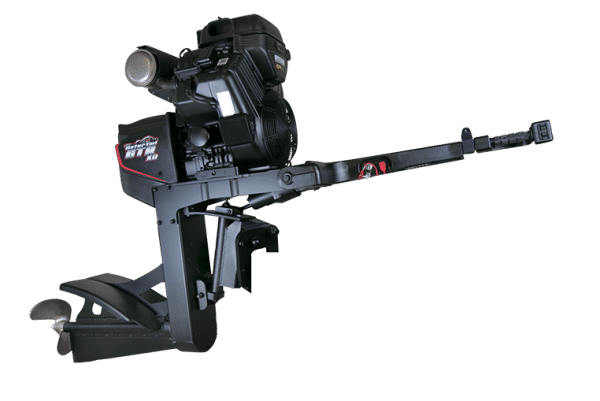
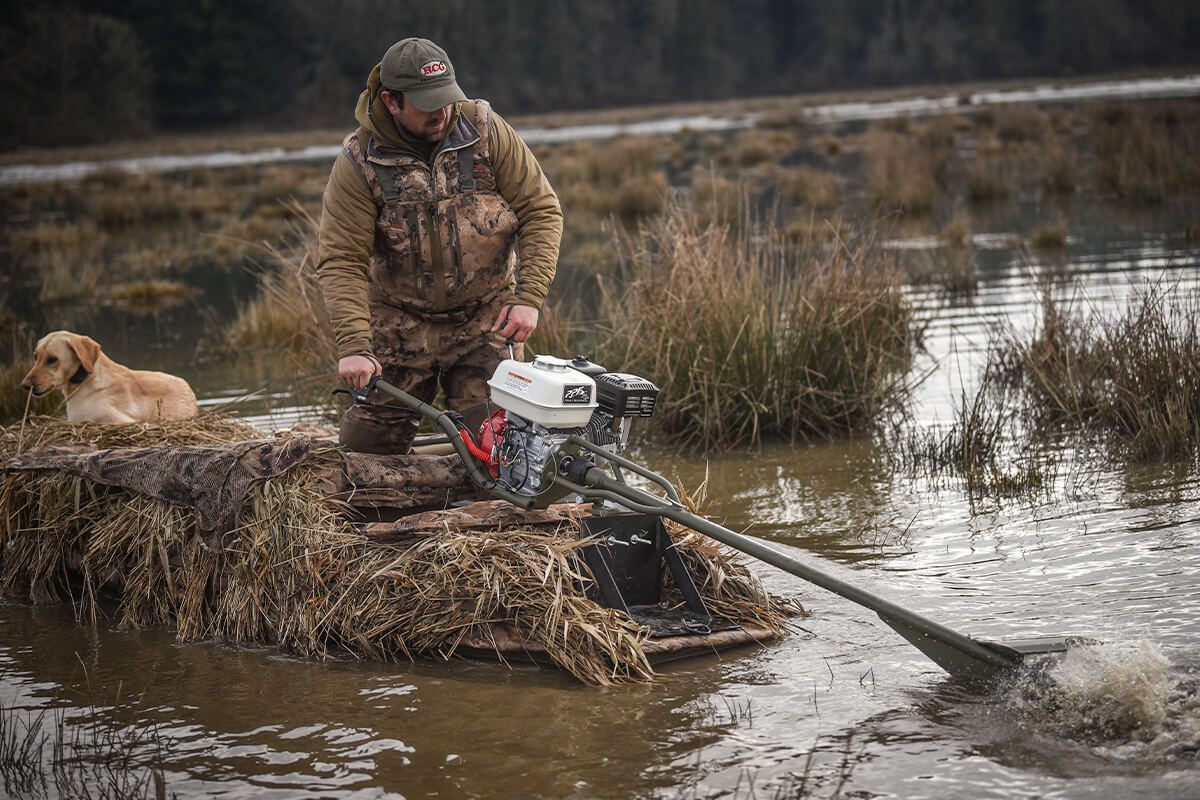
The global outboard motor market, fueled by rising recreational boating activities and advancements in marine propulsion technology, is experiencing steady growth. According to Grand View Research, the global outboard motors market was valued at USD 4.8 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.3% from 2023 to 2030. A key segment within this growth trajectory is the swamp motor niche—specialized outboard motors designed for shallow water navigation, commonly used in marshlands, bayous, and flooded areas. Driven by increasing demand from hunting, fishing, and eco-tourism sectors, particularly in the southern United States, the need for durable, shallow-draft propulsion systems has led to a surge in innovation and competition among manufacturers. As the market evolves, several key players have emerged, combining engineering precision with rugged performance to dominate the swamp motor landscape. Here, we present the top 10 outboard swamp motor manufacturers shaping this specialized segment.
Top 10 Outboard Swamp Motors Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Marine Engines
Domain Est. 2001
Website: vanguardpower.com
Key Highlights: Our commercial engines are the industry-leader for mud boat manufacturers. Integrated features, such as a stainless-steel muffler, high-capacity fuel pump….
#2 Motors
Domain Est. 2010
Website: backwaterinc.com
Key Highlights: We have made a giant leap forward with the introduction of our SWOMP series of mud motors. If you have any questions, call 320-420-8202 to speak with an expert ……
#3 ZF and Gator Tail Introduce New Air
Domain Est. 1996
Website: zf.com
Key Highlights: This innovative product allows specialized aluminum boats to traverse harsh swamp and marsh-type environments with unmatched power and reliability. Field-tested ……
#4
Domain Est. 1998
Website: mercuryracing.com
Key Highlights: Mercury Racing builds the best marine & automotive propulsion systems, accessories, and parts on the market. Learn the value of raw performance and power….
#5 which mud motor is right for you?
Domain Est. 1999
Website: mudbuddy.com
Key Highlights: As the world’s largest mud motor company, Mud Buddy Motors has a broader range of Longtail and Short Tail Surface Drive Mud Motors than all other mud motor ……
#6 Gator Trax Boats
Domain Est. 2001
Website: gatortraxboats.com
Key Highlights: Gator Trax builds high-quality, shallow water custom aluminum boats so that you can maneuver with ease through whatever water you want to ……
#7 GatorTail Outboards
Domain Est. 2003
Website: gator-tail.com
Key Highlights: Gator Tail Outboards are the toughest mud motors and surface drive boats on the planet. Gator Tail can take you places you never thought possible….
#8 Pro
Domain Est. 2003
Website: prodriveoutboards.com
Key Highlights: Pro-Drive full power reverse system forces water under the boat, creating a lifting action which can pull the boat backward in the mud and weeds….
#9 Aliboats Swamp Cruiser 7m
Domain Est. 2005
Website: epropulsion.com
Key Highlights: System at a Glance. This 2024 Swamp Cruiser 7m is an electric Utility Boat from Aliboats, powered by a 40 kW ePropulsion motor and a 200 kWh battery pack, ……
#10 PFF Mud Motors
Domain Est. 2013
Expert Sourcing Insights for Outboard Swamp Motors

H2: Market Trends for Outboard Swamp Motors in 2026
As we approach 2026, the market for outboard swamp motors—specialized propulsion systems designed for shallow, marshy, and vegetation-heavy water environments—is undergoing significant transformation. Driven by technological innovation, shifting consumer preferences, and evolving environmental regulations, this niche segment of the marine industry is poised for both growth and disruption. Below is an analysis of key market trends expected to shape the outboard swamp motor landscape in 2026.
1. Increased Demand for Electric and Hybrid Models
One of the most prominent trends in 2026 is the accelerated shift toward electric and hybrid outboard swamp motors. Driven by environmental concerns and regulatory pressures, manufacturers such as Minn Kota, Polaris (through its RANGER brand), and newer entrants like Mud Buddy Electric are investing heavily in battery-powered solutions. These motors offer silent operation, zero emissions, and minimal disturbance to wildlife—key advantages for hunters, eco-tourism operators, and conservationists.
- Battery Advancements: Improvements in lithium-ion and solid-state battery technology have extended run times and reduced charging intervals, making electric swamp motors more practical for extended use.
- Hybrid Options: Some manufacturers are introducing hybrid systems that combine small internal combustion engines with electric assist, providing flexibility in remote areas where charging infrastructure remains limited.
2. Integration of Smart Technology and Connectivity
By 2026, smart features are becoming standard in high-end swamp motors. IoT integration allows users to monitor performance metrics (e.g., battery life, thrust output, motor temperature) via smartphone apps or onboard displays.
- GPS and Auto-Pilot Functions: Advanced models now offer GPS waypoint navigation and hands-free steering, enabling precise movement through complex marsh environments.
- Remote Diagnostics: Real-time diagnostics and over-the-air updates improve reliability and reduce maintenance downtime.
3. Growth in Recreational and Conservation Applications
While swamp motors have traditionally been used by hunters and commercial guides, their application is expanding into eco-tourism, wildlife research, and environmental monitoring.
- Eco-Tourism Boom: Nature-based tourism in wetlands and bayous is rising, particularly in regions like the Florida Everglades, Louisiana bayous, and the Mississippi Delta. Operators are favoring quiet, eco-friendly motors to enhance guest experience and comply with park regulations.
- Scientific Use: Conservation groups and universities are adopting swamp motors for low-impact data collection in sensitive ecosystems.
4. Regulatory and Environmental Pressures
Environmental regulations are tightening globally, with stricter emissions standards affecting traditional gas-powered motors. In the U.S., the EPA and state agencies are incentivizing the adoption of cleaner propulsion systems.
- Emission Standards: Some states are considering phasing out high-emission two-stroke engines in protected wetlands.
- Incentive Programs: Federal and state grants are emerging to support the transition to electric swamp motors, especially for commercial and public use.
5. Material and Design Innovation
Manufacturers are using lightweight composites, corrosion-resistant alloys, and modular designs to improve durability and ease of transport.
- Portability: New quick-disconnect systems allow for rapid deployment and stowage, a critical feature for users navigating dense vegetation or transporting gear.
- Vegetation Management: Propeller and intake designs are being optimized to resist clogging, with weedless blades and self-cleaning mechanisms becoming more common.
6. Market Expansion and Competitive Landscape
The market is seeing increased competition, with traditional marine brands entering the space and startups introducing disruptive technologies.
- Geographic Expansion: Demand is rising not only in the U.S. South but also in international markets such as Southeast Asia, Africa, and South America, where wetland ecosystems are extensive.
- Aftermarket and Accessories: A growing ecosystem of accessories—such as custom mounts, battery sleds, and solar charging kits—is enhancing user customization and utility.
7. Sustainability and Brand Image
By 2026, sustainability is a key differentiator. Brands that emphasize eco-design, recyclable components, and carbon-neutral manufacturing are gaining consumer trust and market share.
- Circular Economy Initiatives: Some companies are launching take-back programs for old motors and batteries to promote recycling and reduce landfill waste.
Conclusion
The outboard swamp motor market in 2026 is characterized by rapid technological advancement, growing environmental consciousness, and diversification of use cases. Electric and smart-enabled models are leading the charge, supported by regulatory tailwinds and expanding applications in recreation and conservation. As the industry evolves, manufacturers who prioritize innovation, sustainability, and user-centric design will be best positioned to capture market share in this dynamic and ecologically sensitive niche.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Outboard Swamp Motors (Quality, IP)
Sourcing outboard swamp motors—specialized motors designed for shallow water and marshland navigation—requires careful attention to both quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these aspects can lead to performance failures, legal risks, and financial loss. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Build Quality and Material Selection
Many low-cost swamp motors are constructed with substandard materials that cannot withstand prolonged exposure to water, mud, and vegetation. Aluminum housings may corrode quickly, propellers can warp under strain, and seals often fail, leading to water ingress and motor failure. Always verify the use of marine-grade materials, robust sealing (e.g., double-lip seals), and corrosion-resistant components. Request third-party test reports or certifications (e.g., IP68 rating) to validate durability claims.
Inadequate Ingress Protection (IP) Rating
A common issue is motors advertised as “waterproof” without a legitimate IP rating. Without proper certification, such claims are unreliable. Swamp motors operate in extreme conditions, so an IP68 rating (dust-tight and submersible beyond 1 meter) is essential. Verify that the IP rating applies to the entire motor assembly, not just individual components, and ensure it’s tested under real-world conditions, not just lab simulations.
Misrepresentation of Power and Performance
Suppliers may exaggerate thrust, horsepower, or battery life. Motors might deliver peak power only briefly before overheating or throttling down. Always demand real-world performance data, including sustained thrust tests in muddy or vegetated water. Be wary of vague specifications or missing test methodologies.
Lack of Compliance with Regional Regulations
Swamp motors may be subject to environmental and emissions regulations (e.g., CARB in California, EPA standards). Sourcing non-compliant motors can result in fines or import bans. Ensure the supplier provides documentation proving compliance with relevant environmental and safety standards in your target market.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Many swamp motor designs incorporate patented technologies—such as specialized propeller geometries, mounting systems, or electronic controls. Sourcing from manufacturers that copy branded designs (e.g., mimicking Minn Kota or Mud Buddy features) exposes buyers to IP litigation. Conduct due diligence: request proof of IP ownership or licensing agreements, and avoid suppliers offering “compatible” or “OEM-style” versions of well-known models.
Insufficient After-Sales Support and Warranty
Low-quality suppliers often offer limited or no warranty, and spare parts may be unavailable. Given the harsh operating environment, parts like seals, propellers, and control boards wear out quickly. Confirm warranty terms, availability of replacement components, and access to technical support before purchasing.
Supply Chain Opacity and Counterfeit Risk
Some suppliers source from unknown subcontractors or rebrand generic motors. This lack of transparency increases the risk of receiving counterfeit or refurbished units sold as new. Audit your supplier’s manufacturing process, request factory certifications (e.g., ISO 9001), and consider on-site inspections or third-party quality checks.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires thorough vetting of suppliers, insistence on verifiable specifications, and proactive IP due diligence. Investing time upfront ensures reliable performance and legal safety in the demanding swamp boating environment.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Outboard Swamp Motors
Outboard swamp motors, specialized for shallow-water and marshland navigation, require careful attention to logistics and regulatory compliance due to their unique design and operational environment. This guide outlines key considerations for safe, legal, and efficient handling, transport, and operation.
Product Classification and Regulatory Overview
Outboard swamp motors are typically classified under marine propulsion equipment. Depending on the jurisdiction and motor specifications (e.g., electric vs. gasoline-powered), they may fall under regulations from environmental protection agencies, maritime safety authorities, and transportation departments. In the U.S., compliance with Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) emissions standards and U.S. Coast Guard (USCG) guidelines for marine engines is essential. Electric models may have fewer emissions concerns but must still meet safety and labeling requirements.
Transportation and Shipping Requirements
When shipping outboard swamp motors, proper packaging is critical to prevent damage. Motors should be securely crated or boxed with protective padding, especially around the lower unit and propeller. For international shipments, ensure compliance with International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code if transporting fuel-powered units with residual fuel. Electric motors with lithium-ion batteries must comply with IATA/IMDG regulations for lithium battery transport, including proper labeling, state-of-charge limits, and packaging standards.
Import/Export Documentation and Duties
Exporting or importing swamp motors requires accurate documentation, including commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. Harmonized System (HS) codes must be correctly applied—typically under 8407 (spark-ignition engines) or 8501 (electric motors), depending on the motor type. Importers should verify tariffs, anti-dumping regulations, and any country-specific restrictions (e.g., noise or emissions limits in the EU or Canada). Certifications such as CE (Europe) or NMEA compliance may be required for market access.
Environmental and Operational Compliance
Operators must adhere to local and federal environmental regulations. In protected wetlands or wildlife refuges, certain motor types or horsepower limits may be restricted. Gasoline-powered swamp motors may require EPA-certified low-emission engines, and fuel systems must be sealed to prevent leaks. Users should also follow state-specific boating regulations, including registration, safety equipment requirements, and no-wake zone compliance.
Storage and Handling Best Practices
Store swamp motors in a dry, temperature-controlled environment to prevent corrosion and damage to electrical components. For long-term storage, remove batteries (if electric), drain fuel (if applicable), and apply protective lubricants. When handling, use proper lifting techniques or equipment to avoid strain or injury, particularly with heavier models.
Warranty and Service Logistics
Ensure all units include clear warranty documentation and service instructions. Distributors and dealers should maintain an inventory of spare parts and have access to technical support. For international sales, establish service partnerships or authorized repair centers to support customers and comply with consumer protection laws.
Training and End-User Compliance
Provide end-users with comprehensive operation and maintenance manuals in applicable languages. Training on safe handling, environmental responsibility, and regulatory compliance (e.g., invasive species prevention, noise ordinances) helps ensure legal and sustainable use. Distribute compliance checklists for boaters operating in regulated zones.
Conclusion for Sourcing Outboard Swamp Motors:
Sourcing outboard swamp motors requires a careful balance between performance, durability, and value. After evaluating various suppliers, models, and market options, it is evident that selecting the right motor depends on specific use cases such as shallow water navigation, vegetation-heavy environments, and load requirements. Key factors to consider include thrust power, propeller design, mounting options, battery compatibility (for electric models), and corrosion resistance.
Reputable brands offering reliable customer support, warranty coverage, and proven performance in wetland and marsh conditions should be prioritized. Direct engagement with manufacturers, comparison of dealer networks, and reviewing user feedback can significantly improve sourcing decisions. Additionally, considering total cost of ownership—factoring in maintenance, efficiency, and longevity—leads to more sustainable and cost-effective outcomes.
In conclusion, a strategic sourcing approach that emphasizes quality, suitability for environment, and long-term support will ensure optimal performance and reliability of outboard swamp motors in demanding aquatic conditions.