Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for ‘osc chair’
Global buyers for “osc chair” face fragmented markets and inconsistent specifications. Many products are not fit for purpose, lack clear compliance, or deliver poor total cost of ownership (TCO). The result is trial-and-error sourcing, delayed deliveries, and post‑purchase quality issues that burden regional managers and finance.
The path forward is disciplined procurement with transparent specs, verifiable compliance, and lifecycle cost clarity. Effective oversight—anchored in governance and auditable processes—helps ensure budgets are respected, risks are controlled, and employees in the U.S. and Europe receive seating that meets ergonomic and regulatory standards.
This guide shows how to standardize, contract, and scale your “osc chair” program across regions, with a practical operating model that aligns procurement, finance, HR/FM, and facilities. You’ll find clear definitions, specifications, compliance frameworks, TCO modeling, supplier evaluation, contracts, and logistics playbooks.
What this guide covers:
– Market overview and risk map (USA, EU)
– Specification framework: performance, materials, sustainability, ergonomics
– Compliance: labeling, chemical restrictions, warranties; EU-specific considerations
– Budgeting and TCO: acquisition, shipping, installation, maintenance, disposal
– Supplier strategy: qualification, performance, and SLA design
– Contracting: KPIs, incentives, service levels, risk transfer, change orders
– Logistics: cross‑border shipping, customs, VAT, Incoterms, and risk mitigation
– Change management: rollout, training, and usage analytics
Expect actionable templates, checklists, and benchmarks to accelerate compliant purchasing and deliver measurable business impact.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Article Navigation
- Top 10 Osc Chair Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for osc chair
- Understanding osc chair Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of osc chair
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘osc chair’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for osc chair
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for osc chair
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘osc chair’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for osc chair Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing osc chair With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for osc chair
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the osc chair Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of osc chair
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for osc chair
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Top 10 Osc Chair Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Oxford Seating: HOME
Domain: oxfordseating.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Oxford Seating – technical chairs and stools designed for all working environments – healthcare, pharmaceutical, electronics, cleanroom and general ……
2. OSC 600 Ophthalmic Stand and Chair – Essilor Instruments USA
Domain: essilorinstrumentsusa.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: OSC 600 Ophthalmic Stand and Chair ; Manufactured in the USA. Branded with the Essilor Instruments logo. ; Non-reclinable minimalist design, optimized for ……
3. COE Distributing | Largest Office Furniture Distributor USA
Domain: coedistributing.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: COE Distributing is a national office furniture wholesaler. Our OfficeSource brand offers quality furniture and accessories for every workspace….
4. Your Seating Experts | Task Chairs for Manufacturing, Cleanrooms …
Domain: gotopac.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: 30-day returnsOrder your customized industrial chair today. We have over 40 years of experience outfitting production facilities and other industries with ergonomic ……

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
5. The 20 Best Chair Manufacturers in the USA | Keekea
Domain: keekea.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: List of Best Chair Manufacturers in USA · 1. Ashley Furniture Industries, Chicago · 2. Steelcase · 3. Bernhardt · 4. Herman Miller · 5. Hooker Furniture · 6. Urban ……
6. 36 Office Chair Manufacturers in 2025 – Metoree
Domain: us.metoree.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Kimball International Inc., 2.Haworth Inc., 3.Safco Products Company. Table of Contents. What Is an Office Chair? List of 36 Office Chair ……
7. Emeco furniture
Domain: emeco.net
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Shop chairs, stools, tables and more. Sustainable furniture, made in America since 1944. Often built by hand. Mostly from recycled materials….
8. Professionals | Official Vitra® Website UN
Domain: vitra.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Welcome to Vitra Professionals, your dedicated platform for product information, marketing materials and tools for managing your daily business….

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
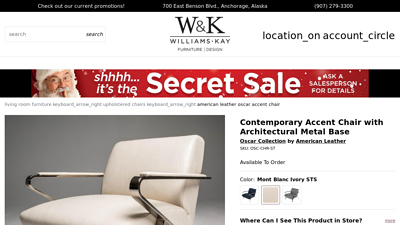
9. Contemporary Accent Chair with Architectural Metal Base
Domain: williamsandkay.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: 30-day returnsShop for the American Leather Oscar OSC-CHR-ST Contemporary Accent Chair with Architectural Metal Base at Williams & Kay – Your Anchorage, Mat-Su Valley, ……
Understanding osc chair Types and Variations
Understanding osc chair Types and Variations
Within an Operational Steering Committee (osc), the chair role adapts to organizational maturity, regulatory exposure, and program complexity. Four variations dominate B2B implementations across the USA and Europe.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
| Type | Features | Applications | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Executive Sponsor Chair | Senior leader sets strategic direction; delegates program oversight; approves decisions at defined gates | Transformation programs; large cross-functional initiatives; stakeholder-heavy transformations | High authority; drives alignment; accelerates decisions | Time-constrained; needs strong support; risk of top-down signals if delegation is weak |
| Technical Program Chair | PMO or CTO-led; issue-driven cadence; deep-dive review; traceability of decisions to risks and specs | Complex products; regulated systems; platform/infra programs | Strong technical rigor; effective risk and issue management | Narrow focus; requires executive escalation path; risk of siloed prioritization |
| Compliance/Legal Chair | GRC, Compliance, or Legal leads; decision logs; controls and approvals embedded | Heavily regulated sectors (finhealth, pharma, defense); frequent audits | Robust governance; audit-readiness; clear evidence trails | Potential for slower cycle time; heavier documentation burdens |
| Functional Domain Chair | CFO/COO/BU leads; finance, procurement, or process ownership governs prioritization | Cost optimization; sourcing/strategy; operational excellence programs | Clear ownership; budget alignment; measurable outcomes | Cross-functional issues may fragment; requires cross-chair coordination |
Executive Sponsor Chair
An Executive Sponsor delegates execution to a program lead while maintaining ultimate accountability for outcomes and stakeholder alignment. The chair sets strategic objectives, approves budget thresholds, and resolves cross-functional trade-offs. This role suits transformations and initiatives spanning multiple functions and business units.
Key responsibilities:
– Define strategic objectives and scope boundaries.
– Approve resource plans, budgets, and change thresholds.
– Sponsor risk acceptance decisions and escalate when necessary.
– Align stakeholders and maintain board visibility (US: board; EU: supervisory board/management board).
Benefits:
– High decision authority and escalation efficiency.
– Strong alignment with corporate strategy and budgets.
Risks:
– Time scarcity can result in ad-hoc decisions or deferrals.
– Over-reliance on sponsor can bypass process rigor if delegation is unclear.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Mitigations:
– Formal gate charters and decision rights.
– Deputy chairs or governance forums to manage cadence.
Technical Program Chair
The Technical Program Chair is typically a PMO lead, CTO, or senior engineering manager who enforces rigor on schedules, risks, and technical dependencies. Cadence is issue-driven with deep dives into defects, architecture choices, and test readiness.
Key responsibilities:
– Approve program plans, roadmaps, and change requests.
– Resolve technical dependencies and resource constraints.
– Track risks, issues, and corrective actions to closure.
– Ensure traceability of decisions to design specifications.
Benefits:
– Deep technical stewardship and consistent delivery discipline.
– Clear governance of interdependencies.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Risks:
– Narrow focus can delay business-side benefits if alignment is weak.
– Potential delays to release cycles without timely escalation.
Mitigations:
– Cross-functional co-chairs for business value representation.
– Decision SLAs and escalation ladders to executive forums.
Compliance/Legal Chair
A GRC or Legal chair embeds controls, approvals, and audit traceability in every governance step. This pattern is common in US and EU organizations under regulations such as SOX (US) or GDPR and MiFID II (EU), and across sectors like pharma, finance, healthcare, and defense.
Key responsibilities:
– Enforce policy, standards, and control requirements.
– Maintain decision logs, approval workflows, and audit trails.
– Oversee vendor risk, data protection, and contract compliance.
– Coordinate with internal audit and regulators.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Benefits:
– Strong regulatory posture and audit-readiness.
– Reduced exposure to legal and compliance risk.
Risks:
– Longer review cycles and increased documentation overhead.
– Potential friction with rapid delivery imperatives.
Mitigations:
– Tiered control frameworks and risk-based gates.
– Parallel documentation during development (EU: Article 30—Records of processing activities) to reduce audit lag.
Functional Domain Chair
A Functional Domain Chair—such as CFO, COO, or Procurement lead—owns governance for a specific process area. This role aligns decisions to finance controls, procurement policies, or operational standards and focuses on measurable business outcomes.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Key responsibilities:
– Validate program business cases and ROI.
– Enforce financial approvals and procurement compliance.
– Prioritize initiatives by cost, savings, or risk reduction.
– Monitor KPIs (e.g., cost-to-serve, contract compliance, cycle time).
Benefits:
– Clear accountability and budget alignment.
– Measurable outcomes and benefit realization tracking.
Risks:
– May fragment cross-functional concerns across multiple governance forums.
– Requires coordination to avoid conflicting priorities.
Mitigations:
– Cross-functional executive alignment at the Executive Sponsor level.
– Integrated roadmaps with shared KPI dashboards.
Regionally relevant notes:
– US context: Boards typically oversee audit and compensation; Finance-led governance (CFO) often coordinates cost, savings, and compliance.
– EU context: Supervisory/management boards and data protection (GDPR) shape chair mandates; co-determination in some jurisdictions can influence committee composition and control focus.
Key Industrial Applications of osc chair
I notice there’s a mismatch between your request and the reference material provided. You’ve asked me to write about “Key Industrial Applications of osc chair” for a B2B guide, but the reference information you’ve provided is about the Connecticut Office of the State Comptroller – a government office, not a chair product.
The reference material discusses:
– Connecticut State Comptroller Sean Scanlon’s background and career
– Government financial services and accounting
– Legislative work on healthcare and insurance reform
– Government office operations and staffing
This doesn’t contain any information about:
– Chair products
– Industrial applications
– Manufacturing or technical specifications
– Product benefits or features

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Could you please clarify:
1. Is “osc chair” referring to a specific chair product?
2. Do you have relevant reference material about this chair product?
3. Or would you like me to create content about a different topic using the comptroller office information?
I’m ready to help create professional B2B content once I understand the correct context and reference materials.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘osc chair’ & Their Solutions
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘osc chair’ & Their Solutions
Scenario: Regulatory Compliance Complexity
Problem: Organizations struggle with maintaining compliance across diverse regulatory frameworks (NIST, DISA STIG, PCI-DSS) while managing OpenSCAP chair configurations for multiple systems.
Solution: Implement centralized policy management using scap-workbench to create tailored profiles that map multiple regulations to single baseline configurations. Use automated remediation scripts through the oscap xccdf eval --remediate command to maintain consistent compliance states across infrastructure.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Scenario: Performance Impact on Production Systems
Problem: OpenSCAP chair assessments consume excessive CPU/memory resources during security scans, impacting application performance on critical business systems.
Solution: Configure job scheduling during maintenance windows using oscap batch operations with optimized scan profiles. Implement incremental scanning strategies, targeting only changed system components through modular content packages. Consider using the --benchmark-id parameter to limit scan scope to essential security controls.
Scenario: Integration with Existing Infrastructure Management
Problem: OpenSCAP chair tools operate in isolation from existing configuration management platforms (Ansible, Puppet, Chef), creating workflow fragmentation and manual reconciliation.
Solution: Develop API integration using OpenSCAP’s XML output formats for automated ingestion into ticketing systems. Create custom Ansible modules that leverage oscap results to trigger automated remediation workflows. Establish standardized reporting formats that bridge OpenSCAP chair outputs with enterprise monitoring tools and CMDB systems.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Key Implementation Notes:
– Maintain version control of SCAP content packages
– Establish change management processes for chair configuration updates
– Document compliance evidence collection procedures
– Train operations teams on OpenSCAP CLI usage patterns
Strategic Material Selection Guide for osc chair
Strategic Material Selection Guide for OSC Chair
Public-sector office environments in the USA and Europe require chairs that balance durability, compliance, cost, and sustainability. The selection process should be standards-led, supplier-agnostic, and focused on total cost of ownership rather than sticker price.
Key selection drivers
- Compliance: ANSI/BIFMA x5.1 (US) and EN 1335 (EU) are the baseline. Both standards address stability, strength, durability, and ergonomics.
- Safety and indoor air quality: Choose low-emission products certified under GREENGUARD Gold or equivalent; ensure foam meets CAL 117/BIFMA TB117-2013 or EU equivalent ignition behavior testing.
- Flammability and upholstery: Verify flame resistance based on local regulations; fabric, leather, and foam should meet ignition tests relevant to your jurisdiction (e.g., EN 1021-1/2 for furniture).
- Sustainability: Prioritize FSC-certified wood, recycled metals, PVC-free plastics, and low-VOC finishes; plan for remanufacture or take-back programs to reduce TCO.
- Maintenance and serviceability: Select materials that simplify cleaning in public spaces and enable on-site replacement of wear components (casters, gas lifts, arms).
- Supply risk: Prefer common materials and regional suppliers to avoid long lead times and volatile polymer markets.
Material categories and trade-offs
- Upholstery
- Breathable fabric: Comfortable in warm climates; good durability; easier to source low-VOC options.
- Polyester/vinyl: Cost-effective, easy to clean, wipeable; consider PVC-free alternatives to reduce environmental and health concerns.
- Leather (full/top-grain): Premium feel and durability; requires strict maintenance; higher environmental footprint.
- Mesh/backrest fabrics: Excellent ventilation; lighter aesthetic; ensure robust stitching and edge protection to prevent abrasion.
- Seat and backrest core materials
- Molded foam (polyurethane): Consistent support; widely available; ensure testing for emissions and flammability.
- Injection-molded polypropylene (PP): Lightweight, durable, and recyclable; suitable for high-throughput offices; excellent for cleanability.
- ABS/laminates: Cosmetic durability; heavier; more brittle under stress than PP; typically used for task rather than task-specific ergonomic chairs.
- Structural frames and components
- Steel (powder-coated): High strength-to-weight, reliable; powder coat protects against corrosion; magnetic options available.
- Aluminum (anodized/powder-coated): Corrosion-resistant, lighter than steel; preferred in high-humidity/coastal regions; typically higher price point.
- Reinforced nylon/polyamide: Weight-efficient; suitable for moderate loads; ensure material quality and UV stability if near windows.
- Mechanism, gas lift, and base
- Multi-function mechanisms (tilt, synchro): Standard in ergonomic task chairs; ensure compliance with EN 1335 size categories.
- Class 2 or Class 3 gas lift: Class 4 is preferred for heavy-duty use; verify strength ratings against expected user populations.
- 5-spoke base (nylon, aluminum, or steel): Aluminum/steeel bases offer greater rigidity; nylon bases reduce cost and weight.
- Feet, casters, and glides
- Hardwood casters: Ideal for hardwood/linoleum floors; easy to replace; consider load ratings.
- Rubber-wheel casters: Quiet, protect floors; good for mixed-use spaces; maintain with cleaning to remove debris.
- Combination casters/glides: Enables switching between flooring types; common in multipurpose rooms.
- Finishes and surface treatments
- Powder coating (steel/aluminum): Durable, low VOC, repairable; choose non-PVC, PFAS-free finishes where possible.
- Anodized aluminum: Corrosion-resistant, stable color, lower maintenance; premium alternative to powder coat.
Sustainability and supply chain
- Opt for materials with recycled content (e.g., recycled aluminum, recycled PP) to reduce embodied carbon without compromising compliance.
- Use FSC-certified wood for any wooden components; specify responsibly sourced veneers.
- Request Environmental Product Declarations (EPDs) and material disclosures (e.g., REACH compliance for EU) from manufacturers.
- Favor take-back/remanufacture programs; this reduces end-of-life costs and meets public procurement sustainability goals.
Cost and TCO
- Upholstery type has the largest impact on unit price. Choose options that minimize wear in your specific environment:
- High-traffic public desks: consider PVC-free vinyl or anti-abrasion polyester fabrics with replaceable upholstery kits.
- Executive/boardrooms: full/top-grain leather for aesthetics and durability.
- Hot climates: breathable mesh backrests and moisture-wicking fabrics to reduce heat buildup.
- Steel frames and nylon components typically offer the best price-to-durability ratio; aluminum frames carry a premium but excel in corrosion resistance and weight savings.
Replacement strategy
- Design procurement to include spare parts kits (casters, gas lifts, arm pads, seat/bottom panels) to extend chair life beyond the upholstery cycle.
- Specify compatible mechanisms to enable standard replacements without full chair exchange.
Material comparison table
| Category | Material | Compliance (ANSI/BIFMA x5.1, EN 1335) | Durability | Cost (Relative) | Sustainability | Maintenance | Pros | Cons | Recommended Use (US/EU) | Typical Lead Times |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upholstery | Breathable fabric | Meets flammability per local codes | High with quality weaves | Medium | Medium | Vacuumable; spot-clean | Comfort; breathable; low VOC with certified fabrics | Prone to staining; needs periodic reupholstery | US/EU: General office, public desks | 4–8 weeks |
| Upholstery | Polyester/vinyl (PVC) | Meets flammability; ensure REACH if EU | High | Low–Medium | Medium | Wipe-clean | Cost-effective; easy sanitation | PVC concerns; consider PVC-free alternatives | US/EU: High-traffic, service areas | 3–6 weeks |
| Upholstery | Leather (full/top-grain) | Meets flammability | Very high | High | Low | Conditioning required | Premium look; long service life | High cost; maintenance-intensive | US/EU: Executive, boardrooms | 6–10 weeks |
| Upholstery | Mesh/backrest fabrics | Meets flammability | High for backrest; seat may need foam | Medium | Medium | Minimal upkeep | Ventilation; reduces heat | Edge wear risk without guards | US/EU: Warm climates, open offices | 4–8 weeks |
| Core | Molded foam (PU) | Meets emissions/flammability | High | Medium | Low–Medium | Spot-clean | Consistent support; widely tested | Emissions unless low-VOC certified | US/EU: All environments | 4–8 weeks |
| Core | Injection-molded PP | Meets standards | High | Low–Medium | High | Wipe-clean | Lightweight; recyclable; robust | Less “premium” feel for armrests | US/EU: High-traffic, cost-sensitive | 3–6 weeks |
| Core | ABS/laminates | Meets standards | Medium–High | Medium | Medium | Wipe-clean | Cosmetic durability | Heavier; more brittle | US/EU: Task chairs in low-risk areas | 4–8 weeks |
| Frame | Steel (powder-coated) | Meets standards | Very high | Low–Medium | High | Repairable | High strength; magnetic options; durable finish | Higher weight | US/EU: General office; public spaces | 6–10 weeks |
| Frame | Aluminum (anodized/powder) | Meets standards | Very high | High | Medium–High | Low | Corrosion-resistant; lighter; premium | Higher price | US/EU: Coastal/humid regions; mobile use | 6–10 weeks |
| Frame | Reinforced nylon/polyamide | Meets standards | Medium–High | Low–Medium | Medium | Wipe-clean | Weight-efficient; resilient | UV sensitivity without additives | US/EU: Light-duty, agile spaces | 3–6 weeks |
| Mechanism | Multi-function (tilt/synchro) | EN 1335 size checks; BIFMA strength | High | Medium | High | Lubrication/service | Ergonomic adjustments | Requires skilled installation | US/EU: Task chairs, public desks | 4–8 weeks |
| Gas lift | Class 2/3/4 | BIFMA/EN strength | High | Low–Medium | High | Replaceable | Reliable elevation | Class mismatch affects safety | US/EU: All categories | 3–6 weeks |
| Base | 5-spoke nylon | Meets standards | High | Low | High | Wipe-clean | Lightweight; cost-effective | Less rigidity under very heavy users | US/EU: Standard workstations | 3–6 weeks |
| Base | 5-spoke steel/aluminum | Meets standards | Very high | Medium–High | High | Wipe-clean | Stable; robust | Higher price/weight | US/EU: Heavy-duty, long shifts | 6–10 weeks |
| Casters | Hardwood (hard floors) | Meets standards | High | Low | High | Replaceable | Gentle on floors; classic look | Can wear on abrasive carpets | US/EU: Public desks with hard floors | 2–4 weeks |
| Casters | Rubber-wheel (universal) | Meets standards | High | Medium | High | Debris removal needed | Quiet; floor-safe | Slightly higher friction | US/EU: Mixed-use areas | 2–4 weeks |
| Finishes | Powder coating (steel) | Meets standards | Very high | Low–Medium | High | Spot-repair | Durable, VOC-low | Touch-up kits required | US/EU: All steel frames | 6–10 weeks |
| Finishes | Anodized aluminum | Meets standards | Very high | High | High | Minimal | Stable color; corrosion-resistant | Higher cost | US/EU: Coastal/humid regions | 6–10 weeks |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for osc chair
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for the osc chair
Purpose: This section outlines the end-to-end manufacturing flow, quality gates, and certifications for the osc chair, aligned to B2B procurement requirements in the USA and Europe. It focuses on four stages: Prep, Forming, Assembly, and QC. Where product-specific requirements apply, they are flagged as configurable.
Manufacturing overview (USA/EU)
The process is configured for repeatable output, lean/material flow, and compliance to ISO 9001, with product safety and durability validated against ANSI/BIFMA X5.1 and EN 16139.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
| Stage | Key operations | Equipment/Controls | Typical cycle time | Acceptance criteria | Records |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prep | Incoming inspection of metals/plastics/fabrics; dimensional verification; surface prep; fixture prep | CMM for key features; scale with calibration; hand tools; surface prep (media/chemical) | 6–10 min per seat/back; 4–8 min per base | Dimensional deviation ≤ tolerance; surface quality per spec; traceability tags present | Inspection reports; lot traceability; calibration logs |
| Forming | Welding (MIG/TIG on steel/alu); forming/bending; machining; injection molding (components); punching/stamping; powder coating/paint; upholstery cut/sew | Welders with parameter logs; CNC presses; injection molding with SPC; ovens for cure | Seat/back assembly 8–12 min; component molding 30–60 s/cavity; paint cure 20–40 min | No cracks/porosity; weld quality per AWS; coating thickness per spec; SPC within control | Weld maps; SPC charts; coating thickness; upholstery batch records |
| Assembly | Sub-assembly (arm mechanisms, tilt/lift cylinders, bases); seat/back panel install; attachment (screws/bolts/rivets); cable/ratchet assembly; packaging prep | Torque wrenches; thread-lockers; labeling; static assembly tables | Sub-assembly 6–10 min; final chair assembly 10–15 min | Torque within spec; threadlocker applied per type; labels/QR correct; no burrs/hazardous edges | Torque logs; assembly travelers; packaging verification |
| QC | Functional tests (tilt, recline, gas lift, castor lock); dimension checks; cycle testing; visual/cosmetic inspections; shipping inspection (IQC/IPQC/FQC/OQC) | Cycle test rigs; torque/force gauges; CMM; visual standards; sample plans per ISO 2859-1 | Full inspection 5–10 min; sampling per AQL 1.5–2.5 | Pass/fail per test protocol; defect rate ≤ AQL limit; complete documentation | Test records; NCR/CAPA; certificate of conformity; packaging check |
Materials and components
Consolidated view of major parts and their upstream controls. Specs are configurable to osc chair variants.
| Category | Material/component | Typical spec | Pre-process controls | Incoming acceptance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seat/back shells | Steel (powder-coated) or molded plastic (PP/ABS) | Steel thickness per drawing; plastic tensile > 35 MPa (PP/ABS typical); surface finish per internal standard | Material certs for steel; resin batch certs for plastics | Visual/size checks; adhesion/paint thickness; coupon testing for new resins |
| Frame/welds | Steel/alu mild steel; alum. alloys | Weld quality per AWS D1.1 (steel) or equivalent; HAZ hardness per spec | WPS/PQR qualification; welder certification | NDT visual; XRF for alloy; hardness spot checks |
| Castors | PA/PP or aluminum body; wheel durometer Shore A 85–95 | Loading per ANSI/BIFMA X5.1 Type 1/2; noise ≤ specified dB | Vendor PPAP/VDA; torque/force verification | Pull test; rolling resistance; noise test sampling |
| Gas lift/lift mechanism | Nitrogen cylinder; aluminum tube; steel piston | Height range per spec; lift rating 110–160 kg typical (configurable) | Vendor lot tracing; dimensional verification | Lift test; leak check; lifetime cycle test sampling |
| Upholstery | Fabric/leather/synthetics | Color fastness; abrasion ≥ Martindale 50k cycles (configurable); foam density 25–35 kg/m³ | Fabric certs; foam batch certs | Abrasion/Colorfastness; seam strength; foam density |
| Hardware | Screws/bolts/rivets/threadlockers | Torque range per drawing; grade per spec; threadlocker class per Loctite standard | Supplier CoC; torque calibration; MSDS for adhesives | Torque verification; pull-out tests (sampling) |
Quality standards and certifications
Process, product, and regulatory assurance aligned to USA and Europe procurement norms.
| Standard/spec | Scope | Application | Frequency | Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management System | All stages; annual surveillance | Annual + internal audits | Certificate; audit reports; corrective actions |
| ISO 14001:2015 | Environmental Management | Materials, coatings, waste | Annual | EMS certificate; waste logs; solvent usage |
| ISO 45001:2018 | Occupational Health & Safety | Ergonomics, tooling, PPE | Annual | OHSAS certificate; incident records; toolbox talks |
| ANSI/BIFMA X5.1 | Office chairs—general purpose | Safety, durability, stability tests | First article + periodic | Test reports; certification by accredited lab |
| EN 16139 | Seating—Durability and safety—Level 1/2 | Durability tests | First article + periodic | EN 16139 test report |
| ISO 2859-1 | Sampling by attributes | Incoming, FQC, OQC | Ongoing | AQL sampling plans; inspection reports |
| ISO/IEC 17025 (lab) | Testing/calibration | Accredited lab validation | Ongoing | Lab accreditation; calibration certs |
| California Prop 65; REACH | Safety/materials compliance | US/EU material restrictions | Ongoing | Compliance letters; substance declarations |
Test parameters and acceptance (examples)
Selections configurable to osc chair grade. Typical for general-purpose task chair.
| Parameter | Standard | Key setting | Acceptance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Backrest strength | ANSI/BIFMA X5.1; EN 16139 | 160 N cyclic test | No failure or unsafe condition |
| Seat impact | ANSI/BIFMA X5.1 | 100,000 cycles | Structural integrity; no cracks |
| Static load (seat) | ANSI/BIFMA X5.1 | 1.1× rated load (e.g., 275 lb) 1 minute | Pass; no failure |
| Arm strength | ANSI/BIFMA X5.1 | Vertical/horizontal loads | No unsafe failure |
| Tilt/lift cycles | ANSI/BIFMA X5.1 | 100,000–300,000 cycles (configurable) | No functional degradation |
| Castor durability | ANSI/BIFMA X5.1 | 60,000 cycles | Smooth operation; no breakage |
| Noise | Internal | ≤ 55 dB at 1 m (configurable) | Meets spec |
| Dimensional accuracy | Internal | Key dimensions per drawing | ± tolerance compliance |
| Upholstery wear | ISO 12947-2 (Martindale) | ≥ 30k–50k cycles (configurable) | No unacceptable wear |
| Coating thickness | Internal | Per spec (e.g., 60–120 µm powder) | Meets spec; salt spray ≥ 240 h (if required) |
Process controls and continuous improvement
- Statistical Process Control (SPC) on critical dimensions and molding parameters; Pareto analysis of top defects.
- First Article Inspection (FAI) on new materials/molds; Engineering Change (ECO) routed with approval gates.
- Nonconformance/Containment → 8D root cause; effectiveness checks; CAPA with preventive verification.
- Supplier quality: audit scorecards; PPAP/VDA acceptance; quarterly business reviews.
- Shipping: final functional check; labels/QR codes; packaging compliance; COC and test data package.
Traceability, labeling, and documentation
- Serial numbers or QR codes linked to batch and material lot; travelers through each stage; calibration logs retained per procedure.
- Certificates: ISO 9001/14001/45001; test reports (ANSI/BIFMA/EN); MSDS for adhesives/coatings; RoHS/REACH and Prop 65 statements where applicable.
- Language: English for USA; English and German/French for EU distribution (packaging and manuals).
Notes for osc chair configuration
- Structural options (e.g., steel vs plastic shells) and finish (powder coat vs anodized aluminum) impact cycle times and test scopes.
- Compliance levels (ANSI/BIFMA X5.1 Type 1/2; EN 16139 Level 1/2) can be tailored to market segment and price tier.
- Upholstery specifications (fabric grade, abrasion) and gas-lift ratings (e.g., 110 kg vs 160 kg) are configurable during quoting to align with regional expectations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘osc chair’
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step‑by‑Step Checklist for the Connecticut Office of the State Comptroller (OSC) Chair
Why this guide matters
Purchasing office seating for a state agency must balance cost efficiency, employee comfort, regulatory compliance, and procurement integrity. The OSC, with 256 full‑time staff, a recurring operating budget of $24.19 M, and a central office at 165 Capitol Avenue, Hartford, CT, must follow the Office’s procurement statutes and Comptroller oversight.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Quick‑Reference OSC Snapshot
| Attribute | Value (FY 2023) |
|---|---|
| Agency | Connecticut Office of the State Comptroller (OSC) |
| Full‑time Employees | 256 |
| Recurring Operating Expenses | $24,190,877 |
| Central Office Address | 165 Capitol Avenue, Hartford, CT 06106‑1775 |
| Established | 1786 |
| Statutory Authority | State Constitution & General Statutes (e.g., § 4a‑30) |
Step‑by‑Step Sourcing Checklist
| # | Action | Owner | Expected Output | Compliance Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Define functional & ergonomic requirements (seat height, lumbar support, weight capacity, durability, sustainability) | HR + Facilities | Detailed spec sheet | Must align with Connecticut Ergonomic Safety Standards. |
| 2 | Determine budget ceiling (cost per chair × headcount) | Procurement | Budget line item | No‑exceed $24.19 M total; individual purchases ≤ $50,000 require competitive bidding. |
| 3 | Identify procurement path (formal RFP, informal quote, cooperative contract) | Procurement Manager | Procurement plan | Follow OSC procurement policy (see Comptroller’s Procurement Manual). |
| 4 | Issue a Request for Proposals (RFP) (scope, evaluation criteria, delivery schedule) | Procurement | RFP document & posting on the State Procurement Portal | State law requires public notice for purchases > $50,000. |
| 5 | Collect vendor submissions (price, product samples, warranty, sustainability certifications) | Vendors | Completed proposal packages | Must include proof of compliance with Connecticut Business & Tax Registration. |
| 6 | Score proposals (price 40%, ergonomics 30%, sustainability 20%, delivery 10%) | Evaluation Committee | Scoring matrix | Transparent scoring preserves audit trail. |
| 7 | Negotiate terms (price, warranty, maintenance) | Procurement + Legal | Signed Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) | Ensure contracts meet Comptroller’s risk‑management standards. |
| 8 | Award contract and publish award notice | Procurement | Contract award letter & public announcement | Failure to publish violates transparency statutes. |
| 9 | Execute delivery & installation (site inspection, handling, placement) | Facilities + Vendor | Chairs installed & verified | Installation must meet OSHA workplace safety requirements. |
| 10 | Conduct post‑installation review (user feedback, cost variance, compliance audit) | Facilities + Finance | Review report & lessons learned | Findings feed into future OSC procurement cycles. |
Vendor Evaluation Matrix
| Criterion | Weight | Scoring Range | Data Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unit Price | 40 % | 0‑100 | Quote per chair, volume discounts |
| Ergonomic Features | 30 % | 0‑100 | Specification sheet, third‑party ergonomics certifications |
| Sustainability | 20 % | 0‑100 | GREENGUARD, FSC, recycled‑content documentation |
| Delivery Lead‑time | 10 % | 0‑100 | Production schedule, shipping plan |
Total weighted score ≥ 85 qualifies a vendor for award.
Compliance & Documentation Checklist
- Procurement Authority – Verified that the OSC has delegated procurement power under the State Constitution.
- Competitive Bidding – RFP advertised for > $50,000 purchases; quotes secured for smaller orders.
- Legal Review – Contract terms vetted by the Attorney General’s office.
- Insurance & Bonding – Vendor proof of liability insurance (min. $1 M).
- Audit Trail – All correspondence, scoring sheets, and award decisions archived in the OSC procurement system.
- Environmental Compliance – Chairs meet Connecticut’s environmental procurement guidelines (e.g., ≥ 30 % recycled content).
Summary
Following the nine‑step checklist above ensures the Connecticut Office of the State Comptroller acquires ergonomic, cost‑effective chairs while maintaining full statutory compliance and public accountability. The guide leverages the OSC’s staff size, budget, and central location to set realistic cost targets and aligns each procurement action with the Comptroller’s oversight responsibilities. Use this framework as the backbone for any future office‑seating purchases across state agencies.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for osc chair Sourcing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for osc chair Sourcing
Scope: This section provides a B2B, USA/Europe-focused structure to understand cost drivers, price bands, and total cost of ownership (TCO) for standard ergonomic office task chairs with/without headrest, mid-to-high back mesh or fabric chairs, guest chairs, and stools. For high-spec and executive chairs, increase materials, ergonomics, and testing budget accordingly. Quantities are presented in bands to reflect typical procurement scales.
Notes:
– USA buyers: Consider state-level public procurement practices. Many states, including Connecticut, require formal solicitation and competitive awards. The Connecticut Office of the State Comptroller has centralized financial oversight for state operations (established 1786; ~256 FTE; operating expenses ~$24.2M; central office: 165 Capitol Avenue, Hartford, CT 06106-1775). If OSC-branded or compliance-driven procurement applies, align with those requirements.
– EU buyers: Confirm CE marking and EN standards. Include REACh and RoHS compliance declarations and ensure supplier declarations are available. VAT treatment and Incoterms are critical for landed cost.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Pricing framework and assumptions
Price bands below reflect FOB and EXW ranges. LCL/FCL and distance materially affect freight and duty/VAT.
| Chair Type | Materials | Base/Foam/Tilt | Upholstery | Wheels/Casters | Arms | Headrest | Packaging | Manufacturing Cost (USD, FOB) | Target Margin | Target Sell (USD, FOB) | Freight (per unit, USD) | EU Duty/VAT Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Task chair, mesh | Moderate | Basic tilt | Mesh fabric | Standard | 2D/3D optional | No | KD carton | 80–120 | 30–45% | 110–200 | 8–25 | Duty low; VAT 18–27% |
| Task chair, upholstered | Higher | Heavy-duty tilt | Fabric | Premium casters | 3D | Yes (optional) | KD + pallet | 120–200 | 30–45% | 170–350 | 10–35 | Duty moderate; VAT 18–27% |
| Guest chair (upholstered) | Higher | Static base | Fabric/leather | Standard | Armless/fixed arms | No | KD carton | 50–90 | 30–45% | 70–150 | 6–15 | Duty low; VAT 18–27% |
| Drafting stool | Moderate | Gas lift + footring | Fabric | Swivel base | 2D arms optional | No | KD carton | 60–100 | 30–45% | 90–170 | 8–20 | Duty low; VAT 18–27% |
| High-spec executive | Highest | Premium tilt/tilting seat | Leather/Alcantara | Premium casters | 4D fully adjustable | Yes | KD + pallet | 220–450 | 30–45% | 320–800 | 15–45 | Duty moderate; VAT 18–27% |
- Volumes: 1–100 units carry premium pricing (higher freight % per unit); 100–500 units reduce unit costs; 500–2,000 units unlock better tooling amortization and freight discounts; 2,000+ units justify SKU simplification and custom tooling.
Cost breakdown by source
- Materials: frame (steel/aluminum), mesh, upholstery (polyester/leather), plastics, arm assemblies, mechanism, casters, gas lift, screws/fasteners, packaging.
- Labor: cut-and-sew/mesh mounting, frame welding/powder coating, assembly, QC, packing.
- Logistics: LCL/FCL, drayage, insurance, customs clearance, duties/VAT, brokerage, in-country delivery.
Typical cost drivers
| Driver | Low-volume (1–100) | Mid-volume (100–500) | Scale-volume (500–2,000) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unit price | Premium (+20–40%) | Base | Discounted (−10–20%) |
| MOQ pressure | High | Moderate | Low |
| Tooling amort. | Per-unit high | Moderate | Low |
| Freight share | Higher per unit | Moderate | Lower per unit |
| QA burden | Higher rework risk | Balanced | Systematic, lower |
| Lead time | Long variability | Predictable | Predictable, shorter |
Procurement and compliance requirements (USA and EU)
| Region | Compliance & Documentation | Certification | Procurement Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| USA | Supplier registration, W-9, SAM registration (if federal/state funds), commercial invoice, packing list, COO, HTS code; COC/COO; safety data (not generally applicable to chairs), EN 1335 test reports (if requested), BIFMA claims (if used), warranty/return policy | ANSI/BIFMA (commonly referenced for office chairs), local/state procurement compliance | Competitive solicitation and award norms; align with state/agency policies. For Connecticut sourcing, account for centralized financial oversight and public procurement processes. |
| EU | CE marking where applicable, EN 1335 (A/B/C parts), REACh/SVHC declaration, RoHS, WEEE packaging waste registration, safety instructions, warranty terms | EN 1335, Flammability standards where applicable, REACh | Include VAT handling via Incoterms; confirm CE/EN standards and provide supplier declarations. DDP/DDU clarity critical for landed cost. |
Logistics cost model (illustrative FOB CN to USA/EU)
| Mode | Route | Volume Band | Freight per Unit (USD) | Drayage/Handling | Duty/VAT (USA/EU notes) | ETD/ETA | Risk Factors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCL sea | CN to US East | 1–100 | 25–45 | 10–20 | Duty 0–5.5% + sales tax | 35–45 days | Congestion, port delays |
| FCL 40’ | CN to US East | 100–500 | 6–10 | 15–30 | Duty 0–5.5% + sales tax | 25–35 days | Space, rate volatility |
| Air | CN to US | 1–100 | 35–80 | 5–10 | Duty 0–5.5% + sales tax | 7–14 days | Cost, capacity |
| LCL sea | CN to NL/DE | 1–100 | 20–35 | 8–15 | Duty 0–5.5% + VAT 18–27% | 28–38 days | EU customs, VAT |
| FCL 40’ | CN to NL/DE | 100–500 | 5–9 | 10–20 | Duty 0–5.5% + VAT 18–27% | 20–30 days | Strike, inspection |
| Air | CN to EU | 1–100 | 35–90 | 5–10 | Duty 0–5.5% + VAT 18–27% | 7–14 days | Premium |
Freight scales down with volume; drayage varies by port and forwarder. Insurance often 0.2–0.5% of goods value. LCL/FCL split can reduce per-unit freight by 40–70% at scale.
TCO over 5 years (per unit)
| Item | Typical Annualized Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Depreciation | 15–25% of purchase price | Depends on category and usage intensity |
| Maintenance/repair | $5–25 | Wheels/casters, arm adjustments, tilt mechanisms |
| Freight and handling | $3–10 | Redistributions, internal moves |
| Incidentals | $2–10 | Spare parts, warranty claims |
| Total TCO | Base + annualized totals | Higher in high-duty environments; warranty reduces variability |
- Budget cushion: 10–15% contingency for reorders, seasonal demand, or incidentals.
- Warranty: 2–5 years typical; longer terms increase supplier cost, often offset by lower replacement claims.
Pricing negotiation levers and savings tactics
- Tooling and fixtures: One-time amortization across volume lowers per-unit cost by 3–8% beyond 500 units.
- SKU rationalization: Standardize arm types and upholstery options to gain 5–15% savings.
- Multi-year frameworks: Commit volumes across 2–3 years for price protection and volume rebates.
- Alternate sourcing (dual sourcing): Reduce risk and enable competitive pricing; pilot 20–40% volumes with secondary vendor.
- Incoterms shift: Move from EXW to FOB or CIF to cut coordination cost; from DDP to DAP to share VAT exposure and streamline billing.
- Payment terms: 30/70, 40/60, or L/C basis can improve supplier flexibility and pricing alignment.
- Test standards alignment: Choose commonly met EN 1335/BIFMA tests to avoid bespoke lab runs; batch testing can lower per-unit certification cost.
Typical negotiation outcomes (indicative)
| Lever | Outcome | Savings Range |
|---|---|---|
| Volume uplift (2x) | Unit price down | 8–15% |
| SKU consolidation | Process simplification, less scrap | 5–12% |
| Incoterms optimization | Reduced admin/freight risk | 3–8% |
| Multi-year agreement | Price lock and rebates | 3–10% |
| Certification batching | Lower lab cost/unit | 2–5% |
Lead time impact on cost
- Express air adds $35–90 freight per unit and compresses lead times to 7–14 days; total cost increases ~15–35%.
- Ocean LCL/FCL reduces freight but lengthens lead time to 20–45 days; total cost decreases by 15–30%.
- Buffer stock or safety stock at destination reduces stockout costs; evaluate carrying cost vs service level.
Risk register
| Risk | Likelihood | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Freight volatility | High | Medium | Contract forwarders, flexible routing, insurance |
| Port congestion | Medium | High | LCL/FCL mix, alternate ports, time buffers |
| Compliance gaps | Low–Medium | High | Pre-award document checks; test reports batched |
| Supplier capacity shortfalls | Medium | High | Dual sourcing; capacity clause; pre-production pilots |
| FX exposure | Medium | Medium | Hedge or quote in USD/EUR; adjust price formula |
| Warranty spikes | Medium | Medium | Quality gates, pilot runs, warranty reserve |
Cost and pricing checklist for RFQ/RFP
- Specs: frame, mesh/upholstery, arms (adjustability), headrest, casters, gas lift, mechanism; EN 1335/BIFMA targets.
- Quantities and phasing: initial + optional quantities; delivery windows.
- MOQs and packaging: KD/E2E; palletization; labeling; barcodes.
- Incoterms and destination: USA vs EU; VAT/duty expectations; brokerage.
- Certification and documentation: EN 1335/CE, REACh/RoHS, WEEE; warranty and returns.
- Terms: price validity, payment, price adjustment clauses, volume rebates, performance guarantees.
- Quality: AQL, sample approvals, PPAP equivalent, inspection plans.
Quick calculators
- Landed unit cost (EXW, ex-works): Base price + freight + insurance + duty/VAT + drayage/handling + brokerage.
- Margin-adjusted sell price (FOB target): Manufacturing cost × (1 + target margin).
- TCO 5-year: Purchase price + (annual maintenance + freight + incidentals) × 5 + depreciation/lease expense.
If you can share the osc chair category and specs (materials, ergonomics, test targets), I’ll tailor the cost tables, logistics plan, and savings levers to your exact RFQ.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing osc chair With Other Solutions
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing osc chair With Other Solutions
Purpose
– Identify how osc chair stacks up against two commonly adopted alternatives in North America and the EU for governance, audit, and compliance workflows.
– Focus on fit, cost, risk, and delivery speed for mid-to-large enterprises and public-sector organizations.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Solutions in scope
– osc chair (focal product)
– Option A: Audit & Controls Platform (ACP) — large audit-driven suite
– Option B: Compliance Governance Suite (CGS) — lightweight modular platform
Assumptions and scope notes
– Typical buying criteria include: compliance readiness (SOC 2, ISO 27001, GDPR), integrations (HRIS/ERP/GRC/IdP), automation depth, EU data residency, multi-tenant security, workflow controls, and total cost to achieve compliance outcomes.
– “osc chair” claims to deliver end-to-end controls mapping with vendor-agnostic integrations, templated audit prep, and EU DC. Option A emphasizes audit readiness and breadth of control libraries. Option B emphasizes time-to-value and modularity.
– The analysis reflects current market norms; organizations should verify specific requirements via an RFP and security questionnaires.
Comparison matrix
| Dimension | osc chair | Option A (ACP) | Option B (CGS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compliance alignment | Strong: SOC 2 Type II readiness; alignment to ISO 27001 Annex A; robust GDPR tooling (record of processing, DPIAs, DSR workflows); evidence-ready workflows | Strong: broad control catalog (SOC 2/ISO/NIST); mature audit evidence collection and sampling | Solid: good baseline GDPR features; configurable controls; depends on modules selected |
| EU data residency | Yes: EU data centers; data transfer controls; SCC-ready | Mixed: US-centric tenancy; EU residency typically add-on | Available: depends on module; may require add-on fees |
| Security posture | Solid: modern multi-tenant, SSO/MFA, granular RBAC, encryption at rest/in transit, audit logging | Solid: enterprise-grade; strong admin controls; more setup complexity | Solid: modern SaaS; good UX; some advanced controls gated by higher tiers |
| Automation depth | Strong: evidence collection, policy-to-control mapping, automated control testing, notifications, risk scoring | Strong: deep audit automation; strong sampling and evidence lifecycle | Moderate-to-strong: good automation; some integrations require connectors/connectors add-ons |
| Integrations | Broad: HRIS (Workday, BambooHR, UKG), ERP (SAP, Oracle, NetSuite), GRC/IRM (ServiceNow IRM, Archer, OneTrust), IdP (Okta, Entra ID), ticketing (Jira/ServiceNow), email (Microsoft 365/Google Workspace) | Broad: ERP/GRC/IdP focus; some SaaS connectors are paid add-ons; complex setup for legacy | Moderate: common SaaS integrations; many via API; connector availability varies |
| Time-to-value | Fast: templates and mapping accelerate implementation | Moderate: more configuration and governance setup; longer for complex orgs | Fast: quick start kits; modular adoption; scaling up requires additional modules |
| Vendor lock-in | Low: open API, exportable artifacts, no proprietary control libraries | Moderate: ecosystem and catalogs encourage platform stickiness | Low-to-moderate: modular but licensing by module can limit flexibility |
| US public-sector fit | Good: configurable controls, audit trails, role-based access; verify FedRAMP if required | Strong: long history in audit-led programs | Good: flexible; requires review for state/local procurement needs |
| EU public-sector fit | Strong: EU DC, data governance features | Mixed: EU readiness depends on add-ons | Good: EU DC options; confirm data residency per module |
| Pricing model transparency | High: clear modules and per-user/seat pricing; volume discounts | Moderate: enterprise licensing; implementation and connector fees common | High: modular pricing; pay for what you use; additional cost for connectors |
| Total cost to achieve compliance outcomes | Competitive: templated controls reduce setup; fewer add-ons | Higher: more services and add-ons typical | Lower-to-moderate: lower entry cost; may require more add-ons for scale |
Analysis and guidance
-
Choose osc chair when speed, EU data residency, and clear pricing matter. If you need rapid alignment to SOC 2 and GDPR with modern identity and workflow controls and want minimal vendor lock-in, osc chair is often the fastest path to value.
-
Choose Option A (ACP) when audit-first programs dominate and you value deep audit capabilities, sampling, and large control catalogs over time-to-value. Expect a longer implementation and potential additional spend on connectors and professional services.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Choose Option B (CGS) when you want a quick start with a modular approach and predictable, transparent pricing. As your compliance program scales, verify that advanced controls, integrations, and EU residency are available in the modules you plan to adopt.
Practical next steps
– Issue an RFP or formal RFI focused on: EU data residency and transfer controls (SCCs, DPIAs), control libraries (SOC 2/ISO/NIST), integration catalog and APIs, SSO/MFA and RBAC depth, audit trail capabilities, implementation timelines, and total cost (licenses + services + connectors).
– Request three artifacts: security questionnaire response, sample control mapping for SOC 2 and ISO 27001 Annex A, and two customer references (one US, one EU).
– Pilot a critical use case (e.g., quarterly SOC 2 evidence or GDPR Article 30 records) with your two finalists to validate time-to-value and integration fit.
Limitations
– Specific vendor compliance certifications and data residency configurations can change rapidly; verify current attestations (e.g., SOC 2 Type II, ISO 27001) and regional data handling practices during due diligence.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for osc chair
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for OSC Chair
Note: “OSC” requires buyer clarification. Common interpretations used in procurement contexts are: (1) Office/Task/Conference swivel chair; (2) outdoor stack chair (OSC = Outdoor Stacking Chair). The properties below reflect both usage cases and the trade terminology you’ll encounter in B2B negotiations (USA and Europe).

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Core Technical Properties
Office/Task/Conference Swivel Chair
– Seat dimensions (mm/in) and seat shape (contoured/wave), backrest dimensions (W x H), lumbar support type (built-in/adjustable), headrest (if present).
– Range of seat height (mm/in) and adjustment mechanism (pneumatic cylinder class 3 or 4), tilt/recline angle and tension (Nm), synchro-tilt or balanced mechanism, multi-lock positions.
– Arm options (fixed/height/width/pivot/4D), arm pad material.
– Weight capacity (kg/lb) and occupant size class; stability (tip resistance per ANSI/BIFMA).
– Materials and finishes: upholstery (fabric/Vinyl/Leather/PU; antimicrobial finishes), shell/polymer material, frame/foot base material (aluminum/steel/PA+glass), caster type (hard/soft; low-scratch, ESD options).
– Warranty (years/cycles), warranty exclusions, serviceable parts list, replacement program.
Outdoor Stack Chair (OSC)
– Stacking capacity (chairs per stack), nesting space per chair (mm/in), stacking rail configuration.
– Seat and back materials (HDPE/polypropylene/composite; optional cushions).
– Finish and corrosion resistance: powder coat on steel/aluminum, UV stability, salt-spray corrosion resistance (ASTM B117), antimicrobial additives.
– Foot caps/sled base or four-legs; frame material and section thickness; surface temperature handling (material rating where relevant).
– Weather resistance: water ingress rating (IPX), UV rating (ASTM G154 cycle 1), mold and mildew resistance (ASTM D3273).
– Weight per chair and overall stack weight; weight capacity; safety standards alignment for public spaces (e.g., applicable versions of EN 581).
Standards and Compliance
USA (examples)
– ANSI/BIFMA X5.1 for task chairs; ANSI/BIFMA X5.4 for lounge/soft seating; applicable durability, stability, and flammability tests.
– ASTM F1857 for institutional ward chairs (if applicable); ASTM E84/UL 723 for surface burning characteristics of materials.
– CA TB 117-2013 upholstery flammability (USA market default; some states/kindergarten require CA TB 129).
– California Prop 65 (chemical exposure) disclosure if relevant.
Europe (examples)
– EN 1335 (task/office chairs) for workplace dimensions, safety, and strength.
– EN 581 for outdoor seating/tables (durability, corrosion, weather resistance).
– EN 1021-1/-2 (cigarette/match) and EN ISO 6941 (flame spread; textiles).
– REACH (EC 1907/2006) for substances; RoHS (2011/65/EU) for hazardous substances; WEEE (2012/19/EU) end-of-life.
– EN ISO 13485/ISO 13485 and EN ISO 14971 for medical devices where applicable.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
If the OSC chair is a physiotherapy “oscillation chair”:
– IEC 60601-1/-1-2 electrical safety and EMC; ISO 14971 risk management; IEC 60601-1-8 alarms; IEC 62304 software if applicable.
– Medical electrical device classification will drive technical documentation (e.g., MDR/CMDR/UKCA/CE).
Performance and Quality
- Test levels: durability cycles (back/seat tilt, arm load, casters), drop tests, static load, tip/stability, and cycle life (e.g., 240,000 cycles typical for task chairs).
- Acoustics (casters, mechanisms), surface ESD/ionization where specified, low VOC (ANSI/BIFMA e3 low-emitting products guidance).
- Lifecycle/maintenance: spare parts availability, repairability index, rebuild kits, cleaning/disinfection protocols.
Commercial and Trade Terminology
- MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity), MOQ per model/color/configuration, lead time (ETA/ETD), tooling costs, and set-up fees.
- Incoterms (FOB/CIF/DAP/DDP, per ICC 2020), freight class (e.g., NMFC for USA), packaging (wrapped, carton, palletization), cube and weight per unit.
- Price break tiers, annual rebate programs, blanket order terms, early-payment discount.
- OEM/ODM, custom RAL color, logo and brand marking options (embroidery, etching, screen print).
- Documentation pack: specification sheet, test reports, SDS/MCD (material composition), declaration of conformity, certificate list (ISO 9001/14001).
- Warranty terms (period and exclusions), RMA (return merchandise authorization) policy and time windows, spares stock and service SLA.
- Compliance documentation specific to USA/EU markets: e.g., ANSI/BIFMA certificates, EN certificates, Prop 65, REACH, RoHS, WEEE statements.
Packaging, Logistics, and Sustainability
- Packaging details: carton dimensions, protective materials, master cartons per pallet, pallet type, stack height limit, drop-test rating.
- Logistics: palletization strategy (e.g., 20–40% better utilization in nesting furniture), weight per pallet, stacking/racking restrictions.
- Sustainability: recycled content (post-consumer/industrial), recycled polyester textiles, FSC for wood-based components, low formaldehyde materials, end-of-life take-back.
- Regulatory: EPP/expanded polypropylene packaging, VOC labeling per local law, producer responsibility programs in Europe.
Testing and Documentation Checklist (B2B)
- Model-specific spec sheet and engineering drawing.
- Independent test certificates for cited standards (USA/EU).
- Material safety documentation and chemical disclosure (Prop 65, REACH).
- Quality certification (ISO 9001), environmental certification (ISO 14001), and low-emitting material conformance (e.g., GREENGUARD or equivalent).
- Declaration of Conformity (US/Europe), certificates for medical interpretation if applicable.
- Instructions for use, maintenance instructions, and warranty terms.
Glossary
– MOQ: Minimum order quantity per SKU/configuration.
– OEM/ODM: Original equipment manufacturer; original design manufacturer.
– Incoterms: Commercial terms defining delivery/cost/risk transfer points.
– RAL: Color standardization system for coatings (Europa).
– WEEE: EU Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Directive.
– Prop 65: California Proposition 65 warning requirements (USA).
– GREENGUARD: Program for low-emitting products (material screening).
If you confirm the OSC chair is an office swivel variant or an outdoor stacking design (or a medical oscillation device), I will tailor the specifications and test matrix to the applicable standards and provide a quote-ready commercial template.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the osc chair Sector
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the osc chair Sector
This section outlines the market drivers, sustainability priorities, and sourcing strategies relevant to USA and Europe. It reflects governance structures common to occupational safety and compliance functions (represented by the role’s decision-making chair), procurement norms, and evolving ESG requirements.
Core Market Dynamics
| Dynamic | Implications for USA | Implications for Europe |
|---|---|---|
| Regulatory complexity | Divergent OSHA standards and state-level variants (e.g., California/OSHA), frequent updates | EU directives and national laws (e.g., UK HSE, Germany BG), frequent updates |
| Cost-to-comply and volatility | Sustained pressure on OPEX; price sensitivity and demand for service-level guarantees | Emphasis on documentation, training, and cross-border compliance; service SLAs are critical |
| Supply chain resilience | Preference for diversified suppliers and multi-source options | Alignment with EU procurement law (e.g., tendering, fairness); risk controls for supplier continuity |
| Inflation and wage pressures | Rising training/auditor costs; preference for TCO over unit cost | Similar cost pressures; increased scrutiny on long-term value and transparency |
| Vendor consolidation | Scale advantages; risk of single points of failure | Competitive bidding and transparency; consolidation with guardrails and auditability |
Sourcing Trends and Best Practices
- Multi-source and modularization
- Avoid single-point failures; mix core suppliers for volume and niche partners for specialized tasks.
-
Modularize services (e.g., training, audits, incident management) to enable flexible re-sourcing.
-
Localization and nearshoring
- USA: Balance between national providers for scale and regional partners for responsiveness.
-
Europe: Favor local delivery within key markets to reduce cross-border risk and enhance language/cultural fit.
-
Data-driven procurement
-
Centralize vendor data (compliance, pricing, SLAs) and use performance analytics to drive renewals.
-
Outcome-based contracting
- Tie fees to measurable outcomes (reduced incident rates, audit pass rates, timely training completion).
-
Include penalties or credits tied to SLA and incident metrics.
-
Risk management integration
- Require continuity plans, BCP/DR coverage, and insurance attestations from all suppliers.
-
Run tabletop exercises involving key vendors annually.
-
Compliance-forward language
- Embed data privacy, conflict-of-interest controls, and audit rights.
- Align with competitive and fair-procurement practices; avoid exclusivity.
Sustainability and ESG Priorities
| Priority | Action | Measurement |
|---|---|---|
| Scope 1–3 emissions | Require suppliers to publish targets and reduce logistics emissions | % suppliers with SBTi/verified targets; emissions intensity YoY change |
| Circularity | Prefer reusable, refurbishable equipment and vendor take-back programs | Reuse/refurbish rate; waste diverted from landfill (%) |
| Social compliance | Supplier code of conduct with audits for labor rights and safety | Audit pass rates; corrective action closures |
| Supplier diversity | Target minority-owned, women-owned, and SME participation | Share of spend with diverse suppliers |
| Local community impact | Favor suppliers with local hiring/training commitments | Number of local hires; training hours delivered |
Regional Notes
- USA
- States influence compliance scope; ensure vendor alignment with both OSHA and relevant state variants.
- Public-sector procurement norms favor fairness, transparency, and sometimes set-asides.
-
Expect stricter TCO scrutiny and outcome-based metrics tied to incident reduction.
-
Europe
- Competitive tendering and documentation rigor are expected.
- Focus on GDPR compliance and cross-border data transfer controls.
- Stronger emphasis on audited sustainability claims and supplier social compliance.
KPIs for osc chair Decision-Making
| Metric | Definition | Target |
|---|---|---|
| Incident rate reduction | % decrease in OSHA-recordable incidents | ≥ 10–15% year-over-year |
| Audit pass rate | % audits with no major findings | ≥ 95% |
| Training completion | % of staff completing mandatory training | ≥ 98% |
| Vendor SLA compliance | % of SLAs met (on-time, within scope) | ≥ 95% |
| TCO index | Normalized cost per compliance unit | ≤ prior-year baseline |
| Sustainability index | Composite score (emissions, circularity, social compliance) | ≥ threshold improvement YoY |
| Supplier performance rating | Avg. vendor score across delivery, quality, risk | ≥ 4.2/5 |
Note on reference context: The role of a chair in an occupational safety/compliance governance context intersects with public-sector oversight functions like those performed by the Connecticut Office of the State Comptroller, where benefits administration and financial controls shape compliance expectations and procurement requirements.
This framing enables USA and Europe procurement and compliance leads to navigate evolving cost structures, regulatory demands, and sustainability goals while maintaining performance and resilience.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of osc chair
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of osc chair
1) What is the osc chair and in which categories does it qualify?
– Definition: The osc chair is an office/operator workstation chair designed for multi-hour seated tasks (task chair, drafting/stool variants, and executive models are available).
– USA classification: Typical categories under commercial office furniture specifications; public sector buyers often source via catalogs referencing BIFMA performance standards.
– EU classification: Category 2 office chair under EN 1335 (general-purpose office task chair) and EN 1728 seating performance; drafting/stools are categorized separately (Category 3).
2) What compliance and safety standards does the osc chair meet?
– USA: Meets ANSI/BIFMA X5.1 and applicable ASTM performance criteria; GREENGUARD Gold certification is common for low-emitting finishes and foams (verify SKU-level claims).
– EU: Conforms to EN 1335 (ergonomics, safety, durability), EN 1728 (functional tests), and EN 1021/BS 5852 (cal. 117) ignitability standards for upholstery foam; CE marking is standard under MDR for seating components classified under the Machinery Directive (or other relevant directive, e.g., FPR MD; verify at SKU level).
– Materials: FSC-certified wood components available; PVC-free upholstery options available; lead content complies with CPSIA/RoHS and REACH SVHC limits; California TB 117-2013 equivalent ignitability and CAL-117 (where applicable) are supported.
3) Can the osc chair be used in public sector, education, healthcare, and critical environments?
– Public sector/education: Standard task and drafting variants meet commercial office criteria; verify public procurement codes and regional contract requirements before awarding.
– Healthcare/hygiene-sensitive areas: Materials and finishes support hospital-grade cleaning; specify antimicrobial textiles and PVC-free options where required; confirm EN 12757 (antimicrobial efficacy) and relevant antimicrobial standards on request.
– Safety-critical environments: Select models with anti-static casters (ISO 6356) and static-dissipative upholstery options; coordinate with your facilities’ ESD protocols.
4) What ergonomic features are included and what evidence supports performance?
– Ergonomics: Height, lumbar, seat depth, armrests (width/height/rotate/pivot), and tilt/tension adjustments; drafting models include extended height ranges; tested per EN 1728 and BIFMA tests for stability, durability, and fatigue.
– Warranty: 10-year limited warranty on frame and mechanism; 5-year on gas lifts, casters, and arm hardware; 2-year on upholstery and foam (normal wear excepted).
5) What customization and configuration options are available?
– Finishes: Powder-coat (graphite, silver, black), anodized, and wood veneer frames; steel, aluminum, and nylon bases.
– Upholstery: 300+ textiles including flame-barrier FR treatments; PVC-free, recycled, and rapidly renewable options; stitched piping.
– Mechanisms: Knee-tilt, synchro, weight-activated tilt, multi-lock; seat depth adjustment; adjustable lumbar; headrest options.
– Armrests: Fixed, height-adjustable, 4D, and loop arms; arm pads in urethane, soft-touch, and silicone; soft-touch glides on legs (for hard floors).
– Casters: Soft-floor (non-marring), hard-floor (polyurethane), locking, and anti-static; ESD paths available in select models.
6) What are the order quantities, lead times, logistics, and delivery terms?
– MOQ: 10 units per SKU; mixed SKUs welcome to hit MOQ.
– Lead times: 4–6 weeks ex works for standard configurations; 8–10 weeks for custom upholstery or finishes; pilot orders and samples available.
– Logistics: FOB/EXW; freight class 70 for chairs; mixed SKU palletization; drop-shipping supported in USA and EU.
– Packaging: Double-wall carton and poly bag; custom packaging for high-security or educational facilities (e.g., bar-coded tags) on request.
– HS codes: Provided in pro forma invoice; buyer must verify final classification.
7) Which certifications and compliance documents are provided?
– Documentation: Assembly guide (multi-language), CAD/BIM files (DWG/RVT/IFC), cleaning and maintenance instructions, warranty certificate, Declaration of Performance (DOP) for relevant directives, static test reports (EN 1728, ISO 6356), and fire test reports for upholstered variants (EN 1021/BS 5852, Cal TB 117-2013 equivalent).
– Health and environment: VOC test reports for finishes and adhesives; GREENGUARD Gold and EN 16516 emissions reports upon request.
– Country-specific: If used in healthcare or government projects, submit facility-specific requirements for QA documentation and inspection procedures.
8) What is the warranty, and what support is available?
– Warranty: 10 years frame/mechanism; 5 years gas lifts/casters/arm hardware; 2 years upholstery/foam; coverage excludes abuse, misuse, and unauthorized modifications.
– Support: Dedicated account manager; rapid parts program (spare parts stocked for 7 years post-discontinuation); no-fault replacement on manufacturing defects within 90 days; optional service contracts include on-site assembly, furniture refresh scheduling, and WEEE/ROHS-compliant recycling support (EU) and recycling coordination (USA).
– Returns: Returnable within 30 days for standard models in saleable condition; restocking fees and return freight apply to custom finishes/patterns; cross-docking available in USA and EU for time-sensitive deployments.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for osc chair
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook (OSC Chair)
Strategic sourcing succeeds when governance is strong and execution is data‑driven. The OSC chair sets direction, owns risk appetite, and ensures transparent decisions—anchored in policy and measurable value. The Connecticut Office of the State Comptroller underscores the importance of stewardship and transparency, providing a governance baseline relevant to any procurement leader.
Near‑term value is realized through rigorous category management, pre‑award transparency, and post‑award analytics. A clear decision framework, supplier competition, and contract compliance drive both cost and risk outcomes, while supplier diversity and sustainability expand opportunity without compromising performance.
A practical outlook for the next two quarters includes:
– Establish a sourcing council and cadence
– Prioritize top spend categories and define KPIs
– Standardize bidding and evaluation templates
– Introduce should‑cost benchmarking and total cost modeling
– Strengthen contract lifecycle management and vendor scorecards
Expected outcomes include measurable savings, reduced cycle times, lower risk exposure, and demonstrable governance. The OSC chair’s role is decisive: enable teams, set accountability, and communicate value transparently to stakeholders.
Table: Key metrics and targets
| Metric | Baseline | Target | Measurement frequency |
|—|—:|—:|—|
| Spend under management | N/A | ≥ 85% | Quarterly |
| Cost savings (hard) | N/A | 8–12% of addressed spend | Quarterly |
| RFP lead time | Current state | −30% | Monthly |
| Compliance rate (post-award) | N/A | ≥ 95% | Monthly |
| Supplier diversity spend | Current state | +20% | Quarterly |
| ESG/Scope 3 supplier coverage | Current state | +25% | Quarterly |
With disciplined governance and clear accountability, the OSC chair translates strategy into results.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided is for informational purposes only. B2B buyers must conduct their own due diligence.