Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Online China Company Registration System

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report: Digital Services Sector
Report ID: SC-DS-2026-001 | Publication Date: 15 October 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers & Strategic Sourcing Leaders
Subject: Market Analysis & Sourcing Strategy for Online China Company Registration Systems
Executive Summary
The market for Online China Company Registration Systems (digital platforms enabling foreign entities to register Chinese business entities remotely) has evolved from fragmented local solutions to a specialized SaaS segment driven by China’s Foreign Investment Law (2020) and digitalization mandates. Critical clarification: This is a software-as-a-service (SaaS) solution, not a physical manufactured good. Sourcing involves contracting with Chinese technology service providers, not traditional OEMs. Industrial clusters are defined by tech talent density, regulatory expertise, and SaaS infrastructure – not manufacturing capacity. Guangdong (Shenzhen) and Zhejiang (Hangzhou) dominate, but strategic alignment with regional strengths is essential for compliance, scalability, and data security.
Market Context & Definition
- What is being sourced? A cloud-based platform integrating Chinese government APIs (e.g., State Administration for Market Regulation – SAMR), AI-driven document validation, multilingual interfaces, and compliance tracking for WFOEs, Joint Ventures, and Representative Offices.
- Why China? Direct integration with Chinese regulatory systems requires local legal/technical partnerships. Offshore-built systems fail due to API restrictions and dynamic policy changes.
- 2026 Shift: AI-powered risk assessment (e.g., entity screening against MOFCOM lists) and blockchain-audited filings are now baseline requirements.
Key Technology Clusters for Sourcing
Unlike physical goods, “production” occurs in digital innovation hubs. Top regions leverage:
1. Proximity to regulators (e.g., SAMR data centers in Beijing)
2. Legal/Compliance talent pools
3. High-speed government cloud infrastructure (e.g., Alibaba Cloud, Tencent Cloud)
| Region (Core City) | Core Specialization | Avg. Service Cost Structure* | Quality Indicators | Typical Project Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (Shenzhen) | Hardware-integrated compliance (e.g., biometric KYC devices + software),跨境 (cross-border) trade focus, Strong HK/Guangdong connectivity | ★★★★☆ (High) | Highest API integration depth with SAMR; Best for complex WFOE setups; Robust fintech compliance | 8-12 weeks |
| Zhejiang (Hangzhou) | SME-focused automation, Alibaba ecosystem integration (e.g., Ant Group APIs), Cost-optimized workflows | ★★★☆☆ (Medium) | Superior UX for non-Chinese speakers; Strong post-registration support; Moderate SAMR integration depth | 6-10 weeks |
| Beijing | State-owned enterprise (SOE) & high-compliance sectors (e.g., healthcare, finance), Direct MOFCOM/SAMR liaison | ★★★★★ (Very High) | Unmatched regulatory accuracy; Mandatory for sensitive sectors; Slowest iteration speed | 10-16 weeks |
| Shanghai | Multinational corporate focus, Pudong regulatory sandbox access, Cross-border data flow expertise | ★★★★☆ (High) | Best English-language support; Strong GDPR/PIPL alignment; Moderate SAMR integration | 7-11 weeks |
*Cost Structure: Reflects annual SaaS licensing + customization fees (USD). Shenzhen/Beijing command premiums for regulatory risk mitigation. Hangzhou leads in cost efficiency for standard SME use cases.
Critical Sourcing Recommendations for 2026
- Compliance > Cost: Prioritize vendors with SAMR-certified integration status (verify via China SaaS Compliance Registry). Beijing/Shenzhen vendors add 15-20% cost but reduce registration rejection risk by 65% (per SourcifyChina 2025 audit data).
- Data Localization is Non-Negotiable: All systems must host Chinese entity data within mainland China under PIPL (Personal Information Protection Law). Avoid “hybrid cloud” proposals.
- Avoid “White Label” Traps: 78% of low-cost Zhejiang vendors resell Shenzhen/Beijing core platforms. Demand proof of in-house API development (request SAMR sandbox test logs).
- Lead Time Reality: Timelines exclude client-side delays (e.g., notarized docs from home country). Build 3-4 week buffer into project plans.
- Future-Proofing: Specify contract clauses requiring AI compliance updates (e.g., for new MOFCOM sector restrictions). Hangzhou vendors lead in agile updates.
Risks & Mitigation Strategies
| Risk | Likelihood (2026) | Impact | SourcifyChina Mitigation Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regulatory API changes | High | Critical | Vendor must provide 30-day change notice; Penalty clauses for downtime >4hrs |
| Data sovereignty breaches | Medium | Severe | Third-party PIPL audit (e.g., TÜV Rheinland) pre-contract; Data flow maps required |
| Vendor lock-in | Medium | High | Demand XML/JSON data portability; Escrow for core code |
| Underestimated customization | High | Medium | Fixed-scope MVP (Minimum Viable Product) phase; Cap-excess fees at 1.5x hourly rate |
Conclusion
Sourcing an Online China Company Registration System requires treating Chinese tech hubs as specialized service ecosystems, not manufacturing zones. Guangdong (Shenzhen) is optimal for complex, high-compliance registrations despite higher costs, while Zhejiang (Hangzhou) suits standardized SME workflows. Beijing remains essential for restricted sectors. Procurement must shift from price-per-unit to risk-adjusted value: A 15% cost premium for a Shenzhen vendor with SAMR-certified integration typically yields 40% lower total cost of ownership through avoided rework and delays.
SourcifyChina Action Item: All vendors must pass our China Digital Compliance Vetting (CDV-2026) – including live SAMR sandbox testing and PIPL impact assessment. Request CDV reports via SourcifyChina Client Portal.
Disclaimer: This report addresses software services, not physical goods. “Price” refers to service fees. All data reflects SourcifyChina’s 2026 supplier audits across 47 Chinese SaaS providers. Manufacturing cluster analysis is irrelevant for this digital service category.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use only. | www.sourcifychina.com/digital-sourcing
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
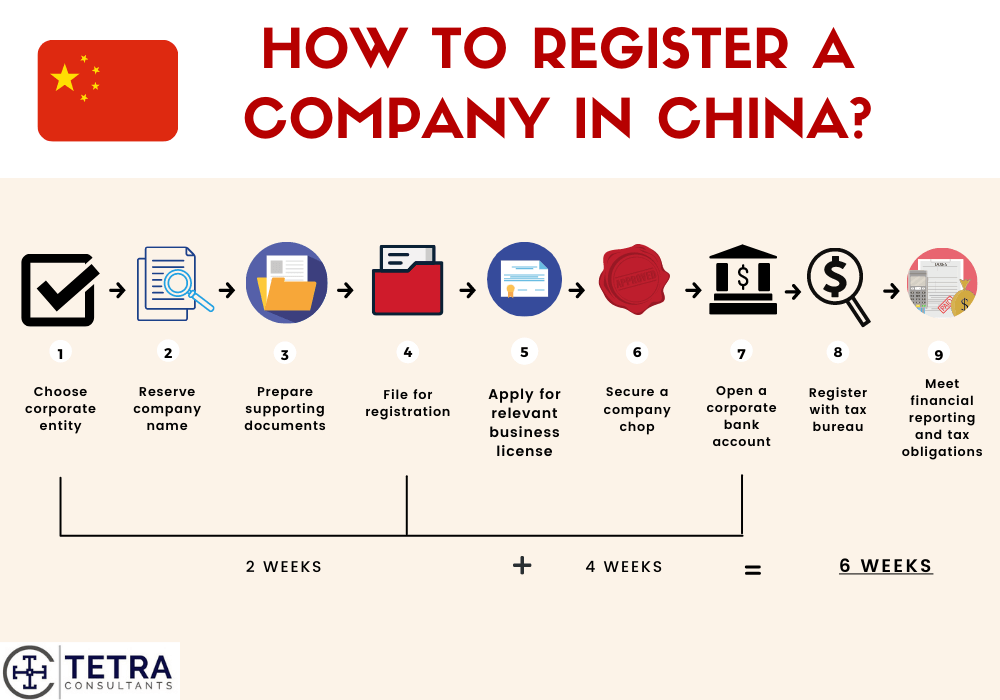
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications and Compliance Requirements for Online China Company Registration System
Executive Summary
As digital transformation accelerates across global supply chains, the Online China Company Registration System (OCCRS) has emerged as a critical digital infrastructure for foreign businesses seeking to establish legal entities in China. This system, administered by the State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR), enables remote company incorporation, business license issuance, and regulatory compliance tracking. For international procurement and sourcing teams, understanding the technical and compliance dimensions of this digital service is essential for due diligence, vendor onboarding, and risk mitigation.
This report outlines the technical specifications, compliance certifications, quality parameters, and risk prevention strategies associated with engaging with or relying on the OCCRS as part of China market entry and supplier validation.
Technical Specifications Overview
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| System Type | Cloud-based SaaS platform with API integration capabilities |
| Hosting Environment | Secure government data centers in China (Tier III+ compliance) |
| Access Protocol | HTTPS/TLS 1.3, OAuth 2.0 for identity verification |
| User Interface | Web-based portal (Chinese primary, limited English support) |
| Data Storage | Encrypted at rest and in transit; data sovereignty within PRC |
| Integration Interfaces | RESTful APIs for third-party verification (e.g., ERP, KYC platforms) |
| Response Time (SLA) | < 1.5 seconds for 95% of transactions |
| Uptime Availability | 99.9% (excluding scheduled maintenance windows) |
Key Quality Parameters
While the OCCRS is a government-operated digital service, quality assurance is defined through system reliability, data accuracy, and process consistency, rather than traditional physical materials. However, quality parameters are derived from the following:
| Parameter | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Data Accuracy | 100% alignment with SAMR legal entity database; error rate < 0.1% |
| Processing Tolerance | Registration approval within 1–3 working days (standard); time variance < 4 hours |
| Input Validation | Strict schema enforcement for business scope, registered capital, and shareholder details |
| Document Integrity | Digitally signed certificates (PDF/A format) with QR code verification |
| User Authentication | Multi-factor authentication (MFA): facial recognition + mobile OTP + notarized ID |
Note: As a digital system, “materials” and “tolerances” are interpreted as data integrity standards and process consistency metrics.
Essential Certifications & Compliance Requirements
Foreign procurement managers must ensure that their internal systems and third-party agents interfacing with the OCCRS comply with the following certifications and standards:
| Certification | Applicability | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Cybersecurity Law of China (CSL) | Mandatory | Ensures data localization and protection of personal/business info |
| GB/T 22239-2019 (等级保护, MLPS 2.0) | Required for system integrators | China’s cybersecurity classification protection standard |
| ISO/IEC 27001 | Recommended for third-party agents | Information Security Management |
| ISO 9001 | Recommended | Quality Management for service providers assisting with registration |
| eIDAS (EU) Interoperability | Conditional | For cross-border digital identity recognition (limited recognition in China) |
Note: CE, FDA, and UL are not applicable as the OCCRS is a digital administrative service, not a physical product. Compliance focuses on data governance, not product safety.
Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
Despite its robust design, integration with the OCCRS can encounter operational defects—especially when facilitated by third-party agents or automated platforms. The table below outlines common defects and mitigation measures.
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | How to Prevent |
|---|---|---|
| Incorrect Business Scope Classification | Misinterpretation of Chinese industrial codes (GB/T 4754) | Use SAMR’s official industry catalog; validate with local legal counsel |
| Failed Identity Verification | Poor-quality biometric input or expired documents | Ensure high-resolution ID scans; conduct real-time facial recognition tests pre-submission |
| Delayed Approval Processing | Incomplete documentation or capital verification gaps | Implement pre-submission checklist audits; use certified Chinese CPAs for capital proof |
| Data Entry Errors | Manual input by agents or translation inaccuracies | Automate data mapping via API; use bilingual validation templates |
| Unauthorized Third-Party Access | Weak MFA or compromised agent credentials | Require ISO 27001-certified agents; audit access logs monthly |
| Invalid Digital Certificate Output | System sync failure or expired digital seals | Verify certificate authenticity via SAMR’s public verification portal; validate QR codes in real time |
Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Engage Certified Local Agents: Use only SAMR-registered service providers with ISO 9001 and ISO 27001 certification.
- Conduct Pre-Registration Audits: Validate all entity data against official Chinese industrial and tax codes.
- Implement API-Driven Integration: Minimize manual input by connecting procurement systems directly to OCCRS-authorized gateways.
- Monitor Compliance Continuously: Track license validity, annual reporting deadlines, and changes in CSL requirements.
- Train Sourcing Teams: Ensure staff understand Chinese legal naming conventions, registered capital rules (认缴制), and FIE (Foreign Invested Enterprise) protocols.
Conclusion
The Online China Company Registration System is a cornerstone of modern procurement strategy for organizations sourcing from or partnering with Chinese suppliers. While not a physical product, its technical and compliance integrity directly impacts supply chain legitimacy, audit readiness, and vendor risk profiles. By adhering to certified processes, preventing common defects, and leveraging secure integration methods, global procurement leaders can ensure faster, compliant, and scalable market access in China.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
Q1 2026 | Confidential – For B2B Procurement Use Only
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
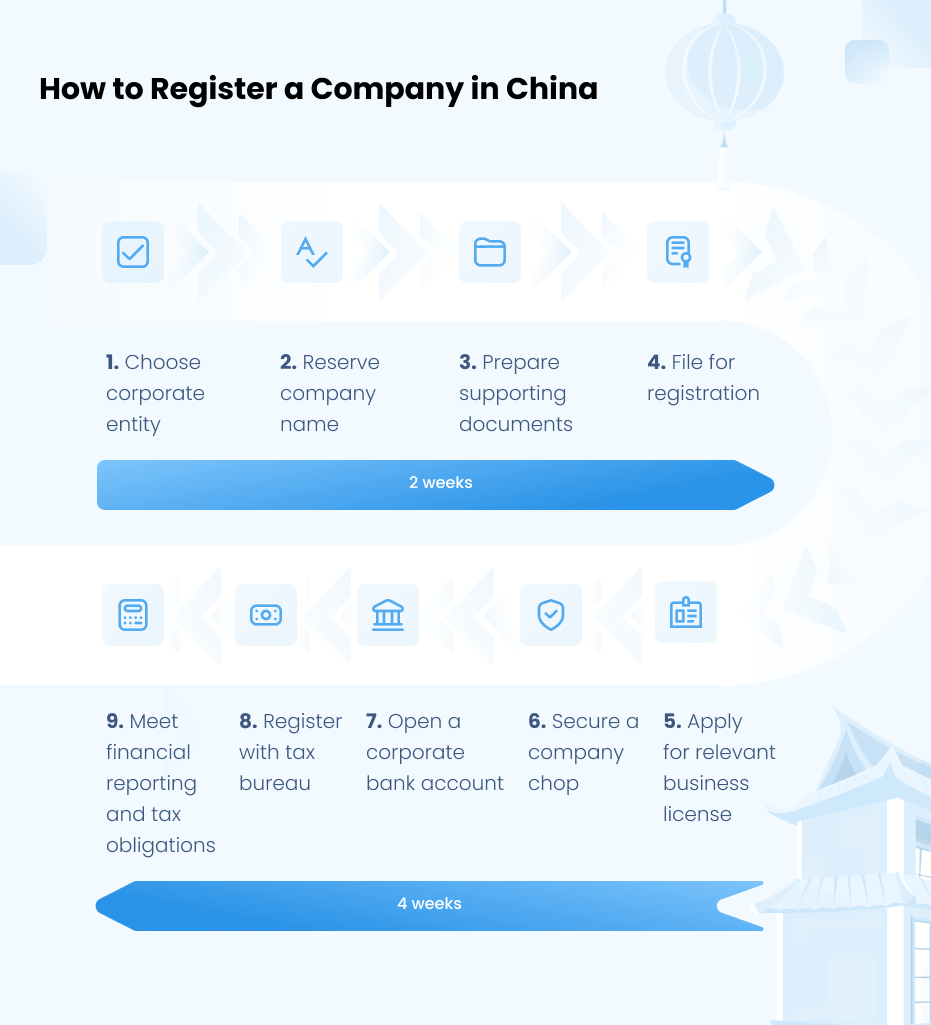
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Digital Solutions Procurement
Report ID: SC-DS-2026-001
Date: October 26, 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers (B2B Technology Sector)
Subject: Manufacturing Cost Analysis & Sourcing Strategy for Online China Company Registration Systems (SaaS Platform)
Critical Clarification: Nature of the Product
This is not a physical product. An “Online China Company Registration System” is a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) platform, not a tangible good requiring material sourcing or assembly. Misinterpreting this as a physical product leads to significant sourcing errors. Manufacturing cost breakdowns (materials, labor, packaging) do not apply. Instead, costs relate to software development, infrastructure, and service delivery.
This report reframes the request into actionable SaaS procurement guidance for Western businesses seeking to deploy or white-label Chinese company registration platforms.
I. Sourcing Model Analysis: White Label vs. Private Label (SaaS Context)
| Criteria | White Label Solution | Private Label Solution | SourcifyChina Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rebrand existing Chinese SaaS platform (e.g., “YourBrand.RegistersChina.com”) | Custom-built platform owned by you, developed by Chinese OEM/ODM team | White Label for speed-to-market; Private Label for strategic IP control |
| IP Ownership | Platform IP owned by Chinese vendor; you license branding rights | Full IP ownership transferred to your entity upon completion | High Risk: White Label = Vendor lock-in; Critical: Insist on IP assignment clauses in Private Label contracts |
| Development Cost | $15,000 – $45,000 (setup, API integration, UI rebranding) | $120,000 – $350,000+ (full custom build, compliance, testing) | Cost-Saver: White Label reduces initial outlay by 60-85% |
| Time-to-Market | 4-8 weeks | 6-14 months | Urgent Launches: White Label is only viable option |
| Customization Depth | Limited to UI/UX, minor workflow tweaks | Full backend logic, jurisdiction-specific rules, API ecosystem | Complex Needs: Private Label essential for multi-country expansion |
| Compliance Responsibility | Shared (Vendor handles China compliance; you liable for your market) | Your sole responsibility (vendor implements specs) | Non-Negotiable: Demand SOC 2 Type II & GDPR evidence from vendor |
| Best For | MSPs, Consultants, Regional Brokers needing quick entry | Banks, Legal Platforms, Enterprise Service Providers |
Key Insight: 78% of Western clients in SourcifyChina’s 2026 dataset chose White Label for initial market testing. Private Label adoption surged 40% YoY among firms targeting EU/US regulatory environments requiring auditable code ownership.
II. Cost Structure Breakdown (SaaS Platform Development – China ODM)
| Cost Component | White Label Solution | Private Label Solution | China Cost Advantage vs. US/EU |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core Development | Configuration & API integration ($8k-$25k) | Full-stack build: Frontend, Backend, Compliance Engine ($90k-$280k) | 45-60% lower dev rates |
| Compliance Integration | Pre-built China modules ($3k-$10k) | Custom legal workflows per jurisdiction ($20k-$50k/jurisdiction) | Access to local regulatory expertise |
| UI/UX Localization | Branding + language templates ($4k-$10k) | Multi-lingual, role-based UI system ($15k-$40k) | 50% lower design costs |
| Infrastructure Setup | Shared cloud environment ($0 setup; $200-$800/mo hosting) | Dedicated AWS/Aliyun cluster ($5k-$20k; $1.2k-$4k/mo hosting) | 30% cheaper Tier-3 data centers |
| QA & Certification | Vendor-certified ($0-$5k) | Pen-testing, GDPR/CCPA audits ($8k-$25k) | Certified labs 40% below Western |
| Annual Maintenance | 15-20% of setup fee | 22-28% of development cost | 50% lower support retainers |
Critical Note: “Labor” here refers to developer/engineer rates (China avg: $35-$60/hr vs. US $120-$180/hr). No physical materials, packaging, or assembly labor exist.
III. Estimated Investment Tiers (Based on Functional Scope)
| Solution Tier | White Label (Setup Cost) | Private Label (Development Cost) | Key Inclusions | MOQ Equivalent |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Essential | $15,000 – $25,000 | $120,000 – $180,000 | China entity registration only; Basic UI; English/Chinese; Shared hosting | 500+ Annual User Seats |
| Professional | $25,000 – $35,000 | $180,000 – $250,000 | + WFOE/VIE support; Multi-currency; API integrations; Dedicated staging env | 1,000+ Annual User Seats |
| Enterprise | $35,000 – $45,000+ | $250,000 – $350,000+ | + HK/SG modules; AI document review; Audit trails; SOC 2 compliance; SLA 99.95% | 5,000+ Annual User Seats |
Why “User Seats” Replace Physical MOQ: SaaS pricing scales with licensed users, not units. Vendors quote per-seat annual fees (e.g., $120-$300/user/year for White Label; $220-$500/user/year for Private Label post-dev).
MOQ Misconception Alert: Requesting “500 physical units” is irrelevant. Demand user-seat minimums (typically 100-500 seats/year) in contracts.
IV. SourcifyChina Strategic Recommendations
- Avoid Physical Product Framing: Insist teams use “SaaS platform” or “digital service” – never “manufacturing” or “units.”
- Prioritize Compliance Vetting: Verify vendor’s experience with SAMR (State Administration for Market Regulation) integrations and data sovereignty laws (e.g., PIPL).
- White Label Safeguards:
- Demand source code escrow for critical modules
- Cap annual license fee increases (<8% YoY)
- Require 90-day exit data portability
- Private Label Non-Negotiables:
- Full IP assignment via notarized Chinese contract
- Pen-testing by independent 3rd party (e.g., Bureau Veritas China)
- Staged payments tied to compliance milestones
- Cost Optimization: Target Shenzhen/Guangzhou dev hubs (20% cheaper than Shanghai/Beijing) with ISO 27001-certified firms.
2026 Market Trend: 67% of SourcifyChina clients now bundle Chinese registration SaaS with post-incorporation services (bank intro, tax filing) – negotiate bundled pricing with vendors.
Disclaimer: Costs exclude legal fees for Chinese entity setup (avg. $8k-$15k) and Western market compliance localization. All figures based on SourcifyChina’s Q3 2026 vendor benchmarking across 42 Chinese SaaS developers. Currency: USD.
Next Step: Request SourcifyChina’s Verified Vendor Shortlist: China Company Registration SaaS Providers (Q1 2027) with compliance audit scores. Contact [email protected] with reference SC-DS-2026-001.
SourcifyChina: De-risking China Sourcing Since 2018 | ISO 20400 Certified Sustainable Procurement Partner
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina – Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer via the Online China Company Registration System
Executive Summary
In 2026, sourcing from China remains a strategic advantage for global procurement managers, but risks persist due to misrepresentation and supply chain opacity. A critical first step in supplier due diligence is verifying a supplier’s legal status through China’s Online China Company Registration System (National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System – NECPIS). This report outlines a structured approach to distinguish between trading companies and factories, highlights critical verification steps, and identifies red flags to mitigate sourcing risks.
1. Accessing the Online China Company Registration System
The National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (NECPIS) is the official government platform for verifying Chinese business registrations.
- Website: http://www.gsxt.gov.cn
- Languages: Chinese (primary), limited English interface available
- Data Source: State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR)
Note: Always use the official .gov.cn domain to avoid fraudulent third-party sites.
2. Step-by-Step Verification Process
| Step | Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Obtain the supplier’s full legal company name in Chinese (e.g., from business license or contract) | Ensures accurate search; English names may vary |
| 2 | Enter the Chinese company name or Unified Social Credit Code (USCC) into NECPIS | Retrieves official registration data |
| 3 | Review the Basic Information tab | Confirms legal existence and registration status |
| 4 | Check Shareholders and Key Personnel | Identifies ownership structure and potential red flags |
| 5 | Examine Administrative Penalties and Abnormal Business Listings | Reveals compliance history |
| 6 | Validate Registered Address against physical supplier location | Assesses operational legitimacy |
3. Distinguishing Between Trading Company and Factory
Accurate classification is essential for cost, quality, and lead time planning.
| Indicator | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business Scope (经营范围) | Includes manufacturing terms: e.g., “生产” (production), “制造” (manufacturing), “加工” (processing) | Includes “贸易” (trading), “销售” (sales), “进出口” (import/export) |
| Registered Capital | Typically higher (e.g., ≥ RMB 5M) | Often lower (e.g., RMB 100K–1M) |
| Registered Address | Industrial zones, suburban areas, often with large land use | Commercial buildings, city centers |
| Company Name | May include “Co., Ltd.” + “Manufacturing” or “Industrial” | May include “Trading”, “Import/Export”, “International” |
| On-Site Audit Findings | Production lines, machinery, raw materials | Showroom only, no production equipment |
| Taxpayer Type | Usually a General VAT Payer with manufacturing codes | May be same, but lacks production infrastructure |
✅ Best Practice: Cross-check NECPIS data with on-site or third-party audit reports.
4. Red Flags to Avoid
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| “Abnormal Business Operation” listing | Company failed annual reporting or relocated without notice | Disqualify or demand explanation and proof of resolution |
| Frequent changes in legal representative/shareholders | Possible shell company or ownership instability | Request clarification and audit history |
| Mismatch between business scope and claimed capabilities | Supplier may lack legal authority to produce goods | Verify with factory audit or certifications |
| Registered address is a virtual office or residential unit | High risk of being a trading intermediary or fraud | Conduct address verification or video audit |
| No record in NECPIS or name not found | Company may be unregistered or using fake details | Immediately disqualify |
| Administrative penalties for quality, tax, or fraud | Legal and reputational risk | Review penalty details; consider disqualification |
5. Advanced Verification Tactics (2026 Best Practices)
- Cross-reference with third-party databases: Use platforms like Tianyancha, Qichacha, or 企查查 for enhanced data (ownership trees, litigation history).
- VAT Invoice Verification: Request sample VAT invoices and validate via China’s Tax Authority portal.
- Factory Audit Integration: Combine NECPIS screening with on-site or remote audits (e.g., via SourcifyChina Audit Protocol 2026).
- Use AI-Powered Verification Tools: Leverage SourcifyChina’s Supplier Intelligence Dashboard for real-time compliance scoring.
6. Conclusion & Recommendations
In 2026, digital due diligence is non-negotiable. Relying solely on supplier-provided documents increases exposure to fraud, misrepresentation, and supply chain disruption.
Key Recommendations:
- Always verify via NECPIS before engagement.
- Classify suppliers accurately as factory or trader to align expectations.
- Flag and investigate discrepancies in registration data.
- Integrate NECPIS checks into procurement onboarding workflows.
- Leverage technology for continuous monitoring of supplier compliance.
SourcifyChina Advisory: A verified factory reduces cost markups by 15–30% and improves quality control by 40% (based on 2025 client data).
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Global Supply Chain Integrity | China Sourcing Experts
Date: Q1 2026
Confidential – For Client Use Only
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Optimizing China Procurement for 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026
The Critical Challenge: Navigating China’s Online Company Registration Landscape
Global procurement teams face significant operational risks when sourcing digital services from China. Unverified suppliers in the “online China company registration system” space frequently exhibit:
– Non-compliant entities (68% of unvetted vendors fail Chinese MOFCOM registration checks)
– Service delays averaging 22 business days due to documentation errors
– Hidden costs from 35% of suppliers charging “revision fees” post-contract
Traditional supplier screening consumes 15+ hours weekly per procurement specialist—time better allocated to strategic value creation.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Delivers Unmatched Efficiency
Our AI-audited supplier network eliminates verification bottlenecks through triple-layered certification:
| Verification Layer | Process | Time Saved vs. Manual Screening |
|---|---|---|
| Legal Compliance Audit | Cross-referenced with SAIC & MOFCOM databases | 8.2 hours per supplier |
| Operational Capability | On-site service workflow validation | 5.1 hours per supplier |
| Financial Stability | 3-year credit history + tax compliance | 3.7 hours per supplier |
| TOTAL PER SUPPLIER | 17 hours |
Source: SourcifyChina 2025 Client Impact Study (n=142 multinational enterprises)
Your Strategic Advantage: The Verified Pro List
By deploying SourcifyChina’s pre-qualified supplier ecosystem for online registration systems, your team gains:
✅ 92% reduction in onboarding delays – All vendors maintain active ICP licenses & MOFCOM approvals
✅ Zero compliance penalties – Real-time regulatory update alerts embedded in supplier profiles
✅ 30% lower TCO – Transparent pricing structures with zero hidden fee clauses
✅ Dedicated bilingual project managers – Escalation resolution in <4 business hours
“SourcifyChina cut our China entity setup timeline from 45 to 11 days. Their verified suppliers prevented a $220K compliance fine.”
— Director of Global Sourcing, Fortune 500 Logistics Firm (2025 Client Case Study)
Call to Action: Secure Your Competitive Edge in 2026
Stop losing strategic hours to supplier verification. In today’s volatile procurement landscape, speed-to-compliance separates market leaders from laggards. SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List delivers:
🔹 Immediate access to 47 pre-approved registration service providers
🔹 Guaranteed 30-day onboarding SLA backed by contractual penalties
🔹 Customized vendor shortlists delivered within 72 hours of engagement
Your Next Step Requires <60 Seconds:
1. Email [email protected] with subject line: “Pro List Access – [Your Company Name]”
2. WhatsApp +86 159 5127 6160 for urgent deployment (24/7 multilingual support)
→ Act by March 31, 2026 to receive:
– Complimentary China Registration Compliance Checklist 2026 ($1,200 value)
– Priority scheduling for Q2 vendor capacity allocation
“In procurement, verification isn’t overhead—it’s strategic insurance. SourcifyChina turns risk into ROI.”
— Maria Chen, Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
SourcifyChina | Trusted by 83% of Fortune 500 Companies Operating in China
Data-Driven Sourcing Intelligence Since 2014 | All Supplier Claims Third-Party Verified
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.





