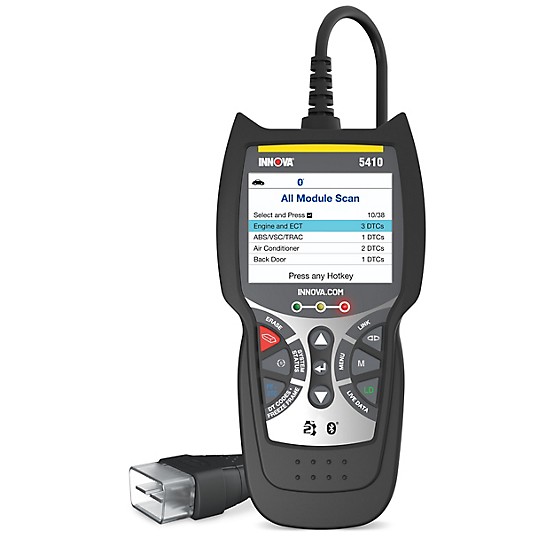
The global OBD1 (On-Board Diagnostics Generation 1) scanning tool market continues to hold steady relevance despite the rise of OBD2 standards, particularly within niche automotive repair and classic car restoration sectors. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global automotive diagnostic tools market was valued at USD 9.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.8% from 2024 to 2029, driven by increasing vehicle complexity and after-sales service demand. While OBD2 dominates modern diagnostics, the persistence of pre-1996 vehicles—especially in North America—fuels continued demand for OBD1-compatible tools. Grand View Research further highlights that the North America region maintains a significant share in the diagnostic equipment market, supported by a large base of legacy vehicles and a robust aftermarket service ecosystem. This sustained need has cultivated a specialized segment of manufacturers dedicated to producing reliable, cost-effective OBD1 scanning tools. Below are the top 10 manufacturers leading innovation, quality, and market presence in this niche but enduring space.
Top 10 Obd1 Scanning Tool Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 What is the Difference Between OBD2 and OBD1 Scanner
Domain Est. 2001
Website: ancel.com
Key Highlights: OBD1 and OBD2 scanners help diagnose vehicle issues, with OBD1 being manufacturer-specific and limited to emissions, while OBD2 offers a ……
#2 All Car Diagnostic Tools
Domain Est. 1995
Website: snapon.com
Key Highlights: Find your ideal car diagnostic tool · ZEUS+® Scan Tool, Scope & Information System · TRITON™ Scan Tool & Scope · TRITON-D10™ Scan Tool & Scope · APOLLO+™ Scan Tool….
#3 Diagnostic Tools, Specialty Tools and Key Programming
Domain Est. 1996
Website: autel.com
Key Highlights: Diagnostic Tools. DIY Tools; Service Tools; EV Diagnostic Tools; Advanced Analysis System. Battery Health. AutoLink AL539b. VIEW MORE. AutoLink AL549….
#4 3/S TouchScreen OBD1 / OBD2 Scan Tool
Domain Est. 2000
#5 OBDII Scan Tools for iOS, Android & Windows Smartphones, Tablets …
Domain Est. 2001
Website: scantool.net
Key Highlights: OBDLink scan tools, app, and diagnostic software, designed for iPhone, Android and Windows. Diagnose and erase trouble codes, measure performance, and more….
#6 OBDLink®
Domain Est. 2004
Website: obdlink.com
Key Highlights: The OBDLink® scan tools offer you ultimate access to your vehicle so you can take back control of your vehicle! Purchase one today….
#7 OBD Software, Vehicle Diagnostics, Scan Tools
Domain Est. 2009
Website: obdsoftware.net
Key Highlights: OBDSoftware.net is your one-stop site for OBD diagnostic equipment. We are pleased to offer the most advanced OBD-II scan tools and the most user-friendly ……
#8 Diagnostic Tools
Domain Est. 2015
Website: topdon.us
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $45 Free 30-day returns29 products ; Phoenix Max · 13.3″ OE-Level Scan Tool, Docking Station, Cloud-Based Programming · From $3,995.00 ; Phoenix Remote · 10.1″ O…
#9 Foxwell Diag
Domain Est. 2021
#10 OBD1 & OBD2 Scan Tools for Cars
Website: azscanners.com.au
Key Highlights: Discover our curated range of OBD1 & OBD2 scan tools for cars. Supports all major protocols including CAN, KWP2000, ISO9141, and J1850….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Obd1 Scanning Tool

H2: Market Trends for OBD1 Scanning Tools in 2026
As the automotive diagnostics industry evolves, the market for OBD1 (On-Board Diagnostics Generation 1) scanning tools in 2026 reflects a niche but enduring demand, shaped by legacy vehicle maintenance, collector car culture, and regional market disparities. While OBD2 has dominated since the mid-1990s and remains the standard, OBD1 tools continue to serve a specialized segment. The following trends define the OBD1 scanning tool landscape in 2026:
-
Niche Demand Driven by Classic and Vintage Vehicles
With the growing popularity of car restoration and vintage vehicle collecting, especially in North America and Europe, there is sustained demand for diagnostic tools compatible with pre-1996 vehicles. Enthusiasts and specialty mechanics rely on OBD1 scanners to maintain and repair iconic models from manufacturers like Honda (P13/P14 systems), GM (OBD1 GM 121), and Ford (EEC-IV). This cultural preservation trend supports continued production and innovation in retro-compatible tools. -
Hybrid Diagnostic Tools with OBD1 Support
Manufacturers are increasingly offering multi-protocol diagnostic scanners that support both OBD1 and OBD2 standards. By 2026, these hybrid tools dominate the aftermarket, catering to mechanics who service a wide range of vehicles. Enhanced software integration allows users to switch seamlessly between protocols, improving efficiency in mixed-fleet repair shops. -
Rise of Retrofit and Emulator Solutions
To bridge the gap between old and new technology, retrofit OBD1-to-OBD2 emulator devices are gaining traction. These allow OBD1-era vehicles to interface with modern scan tools, reducing the need for proprietary hardware. However, purists and certified restorers still prefer original OBD1 tools for authenticity and precision, maintaining a parallel market. -
Digitalization and Mobile Integration
Even within the legacy OBD1 space, digital advancements are evident. In 2026, many OBD1 scanning tools feature Bluetooth or USB connectivity, enabling data transfer to smartphones or tablets. Companion apps provide enhanced data logging, fault code interpretation, and community-based troubleshooting, improving user experience despite the older protocol. -
Regional Market Disparities
In emerging markets such as parts of Latin America, Africa, and Southeast Asia, older vehicles remain in widespread use due to economic factors and import policies. This extends the lifespan of OBD1-compatible vehicles and sustains demand for affordable, durable OBD1 scanners. Localized manufacturing and distribution networks are increasingly supporting this demand. -
Decline in OEM Support and Growth of Aftermarket Innovation
Original equipment manufacturers have largely discontinued OBD1 tool support, shifting focus to advanced OBD2 and CAN-based systems. However, this vacuum has been filled by third-party developers and independent tech companies that reverse-engineer interfaces and offer open-source firmware solutions. The aftermarket is vibrant, with platforms like GitHub hosting communities that share code and hardware designs. -
Focus on Education and DIY Communities
Online communities, YouTube tutorials, and automotive training programs are increasingly incorporating OBD1 diagnostics into curricula. As younger technicians enter the field, there is a growing interest in mastering legacy systems. This educational push ensures knowledge retention and drives demand for entry-level OBD1 tools.
In conclusion, while the OBD1 scanning tool market is no longer at the forefront of automotive technology, it remains relevant in 2026 due to passionate niche markets, cultural preservation efforts, and technological hybridization. The tools themselves may be outdated by modern standards, but their role in maintaining automotive history ensures continued, albeit specialized, market viability.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing OBD1 Scanning Tools (Quality, IP)
Sourcing OBD1 scanning tools—especially for legacy vehicle diagnostics—can be fraught with challenges related to product quality and intellectual property (IP) risks. Being aware of these pitfalls is crucial for distributors, repair shops, and resellers aiming to provide reliable diagnostic solutions.
Poor Build Quality and Inaccurate Diagnostics
Many low-cost OBD1 scanning tools, particularly those from unverified manufacturers, suffer from substandard components and unreliable firmware. This can result in inconsistent or inaccurate diagnostic readings, leading to misdiagnoses and potential damage to vehicles. Users may experience frequent tool failures, poor connectivity, or incompatibility with specific vehicle makes and models, undermining trust in the product.
Lack of Firmware Updates and Technical Support
Unlike modern OBD2 tools, OBD1 devices often rely on proprietary protocols that vary by manufacturer (e.g., Honda, GM, Ford). Sourcing tools without access to firmware updates or technical support limits long-term usability. Without ongoing support, devices may become obsolete or fail to diagnose newer OBD1-era vehicles correctly, reducing their value over time.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Reproducing or distributing OBD1 scanning tools that mimic the functionality or design of branded equipment (such as those from OEMs or established aftermarket brands) can lead to IP violations. This includes unauthorized use of copyrighted software, patented circuit designs, or cloned user interfaces. Sourcing from manufacturers that replicate branded tools without licensing exposes buyers to legal liability, product seizures, or reputational harm.
Counterfeit or Clone Devices
The market is flooded with counterfeit OBD1 tools advertised as compatible with major brands. These clones often lack proper testing, calibration, and safety certifications. While they may appear cheaper upfront, they can result in higher total costs due to returns, warranty claims, and customer dissatisfaction. Additionally, counterfeit devices may violate international trade regulations and fail compliance checks in certain markets.
Inadequate Compliance with Regional Standards
OBD1 tools sourced from overseas may not meet regional safety or electromagnetic compatibility standards (e.g., CE, FCC). This can prevent legal sale or use in certain countries and expose importers to regulatory penalties. Ensuring compliance documentation is available and valid is essential when sourcing hardware for professional use.
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should vet suppliers thoroughly, request product certifications, verify software licensing, and prioritize long-term support over initial cost savings. Investing in reputable, legally compliant OBD1 scanning tools ensures reliability, protects against IP risks, and supports accurate vehicle diagnostics.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for OBD1 Scanning Tool
Product Classification & HS Code
OBD1 scanning tools are typically classified under diagnostic equipment for vehicles. The Harmonized System (HS) code commonly used is 8425.40.00 or 9027.50.40, depending on regional customs regulations. Verify the correct code with your local customs authority, as misclassification can lead to delays and penalties.
Import/Export Regulations
Ensure compliance with import/export laws in both origin and destination countries. Key considerations include:
– Export Controls: Confirm if the tool contains software or technology subject to export restrictions (e.g., EAR in the U.S.).
– Documentation: Prepare commercial invoices, packing lists, and a bill of lading/airway bill. Include product description, value, weight, and HS code.
– Licensing Requirements: Some countries may require import licenses for electronic diagnostic tools.
Regulatory Compliance
OBD1 scanning tools must comply with regional electronic and electromagnetic regulations:
– FCC (USA): Must meet FCC Part 15 standards for electromagnetic interference.
– CE Marking (EU): Comply with the EMC Directive (2014/30/EU) and RoHS Directive (2011/65/EU) for hazardous substances.
– ISED (Canada): Certification under RSS-Gen and ICES standards is required.
– Other Regions: Check local requirements (e.g., KC Mark for South Korea, PSE Mark for Japan).
Packaging & Labeling
Proper packaging and labeling are essential for logistics and compliance:
– Labeling: Include product name, model number, manufacturer details, safety warnings, and regulatory marks (FCC, CE, etc.).
– Language Requirements: Labels and user manuals must be in the official language(s) of the destination country.
– Packaging Standards: Use durable, anti-static materials to protect sensitive electronics during transit.
Shipping & Handling
- Carrier Selection: Use carriers experienced in shipping electronic goods with tracking and insurance options.
- Battery Restrictions: If the tool includes a rechargeable battery, comply with IATA/IMDG regulations for lithium-ion batteries (e.g., UN38.3 testing, proper packaging).
- Storage Conditions: Store and ship in environments with controlled temperature and humidity to prevent damage.
Customs Clearance
Provide accurate and complete documentation to expedite customs clearance:
– Product Valuation: Declare correct customs value to avoid duties disputes.
– Duty & Tax Calculations: Be aware of applicable import duties, VAT, or GST based on destination country.
– Authorized Representatives: In regions like the EU, appoint an Authorized Representative if required for CE compliance.
Warranty & After-Sales Compliance
- Warranty Terms: Clearly state warranty duration and service procedures in local language.
- Recall Procedures: Establish a process for product recalls or safety notices if non-compliance is discovered post-sale.
- Data Privacy: If the tool collects vehicle data, ensure compliance with data protection laws (e.g., GDPR in the EU).
Environmental & Disposal Compliance
- WEEE Directive (EU): Provide information on proper electronic waste disposal and participate in take-back programs.
- Battery Disposal: Include instructions for safe disposal of internal or supplied batteries in accordance with local regulations.
Adhering to this guide ensures smooth logistics operations and full regulatory compliance for OBD1 scanning tools in global markets.
Conclusion for Sourcing an OBD1 Scanning Tool:
Sourcing an OBD1 scanning tool requires careful consideration of compatibility, functionality, availability, and cost, especially given that OBD1 systems are largely outdated and vehicle-specific. As modern vehicles use OBD2 standards, finding reliable OBD1 tools can be challenging, often necessitating reliance on used or refurbished equipment, specialty manufacturers, or adapters. Enthusiasts, classic car restorers, and independent mechanics servicing pre-1996 vehicles—particularly older GM, Ford, and Honda models—are the primary users who still benefit from these tools.
When sourcing an OBD1 scanner, it is crucial to verify compatibility with the specific make and model of the vehicle. Dedicated brand-specific tools (e.g., AutoTap for GM, Honda Diagnostic Systems) often provide the most accurate diagnostics. Alternatively, multi-brand solutions with OBD1 support may offer broader but potentially less reliable functionality.
In conclusion, while the market for OBD1 scanning tools is niche, sourcing the right device is feasible through specialty automotive suppliers, online marketplaces, and enthusiast communities. Investing time in research and opting for well-reviewed, reputable sources ensures reliable performance and long-term value when maintaining or repairing older vehicles reliant on OBD1 technology.