The global absorbable sutures market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising surgical volumes, advancements in suture technology, and increasing demand for minimally invasive procedures. According to Grand View Research, the global absorbable sutures market size was valued at USD 2.1 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.3% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is further supported by an aging population and expanding access to healthcare in emerging economies. Within this landscape, nylon—though traditionally associated with non-absorbable sutures—has seen innovative modifications to enable partial absorbability, blurring the lines between suture categories and creating niche opportunities. As demand for reliable, biocompatible closure materials increases, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders in developing advanced nylon-based absorbable suture solutions, combining tensile strength with controlled degradation profiles. The following analysis highlights the top seven manufacturers pioneering this segment, leveraging innovation, regulatory approvals, and global distribution networks to capture market share.
Top 7 Nylon Suture Absorbable Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
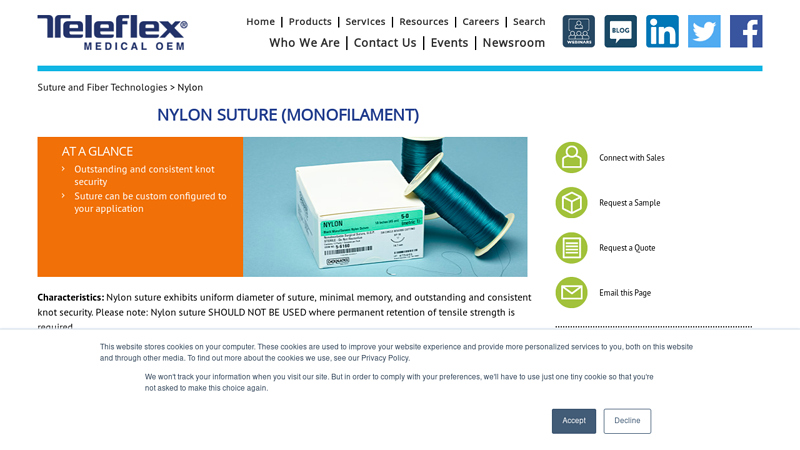
#1 nylon suture (monofilament)
Domain Est. 2004
Website: teleflexmedicaloem.com
Key Highlights: Teleflex Medical OEM’s nylon suture meets all requirements established by the USP for sterile, non-absorbable surgical sutures….
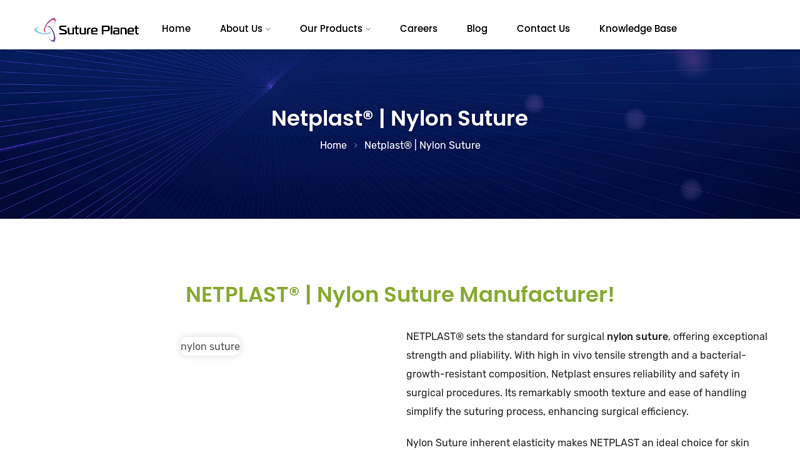
#2 NETPLAST®
Domain Est. 2012
Website: sutureplanet.com
Key Highlights: NETPLAST sets the standard for surgical nylon suture, offering exceptional strength and pliability. With high in vivo tensile strength and a bacterial-growth- ……
#3 Sutures
Domain Est. 1990
Website: medtronic.com
Key Highlights: Dermalon™ monofilament nylon sutures are inert, nonabsorbable, sterile surgical sutures used in general soft tissue approximation and/or ……
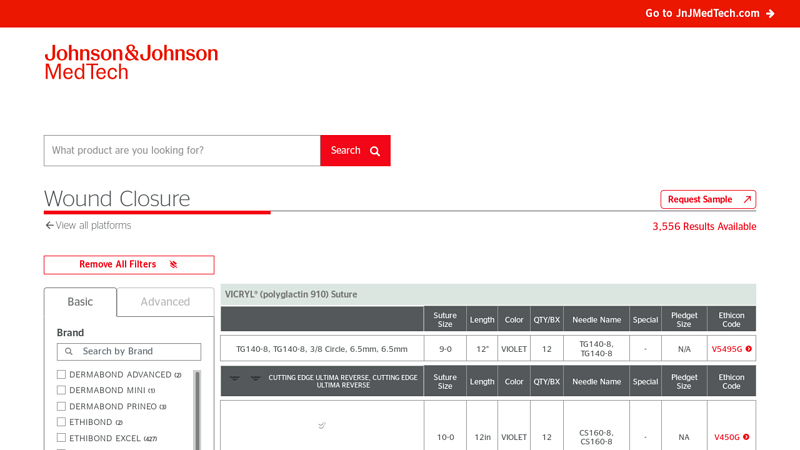
#4 Wound Closure Search
Domain Est. 1995
Website: ethicon.com
Key Highlights: ETHILON® Nylon Suture. Needle Image. Suture Size, 11-0. Length, 5in. Color, BLACK … This site is published by Ethicon US, LLC, which is solely responsible ……
#5 SMI
Domain Est. 2003 | Founded: 1987
Website: sutures.be
Key Highlights: SMI AG was established in 1987 – the first Belgian company to manufacture surgical, ophthalmic and dental sutures. Today it is recognized as an experienced ……
#6 Nylon Sutures
Domain Est. 2008
Website: dolphinsutures.com
Key Highlights: Nylon suture is a monofilament non-absorbable surgical suture. Nylon sutures are available from U.S.P. size 2 to size 10-0. Suture is available in black colour….
#7 DSI Nylon Sutures
Domain Est. 2016
Website: dsisrael.com
Key Highlights: DSI Nylon sutures are monofilament non-absorbable sutures and are remarkably smooth, soft and gives excellent knot security. Improved sharpened needle….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Nylon Suture Absorbable

H2: Projected Market Trends for Absorbable Nylon Sutures in 2026
By 2026, the market for absorbable nylon sutures is expected to experience moderate growth driven by advancements in surgical techniques, rising demand for minimally invasive procedures, and increased focus on infection control and patient recovery. Although traditional absorbable sutures such as polyglycolic acid (PGA) and polydioxanone (PDS) remain dominant, innovations in nylon-based absorbable formulations are creating new niches within the global suture market.
One key trend shaping the 2026 landscape is the development of hybrid absorbable nylon sutures—blends engineered to combine the tensile strength and handling characteristics of nylon with controlled biodegradability. These next-generation sutures aim to retain nylon’s favorable knot security and low tissue reactivity while offering absorption profiles suited for mid-term wound support (typically 60–90 days), making them ideal for subcutaneous and soft tissue closure in general and plastic surgery.
The increasing volume of outpatient surgeries and ambulatory surgical centers (ASCs) is also boosting demand for reliable, easy-to-use absorbable sutures. Absorbable nylon variants are gaining favor among surgeons seeking materials that reduce follow-up visits for suture removal without compromising healing integrity. Additionally, rising healthcare digitization and surgical training platforms are promoting standardized techniques that favor consistent suture performance—another advantage of engineered absorbable nylon products.
Regionally, North America and Europe are expected to lead market adoption due to advanced healthcare infrastructure and regulatory support for innovative medical devices. Meanwhile, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific—particularly India, China, and Southeast Asia—are projected to see accelerated growth, fueled by expanding surgical volumes, rising medical tourism, and government initiatives to improve surgical care access.
Despite these positive trends, challenges remain. True absorbable nylon is still in developmental or early commercial stages, as conventional nylon is non-absorbable. Most “absorbable nylon” products on the market may refer to copolymers or coated variants rather than pure absorbable nylon. As such, market players must navigate regulatory scrutiny and invest in clinical evidence to validate absorption rates and safety.
Key manufacturers—including Ethicon (Johnson & Johnson), Medtronic, B. Braun, and Sutures India—are expected to increase R&D investments in bioresorbable polymers, with partnerships between material science firms and medical device companies likely to accelerate product commercialization by 2026.
In summary, the 2026 market for absorbable nylon sutures will be characterized by innovation-driven differentiation, growing clinical acceptance in specific surgical applications, and strategic expansion in emerging economies. While still a niche segment within the broader absorbable suture market, absorbable nylon variants are poised to capture incremental market share by addressing unmet needs for strong, biocompatible, and absorbable wound closure solutions.

H2: Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Nylon Suture – Absorbable (Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns)
When sourcing surgical sutures, it is critical to distinguish between absorbable and non-absorbable types. A common and significant pitfall arises when misidentifying or mislabeling nylon sutures as absorbable, which can lead to serious quality, safety, and regulatory issues.
1. Misunderstanding Material Properties
Nylon is inherently a non-absorbable synthetic polymer. It does not degrade significantly in the body over time. A key pitfall occurs when suppliers or buyers incorrectly label nylon sutures as “absorbable,” either due to misinformation or intentional misrepresentation. This creates a serious risk for clinical outcomes, as absorbable sutures are designed to lose tensile strength and be metabolized, whereas nylon retains strength for extended periods.
2. Quality Risks from Inaccurate Specifications
Sourcing “absorbable nylon” may result in receiving substandard or counterfeit products. Suppliers might blend nylon with absorbable polymers (e.g., PGA or PLA) without clear disclosure, leading to unpredictable absorption rates and mechanical performance. This compromises wound support and increases the risk of dehiscence or infection.
3. Regulatory and Compliance Issues
Marketing or using a suture labeled as “absorbable nylon” can violate medical device regulations (e.g., FDA, CE). Regulatory bodies require accurate material classification and performance data. Mislabeling may result in product recalls, legal liabilities, or exclusion from procurement contracts.
4. Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement Risks
Some manufacturers hold patents on specific suture formulations, coatings, or manufacturing processes. Sourcing generic versions without due diligence may lead to unintentional IP violations—especially if the product mimics a proprietary absorbable suture design. Additionally, false claims (e.g., “absorbable nylon”) could infringe on trademarks or misrepresent patented technologies.
5. Supplier Credibility and Traceability Gaps
Suppliers offering “absorbable nylon” may lack verifiable certifications (ISO 13485, GMP) or transparent manufacturing histories. Without proper documentation, traceability during audits or adverse events becomes impossible, increasing liability exposure.
Conclusion
The term “Nylon Suture – Absorbable” is a contradiction in material science and signals a red flag in sourcing. Procurement teams must verify material specifications, demand regulatory documentation, and consult clinical or biomedical experts to avoid quality compromises and IP pitfalls. Always confirm that suture materials align with established medical standards and actual biocompatibility profiles.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Nylon Suture (Absorbable)
Note: There appears to be a discrepancy in the product description. Nylon sutures are non-absorbable, not absorbable. Nylon is a synthetic polyamide fiber known for its strength and durability, and it is not broken down by the body. If you are referring to an absorbable suture, materials such as Polyglycolic Acid (PGA), Polylactic Acid (PLA), or Polydioxanone (PDS) are typically used. For accuracy, this guide assumes you are referring to Nylon Suture (Non-Absorbable). If an absorbable suture was intended, please confirm the correct material.
Product Overview
Nylon sutures are sterile, synthetic, non-absorbable surgical sutures composed of nylon (polyamide). They are commonly used in general soft tissue approximation and ligation. Due to their high tensile strength, excellent knot security, and low tissue reactivity, nylon sutures are suitable for both internal and external applications.
Common forms include:
– Monofilament nylon (e.g., Ethilon®)
– Dyed (black or green) or undyed
– Packaged with or without surgical needles
Regulatory Classification
Global Regulatory Status
- FDA (USA): Class II medical device under 21 CFR 878.4460 (Surgical Sutures). Requires 510(k) clearance.
- EU (EU MDR): Class Is (non-sterile) or Class Ir (sterile reusable) under Regulation (EU) 2017/745. Requires conformity assessment and CE marking.
- Health Canada: Class II medical device under the Medical Devices Regulations (SOR/98-282). Requires Medical Device License (MDL).
- Australia (TGA): Class IIa device. Listed on the Australian Register of Therapeutic Goods (ARTG).
- Other Markets: Local regulatory approval required (e.g., ANVISA in Brazil, PMDA in Japan).
Sterility and Packaging
- Sterilization Method: Ethylene Oxide (EO) gas or gamma irradiation.
- Packaging: Individually sealed in peelable pouches; secondary packaging in boxes.
- Shelf Life: Typically 3–5 years from manufacture date; verify per manufacturer.
- Storage Conditions: Store in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and excessive heat. Avoid exposure to moisture or sterilants.
Labeling Requirements
Labels must comply with regional regulations and include:
– Product name and type (e.g., “Nylon Suture, Monofilament, USP 2-0”)
– Lot number and expiration date
– Sterile indication and sterilization method
– Quantity and needle specifications (if applicable)
– Single-use designation
– Manufacturer name and address
– UDI (Unique Device Identifier) in FDA and EU markets
– Symbols per ISO 15223-1 (e.g., sterile, do not reuse, etc.)
Shipping and Transportation
Domestic and International Shipping
- Mode: Air, ground, or sea depending on urgency and volume.
- Temperature Control: Ambient transport is sufficient; avoid extreme temperatures.
- Hazard Classification: Non-hazardous (unless packaging includes flammable sterilant residues).
- Documentation: Commercial invoice, packing list, certificates of sterility and compliance, and export licenses if required.
Import/Export Compliance
- HS Code Example (USA): 3006.40.0000 (Absorbable surgical sutures) – Note: Nylon sutures may fall under 5604.90.0090 (other twine, cordage, rope, and cables, not elsewhere specified).
- Confirm correct HS code with customs broker.
- Export controls: Generally not subject to ITAR or EAR restrictions, but verify country-specific rules.
Inventory Management
- FIFO (First In, First Out): Critical to manage expiration dates.
- Stock Rotation: Regular audits to prevent expired product distribution.
- Traceability: Full lot traceability from manufacturer to end-user required for recalls and adverse event reporting.
Quality Assurance & Compliance
- ISO 13485 Certification: Required for manufacturers and distributors.
- GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice): Applicable to production and packaging.
- Post-Market Surveillance: Monitor for adverse events and report per FDA MedWatch, EUDAMED, or local systems.
- Recall Procedures: Established process for field alerts, withdrawals, and notifications.
Environmental and Disposal Considerations
- Single-Use Only: Do not reprocess or reuse.
- Waste Stream: Dispose of as regulated medical waste (biohazard) after use.
- Packaging: Plastic and paper components may be recyclable depending on local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Is nylon suture absorbable?
A: No. Nylon is a non-absorbable synthetic suture. It remains in the body indefinitely unless removed.
Q: Can nylon sutures be resterilized?
A: No. They are intended for single use only. Resterilization may compromise integrity.
Q: What is the shelf life of nylon sutures?
A: Typically 3–5 years. Always check the expiration date on the packaging.
Q: Are nylon sutures MRI-safe?
A: Yes. Nylon is non-magnetic and considered MRI-compatible.
Contacts and Support
- Manufacturer Technical Support
- Regulatory Affairs Department
- Distributor Service Line
- Adverse Event Reporting Portal (per local requirements)
Disclaimer: This guide is for informational purposes only. Always refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for use (IFU), regulatory body requirements, and internal compliance protocols.
Conclusion for Sourcing Absorbable Nylon Sutures
In conclusion, sourcing absorbable nylon sutures requires a careful evaluation of material properties, regulatory compliance, supplier reliability, and clinical requirements. Although traditional nylon is inherently non-absorbable, advances in polymer technology have led to modified absorbable variants or nylon-combined blends designed to offer temporary tensile strength with gradual degradation. When sourcing such sutures, it is critical to verify the product’s absorbable characteristics through certified biocompatibility testing and regulatory approvals (e.g., FDA, CE).
Key considerations include selecting suppliers with a proven track record in surgical suture manufacturing, adherence to ISO 13485 quality standards, and the ability to provide consistent product performance. Additionally, factors such as sterility, packaging, shelf life, and cost-effectiveness must align with healthcare facility or manufacturing needs.
Ultimately, successful sourcing of absorbable nylon sutures hinges on balancing clinical efficacy, safety, and supply chain dependability. Engaging with trusted manufacturers and conducting thorough due diligence ensures that the chosen product supports optimal patient outcomes and meets the evolving demands of modern surgical practice.