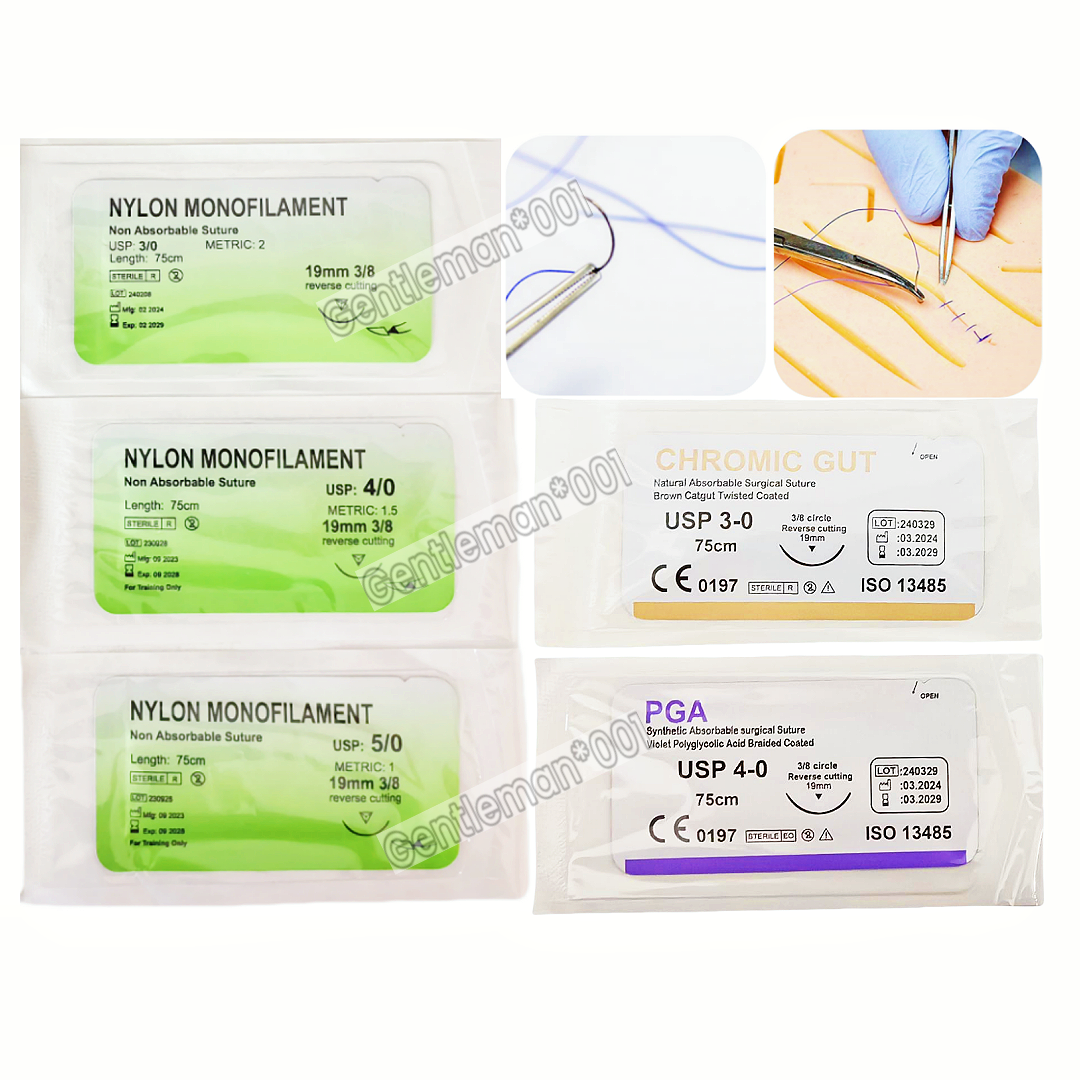
The global surgical sutures market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising surgical volumes, advancements in suture materials, and expanding healthcare infrastructure. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global surgical sutures market was valued at USD 3.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.2% from 2024 to 2029. Nylon sutures, known for their high tensile strength, excellent elasticity, and resistance to infection, remain a cornerstone in both absorbable and non-absorbable suture applications. As demand for reliable and cost-effective wound closure solutions increases—particularly in emerging economies—the role of key nylon suture manufacturers becomes increasingly critical. This list highlights the top eight companies leading innovation, scalability, and quality assurance in nylon suture production, based on market presence, product range, regulatory compliance, and global distribution networks.
Top 8 Nylon Suture Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 nylon suture (monofilament)
Domain Est. 2004
Website: teleflexmedicaloem.com
Key Highlights: Teleflex Medical OEM’s nylon suture meets all requirements established by the USP for sterile, non-absorbable surgical sutures….
#2 Sutures
Domain Est. 1990
Website: medtronic.com
Key Highlights: Surgilon™ braided nylon sutures are nonabsorbable surgical sutures indicated for use in general soft tissue approximation and/or ligation….
#3 Wound Closure Search
Domain Est. 1995
Website: ethicon.com
Key Highlights: This site is intended for Healthcare Professionals. Not all products are … ETHILON® Nylon Suture. Needle Image. Suture Size, 11-0. Length, 5in. Color, BLACK….
#4 Sutures
Domain Est. 1999
Website: securos.com
Key Highlights: 250 different suture options is made in the United States with premium materials, industry-leading tensile strength, and needles that require 12-20% less force ……
#5 SMI
Domain Est. 2003 | Founded: 1987
Website: sutures.be
Key Highlights: SMI AG was established in 1987 – the first Belgian company to manufacture surgical, ophthalmic and dental sutures. Today it is recognized as an experienced ……
#6 BOENMED® Nylon Suture
Domain Est. 2006
Website: boenmedical.com
Key Highlights: BOENMED manufactures NYLON SUTURE. The Nylon Sutures are high-quality, synthetic, non-absorbable monofilament sutures made from durable nylon (polyamide)….
#7 Nylon Sutures
Domain Est. 2008
Website: dolphinsutures.com
Key Highlights: Nylon sutures are also known as polyamide sutures. Nylon sutures are monofilament sutures and are remarkably smooth, soft and gives excellent knot security….
#8 AD SURGICAL
Domain Est. 2010
Website: ad-surgical.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $250 90-day returnsAD Surgical is a supplier of top surgical essentials, including sutures … Nylon Sutures · PTFE Sutures · Polypropylene Sutures · Silk Suture…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Nylon Suture

H2: Market Trends for Nylon Suture in 2026
As the global healthcare sector continues to evolve, the market for surgical sutures—particularly nylon sutures—is expected to witness steady growth and transformation by 2026. Driven by advancements in surgical techniques, rising volumes of elective and emergency procedures, and increasing emphasis on infection control and wound management, nylon sutures remain a mainstay in clinical settings due to their strength, durability, and biocompatibility. Below are the key market trends projected for nylon sutures in 2026:
1. Sustained Demand in General and Specialty Surgeries
Nylon sutures, known for their high tensile strength and excellent knot security, are widely used in dermatologic, cardiovascular, ophthalmic, and orthopedic procedures. By 2026, the rising global incidence of chronic diseases and an aging population will continue to drive surgical volumes, particularly in emerging economies. This sustained clinical demand will support stable market growth for non-absorbable sutures like nylon.
2. Shift Toward Premium and Coated Variants
Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on value-added nylon suture products, such as those with silicone or polybutilate coatings, which enhance handling, reduce tissue drag, and minimize inflammatory response. In 2026, demand for these advanced coated nylon sutures is expected to rise, especially in minimally invasive surgeries where precision and tissue compatibility are paramount.
3. Regional Market Expansion in Asia-Pacific and Latin America
The Asia-Pacific region is anticipated to lead market growth by 2026, fueled by expanding healthcare infrastructure, increased medical tourism, and rising adoption of modern surgical practices in countries like India, China, and Indonesia. Similarly, Latin America is witnessing improved access to surgical care, contributing to higher consumption of nylon sutures in public and private hospitals.
4. Regulatory Harmonization and Quality Standards
With growing scrutiny on medical device safety, regulatory bodies such as the FDA, EU MDR, and local agencies are enforcing stricter quality and traceability standards. By 2026, manufacturers of nylon sutures will need to comply with enhanced documentation, sterilization protocols, and post-market surveillance, pushing smaller players toward consolidation or partnerships with larger firms.
5. Competitive Landscape and Innovation Pressure
While nylon sutures are considered a mature product category, competition remains intense among key players such as Ethicon (Johnson & Johnson), Medtronic, B. Braun, and Sutures India. In response, companies are investing in R&D to improve suture performance and packaging (e.g., pre-threaded needles, ergonomic dispensers), aiming to differentiate their offerings in a price-sensitive market.
6. Sustainability and Environmental Concerns
Environmental sustainability is becoming a priority in healthcare procurement. Although nylon is a synthetic polymer, some manufacturers are exploring eco-friendly packaging and sterile delivery systems to align with green hospital initiatives. While biodegradability remains a challenge for non-absorbable sutures, sustainability in production and waste management will influence brand perception by 2026.
7. Impact of Digitalization and Supply Chain Resilience
The integration of digital tools in supply chain management—such as blockchain for traceability and AI-driven inventory forecasting—will enhance the reliability of suture distribution. Post-pandemic lessons have led to more resilient, regionalized manufacturing, reducing dependency on single-source suppliers and ensuring consistent availability of nylon sutures globally.
Conclusion
In 2026, the nylon suture market will remain robust, underpinned by enduring clinical utility and incremental innovation. While facing competition from absorbable and synthetic alternatives, nylon sutures will maintain a critical role in surgical practice. Success in this market will depend on product differentiation, regulatory compliance, and strategic expansion into high-growth regions.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Nylon Sutures (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing nylon sutures involves navigating critical challenges related to both product quality and intellectual property (IP) rights. Failure to address these pitfalls can lead to regulatory non-compliance, patient safety risks, reputational damage, and legal liabilities.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
- Inconsistent Material Purity and Biocompatibility: Sourcing from suppliers without rigorous quality management systems can result in nylon raw materials containing impurities or additives that compromise biocompatibility, potentially causing adverse tissue reactions or inflammation.
- Poor Manufacturing Process Control: Inadequate control over extrusion, drawing, coating (e.g., with silicone or antimicrobials), and sterilization processes can lead to inconsistent suture diameter, weak tensile strength, unreliable knot security, or compromised sterility, increasing the risk of suture failure.
- Lack of Traceability and Documentation: Suppliers failing to provide comprehensive documentation (Certificates of Analysis, Certificates of Conformance, sterilization records, material traceability) make it difficult to verify compliance with regulatory standards (e.g., USP, ISO 13485) and trace issues back to their source during audits or field complaints.
- Inadequate Packaging and Sterility Assurance: Poor packaging design or breaches during handling can compromise the sterile barrier, leading to product contamination. Sourcing without verifying validated packaging and sterilization methods (e.g., EO, gamma) risks delivering non-sterile devices.
- Non-Compliance with Regulatory Standards: Selecting suppliers whose products do not meet essential regulatory requirements (e.g., FDA 510(k), CE Marking under MDR, local country registrations) can result in shipment rejections, market access denial, or product recalls.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
- Infringement of Patented Technologies: Sourcing sutures incorporating proprietary features (e.g., specific needle attachment methods, specialized coatings, unique braiding techniques) without proper licensing can lead to patent infringement lawsuits, injunctions, and significant financial penalties.
- Unauthorized Use of Trademarks and Branding: Sourcing products that mimic established brand names, logos, or packaging (counterfeit or “look-alike” products) exposes the buyer to trademark infringement claims and severe reputational harm.
- Misappropriation of Trade Secrets: Engaging with suppliers who may have acquired manufacturing know-how, formulations, or process details through improper means (e.g., former employees of innovator companies) creates legal and ethical risks.
- Ambiguous IP Ownership in Custom Designs: Failure to establish clear contractual agreements defining IP ownership (especially for custom-engineered sutures or packaging) can lead to disputes over rights to use, modify, or sell the developed product.
- Insufficient Supplier IP Due Diligence: Not verifying a supplier’s freedom to operate (FTO) – confirming they have the right to manufacture and sell the suture without infringing third-party IP – is a critical oversight that can transfer liability to the buyer.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Nylon Suture
Regulatory Classification and Documentation
Nylon suture is classified as a medical device and is subject to stringent regulatory oversight. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates sutures under 21 CFR Part 878, typically as Class II devices requiring 510(k) premarket notification. In the European Union, nylon sutures must comply with the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) (EU) 2017/745 and carry the CE mark. Manufacturers must maintain a Technical File or Design Dossier demonstrating conformity with essential safety and performance requirements. Required documentation includes device master records, sterilization validation reports, biocompatibility test results (ISO 10993), and labeling compliant with local regulations.
Labeling and Packaging Requirements
Labeling for nylon suture must adhere to international standards such as ISO 15223-1 (symbols for medical devices) and include essential information: product name, sterile status, expiration date, lot number, quantity, size, needle specifications (if applicable), manufacturer details, and UDI (Unique Device Identifier) in jurisdictions requiring it (e.g., FDA U.S. and EU MDR). Primary packaging must maintain sterility and integrity throughout distribution; common methods include peelable pouches or rigid blister packs. Packaging must withstand environmental stresses during shipping and storage and comply with ISO 11607 for packaging of terminally sterilized medical devices.
Storage and Handling Conditions
Nylon sutures must be stored in a clean, dry environment with controlled temperature and humidity. Recommended storage conditions are typically 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) and relative humidity below 60%. Exposure to direct sunlight, excessive heat, or moisture may compromise packaging integrity or material properties. Sutures should be handled with clean hands or gloves to prevent contamination, and packages should not be used if damaged, punctured, or past the expiration date. Rotation of stock using a first-expired, first-out (FEFO) system is recommended to ensure product efficacy.
Transportation and Distribution
Transport of nylon sutures must ensure product integrity and sterility. Shipments should be protected from physical damage, extreme temperatures, and moisture. Use of validated cold chain solutions is not typically required unless specified by the manufacturer, but ambient-controlled transport is advised. Domestic and international shipments must comply with carrier-specific requirements and relevant regulations such as the FDA’s Current Good Transportation Practices (CGTP) and EU GDP (Good Distribution Practice) guidelines. Documentation accompanying shipments should include commercial invoices, packing lists, certificates of conformity, and, where applicable, customs declarations referencing correct HS codes (e.g., 3006.40 for sterile surgical sutures).
Import/Export Compliance
Exporting or importing nylon sutures requires adherence to destination country regulations. Prior to shipment, confirm that the product is registered or notified in the importing country (e.g., FDA registration for U.S. imports, CE marking for EU entry). Required certifications may include a Certificate to Foreign Government (CFG) issued by the FDA or a Statement of Registration from the manufacturer. Ensure compliance with International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF) guidelines and local customs requirements. Restricted regions may require additional permits or pre-approval. Accurate HS code classification, proper valuation, and adherence to Incoterms® 2020 are essential for smooth customs clearance.
Post-Market Surveillance and Adverse Event Reporting
Manufacturers and distributors are responsible for post-market surveillance under applicable regulations. Any adverse events, product complaints, or malfunctions related to nylon suture must be documented and reported according to timelines specified by regulatory bodies (e.g., FDA MedWatch 30-day or 5-day reports, EU MDR vigilance reporting). A quality management system compliant with ISO 13485 must be in place to manage non-conformances, conduct root cause analysis, and implement corrective and preventive actions (CAPA). Regular auditing of distribution channels ensures continued compliance with regulatory and quality standards.
Conclusion for Sourcing Nylon Sutures:
Sourcing nylon sutures requires a strategic approach that balances quality, regulatory compliance, cost-efficiency, and supplier reliability. As a widely used non-absorbable suture material, nylon offers excellent tensile strength, durability, and minimal tissue reactivity, making it ideal for both superficial and long-term wound closures. When sourcing, it is essential to partner with certified manufacturers or suppliers that adhere to international standards such as ISO 13485 and FDA regulations to ensure product safety and performance.
Key considerations include evaluating sterile packaging, suture sizing, needle attachments, and customization options based on clinical needs. Additionally, conducting thorough due diligence on supplier reputation, supply chain stability, and scalability helps mitigate risks related to shortages or quality variance. Engaging in long-term contracts or bulk purchasing with reliable vendors can lead to cost savings without compromising on quality.
In conclusion, effective sourcing of nylon sutures involves a comprehensive assessment of clinical requirements, regulatory standards, and supplier capabilities. By prioritizing quality assurance and building strong supplier relationships, healthcare providers and medical procurement teams can ensure consistent access to high-performance nylon sutures that support optimal patient outcomes.