The global 3D printing materials market, driven by advancements in additive manufacturing and increasing industrial adoption, is witnessing robust growth, with nylon filament emerging as a key high-performance thermoplastic. According to Grand View Research, the global 3D printing materials market size was valued at USD 1.7 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 20.1% from 2023 to 2030. Nylon filament, known for its durability, flexibility, and resistance to wear, holds a significant share within the engineering thermoplastics segment, particularly in applications spanning automotive, aerospace, and functional prototyping. As demand for reliable, industrial-grade nylon feedstock rises, manufacturers are scaling production and enhancing material formulations to meet stringent performance standards. In this evolving landscape, a select group of nine manufacturers have distinguished themselves through innovation, consistent quality, and global supply capabilities, positioning them at the forefront of the nylon filament 3D printing market.
Top 9 Nylon Filament 3D Printer Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Fiberlogy
Domain Est. 2015
Website: fiberlogy.com
Key Highlights: European 3D filament manufacturer for professionals and enthusiasts. PLA, PETG, ABS, ASA, Flex. Tested materials, consistent quality….
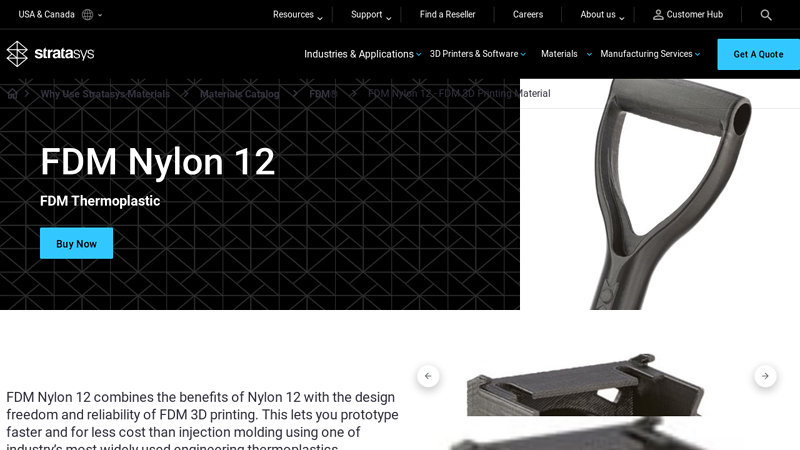
#2 FDM Nylon 12
Domain Est. 1993
Website: stratasys.com
Key Highlights: FDM Nylon 12, an FDM 3D printing material is tough, has good impact resistance and high fatigue resistance, making it suitable for snap fit closures….
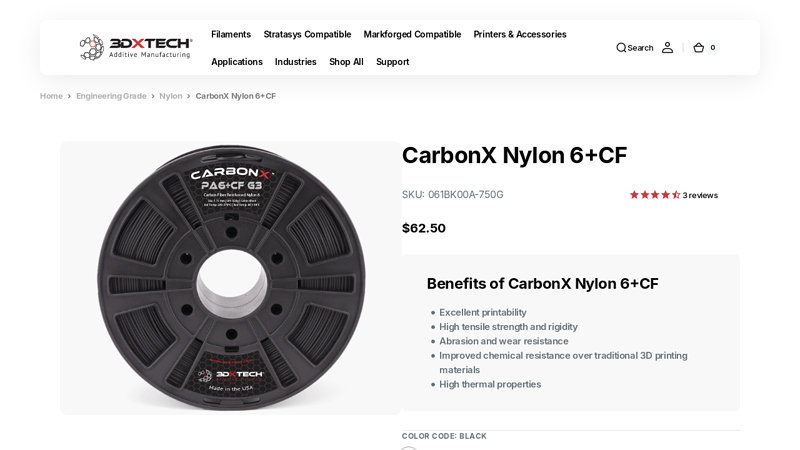
#3 CarbonX Nylon 6+CF Filament
Domain Est. 2013
Website: 3dxtech.com
Key Highlights: In stock Rating 4.3 (3) Excellent printability · High tensile strength and rigidity · Abrasion and wear resistance · Improved chemical resistance over traditional 3D printing mat…
#4 Nylon
Domain Est. 2013
Website: prusa3d.com
Key Highlights: $127.86 delivery · Free 60-day returnsNylon (polyamide) is a versatile material with excellent thermal and mechanical resistance. It is suitable for printing functional technical …
#5 Polymaker
Domain Est. 2013
Website: polymaker.com
Key Highlights: Polymaker is an international team passionate about 3D printing. We produce the very best 3D printing materials by controlling every stage of production….
#6 Nylon White
Domain Est. 2013
Website: markforged.com
Key Highlights: Nylon is an unfilled thermoplastic. It’s a non-abrasive material that is great for ergonomic surfaces and workholding for pieces that are easily marred….
#7 NYCOA Grades for Filament 3
Domain Est. 2014
Website: nycoa.com
Key Highlights: Nylon grades are less brittle and stronger than PLA and ABS. The interlayer adhesion of nylon results in high quality homogeneous 3-D molded components ……
#8 Nylon Filament (PA)
Domain Est. 2019
Website: us.store.bambulab.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery · 14-day returnsBambu Lab is a consumer tech company focusing on desktop 3D printers. Starting with the X1 series, Bambu Lab builds state-of-the-art 3D printers….
#9 Nylon (PA) Filament
Domain Est. 2012
Website: 3dprintingusa.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $75Elevate your 3D printing with our PA (Nylon) Filaments. Renowned for its exceptional strength and durability, PA is ideal for high-performance parts….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Nylon Filament 3D Printer
2026 Market Trends for Nylon Filament 3D Printers
Advancing Material Performance and Specialization
By 2026, the nylon filament 3D printer market is expected to see a significant shift towards high-performance and specialized nylon variants. Printers will increasingly be optimized for engineering-grade nylons such as PA6, PA66, PA12, and copolymers like Nylon-CF (carbon fiber reinforced) and Nylon-GF (glass fiber reinforced). Enhanced chamber heating, improved bed adhesion systems (e.g., PEI-coated, magnetic flex plates), and dual or multi-material extrusion capabilities will become standard in mid-to-high-end machines. This evolution supports industrial applications demanding superior mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, particularly in automotive, aerospace, and robotics sectors.
Integration of Smart Manufacturing and Automation
Nylon filament 3D printers in 2026 will feature deeper integration with smart manufacturing ecosystems. Expect widespread adoption of AI-powered print monitoring, real-time defect detection, and humidity-controlled filament drying systems directly built into printer enclosures. Connectivity via IoT platforms will allow remote print management, predictive maintenance, and seamless integration with digital inventory systems. Automated calibration and material changeover processes will reduce operator dependence, making nylon printing more accessible and reliable for production environments.
Growth in Industrial and End-Use Part Production
Driven by demand for lightweight, durable components, nylon 3D printing will transition from prototyping to direct digital manufacturing. By 2026, industries such as automotive and defense will increasingly adopt nylon printers for low-volume, high-complexity end-use parts—ranging from ducting and brackets to custom gears and housings. This trend is supported by advancements in print repeatability, quality assurance software, and post-processing automation, enabling certified part production compliant with industry standards like ISO 9001 and AS9100.
Sustainability and Closed-Loop Material Cycles
Environmental considerations will play a larger role in the nylon 3D printing market. By 2026, manufacturers will emphasize recyclable nylon filaments and closed-loop systems that allow on-site reprocessing of failed prints and support waste. Printer designs will incorporate energy-efficient heaters, reduced material waste through optimized slicing algorithms, and compatibility with bio-based or recycled nylons. Regulatory pressure and corporate sustainability goals will accelerate adoption of eco-conscious nylon printing solutions across European and North American markets.
Expansion of Accessible High-Performance Printing
While industrial systems advance, the consumer and prosumer segments will benefit from more affordable, user-friendly nylon-capable printers. By 2026, key players will release mid-range models with enclosed chambers, active humidity control, and simplified calibration—lowering the entry barrier for engineering designers, educators, and small manufacturers. This democratization, combined with improved filament availability and community-driven support, will broaden the adoption of nylon printing beyond niche technical users.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Nylon Filament for 3D Printing
Inconsistent Material Quality
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing nylon filament is variability in quality. Nylon is highly sensitive to moisture absorption, and poorly manufactured or improperly stored filament can lead to print defects such as bubbling, poor layer adhesion, or nozzle clogs. Low-cost suppliers may use inconsistent polymer batches or inadequate drying processes, resulting in filament with variable diameter, moisture content, or mechanical properties. This inconsistency undermines print reliability and part performance, especially in demanding applications.
Lack of Intellectual Property (IP) Protection and Material Authenticity
Another significant pitfall involves intellectual property risks and material authenticity. Some suppliers offer “engineered” or “branded” nylon blends (e.g., mimicking知名品牌 like PA6, PA66, or specialty variants such as carbon-filled nylon) without proper licensing or technical validation. These knock-off materials may infringe on patents or trademarks, exposing buyers to legal liability. Additionally, misrepresented formulations can lead to unexpected material behavior, compromising product safety and regulatory compliance—particularly critical in industrial, medical, or aerospace applications. Always verify material datasheets, manufacturer credentials, and IP compliance when sourcing high-performance nylon filaments.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Nylon Filament 3D Printer
Material Classification and Regulations
Nylon filament, commonly used in 3D printing, is typically a thermoplastic polymer such as polyamide (PA6, PA66, or other variants). While generally considered non-hazardous in solid form, specific handling, shipping, and storage regulations may apply depending on formulation, additives, and regional regulations. It is essential to review the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) provided by the manufacturer for exact classification.
Shipping and Transportation
Nylon filament spools are generally non-regulated for transport under international standards (e.g., IATA, IMDG, ADR) when shipped in solid, unprocessed form. However, ensure the following:
– Packaging must protect the filament from moisture, physical damage, and environmental exposure.
– Spools should be vacuum-sealed with desiccant to maintain material integrity.
– Declare contents accurately on shipping documentation (e.g., “Thermoplastic filament for 3D printing – Non-hazardous”).
– For commercial shipments, retain a copy of the SDS for compliance audits.
Storage Conditions
To maintain filament quality and ensure workplace safety:
– Store in a dry, climate-controlled environment (relative humidity < 40%).
– Use sealed containers or dry boxes with desiccants.
– Keep away from direct sunlight and heat sources to prevent warping or degradation.
– Label storage areas clearly and inventory regularly to prevent expired or degraded material use.
Workplace Safety and Handling
While nylon filament is not classified as hazardous, safe handling practices are recommended:
– Use gloves when handling dirty or contaminated spools.
– Avoid inhalation of dust or fumes during printing—ensure printers are used in well-ventilated areas or equipped with filtration systems.
– Follow manufacturer guidelines for printer operation, including nozzle temperature and enclosure use.
– Provide employee training on filament handling, printer safety, and emergency procedures.
Environmental and Disposal Compliance
Nylon filament waste (e.g., failed prints, support structures) is typically non-hazardous. Disposal should follow local regulations:
– Recycle if facilities accept polyamides (PA6/PA66).
– Do not incinerate without proper emission controls, as combustion may release toxic fumes.
– Minimize waste through optimized print settings and material reuse programs.
Regulatory Documentation
Maintain the following documentation for compliance:
– Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for each filament batch.
– Records of employee training on handling and safety.
– Shipping manifests and customs declarations (for international shipments).
– Certifications (e.g., RoHS, REACH) if applicable, especially for filaments used in regulated industries.
Import/Export Considerations
For cross-border shipments:
– Verify tariff classification codes (e.g., HS Code 3916.20 for plastic monofilament).
– Comply with destination country’s chemical and plastic regulations (e.g., EU REACH, U.S. TSCA).
– Declare accurate material composition and intended use.
– Consult a customs broker or compliance expert for high-volume or regulated applications.
Conclusion
Nylon filament 3D printing operations require attention to storage, handling, and documentation to ensure safety and regulatory compliance. By adhering to best practices in logistics and maintaining up-to-date compliance records, businesses can operate efficiently while meeting international standards. Always consult filament manufacturers and local authorities for region-specific requirements.
In conclusion, sourcing nylon filament for a 3D printer requires careful consideration of several key factors to ensure optimal print quality, performance, and reliability. Nylon is a high-performance engineering thermoplastic known for its strength, flexibility, and resistance to wear and heat, making it ideal for functional and mechanical parts. However, it also presents challenges such as hygroscopicity, warping, and the need for higher printing temperatures and a heated build chamber.
When sourcing nylon filament, it is essential to prioritize quality and consistency from reputable suppliers. Look for filaments that are properly dried and packaged with desiccants, and consider brands that offer enhanced formulations (e.g., nylon composites like carbon-filled or glass-filled) for specific applications. Proper storage and handling are critical to prevent moisture absorption, which can severely impact print quality.
Additionally, ensure your 3D printer is capable of handling nylon’s demanding requirements—such as a high-temperature hot end (240–260°C), a heated bed (80–110°C), and an enclosed chamber to maintain consistent temperature and reduce warping.
Ultimately, successful nylon 3D printing hinges on balancing material quality, environmental control, and printer compatibility. By sourcing high-quality nylon filament from trusted manufacturers and maintaining proper print conditions, users can fully leverage the material’s advantages to produce durable, high-strength components suitable for industrial and engineering applications.