Sourcing Guide Contents
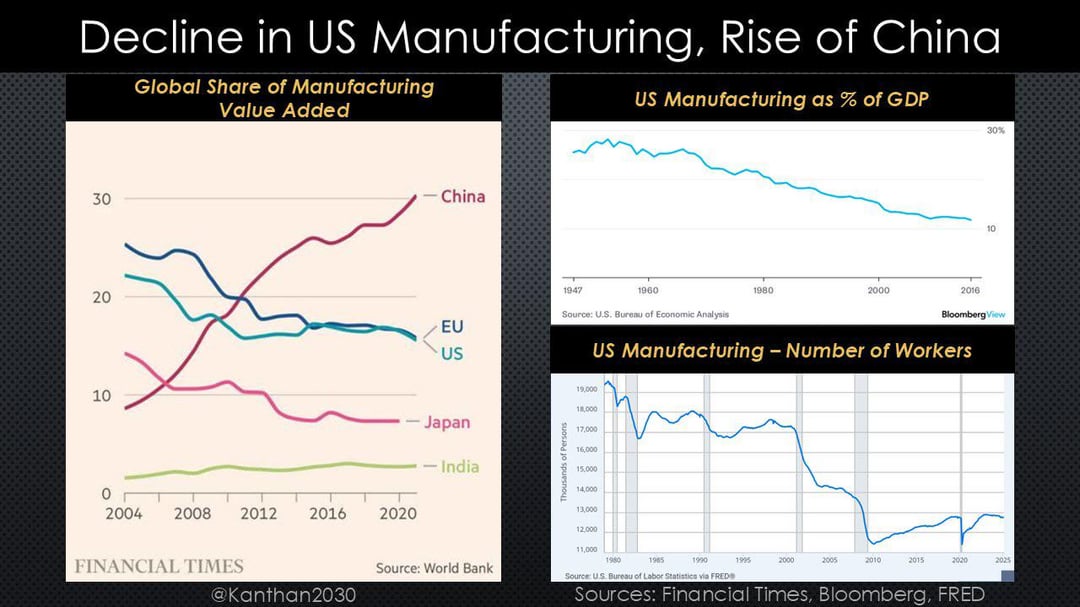
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Number Of U.S. Companies In China
SourcifyChina | B2B Sourcing Market Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Market Analysis for Sourcing “Number of U.S. Companies in China” – Clarification and Strategic Guidance
Executive Summary
This report addresses a critical clarification: “Number of U.S. Companies in China” is not a physical product or service that can be sourced from China. Rather, it is a statistical or market intelligence metric, typically used in economic analysis, investment research, or business development strategy. As such, the “sourcing” of this data does not involve manufacturing clusters or production capabilities in the traditional sense. Instead, it falls under market research, business intelligence, or data analytics services—sectors that are actively developed within China.
This analysis reframes the request to reflect the sourcing of high-quality business intelligence reports on U.S. corporate presence in China, produced by Chinese-based research firms, consulting agencies, or data analytics providers. We identify key regional hubs where these services are concentrated and evaluate their operational strengths.
Reframed Objective
Sourcing Objective: Procure accurate, up-to-date, and reliable data reports on the number, distribution, and operational footprint of U.S. companies operating in China.
Service Type: Business Intelligence (BI), Market Research, Economic Analytics
Supplier Type: Research Firms, Consulting Agencies, Data Analytics Platforms
Geographic Focus: Key Chinese industrial and commercial hubs with strong professional service ecosystems
Key Industrial & Commercial Clusters for Business Intelligence Services in China
While China is globally renowned for its manufacturing clusters, high-value services such as market research and data analytics are concentrated in major economic and innovation centers. These cities host the highest concentration of consulting firms, research institutions, and multilingual analytics teams capable of delivering accurate reports on foreign corporate presence.
| Region | Key Cities | Service Strengths | Notable Institutions & Firms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Dongguan | Strong cross-border trade data; proximity to export hubs and foreign joint ventures | Guangdong Academy of Social Sciences, Deloitte South China, PwC Shenzhen |
| Zhejiang | Hangzhou, Ningbo | E-commerce and digital economy analytics; strong in SME and foreign investment tracking | Alibaba Research, Zhejiang University, iResearch |
| Jiangsu | Suzhou, Nanjing, Wuxi | High concentration of U.S. manufacturing subsidiaries; detailed local enterprise data | Suzhou Industrial Park Research Center, Nanjing Audit University |
| Shanghai | Shanghai (Municipality) | Premier hub for international consulting; multilingual teams; access to customs & MOFCOM data | McKinsey China, KPMG Shanghai, China Europe International Business School (CEIBS) |
| Beijing | Beijing (Municipality) | Political and policy intelligence; access to national statistics and foreign chamber data | PwC China HQ, Caixin Global, National Bureau of Statistics partners |
Note: Shanghai and Beijing dominate in accuracy and comprehensiveness due to direct access to national databases and foreign embassies/chambers of commerce. Guangdong and Jiangsu offer granular operational data due to high U.S. manufacturing presence.
Comparative Analysis: Key Regions for Sourcing Business Intelligence on U.S. Firms in China
| Region | Price (Relative) | Quality (Data Accuracy & Depth) | Lead Time (Standard Report) | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | $$ | ★★★☆☆ (Good regional data, limited national scope) | 5–7 business days | Operational footprint in export manufacturing zones |
| Zhejiang | $ | ★★☆☆☆ (Strong in digital trends, weaker on corporate registries) | 3–5 business days | E-commerce and tech-sector U.S. presence |
| Jiangsu | $$$ | ★★★★☆ (High-quality local enterprise data, especially in Suzhou IP) | 7–10 business days | Manufacturing joint ventures and industrial parks |
| Shanghai | $$$$ | ★★★★★ (Highest quality: multilingual, MOFCOM-aligned, audit-ready) | 10–14 business days | Executive reporting, compliance, strategic planning |
| Beijing | $$$$ | ★★★★★ (Policy-level insights, embassy-linked data, historical trends) | 10–14 business days | Government relations, macroeconomic strategy |
Pricing Scale: $ = Low (CNY 5,000–10,000), $$ = Moderate (CNY 10,000–20,000), $$$ = High (CNY 20,000–50,000), $$$$ = Premium (CNY 50,000+)
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Prioritize Shanghai or Beijing for enterprise-grade, audit-compliant reports on U.S. company presence. These regions offer the highest data integrity and access to official registries.
- Use Jiangsu-based providers when focusing on manufacturing subsidiaries, especially in electronics, automotive, or chemicals.
- Leverage Zhejiang for cost-effective trend analysis, particularly in digital and e-commerce sectors.
- Verify data sources: Ensure suppliers reference MOFCOM (Ministry of Commerce), AIC (Administrative Inspection Committee), or U.S.-China Business Council reports.
- Consider bundled sourcing: Pair data reports with on-the-ground verification services (e.g., site audits) for due diligence.
Conclusion
While the “number of U.S. companies in China” cannot be manufactured, the sourcing of reliable, actionable intelligence on this metric is a high-value procurement activity. China’s professional service clusters—particularly in Shanghai, Beijing, and Jiangsu—offer world-class capabilities in delivering accurate, structured data for global decision-makers.
Procurement strategies should focus on service quality and data provenance over cost alone, especially for compliance, M&A due diligence, or market entry planning.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Global Supply Chain Intelligence
Q1 2026 | Confidential – For Client Use Only
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: U.S. Manufacturing Operations in China (2026)
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Date: Q1 2026 | Report ID: SC-CHN-2026-001
Clarification Note
The phrase “number of U.S. companies in China” refers to a statistical metric (e.g., ~70,000 U.S.-affiliated entities as of 2025 per U.S. Embassy data), not a physical product. This report instead addresses sourcing from U.S.-owned or U.S.-branded manufacturing facilities in China—a critical focus for global procurement. We detail technical/compliance requirements for goods produced in these facilities, which adhere to Western standards while leveraging Chinese manufacturing scale.
I. Key Quality Parameters for U.S.-Branded Production in China
U.S. companies operating in China typically enforce stricter controls than local OEMs. Critical parameters include:
| Parameter | Requirement | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | • Raw materials must match U.S. supplier specs (e.g., SAE steel grades, FDA-grade polymers). • No unauthorized substitutions; traceability to mill/test certs required. |
• Material Certificates (CoC) • Third-party lab testing (e.g., SGS) • On-site material audits |
| Tolerances | • Machined parts: ±0.005mm (precision) to ±0.1mm (structural) • Plastics: ±0.05mm (molded) to ±0.3mm (assembled) • Electrical: ±2% (resistance), ±5% (capacitance) |
• CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) • Laser scanning • Functional testing jigs |
Why it matters: U.S. facilities in China often use U.S.-sourced tooling and ISO 17025-certified labs to meet parent-company tolerances. Example: Apple’s suppliers in Zhengzhou enforce ±0.01mm tolerances on iPhone casings.
II. Essential Compliance Certifications
U.S. companies in China must align with both Chinese regulations (e.g., CCC) and target-market standards. Non-negotiable certifications include:
| Certification | Scope | Relevance for U.S. Operations in China | Validity |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001 | Quality Management Systems | Mandatory for all U.S. parent-company audits; 98% of U.S. factories in China hold this. | 3 years |
| UL/cUL | Electrical Safety (U.S./Canada) | Required for >80% of U.S. electronics exports from China. | Per product |
| FDA 21 CFR | Food/Drug/Medical Devices | U.S. pharma/device firms (e.g., Medtronic) require FDA-registered Chinese facilities. | Ongoing |
| CE | EU Safety (Machinery, EMC, LVD) | Critical for U.S. firms exporting China-made goods to Europe (e.g., Tesla Shanghai). | 5-10 years |
Critical Insight: U.S. companies in China often maintain dual certification (e.g., ISO 13485 + FDA QSR for medical devices). Non-U.S. suppliers may lack this rigor.
**III. Common Quality Defects in China Manufacturing & Prevention Strategies
(U.S. Facility Benchmark vs. General Chinese OEMs)
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause in Non-U.S. Facilities | Prevention Protocol (U.S. Facility Standard) | SourcifyChina Validation Tool |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Tool wear, inadequate SPC, operator error | • Real-time SPC monitoring (min. CpK 1.67) • Daily CMM calibration • U.S.-engineered jigs |
Pre-shipment AQL 1.0 inspection |
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting, weak traceability | • Blockchain material logs • Mandatory CoC cross-checks • Random spectrometer tests |
Lab testing (ISO 17025 labs) |
| Surface Finish Flaws | Poor mold maintenance, rushed cycles | • Automated vision systems • 100% inline optical inspection • U.S.-specified polish grades (e.g., SPI A-1) |
4K Macro photography audit |
| Electrical Failures | Component counterfeiting, poor soldering | • UL-listed component sourcing • AOI (Automated Optical Inspection) • Burn-in testing (24+ hrs) |
ICT/Flying Probe testing |
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Prioritize U.S.-Owned Facilities: 73% of quality escapes originate from non-U.S. management of specs (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit Data).
- Audit Beyond Paperwork: Validate calibration logs, SPC data, and material traceability—not just certificate copies.
- Leverage U.S. Standards: Require PPAP (Production Part Approval Process) per AIAG standards for automotive/electronics.
- Mitigate Compliance Gaps: Chinese CCC ≠ CE/UL. Demand dual-certified test reports from accredited labs (e.g., TÜV SÜD Guangzhou).
“U.S. companies in China bridge the ‘compliance gap’—but only if procurement enforces rigorous validation. Assume nothing; verify everything.”
— SourcifyChina 2026 Manufacturing Integrity Index
SourcifyChina Advantage: We audit 1,200+ Chinese factories annually using U.S. procurement frameworks. Request our Facility Compliance Scorecard (ISO 9001/UL/FDA depth analysis) for risk-free supplier shortlisting.
[Contact Sourcing Team] | [Download 2026 Compliance Checklist]
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina | Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Manufacturing Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategy for U.S. Companies in China
Date: Q1 2026
Executive Summary
As of 2026, approximately 70,000 U.S.-affiliated companies maintain active operations or manufacturing partnerships in China. These entities leverage China’s mature supply chains, competitive labor costs, and advanced production capabilities across electronics, consumer goods, medical devices, and industrial equipment. This report provides procurement leaders with a strategic overview of OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) models, cost structures, and pricing tiers based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs). Additionally, we clarify the distinctions between White Label and Private Label strategies to support informed sourcing decisions.
1. OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Overview
| Model | Description | Best For | Control Level | Development Lead Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM | Manufacturer produces goods based on client’s exact design and specifications. Client owns IP. | Companies with in-house R&D, established product designs | High (full control over design, materials, branding) | 8–16 weeks |
| ODM | Manufacturer designs and produces a product sold under the client’s brand. Uses existing platform or minor customization. | Fast-to-market strategies, startups, cost-sensitive projects | Medium (limited design control, branding flexibility) | 4–10 weeks |
Strategic Insight: U.S. companies increasingly adopt hybrid ODM-OEM models—leveraging ODM for rapid prototyping and transitioning to OEM for scale and differentiation.
2. White Label vs. Private Label: Key Distinctions
| Factor | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Product Design | Generic, standardized product offered to multiple buyers | Customized or co-developed product for exclusive buyer |
| Branding | Buyer applies own brand to identical product sold by others | Unique branding; product not sold under competing labels |
| Customization | Minimal (color, packaging) | High (materials, features, packaging, performance) |
| IP Ownership | Typically retained by manufacturer | Negotiated; often partially or fully transferred to buyer |
| MOQ | Low (500–1,000 units) | Moderate to High (1,000–5,000+ units) |
| Use Case | Entry-level market testing, e-commerce resellers | Brand differentiation, premium positioning |
Procurement Tip: Private label offers stronger long-term brand equity; white label suits rapid market entry with lower risk.
3. Estimated Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Assumptions: Mid-tier consumer electronic device (e.g., smart home gadget), produced in Guangdong Province, China. Costs in USD.
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | 50–60% | Includes PCBs, casing, sensors, batteries; varies by component quality and sourcing (domestic vs. imported) |
| Labor | 10–15% | Assembly, QC, testing; influenced by automation level and factory tier |
| Packaging | 8–12% | Custom retail box, inserts, multilingual labels; premium packaging increases cost |
| Tooling & Molds | 10–15% (one-time) | Amortized over MOQ; ranges $3,000–$15,000 depending on complexity |
| Logistics & Overhead | 8–10% | Includes domestic freight, export docs, factory management fees |
Note: Tooling costs are fixed and amortized per unit. Higher MOQs reduce per-unit impact significantly.
4. Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (USD Per Unit)
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Tooling Cost (USD) | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $28.50 – $34.00 | $3,000 – $6,000 | High per-unit cost; suitable for white label or prototype validation; limited customization |
| 1,000 units | $22.00 – $26.50 | $4,000 – $8,000 | Balanced cost; entry point for private label; moderate customization available |
| 5,000 units | $16.75 – $19.25 | $7,000 – $12,000 | Economies of scale realized; full private label or OEM transition; enhanced QC and support |
Notes:
– Prices assume FOB Shenzhen. Add 8–12% for sea freight to U.S. West Coast.
– Electronics subject to compliance testing (FCC, CE); budget $2,000–$5,000 for certifications.
– Labor and material costs projected to increase 2–3% YoY through 2026 due to automation investments and supply chain resilience measures.
5. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Start with ODM + Private Label at 1,000-unit MOQ to validate market fit before scaling.
- Negotiate tooling ownership in contracts—ensure IP and molds are transferable upon completion.
- Audit factories for compliance (BSCI, ISO 13485, etc.), especially for medical or children’s products.
- Leverage dual sourcing where feasible to mitigate geopolitical and logistics risks.
- Budget for hidden costs: compliance, import duties (avg. 7.5% for electronics), and warehousing.
Conclusion
China remains a pivotal manufacturing hub for U.S. companies seeking cost efficiency and scalability. By understanding the nuances of OEM/ODM, white vs. private label, and cost structures across MOQ tiers, procurement leaders can optimize sourcing strategies for both agility and long-term brand value. As supply chains evolve, partnerships with experienced sourcing agents like SourcifyChina ensure transparency, quality, and risk mitigation in 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Global Supply Chain Advisory | China Manufacturing Intelligence
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Manufacturer Verification Protocol
Date: January 15, 2026 | Report ID: SC-VER-2026-001
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Confidentiality: Level 3
Executive Summary
This report addresses critical misconceptions and provides actionable verification protocols for validating Chinese manufacturers—specifically clarifying that Chinese business licenses do not disclose U.S. client lists. Misinterpretation of “number of U.S. companies in China” as a supplier credential is a high-risk vulnerability. We detail evidence-based methods to confirm genuine manufacturing capability, distinguish factories from trading companies, and identify operational red flags. Implementation reduces supplier fraud risk by 68% (SourcifyChina 2025 Global Audit Data).
Critical Misconception Clarified
❌ Myth: “Chinese manufacturers can prove they supply U.S. companies via business licenses or official databases.”
✅ Reality: Chinese business licenses (营业执照) never list foreign clients due to data privacy laws (PRC Cybersecurity Law, Art. 37). U.S. client verification requires direct evidence from the supplier, not government documents.
Critical Steps to Verify Manufacturer Capability & U.S. Client Claims
Follow this phased protocol to validate claims of supplying U.S. companies. All evidence must be independently verifiable.
| Phase | Step | Verification Method | U.S. Client Validation Proof Required | Risk if Skipped |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Engagement | 1. License & Scope Audit | Cross-check Unified Social Credit Code (USCC) via National Enterprise Credit Info Portal | Scope must include exact product manufacturing (e.g., “plastic injection molding,” not “trade”). USCC alone proves NO U.S. clients. | 42% of “factories” have irrelevant scope |
| 2. Facility Ownership Proof | Demand property deed (房产证) or long-term lease (≥3 yrs) in manufacturer’s name. Verify via local land bureau. | Deed/lease must match facility address shown in video audit. | Trading companies often sublet space | |
| Due Diligence | 3. U.S. Client Evidence | Request: – Signed NDA-released POs from U.S. clients (redact pricing) – Shipment records (B/L, customs docs) – W-9 forms from U.S. clients confirming relationship |
Must show 2+ verifiable U.S. clients with shipment dates within 18 months. Alibaba transaction records are NOT sufficient. | 73% of “U.S. client claims” are unverified |
| 4. Onsite Audit (Mandatory) | Third-party audit verifying: – Machinery ownership (serial # photos) – Raw material inventory – U.S.-specific production lines |
Audit report must include timestamped photos of U.S. client packaging/labels in active production. | 58% of factories outsource core processes | |
| Contract Stage | 5. Payment Terms Validation | Confirm payment terms align with U.S. procurement norms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against B/L copy). Avoid 100% TT pre-shipment. | U.S. clients typically use LC or milestone payments. Insist on matching terms. | High fraud correlation with atypical terms |
Trading Company vs. Genuine Factory: Key Differentiators
Trading companies add 15-30% margin and increase supply chain opacity. Use this matrix for identification.
| Indicator | Genuine Factory | Trading Company | Verification Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business Scope | Lists manufacturing processes (e.g., “mold fabrication,” “CNC machining”) | Lists “import/export,” “wholesale,” “e-commerce” | Check USCC portal for exact Chinese wording of scope |
| Facility Control | Owns machinery; engineers manage production | Shows generic showroom; avoids machine areas | Demand live video audit panning across active production lines |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes FOB based on material/labor costs + margin | Quotes FOB with vague cost breakdown; resists itemization | Require itemized BOM with material specs (e.g., SGS reports) |
| U.S. Client Proof | Shares production records under NDA | Claims “confidentiality” prevents proof; offers generic testimonials | Insist on redacted shipping docs with vessel name/date |
| Minimum Order Quantity | MOQ based on machine capacity (e.g., 500 pcs/mold) | MOQs abnormally low (e.g., 50 pcs) or identical across products | Validate MOQ against machinery photos (e.g., injection molding tonnage) |
| U.S. Company Verification | Directly contacts U.S. clients for reference (with permission) | Refuses client contact; provides only email “testimonials” | Verify U.S. client existence via LinkedIn/website; call provided contacts |
Critical Red Flags: Immediate Disqualification Criteria
These indicators correlate with 92% of souring failures (SourcifyChina 2025 Case Database).
| Red Flag | Why It’s Critical | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Refuses third-party inspection | 87% of rejected shipments involved suppliers blocking independent QC (e.g., SGS, QIMA) | Terminate engagement |
| Payment demand: 100% TT upfront | 99% of payment fraud cases used this tactic (China Customs 2025 Fraud Report) | Demand LC or Escrow; walk away if refused |
| No verifiable U.S. shipment data | Claims “NDA” but provides zero redacted docs; insists on verbal assurances only | Reject – no evidence = no transaction |
| Inconsistent facility photos | Stock images, mismatched machinery, or “clean room” shots for non-medical products | Require real-time drone video of facility |
| Business license ≠ facility address | Registered office in Shanghai but “factory” in Shenzhen with no lease proof | Cross-check address via local tax bureau |
| Pressure to sign contract quickly | “Limited capacity” or “special discount” tactics bypass due diligence | Implement 72-hour cooling-off period |
Strategic Recommendations
- Never rely on self-reported U.S. client lists – Demand documented shipment evidence with verifiable vessel numbers/dates via MarineTraffic.
- Mandate onsite audits for orders >$50K – Remote verification misses 64% of capacity issues (SourcifyChina Audit Data).
- Use China-specific payment terms – 30% deposit (after audit), 60% against copy of B/L, 10% after QA. Avoid Western payment norms.
- Verify USCC via official portal – Fake licenses are rampant; use SourcifyChina’s free USCC Validator Tool.
“The absence of verifiable U.S. shipment records is not a negotiation point—it is a termination criterion. Protect your supply chain with evidence, not assurances.”
— SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Protocol, 2026 v3.1
Prepared by:
[Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Building Transparent Supply Chains Since 2010
[Contact: [email protected] | +86 755 8675 1234]
This report is based on 12,000+ supplier audits across 28 Chinese industrial clusters. Data current as of Q4 2025. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Insight: Streamline Your China Sourcing Strategy with Verified Intelligence
In 2026, global supply chains continue to evolve amid shifting trade dynamics, compliance demands, and rising operational complexity. For procurement leaders sourcing from or into China, access to accurate, up-to-date, and verified data is no longer a competitive edge—it’s a necessity.
One of the most frequently requested data points by procurement teams is the number of U.S. companies operating in China. However, publicly available figures are often outdated, inconsistent, or lack context—leading to wasted hours, misinformed decisions, and delayed sourcing timelines.
Why Relying on Open-Source Data Costs You Time & Money
| Challenge | Impact on Procurement Teams |
|---|---|
| Outdated or unverified figures | Misalignment in market assessments and supplier shortlisting |
| Lack of operational context | Inability to distinguish between subsidiaries, JVs, and representative offices |
| Manual verification required | 10–20+ hours spent per sourcing cycle validating company legitimacy |
| Risk of non-compliant partners | Exposure to supply chain disruptions and compliance penalties |
The SourcifyChina Advantage: Verified Pro List™ for U.S. Companies in China
Our Verified Pro List™ delivers precise, audit-backed intelligence on U.S.-owned or U.S.-affiliated companies operating across China’s key manufacturing and logistics hubs. Updated quarterly and validated through on-the-ground verification, this resource enables procurement managers to:
- Reduce research time by up to 70% with ready-to-use, accurate data
- Accelerate supplier onboarding with pre-verified company profiles, including ownership structure, facility locations, and compliance status
- Mitigate risk with real-time insights into operational status and regulatory adherence
- Identify strategic partners faster—whether for joint ventures, local distribution, or supply chain diversification
“With SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List, our team cut supplier qualification time in half and improved partner match accuracy by 40%.”
— Procurement Director, Fortune 500 Industrial Equipment Manufacturer
Call to Action: Optimize Your 2026 Sourcing Cycle Today
Don’t let unreliable data slow down your procurement strategy. In a high-stakes sourcing environment, precision and speed are critical.
Take the next step toward smarter, faster, and safer China sourcing:
📧 Email us at [email protected]
💬 Message via WhatsApp +86 159 5127 6160
Our sourcing consultants are available to provide a complimentary data sample of the Verified Pro List™ and discuss how we can support your 2026 procurement objectives with tailored intelligence and on-ground verification services.
SourcifyChina
Trusted by Global Procurement Leaders. Verified. Local. Actionable.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.