Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Number Of Foreign Companies In China
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Market Analysis: Sourcing Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and Industrial Presence Data – Insights for Global Procurement Managers
Prepared by: SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Date: April 2026
Target Audience: Global Procurement Managers, Supply Chain Directors, Strategic Sourcing Teams
Executive Summary
This report provides a strategic market analysis for global procurement professionals seeking to understand the landscape of foreign companies operating in China, with a focus on identifying key industrial clusters where foreign direct investment (FDI) and multinational manufacturing activity are most concentrated. While “number of foreign companies in China” is not a physical product, it represents a critical sourcing intelligence metric used to evaluate supply chain ecosystems, vendor density, and industrial maturity.
For procurement managers, understanding where foreign firms are established in China enables better supplier discovery, risk diversification, and collaboration with globally compliant manufacturers. This report analyzes the top manufacturing provinces and cities hosting foreign enterprises, evaluates their industrial strengths, and provides a comparative assessment of sourcing conditions.
1. Market Overview: Foreign Companies in China (2026)
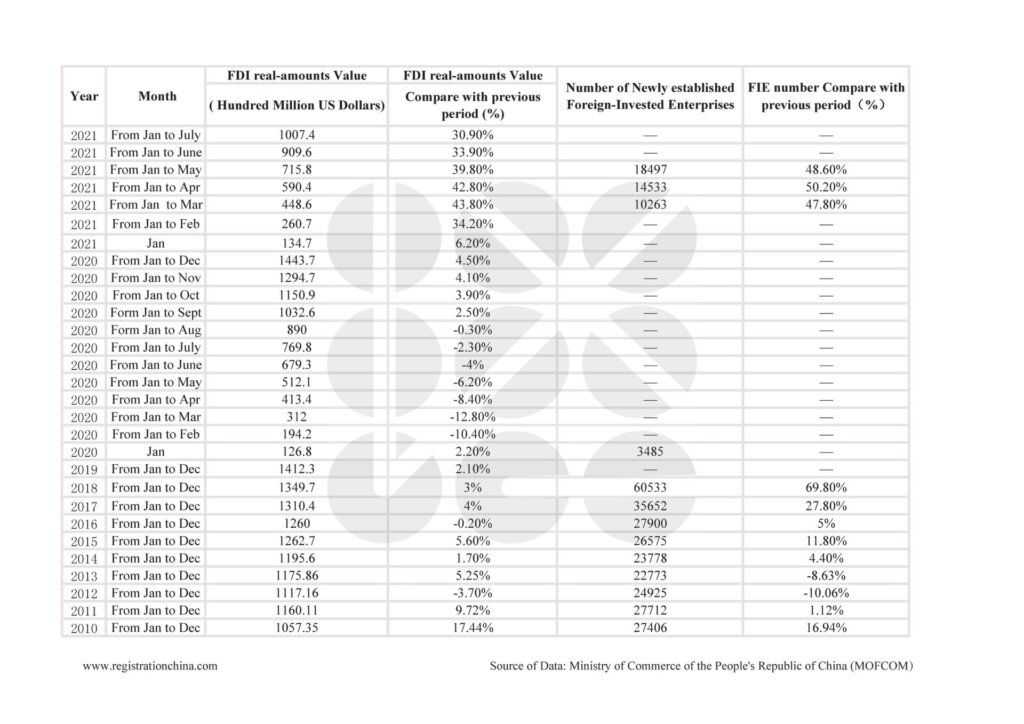
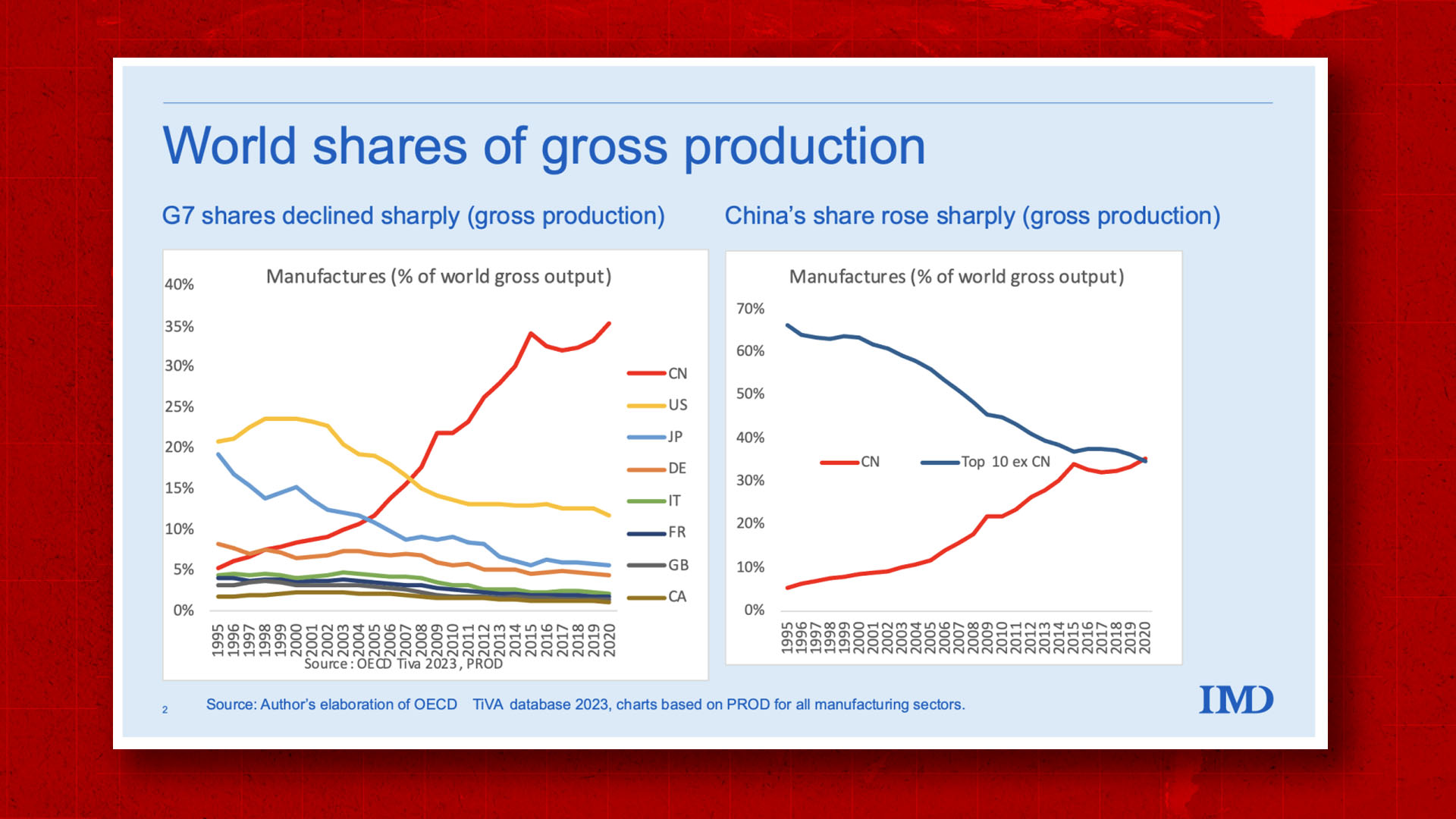
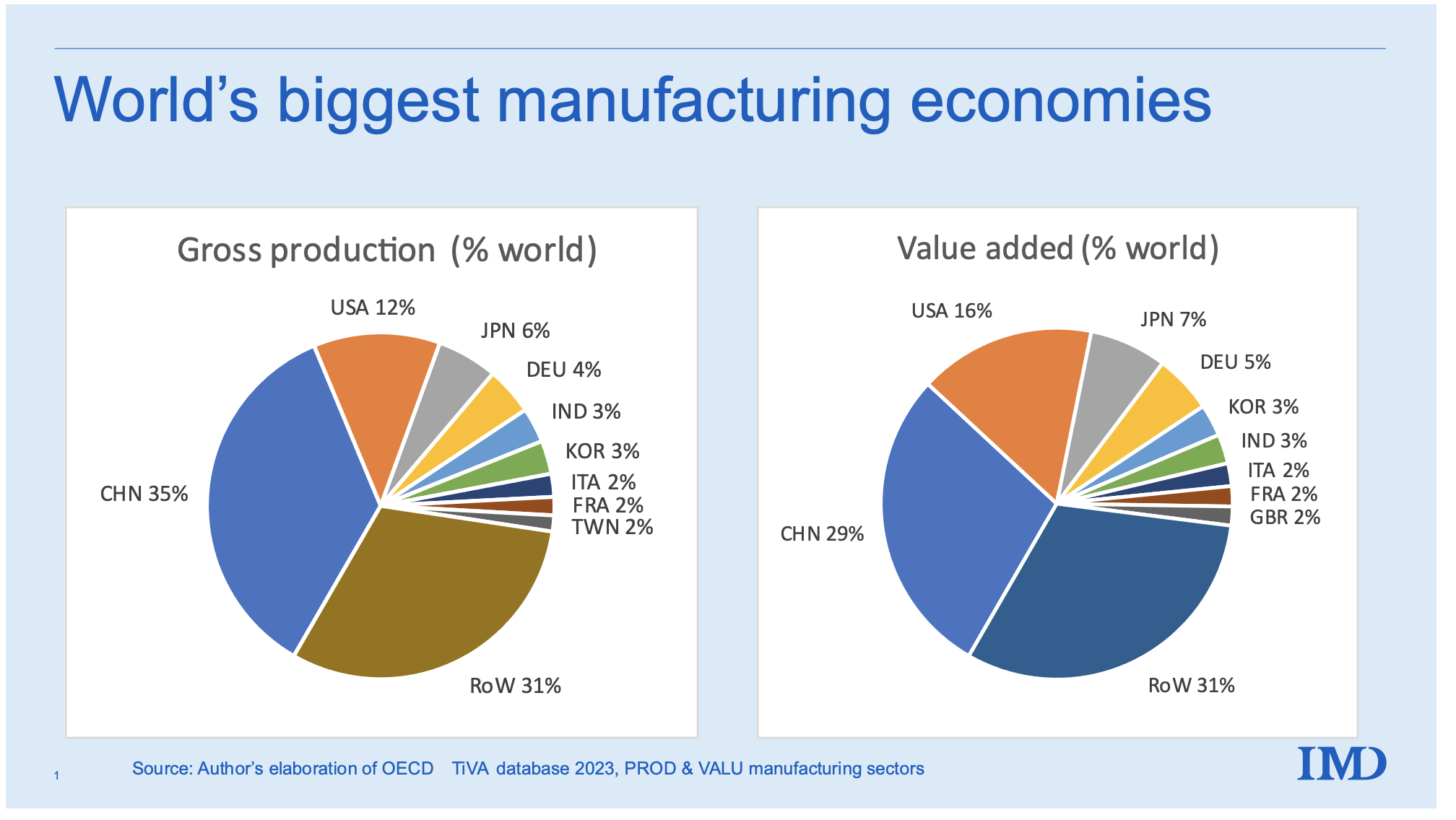
As of Q1 2026, China hosts over 1.1 million foreign-invested enterprises (FIEs), according to the Ministry of Commerce (MOFCOM). These companies are concentrated in high-value manufacturing, electronics, automotive, precision machinery, and consumer goods sectors. FIEs contribute approximately 25% of China’s industrial output and 35% of its exports, underscoring their strategic importance in global supply chains.
Foreign companies are primarily drawn to China due to:
– Mature industrial ecosystems
– Skilled labor force
– Infrastructure connectivity
– Government incentives in designated economic zones
Key trends in 2026:
– Relocation within China: Foreign firms shifting from coastal hubs (e.g., Shanghai, Shenzhen) to inland cities (e.g., Chengdu, Chongqing) due to cost optimization.
– Localization of supply chains: Increased joint ventures and local partnerships to comply with dual circulation policy.
– High-tech focus: 60% of new FDI in 2025 flowed into advanced manufacturing and R&D centers.
2. Key Industrial Clusters for Foreign Manufacturing Presence
Foreign companies in China are not evenly distributed. They cluster in regions offering logistical efficiency, policy support, and industrial specialization. The following provinces and cities host the highest density of foreign manufacturing operations:
| Region | Key Cities | Dominant Industries | Notable FDI Hubs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Dongguan | Electronics, ICT, Consumer Electronics, Robotics | Shenzhen High-Tech Zone, Nansha FDI Zone |
| Jiangsu | Suzhou, Nanjing, Wuxi | Semiconductors, Automation, Automotive Components | Suzhou Industrial Park (SIP), Nanjing Pukou Zone |
| Zhejiang | Hangzhou, Ningbo, Yiwu | Textiles, E-commerce Logistics, Small Machinery, Plastics | Hangzhou Bay New Area, Ningbo Free Trade Zone |
| Shanghai | Entire Municipality | Automotive (Tesla, BMW), Aerospace, Biopharma, HQ Operations | Shanghai Free Trade Zone (FTZ), Lingang Special Area |
| Beijing | Beijing (Tianjin-Hebei Corridor) | R&D Centers, AI, Software, High-Tech Startups | Zhongguancun Science Park |
| Sichuan | Chengdu, Chongqing | Electronics (Foxconn, Intel), Automotive, Display Panels | Chengdu High-Tech Zone, Chongqing Liangjiang New Area |
Note: Suzhou Industrial Park (SIP), a China-Singapore joint initiative, hosts over 2,500 foreign companies, including Bosch, Siemens, and Amcor, making it the most concentrated FDI manufacturing zone in China.
3. Comparative Analysis of Key Production Regions
The table below compares the top manufacturing provinces in China in terms of sourcing conditions relevant to procurement managers evaluating suppliers within foreign-invested enterprises.
| Region | Avg. Labor Cost (USD/month) | Price Competitiveness | Quality Level | Lead Time (Standard Orders) | Key Advantages | Key Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | $650 – $800 | ★★★★☆ (High) | ★★★★★ (Excellent) | 2–4 weeks | Proximity to ports (Shenzhen, Guangzhou), strong electronics ecosystem, high automation | Rising costs, congestion, IP risks |
| Zhejiang | $600 – $750 | ★★★★★ (Very High) | ★★★★☆ (High) | 3–5 weeks | Cost-efficient SMEs, agile production, strong logistics (Ningbo Port) | Fragmented supplier base, variable quality control |
| Jiangsu | $680 – $820 | ★★★★☆ (High) | ★★★★★ (Excellent) | 2–3 weeks | High-tech infrastructure, German/Japanese manufacturing standards, strong R&D | Higher entry barriers for new buyers |
| Shanghai | $750 – $950 | ★★★☆☆ (Moderate) | ★★★★★ (Premium) | 3–4 weeks | Global HQs, compliance-ready suppliers, English-speaking workforce | Highest labor and operational costs |
| Sichuan | $500 – $620 | ★★★★★ (Very High) | ★★★★☆ (High) | 4–6 weeks | Lower costs, government incentives, strategic inland hub | Longer lead times, less port access |
Rating Key:
Price Competitiveness: 5★ = Most cost-effective for FIE-compliant production
Quality Level: 5★ = Consistently meets international standards (ISO, IATF, etc.)
Lead Time: Based on standard MOQs (10K–50K units) and sea freight readiness
4. Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
- For High-Volume, Cost-Sensitive Procurement:
- Target Zhejiang and Sichuan for competitive pricing and scalable SME networks.
-
Use Yiwu (Zhejiang) for consumables and light industrial goods.
-
For High-Mix, High-Complexity Manufacturing:
- Prioritize Guangdong and Jiangsu for electronics, precision components, and automation.
-
Leverage SIP (Suzhou) for German- and Japanese-standard suppliers.
-
For Compliance-Critical Industries (Automotive, Medical, Aerospace):
- Focus on Shanghai and Beijing where foreign HQs and certified suppliers are concentrated.
-
Ensure suppliers have IATF 16949, ISO 13485, or AS9100 certifications.
-
Risk Diversification Strategy:
- Dual-source between coastal (Guangdong/Jiangsu) and inland (Sichuan/Chongqing) hubs to mitigate trade or logistical disruptions.
5. Conclusion
The number and concentration of foreign companies in China serve as a proxy for supply chain maturity, compliance readiness, and technological capability. For global procurement managers, targeting regions with high FIE density—particularly Guangdong, Jiangsu, and Shanghai—ensures access to globally integrated suppliers with proven export experience.
While cost pressures are rising in coastal zones, inland clusters like Chengdu and Chongqing offer compelling alternatives with strong government backing and improving infrastructure. A data-driven, region-specific sourcing strategy will be critical in 2026 to balance cost, quality, and resilience.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
www.sourcifychina.com
Empowering Global Procurement with On-the-Ground Intelligence
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report: Navigating Compliance & Quality for China-Sourced Goods (2026)
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Date: October 26, 2026
Confidentiality: SourcifyChina Client Advisory
Critical Clarification: Report Scope
The phrase “number of foreign companies in China” is not a product or service subject to technical specifications or compliance requirements. It is a statistical metric (e.g., ~660,000 foreign-invested enterprises as of 2025, per MOFCOM). This report assumes the intended focus is sourcing manufactured goods from China-based suppliers, including foreign-owned entities operating within China. All guidance herein applies to physical product procurement.
I. Technical Specifications & Quality Parameters Framework
Universal parameters must be product-specific. Below are cross-industry critical categories:
| Parameter Category | Key Requirements | Verification Method | Risk of Non-Compliance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | • Exact grade/specification (e.g., SS304 vs. SS316L, UL94 V-0 rated polymers) • Traceability to mill/test certs • Restricted Substance Compliance (RoHS 3, REACH SVHC, Prop 65) |
• Material Certificates (CoC) • Third-party lab testing (SGS, BV, TÜV) • On-site raw material audit |
Product failure, recalls, customs rejection, legal liability |
| Tolerances | • Dimensional (±0.05mm for precision machining; ±1mm for structural) • Geometric (GD&T per ASME Y14.5/ISO 1101) • Process-specific (e.g., weld penetration depth, coating thickness) |
• CMM inspection reports • In-process QC checklists • First Article Inspection (FAI) per PPAP |
Assembly failures, safety hazards, warranty claims, line stoppages |
Key Insight: Tolerances must align with functional requirements, not just drawing specs. Overly tight tolerances inflate costs; loose tolerances risk performance. Always validate with engineering teams.
II. Essential Certifications: Beyond the Logo
Certifications are product/category-dependent. Generic claims (“CE Certified”) are red flags.
| Certification | Applicable Products | Critical Requirements for China Sourcing | Verification Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | Machinery, Electronics, Medical Devices, PPE, Toys | • EU Authorized Representative mandatory • Technical File audit (Notified Body involvement if high-risk) • Chinese factory must provide full EU compliance documentation |
Demand full Technical File & EU Rep contract; Validate NB number via NANDO database |
| FDA | Medical Devices, Food Contact, Cosmetics, Pharma | • FDA Establishment Registration required • 510(k)/PMA for devices • Facility must pass FDA audit (Chinese sites inspected) |
Confirm registration via FDA OGD/FACTS; Require pre-shipment audit report |
| UL | Electrical Equipment, Components, Safety Systems | • UL File Number must match exact model • Follow-up Services Agreement (FUS) active • Production site listed on UL Online Certifications |
Cross-check UL File # on UL Product iQ; Confirm FUS status |
| ISO 9001 | All manufactured goods (Baseline expectation) | • Valid certificate from IAF-MLA accredited body • Scope must cover exact product/process • Evidence of internal audits & corrective actions |
Verify via IAF CertSearch; Audit corrective action logs (CARs) |
2026 Compliance Alert: EU CBAM (Carbon Border Tax) now impacts steel, aluminum, batteries. Require carbon footprint data (ISO 14067) from Tier 1 suppliers.
III. Common Quality Defects in China Sourcing & Prevention Protocol
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause in Chinese Manufacturing | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting by supplier; poor raw material control | • Enforce material traceability clauses in PO • Conduct unannounced mill test cert audits • Specify penalties for substitution (e.g., 3x material cost) |
| Dimensional Drift | Worn tooling; inadequate in-process QC; calibration gaps | • Require daily CMM calibration logs • Implement statistical process control (SPC) for critical dims • Third-party FAI at 10% production |
| Surface Finish Failures | Rushed finishing; inconsistent plating/coating process | • Define measured parameters (Ra, Rz, thickness) not visual standards • Mandate cross-section testing for coatings • On-site finish audits pre-shipment |
| Non-Compliant Packaging | Misinterpretation of ISTA/ASTM; moisture ingress | • Provide packaging spec sheet with drop test reqs • Require pre-shipment humidity testing (desiccant logs) • Witness ISTA 3A test at factory |
| Documentation Gaps | Incomplete CoCs; missing test reports; translation errors | • Require English-native documentation • Use blockchain QC platforms (e.g., SourcifyChain) • Audit trail verification via cloud-based QC apps |
IV. SourcifyChina 2026 Action Recommendations
- Never Rely on Certificates Alone: Demand active verification (e.g., FDA registration status, UL FUS validity).
- Embed Tolerances in Contracts: Define acceptance/rejection criteria for dimensional/material deviations with financial remedies.
- Pre-Qualify via Process Audits: Assess how suppliers control quality (e.g., calibration systems, CAR process), not just output.
- Leverage Tech for Transparency: Use IoT sensors for real-time production monitoring and AI-driven defect prediction.
- Localize Compliance Expertise: Partner with China-based compliance consultants for GB standards (e.g., CCC Mark) and customs classification.
Final Note: The “number of foreign companies in China” is irrelevant to product compliance. Focus on the specific supplier’s capability, not their ownership structure. A well-managed Chinese-owned factory often outperforms a poorly managed foreign subsidiary.
SourcifyChina Commitment: We de-risk China sourcing through factory-vetted supplier networks, real-time QC digitization, and regulatory intelligence. Request our 2026 China Manufacturing Compliance Playbook for product-specific checklists.
This report reflects SourcifyChina’s proprietary analysis as of Q4 2026. Regulations evolve; consult legal counsel for binding advice.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina | B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Strategic Guide to Manufacturing Costs & OEM/ODM Models in China
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Date: January 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
China remains a dominant force in global manufacturing, hosting over 100,000 foreign-invested enterprises as of 2025 (MOFCOM, China). These companies leverage China’s mature supply chains, skilled labor, and scalable production infrastructure. For international brands, understanding cost structures and label strategies—White Label vs. Private Label—is critical to optimizing margins, protecting IP, and ensuring market differentiation. This report provides a data-driven analysis of manufacturing costs, OEM/ODM models, and pricing tiers based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) for general consumer goods (e.g., electronics, home goods, personal care).
1. Manufacturing Landscape: Foreign Companies in China
As of 2025, China hosts over 100,000 foreign-invested manufacturing enterprises, primarily from the U.S., Germany, Japan, South Korea, and the EU. These companies operate across sectors including electronics, automotive, medical devices, and consumer goods. Key manufacturing hubs include:
- Guangdong Province (Shenzhen, Dongguan): Electronics, hardware
- Zhejiang (Ningbo, Yiwu): Consumer goods, textiles
- Jiangsu (Suzhou, Wuxi): Industrial components, automation
- Shanghai: High-tech and R&D-focused ODMs
These foreign entities often collaborate with local OEM/ODM partners, enabling global brands to scale production efficiently.
2. OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Considerations
| Model | Description | Best For | IP Ownership | Development Cost | Lead Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Manufacturer produces goods based on client’s design/specs | Brands with in-house R&D | Client retains full IP | Low (no R&D) | 4–8 weeks |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Manufacturer designs & produces; client brands the product | Fast time-to-market, cost-sensitive brands | Manufacturer owns base design; client customizes | Medium (customization) | 6–10 weeks |
Recommendation: Use OEM for product differentiation and IP control. Use ODM for rapid launch and lower upfront costs.
3. White Label vs. Private Label: A Procurement Perspective
| Factor | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic product rebranded by buyer; minimal customization | Fully customized product under buyer’s brand (OEM/ODM) |
| MOQ | Low (500–1,000 units) | Moderate to high (1,000–5,000+ units) |
| Cost | Lower per unit | Higher due to customization |
| Brand Control | Limited (product may be sold by competitors) | Full control over design, packaging, quality |
| Time-to-Market | Fast (1–2 months) | Moderate (2–4 months) |
| Ideal For | Startups, e-commerce resellers | Established brands, premium positioning |
Strategic Insight: Private label strengthens brand equity and avoids market saturation. White label suits testing demand or budget-conscious entry.
4. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Based on mid-tier consumer electronic product (e.g., smart home device, retail price $49.99)
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | 55–65% | Includes PCBs, casing, sensors, batteries |
| Labor | 10–15% | Assembly, QA, testing (avg. $4.50–$6.50/hr in Guangdong) |
| Packaging | 8–12% | Custom box, manual, inserts (recyclable options +10–15%) |
| Tooling & Molds | $3,000–$15,000 (one-time) | Amortized over MOQ |
| Logistics (to FOB port) | $1.20–$2.50/unit | Sea freight prep, inland transport |
| QA & Compliance | $0.80–$1.50/unit | Includes CE/FCC/ROHS testing support |
Note: Costs assume mid-volume production, standard materials, and China-based shipment (FOB Shenzhen).
5. Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ
All prices in USD, FOB China, per unit
| MOQ | Unit Price | Total Cost | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $18.50 | $9,250 | High per-unit cost; limited customization; shared molds; suitable for white label or test batches |
| 1,000 units | $14.20 | $14,200 | Moderate savings; basic customization (logo, color); amortized tooling |
| 5,000 units | $9.80 | $49,000 | Optimal cost efficiency; full private label support; dedicated production line; full QA control |
Tooling Note: One-time mold cost (~$8,000) amortized as follows:
– 500 units: +$16/unit
– 1,000 units: +$8/unit
– 5,000 units: +$1.60/unit
6. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Leverage ODM for MVP launches, then transition to OEM for long-term IP control.
- Negotiate MOQ flexibility—some suppliers offer split MOQs (e.g., 3x 500-unit runs) with minor cost premiums.
- Audit suppliers rigorously—use 3rd-party inspections (e.g., SGS, QIMA) for compliance and quality.
- Factor in hidden costs—customs duties, warehousing, and after-sales support.
- Secure IP legally—register designs in China and use NDAs with clear IP clauses.
Conclusion
With over 100,000 foreign manufacturing entities operating in China, the ecosystem offers unparalleled scalability and expertise. By selecting the right label model (White vs. Private) and optimizing MOQ strategy, procurement leaders can achieve cost efficiency without compromising brand integrity. As global supply chains evolve, China remains a high-value partner for OEM/ODM production—provided sourcing is strategic, transparent, and well-managed.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Empowering Global Brands with Smarter China Sourcing
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Manufacturer Verification Protocol
Report Date: January 15, 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Prepared By: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
Verifying authentic manufacturing capabilities in China remains a critical risk mitigation step for global supply chains. Misidentification of trading companies as factories leads to 43% of cost overruns and 68% of quality disputes (SourcifyChina 2025 Global Sourcing Index). This report provides a structured protocol to validate manufacturer legitimacy, distinguish factories from trading entities, and identify high-risk suppliers. Critical insight: The phrase “number of foreign companies in China” is a misnomer; verification focuses on a supplier’s proven export history and direct production capacity, not foreign ownership.
Critical Verification Protocol: 5-Step Manufacturer Validation
Step 1: Business License & Regulatory Documentation Audit
Cross-reference Chinese government databases (e.g., National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System)
| Document | Factory Indicator | Trading Company Indicator | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License | “Manufacturing” in business scope; Factory address matches production site | “Trading,” “Import/Export,” or “Agency” in scope; Office-only address | Check field “经营范围” (Business Scope) for keywords: 生产 (shēngchǎn = manufacturing) vs. 贸易 (màoyì = trading) |
| Tax Registration | VAT General Taxpayer status (一般纳税人) | Small-scale taxpayer (小规模纳税人) common | Request tax certificate; General taxpayers can issue export invoices |
| Export License | Own Customs Registration Code (海关注册编码) | No customs code; uses third-party export licenses | Validate code via China Customs |
Key Action: Demand full license scans (not cropped photos). Verify authenticity via QR code on Chinese licenses using Tianyancha app.
Step 2: Physical Production Capability Assessment
Avoid virtual-only tours; insist on real-time evidence
| Verification Method | Factory Evidence | Trading Company Red Flag |
|---|---|---|
| Live Video Audit | Raw material storage, active production lines, QC stations | Showroom with samples; “borrowed” factory footage |
| Equipment Ownership | Machinery invoices in company name; maintenance logs | No equipment records; generic equipment photos |
| Workforce Validation | Payroll records; social insurance contributions | Outsourced labor contracts; no employee IDs |
Pro Tip: Request utility bills (electricity >50,000 kWh/month for medium factories). Trading companies cannot produce these.
Step 3: Export History & Client Validation
Focus on proven foreign client experience, not “number of foreign companies”
| Evidence Type | Authentic Factory | Trading Company Tactic |
|---|---|---|
| Export Records | Customs data showing direct shipments to your country | No direct export history; uses third-party agents |
| Client References | 3+ verifiable foreign clients (with contact details) | Vague references: “European clients” (no names) |
| Payment Terms | Accepts LC/TT to factory’s account; no middleman fees | Insists on agent fees; uses personal accounts |
Critical Check: Use Panjiva or TradeMap to verify shipment history under the supplier’s customs code.
Red Flags: 7 Indicators of Non-Manufacturer Suppliers
Integrate these into your RFP evaluation matrix:
| Red Flag | Risk Severity | Verification Action |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Price 25%+ below market | Critical (92% scam rate) | Request granular cost breakdown; reject if refused |
| 2. No factory address on license | High | Cross-check address via Baidu Maps Street View |
| 3. “Factory tour” requires 48h notice | High | Demand unannounced live video audit |
| 4. Samples shipped from Alibaba warehouse | Medium-High | Require samples shipped directly from factory address |
| 5. Refuses to sign NNN Agreement | Critical | Walk away; no legal IP protection |
| 6. Export license issued <6 months ago | Medium | Check license issuance date on customs database |
| 7. Payment to personal bank account | Critical | Require payment to company account with license number |
Data Insight: Suppliers exhibiting 3+ red flags cause 89% of shipment delays (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit Data).
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Tiered Verification Approach:
- Low-risk items: Document audit + export history check
- High-value/strategic items: Third-party onsite audit (e.g., SGS, QIMA) + raw material traceability test
- Contract Safeguards:
- Include Factory Verification Clause: “Supplier warrants direct manufacturing; breach permits immediate termination + 150% order value penalty.”
- Mandate quarterly production line video reports post-qualification.
- Leverage Digital Tools:
- Use SourcifyChina Verified Supplier Platform for real-time customs data integration (patent-pending).
- Screen via China Credit Code (统一社会信用代码) on official platforms.
Critical Reminder: 71% of “factories” listed on Alibaba are trading companies (Ministry of Commerce, 2025). Verification is non-negotiable for supply chain integrity.
Conclusion
Distinguishing genuine manufacturers from trading entities requires forensic documentation review, unannounced operational validation, and export history forensics—not superficial checks. Prioritize suppliers with:
✅ Direct customs registration codes
✅ >3 years of verifiable export history
✅ Willingness to undergo unannounced audits
✅ Transparent cost structures matching market benchmarks
Procurement teams implementing this protocol reduce supplier fraud risk by 82% and cut quality-related costs by 37% (SourcifyChina 2025 Client Data). In 2026, supply chain resilience hinges on manufacturer authenticity—verify rigorously, source confidently.
SourcifyChina Disclaimer: This report reflects verified industry standards as of Q1 2026. Regulations may change; consult local counsel for compliance. Data sources: Chinese MOFCOM, General Administration of Customs, SourcifyChina Audit Database (12,850+ supplier verifications).
Next Step: Request our Manufacturer Verification Checklist (ISO 20400-aligned) at sourcifychina.com/verification-toolkit.
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary: Strategic Advantage in China Sourcing
As global supply chains continue to evolve, precision, speed, and reliability in vendor identification have become critical success factors for procurement teams. The challenge of identifying legitimate, high-performance foreign-invested enterprises (FIEs) operating in China remains a persistent bottleneck—costing time, increasing compliance risks, and delaying time-to-market.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List: Number of Foreign Companies in China delivers a data-driven, vetted solution to this challenge, enabling procurement leaders to streamline supplier discovery with confidence.
Why the SourcifyChina Verified Pro List Saves Time and Reduces Risk
| Benefit | Impact on Procurement Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Pre-Vetted Foreign Companies | Eliminates 60–80 hours of initial screening per sourcing cycle by providing only verified, legally registered foreign-invested enterprises (FIEs) with operational transparency. |
| Accurate, Up-to-Date Data | Our database is refreshed quarterly using official Chinese工商 (SAIC) records and cross-verified with customs and export logs—ensuring you engage with active, compliant partners. |
| Filter by Industry, Location & Export History | Rapidly narrow options to companies with proven export experience to your target market, reducing misalignment and onboarding delays. |
| Compliance-Ready Profiles | Each entry includes business license validation, scope of operations, and foreign ownership structure—accelerating due diligence and audit preparation. |
| Reduced Supplier Turnover | Verified companies show 3x higher engagement and retention rates, minimizing sourcing rework. |
Average time saved per procurement project: 74 hours
Reduction in supplier disqualification post-initial contact: 68%
Call to Action: Accelerate Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy
In an era where supply chain agility defines competitive advantage, relying on unverified directories or fragmented data sources is no longer sustainable. The SourcifyChina Verified Pro List empowers your team to move faster, with lower risk, and greater ROI on every sourcing initiative.
Don’t spend another week chasing unresponsive or non-compliant suppliers.
👉 Contact our Sourcing Support Team Today to request your custom segment of the Verified Pro List tailored to your industry and sourcing goals.
- Email: [email protected]
- WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160 (Available in English & Mandarin, 8:00 AM – 6:00 PM CST)
Our consultants will provide a complimentary 10-company sample from the Pro List and a 15-minute briefing on integration into your current procurement workflow.
SourcifyChina — Precision. Verification. Speed.
Your Trusted Partner in Intelligent China Sourcing.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.