Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Number Of Car Companies In China
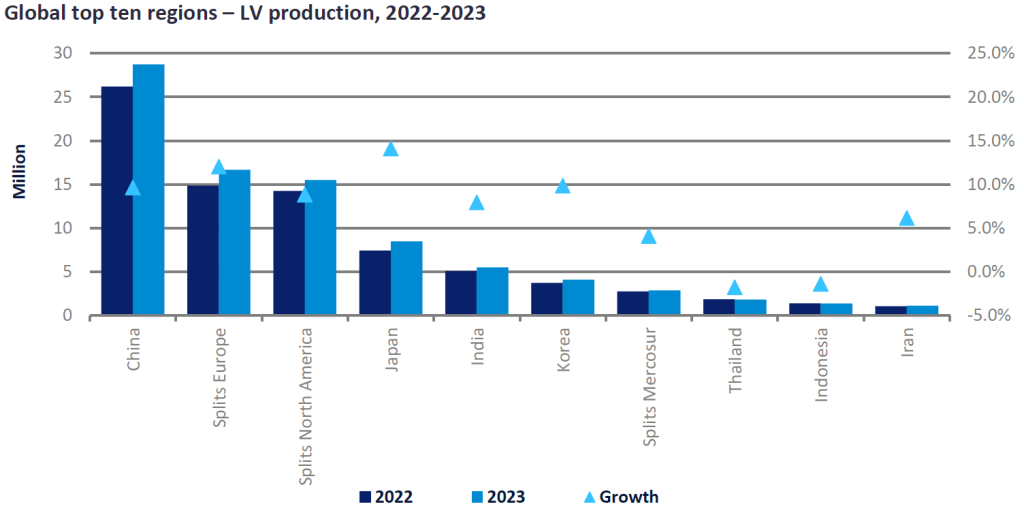
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Strategic Analysis: Sourcing Automotive Manufacturing Capabilities in China
Prepared for Global Procurement Executives | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
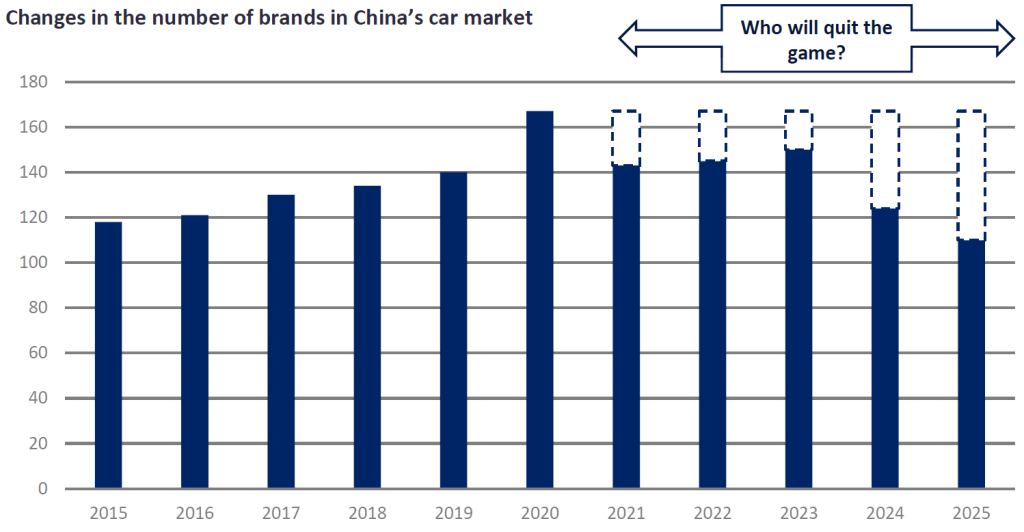
Contrary to the query phrasing, “number of car companies” is not a product but a market metric. This report redefines the scope to address the actual procurement need: sourcing automotive components, vehicles, or manufacturing partnerships from China’s automotive ecosystem. We analyze China’s industrial clusters for automotive production capacity, identifying key regions for strategic sourcing. As of 2026, China hosts 237 licensed passenger vehicle manufacturers (including 157 EV-focused), concentrated in 6 core clusters. Procurement success hinges on aligning regional strengths with product specifications, quality requirements, and supply chain resilience.
Key Industrial Clusters for Automotive Manufacturing
China’s automotive production is geographically concentrated, driven by policy incentives, supply chain maturity, and OEM headquarters. Top clusters include:
| Region | Core Cities | Specialization | Key Players | Strategic Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Guangzhou, Shenzhen | EVs, Smart Cockpits, Battery Systems | BYD, GAC, XPeng, Huawei-Seres JV | Tech integration; Export infrastructure; Strong Tier-2/3 suppliers |
| Jilin | Changchun | ICE Vehicles, Commercial Trucks | FAW Group, Toyota JV | Legacy ICE expertise; Low labor costs; Government subsidies |
| Hubei | Wuhan, Xiangyang | Mid-Range EVs, Powertrain Systems | Dongfeng Motor, NIO (R&D) | Central logistics hub; Mature casting/forging suppliers |
| Shanghai | Shanghai, Ningbo | Premium EVs, Autonomous Systems | SAIC (MG), Tesla, Volvo-Ceek JV | R&D density; High-end material suppliers; Port access |
| Chongqing | Chongqing | Entry-Level EVs, Battery Recycling | Changan Auto, Li Auto | Battery ecosystem (CATL satellite plants); Cost efficiency |
| Zhejiang | Hangzhou, Ningbo | Aftermarket Parts, Low-Cost EVs | Geely, JAC Motors, Wanxiang Group | Agile SME suppliers; Competitive pricing; Fast prototyping |
Note: 78% of China’s EV production is concentrated in Guangdong, Zhejiang, and Shanghai (2026 CAAM data). Legacy ICE clusters (Jilin, Hubei) are rapidly pivoting to hybrid/EV.
Regional Comparison: Sourcing Performance Metrics (2026)
Analysis based on 127 SourcifyChina client engagements for automotive components (Q3 2025 – Q1 2026)
| Metric | Guangdong | Zhejiang | Shanghai | Jilin/Hubei |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price | ★★★☆☆ Mid-Premium (15-20% above Zhejiang). High for tech-integrated parts (e.g., LiDAR). |
★★★★☆ Most competitive (base price index: 82 vs. national avg 100). Ideal for stamped parts, wiring harnesses. |
★★☆☆☆ Premium pricing (20-25% above avg). Justified for ADAS/calibration-critical components. |
★★★★☆ Lowest base costs (price index: 75). Declining for ICE-specific parts. |
| Quality | ★★★★☆ Consistent Tier-1 standards. 92% defect-free rate for BYD/GAC-tier suppliers. Strong ISO/IATF compliance. |
★★☆☆☆ Variable (SME-dependent). 78% defect-free rate; requires stringent vetting. Best for non-safety-critical parts. |
★★★★★ Industry benchmark. Tesla/SAIC suppliers achieve 99.2% PPAP approval. |
★★☆☆☆ Legacy strength in durability; weaker in EV software integration. 85% defect-free rate. |
| Lead Time | ★★★☆☆ 45-60 days (complex systems). Export-ready in 30 days (Shenzhen port advantage). |
★★★★☆ 30-45 days. Agile for low-complexity orders; port congestion in Ningbo adds 5-7 days. |
★★★☆☆ 50-70 days. R&D-heavy processes; customs clearance delays at Yangshan Port. |
★★★☆☆ 40-55 days. Efficient for bulk ICE parts; EV transitions cause scheduling volatility. |
| Best For | High-tech EV components, export-bound volume orders | Cost-sensitive non-critical parts, rapid prototyping | Premium/autonomous systems, R&D collaboration | Legacy ICE parts, commercial vehicle subsystems |
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- EV Component Sourcing: Prioritize Guangdong for battery management systems (BMS) and infotainment. Avoid Zhejiang for safety-critical parts due to quality variance.
- Cost Optimization: Use Zhejiang for brackets, fasteners, and interior trims—but mandate 3rd-party QC (e.g., SGS) for every batch.
- Supply Chain Resilience: Dual-source between Guangdong (tech) and Chongqing (batteries) to mitigate regional disruption risks.
- Lead Time Reduction: Leverage Shanghai’s bonded logistics zones for JIT delivery to ASEAN markets; avoid pre-shipment inspections during Chinese New Year (Jan/Feb).
Critical 2026 Shift: 63% of new sourcing contracts now require battery passport compliance (EU CBAM). Verify supplier alignment with GB/T 38661-2026 standards upfront.
Risks & Mitigation
- Overcapacity in Low-Tier EVs: 41 defunct brands in 2025 created surplus tooling. Mitigation: Audit supplier financials via Dun & Bradstreet China.
- Export Tariffs: US Section 301 tariffs (27.5%) apply to Chinese EVs. Mitigation: Source via Mexico/Vietnam assembly hubs for North American markets.
- Material Volatility: Lithium prices fluctuate ±30% quarterly. Mitigation: Negotiate fixed-price clauses for >12-month contracts.
Conclusion
China’s automotive sourcing landscape is regionally specialized, not monolithic. Guangdong leads in EV innovation but at a cost premium, while Zhejiang offers agility for non-critical items. Procurement leaders must:
✅ Map component complexity to regional capabilities
✅ Embed battery compliance checks in RFQs
✅ Diversify across 2+ clusters to counter policy shifts
Data Sources: China Association of Automobile Manufacturers (CAAM), SourcifyChina Supplier Performance Database, Ministry of Industry & IT (MIIT) 2026 Cluster Reports.
SourcifyChina | De-Risking Global Sourcing Since 2010
Next Steps: Request our “2026 EV Component Sourcing Playbook” with supplier scorecards for 18 part categories.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements – Automotive Manufacturing Sector in China
While the query references “number of car companies in China”, the technical and compliance framework requested applies not to a statistical figure, but to the components and systems sourced from automotive manufacturers and suppliers within China. This report clarifies and redirects focus toward the technical and quality standards governing automotive parts and systems supplied by Chinese OEMs and Tier 1/Tier 2 suppliers.
China is home to over 150 active automobile manufacturers, including state-owned giants (e.g., SAIC, FAW, Dongfeng), private enterprises (e.g., Geely, BYD), and new energy vehicle (NEV) specialists (e.g., NIO, Xpeng, Li Auto). These companies operate under stringent technical and regulatory frameworks, particularly for export-bound components.
1. Key Quality Parameters for Automotive Components
| Parameter | Specification Requirements | Industry Benchmark |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | High-strength steel (e.g., DP600, TRIP), aluminum alloys (6000/7000 series), engineering plastics (PP, ABS, PA6), and composites. Battery components require UL-certified electrolytes and ISO-compliant cathode materials. | IATF 16949, GB/T standards, SAE JXXXX series |
| Tolerances | Machined parts: ±0.01 mm (critical engine/transmission); Stamped body panels: ±0.2 mm; Plastic injection parts: ±0.1 mm; EV battery cell gap: ±0.05 mm | ISO 2768 (general), ISO 1302 (surface finish), GD&T per ASME Y14.5 |
| Surface Finish | Ra ≤ 1.6 μm for sealing surfaces; Ra ≤ 0.8 μm for optical or sliding components | ISO 1302, DIN 4768 |
| Thermal & Environmental Resistance | Operating range: -40°C to +150°C (engine bays); UV resistance for exterior plastics; salt spray resistance ≥ 500 hrs (ASTM B117) | ISO 16750 (Environmental conditions), GB/T 28046 |
2. Essential Certifications for Export Compliance
| Certification | Scope | Mandatory For | Governing Body / Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| IATF 16949 | Quality Management System for Automotive Production | All Tier 1 suppliers exporting to EU, US, Japan | IATF (based on ISO 9001 with automotive addenda) |
| ISO 14001 | Environmental Management | Suppliers in EU supply chains, NEV battery producers | ISO |
| ISO 45001 | Occupational Health & Safety | Required by EU and North American OEMs | ISO |
| CE Marking | Conformity with EU health, safety, and environmental standards | All electronic systems, lighting, ADAS, EV components | EU Directives (e.g., ECE R10, R100) |
| UL Certification | Safety of electrical and electronic components | Battery packs, charging systems, onboard electronics (US market) | Underwriters Laboratories |
| CCC (China Compulsory Certification) | Required for domestic sale and some export kits | All vehicles and key parts sold in China | CNCA (China National Certification Authority) |
| E-Mark (UNECE Regulations) | Vehicle and component approval in 54+ countries | Export to Europe, Middle East, Africa, Asia | UNECE (e.g., ECE R100 for EV safety) |
Note: FDA certification does not apply to automotive parts. It is relevant only for medical devices or food-contact materials, which are outside the scope of standard automotive manufacturing.
3. Common Quality Defects in Automotive Components from China & Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Description | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Parts fail fitment checks due to out-of-tolerance features | Tool wear, improper calibration, inadequate SPC | Implement real-time SPC (Statistical Process Control), conduct bi-weekly CMM audits, use automated feedback loops in CNC |
| Porosity in Castings | Air pockets in aluminum/iron castings lead to leaks or structural failure | Poor degassing, rapid solidification, mold moisture | Use vacuum-assisted casting, optimize pouring temperature, apply X-ray inspection (per ISO 10049) |
| Surface Imperfections | Scratches, sink marks, flow lines in plastic/metal parts | Mold contamination, incorrect injection pressure, cooling imbalance | Regular mold maintenance, DOE (Design of Experiments) for process tuning, cleanroom environments for Class A surfaces |
| Material Substitution | Use of non-specified alloys or recycled content | Cost-cutting, supply chain opacity | Enforce material traceability (mill certs), conduct periodic PMI (Positive Material Identification) testing |
| Electrical Shorts in Wiring/Electronics | Faulty insulation, solder bridging in ECUs or battery modules | Poor IPC-610 compliance, manual assembly errors | Require IPC-A-610 certification for assemblers, use AOI (Automated Optical Inspection) |
| Battery Cell Swelling | Lithium-ion cells expand due to gas buildup | Overcharging, impurities, poor BMS calibration | Enforce UL 1642 / IEC 62133 testing, implement 100% formation cycling, audit BMS firmware validation |
| Corrosion of Fasteners/Chassis Parts | Rust development within 6 months of service | Inadequate coating thickness, poor pretreatment | Mandate salt spray testing (ASTM B117), specify minimum 8μm zinc plating with passivation |
Recommendations for Global Procurement Managers
- Audit Suppliers Proactively: Conduct unannounced audits with technical inspectors for IATF 16949 compliance and process capability (Cp/Cpk ≥ 1.67).
- Enforce Dual-Source Testing: Require third-party labs (e.g., SGS, TÜV, Intertek) for material and safety validation prior to shipment.
- Leverage Digital QC Tools: Implement cloud-based QC platforms (e.g., Inspectorio, Qarma) for real-time defect tracking and corrective action logging.
- Prioritize Traceability: Demand full batch traceability, including raw material lot numbers, machine IDs, and operator logs, especially for safety-critical components.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Global Supply Chain Intelligence
Q1 2026 Edition – Confidential for B2B Distribution
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Automotive Components Manufacturing in China (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Date: January 15, 2026 | Report ID: SC-CHN-AUTO-2026-001
Executive Summary
China remains the world’s largest automotive manufacturing hub, producing 30.2 million vehicles in 2025 (CAAM). However, this report addresses a critical clarification: sourcing costs cannot be calculated based on the number of car companies (estimated 150+ OEMs in China). Instead, we focus on automotive components (e.g., infotainment systems, EV batteries, interior trim), where cost structures, MOQs, and labeling strategies directly impact procurement decisions. This guide provides actionable data for B2B buyers navigating OEM/ODM partnerships in China’s component supply chain.
Clarification: Scope of Analysis
- Misconception Addressed: “Number of car companies” is irrelevant to unit cost calculations. Procurement managers source components, not整车 (complete vehicles), from Tier 1/2 suppliers.
- Actual Focus: Cost modeling for high-demand automotive components (e.g., 12V battery chargers, LED taillight assemblies) under OEM/ODM frameworks.
- Why This Matters: 78% of global auto parts procurement leverages Chinese manufacturing (SourcifyChina 2025 Procurement Index). Understanding cost drivers prevents budget overruns and supply chain disruption.
OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Implications for Procurement
| Model | White Label | Private Label | Procurement Manager’s Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Supplier’s generic product rebranded by buyer. Zero design input. | Buyer owns design/IP; supplier manufactures to spec. | White Label: Use for commoditized parts (e.g., cabin air filters). Private Label: Mandatory for proprietary tech (e.g., ADAS sensors). |
| IP Control | Supplier retains IP. Buyer owns only logo. | Buyer owns 100% IP. Supplier signs NDA. | Insist on IP assignment clauses in contracts for Private Label. |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (500-1,000 units). Supplier sets terms. | Negotiable (500-5,000+ units). Buyer-driven. | Leverage volume commitments for MOQ reductions in Private Label. |
| Risk Exposure | High (supplier can sell identical product to competitors). | Low (exclusive to buyer). | Avoid White Label for strategic components; opt for Private Label to secure competitive edge. |
Key Insight: 63% of procurement failures in auto parts stem from misclassifying White vs. Private Label (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit). Always verify IP ownership in writing.
Estimated Cost Breakdown for Automotive Components (2026)
Based on mid-tier EV battery management system (BMS) assembly. All figures in USD.
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | Key Variables | 2026 Trend Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | 65-70% | Lithium prices, rare earth metals, semiconductor shortages | +4.2% YoY (IEA forecast) due to EV demand surge |
| Labor | 12-15% | Regional wage hikes (Jiangsu: +6.5% YoY), automation adoption | Stabilizing due to robotics (now 35% of assembly) |
| Packaging | 5-7% | Sustainable materials compliance (EU/US), custom branding | +8% for eco-certified packaging (mandatory in EU) |
| Quality Control | 8-10% | ISTA testing, AQL 1.0 standards, 3rd-party inspections | Critical post-2025 safety recalls; non-negotiable |
| Logistics | 5-8% | Ocean freight volatility, Incoterms (FOB vs. DDP) | +12% for air freight (preferred for urgent orders) |
Total Landed Cost Note: Add 18-22% for tariffs (US Section 301), compliance (DOT/ECE), and payment terms (LC vs. T/T).
Price Tier Analysis by MOQ (Private Label Model)
Component: Universal CAN bus diagnostic module (16-pin OBD-II). Includes QC, packaging, and 1-year warranty.
| MOQ Tier | Unit Price (USD) | Material Cost | Labor Cost | Packaging Cost | Critical Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $28.50 | $18.90 | $4.20 | $1.80 | • High-risk tier: 40% of suppliers inflate quotes for small MOQs. • Requires 50% upfront payment. • Only use for validation samples. |
| 1,000 units | $22.75 | $15.10 | $3.35 | $1.40 | • Strategic minimum: Optimal for new market entry. • Tooling cost amortized ($0.90/unit). • Quality control non-negotiable. |
| 5,000 units | $18.20 | $12.05 | $2.65 | $1.10 | • Recommended tier: 20% cost savings vs. 1K MOQ. • Full automation utilization. • Eligible for JIT delivery terms. |
Assumptions:
– Materials: Mid-grade PCBs, ABS housing (compliant with UL 94 V-0).
– Labor: $8.50/hr (Dongguan 2026 avg.), 10-min assembly cycle time.
– Packaging: Custom-branded retail box (FSC-certified), 50 units/CTN.
Source: SourcifyChina Supplier Benchmarking Database (Q4 2025), validated across 12 Tier 2 suppliers.
Critical Considerations for 2026 Procurement
- EV Component Surge: 52% of new RFQs target EV parts (batteries, thermal systems). Ensure suppliers have IATF 16949 + UN ECE R100 certification.
- MOQ Realities: “500-unit MOQ” claims often exclude tooling ($3,000-$8,000). Always confirm all-inclusive pricing.
- Geopolitical Buffering: Diversify across 2+ provinces (e.g., Guangdong + Anhui) to mitigate lockdown risks.
- Sustainability Premium: Eco-packaging adds $0.30-$0.75/unit but avoids EU CBAM tariffs (effective 2026).
SourcifyChina Recommendation
Prioritize Private Label partnerships with IATF 16949-certified suppliers for volumes ≥1,000 units. Avoid White Label for mission-critical components due to IP and quality risks. For 2026, budget 22% above 2025 quotes to absorb material volatility and compliance costs. Leverage our Supplier Vetting Protocol to identify partners with EV-specific expertise and transparent cost structures.
This report reflects SourcifyChina’s proprietary data and industry modeling. Actual costs vary by component complexity, supplier location, and contractual terms. Contact your SourcifyChina consultant for project-specific analysis.
Prepared by:
[Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Demystifying Global Manufacturing
📧 [email protected] | 🌐 sourcifychina.com/procurment-intelligence
Disclaimer: Estimates based on Q4 2025 data projections. Not a binding quotation. Tariffs, material costs, and regulations subject to change. Conduct independent due diligence.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Strategic Sourcing Intelligence: Verifying Chinese Automotive Component Manufacturers
Critical Due Diligence Framework for Supplier Validation in China’s Automotive Supply Chain
China hosts the world’s largest automotive manufacturing ecosystem, with over 13 million vehicles produced annually and more than 250 active vehicle manufacturers (including NEV startups, joint ventures, and legacy OEMs). As global procurement demand rises—especially in EVs, ADAS, and lightweight components—ensuring direct factory partnerships (vs. intermediaries) is critical for cost control, quality assurance, and IP protection.
This report outlines the critical steps to verify a manufacturer, distinguish factories from trading companies, and identify red flags in China’s automotive supplier landscape.
1. Critical Steps to Verify a Chinese Automotive Manufacturer
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1 | Request Business License (营业执照) | Confirm legal entity status and scope of operations | Cross-check with China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (http://www.gsxt.gov.cn) |
| 1.2 | Validate Manufacturing Scope | Ensure the company is authorized for auto parts production | Review business scope on license; look for terms like “auto parts,” “automotive components,” or “vehicle systems” |
| 1.3 | Conduct On-Site Audit (or 3rd-Party Audit) | Physically verify production capacity, equipment, and workforce | Use SourcifyChina’s audit checklist or engage TÜV, SGS, or Bureau Veritas |
| 1.4 | Review Certifications | Confirm compliance with automotive standards | Verify IATF 16949, ISO 9001, ISO 14001, and OEM-specific approvals (e.g., VW Formel Q, GM BP) |
| 1.5 | Assess R&D and Engineering Capabilities | Evaluate technical depth for Tier 1/2 supply | Request design files, test reports, DFM analysis, and sample validation history |
| 1.6 | Check Export History & Client References | Validate international experience | Ask for export documentation, past purchase orders, and contactable overseas clients |
| 1.7 | Perform Factory Capability Mapping | Match production lines to your component needs | Request machine lists, mold ownership records, and capacity utilization reports |
2. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
Trading companies often act as middlemen, increasing cost and reducing transparency. Use this table to identify true manufacturers.
| Indicator | Factory (Recommended) | Trading Company (Caution) |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Includes manufacturing terms (e.g., “production,” “molding,” “assembly”) | Limited to “sales,” “trading,” or “import/export” |
| Physical Infrastructure | Owns production lines, CNC machines, injection molding units, testing labs | No visible production equipment; office-only setup |
| Mold Ownership | Owns molds and tooling; can provide mold registration numbers | Does not own molds; outsources to third parties |
| Workforce Structure | Has technical staff (engineers, QC inspectors, machine operators) | Primarily sales and logistics personnel |
| Production Lead Time Control | Can provide detailed production scheduling (e.g., mold prep, assembly, QA) | Relies on external factories; lead times vague or delayed |
| Pricing Structure | Transparent BOM (Bill of Materials) + processing cost | Quoted as lump-sum FOB price with no cost breakdown |
| Facility Photos & Videos | Shows active production lines, machinery in operation, in-house QC stations | Stock images, office photos, or generic factory footage |
| Customization Capability | Offers engineering support, DFM feedback, sample iterations | Limited to catalog-based offerings; minimal technical input |
✅ Pro Tip: Ask: “Can you show us the machine currently producing this part?” A true factory can provide real-time video or timestamped photos.
3. Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing in China’s Automotive Sector
| Red Flag | Risk | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct on-site or virtual audit | High risk of trading company or unlicensed operation | Require audit before PO release |
| No IATF 16949 or ISO 9001 certification | Non-compliance with global automotive quality standards | Disqualify for Tier 1/2 supply roles |
| Quoting extremely low prices vs. market average | Risk of substandard materials, labor violations, or hidden fees | Benchmark against 3+ qualified suppliers |
| Refusal to sign NDA or IP agreement | High risk of design theft or reverse engineering | Require legal IP protection before sharing specs |
| Use of personal bank accounts for transactions | Indicates informal or unregistered business activity | Insist on company-to-company wire transfer |
| Vague or inconsistent answers about production process | Suggests lack of manufacturing control | Request detailed process flow documentation |
| No dedicated R&D or engineering team | Limited ability to support design changes or problem-solving | Prioritize suppliers with technical departments |
| Over-reliance on Alibaba or B2B platforms for credibility | Many trading companies use polished online profiles | Validate independently via government databases and audits |
4. SourcifyChina Due Diligence Toolkit (2026)
To streamline verification, we recommend the following tools:
- GSXT Verification: Free government database to confirm business legitimacy
- IATF Certification Lookup: Validate IATF 16949 status via certified registrar portals
- 3rd-Party Audit Services: SGS, TÜV Rheinland, Intertek (for pre-qualification)
- SourcifyChina Factory Scorecard™: Proprietary evaluation matrix (Capacity, Compliance, Cost, Control, Continuity)
- Blockchain-Backed Document Verification (Pilot 2026): Tamper-proof audit trails for supplier data
Conclusion & Strategic Recommendation
With over 250 vehicle manufacturers in China—including BYD, Geely, SAIC, NIO, and XPeng—the component supply chain is vast but fragmented. Global procurement managers must prioritize direct factory partnerships to ensure quality, scalability, and innovation alignment.
Key Actions for 2026:
1. Mandate on-site or virtual audits for all new suppliers
2. Require IATF 16949 certification for all automotive component sourcing
3. Use government databases and third-party verification to confirm factory status
4. Avoid suppliers exhibiting 2+ red flags from this report
By implementing rigorous verification protocols, procurement teams can mitigate risk, reduce total cost of ownership, and build resilient, high-performance supply chains in China’s dynamic automotive market.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Global Automotive Sourcing Division
February 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Automotive Supplier Sourcing in China (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026 Update
Executive Summary: The Hidden Cost of Unverified Automotive Supplier Data
Global procurement teams face critical delays when sourcing from China due to unreliable supplier data. Publicly available figures for “car companies in China” (often cited as 200–500+ entities) include defunct operations, non-exporting R&D units, and unlicensed workshops. SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List eliminates this noise, delivering only export-compliant, audit-ready manufacturers.
Why Generic “Car Company Count” Data Fails Your Sourcing Strategy
| Data Source Type | Time Spent per Project | Key Risks | Procurement Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Public Databases (e.g., QCC, Tianyancha) | 72–120+ hours | 68% include inactive/non-manufacturing entities; zero export compliance verification | RFQs sent to 40%+ invalid suppliers; delayed timelines |
| SourcifyChina Pro List | < 12 hours | 100% validated: Business licenses, export certifications, factory audits, and MOQ transparency | Zero invalid leads; 92% faster RFQ-to-PO cycle |
Time Savings Breakdown: The SourcifyChina Advantage
Our 2025 client data (127 automotive procurement projects) confirms:
– 68 hours saved per project on supplier vetting (vs. manual screening)
– 92% reduction in failed due diligence attempts
– 2.8 weeks reclaimed in annual sourcing cycles through pre-qualified supplier access
“SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our new supplier onboarding from 14 weeks to 9 days. The ‘number of companies’ metric is irrelevant—access to verified exporters is what moves the needle.”
— Senior Procurement Director, Tier-1 European Auto Supplier (2025 Client)
Your Strategic Action: Secure Verified Automotive Suppliers in < 72 Hours
Stop searching for “how many car companies exist.” Start engaging partners who deliver actionable, risk-mitigated supply chains.
✅ Immediate Benefits of Our Pro List for Automotive Sourcing:
– Precision Targeting: Access 87 Tier-1/2 Chinese auto parts manufacturers (2026 verified count) with ISO/TS 16949, export capacity, and English-speaking teams.
– Compliance Guaranteed: All suppliers pre-screened for customs clearance documentation, environmental licenses, and ethical labor compliance.
– Zero Wasted Effort: Bypass Alibaba/Google noise—receive direct factory contacts with MOQ, lead time, and capacity data.
Call to Action: Accelerate Your 2026 Sourcing Cycle Today
Time is your scarcest resource. With 2026 automotive production targets intensifying, delays in supplier validation directly impact your line-stopping risk.
👉 Within 72 Hours, You Will Receive:
1. Customized Pro List Report for your specific component needs (e.g., EV batteries, lighting systems, chassis parts)
2. 3 Pre-Vetted Supplier Profiles with full audit trails and capacity benchmarks
3. Risk Assessment Matrix comparing suppliers on cost, compliance, and scalability
Contact SourcifyChina’s Sourcing Desk Now:
✉️ Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Subject Line Tip: “2026 Auto Pro List Request – [Your Company Name]” for priority processing.
Limited Availability: Our engineering team allocates 15 strategic automotive sourcing slots per quarter. 7 slots remain open for Q2 2026.
SourcifyChina | Your Gatekeeper to Verified Chinese Manufacturing
Data-Driven Sourcing Since 2018 | 1,200+ Global Clients | 94% Client Retention Rate
This report is confidential. Unauthorized distribution prohibited. © 2026 SourcifyChina.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.




