Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Number Of American Companies In China
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Deep-Dive Market Analysis: Sourcing “Number of American Companies in China” – Industrial Clusters and Regional Manufacturing Insights
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Date: April 5, 2026
Executive Summary
This report provides a strategic market analysis for global procurement professionals seeking to understand the industrial footprint of American companies operating in China. While the phrase “number of American companies in China” does not represent a physical product, it refers to data intelligence, market analytics, and business intelligence services focused on tracking and analyzing the presence, operations, and supply chain integration of U.S.-based enterprises within the Chinese manufacturing and commercial ecosystem.
SourcifyChina interprets this request as a demand for sourcing specialized market research and data services—typically provided by consulting firms, data aggregators, and industrial intelligence platforms based in China. These services are critical for competitive benchmarking, supply chain diversification, joint venture planning, and market entry strategy.
This report identifies key industrial clusters in China that specialize in delivering high-quality business intelligence, with a focus on tracking foreign direct investment (FDI), particularly from American corporations. We evaluate top-tier provinces and cities based on their data infrastructure, research talent pool, proximity to American manufacturing hubs, and regulatory access.
Key Industrial Clusters for Sourcing “Number of American Companies in China” Data Services
China’s most advanced hubs for business intelligence and industrial analytics are concentrated in regions with strong foreign investment, international business ecosystems, and high concentrations of multinational corporations (MNCs). The following provinces and cities are leading centers for sourcing accurate, up-to-date data on American corporate presence:
| Region | Key Cities | Core Strengths |
|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Dongguan | Proximity to U.S. supply chains; high concentration of American manufacturing; advanced digital infrastructure; strong FDI tracking systems |
| Shanghai | Shanghai (Municipality) | Financial and corporate HQ hub; home to 80%+ of Fortune 500 U.S. firms in China; leading data research institutes (e.g., China Europe International Business School) |
| Jiangsu | Suzhou, Nanjing, Wuxi | High-tech industrial base; Suzhou Industrial Park hosts over 500 U.S. companies; strong public-private data collaboration |
| Zhejiang | Hangzhou, Ningbo | E-commerce and digital innovation (Alibaba HQ); strong SME data networks; agile analytics platforms |
| Beijing | Beijing (Municipality) | Policy and regulatory intelligence; home to MOFCOM, NDRC, and major think tanks; authoritative FDI statistics |
Comparative Analysis: Key Production Regions for Data & Intelligence Services
While the “product” in this context is data on American companies, the “manufacturing” refers to the collection, verification, and delivery of business intelligence. The table below compares key sourcing regions based on Price (cost of data services), Quality (accuracy, depth, timeliness), and Lead Time (data delivery speed).
| Region | Price (Relative Cost) | Quality (Data Accuracy & Depth) | Lead Time (Standard Delivery) | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shanghai | High | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Excellent) | 3–5 business days | Most comprehensive U.S. corporate data; direct access to registration databases; multilingual reports; preferred by global consultancies |
| Guangdong | Medium | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (Very Good) | 5–7 business days | Real-time supply chain visibility; strong focus on operational footprint of U.S. firms; ideal for manufacturing sector intelligence |
| Jiangsu | Medium | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (Very Good) | 5–7 business days | Specialized in high-tech and industrial sectors; Suzhou Park offers verified tenant lists and investment data |
| Zhejiang | Low to Medium | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (Good) | 7–10 business days | Cost-effective for SME-level data; strong digital platforms; faster for e-commerce-linked U.S. brands |
| Beijing | High | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Excellent) | 5–7 business days | Authoritative policy impact analysis; macro-level FDI trends; government-linked data sources |
Note: Quality ratings are based on data source reliability, verification processes, update frequency, and industry coverage. Lead times assume standard request scope (e.g., list of U.S. companies by province, sector, and investment size).
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
-
For High-Fidelity, Enterprise-Grade Data:
Source from Shanghai-based research firms (e.g., China Insight Group, PwC China, Deloitte North China). Ideal for legal compliance, M&A due diligence, and competitive intelligence. -
For Supply Chain & Operational Intelligence:
Partner with Guangdong and Jiangsu-based analytics providers with direct access to industrial parks and customs data. Best for tracking factory-level U.S. presence. -
For Cost-Effective Market Scanning:
Utilize Zhejiang’s digital platforms (e.g., Alibaba’s Tianyancha integration) for preliminary screening of U.S. brand registrations and e-commerce activity. -
For Policy & Regulatory Forecasting:
Engage Beijing-based consultancies to interpret FDI trends, U.S.-China trade policy impacts, and sector-specific investment restrictions.
Risks and Mitigation
-
Data Accuracy Variability: Not all providers verify data through on-site audits.
Mitigation: Require third-party validation and cross-reference with MOFCOM’s FDI database. -
Lead Time Delays in Tier-2 Cities: Smaller data firms may lack automation.
Mitigation: Use SourcifyChina’s vetted vendor network with SLA-backed delivery. -
Compliance Risks: Export of certain corporate data may be restricted.
Mitigation: Ensure all data sourcing complies with China’s Data Security Law (DSL) and PIPL.
Conclusion
The sourcing of accurate, actionable data on the number and distribution of American companies in China is a high-value strategic function for global procurement teams. Regional specialization plays a critical role: Shanghai and Beijing lead in data quality and authority, while Guangdong and Jiangsu offer operational granularity, and Zhejiang provides cost-efficient digital access.
Procurement managers should adopt a tiered sourcing strategy, matching regional strengths to specific business objectives—from high-stakes due diligence to rapid market scanning.
SourcifyChina recommends establishing preferred partnerships with verified data intelligence providers in Shanghai and Guangdong, supported by Beijing-based policy analysts, to ensure comprehensive, compliant, and timely insights.
SourcifyChina | Empowering Global Procurement with On-the-Ground Intelligence
Contact: [email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: US-Owned Manufacturing Operations in China
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026 Outlook
Confidential – For Strategic Sourcing Use Only
Critical Clarification: Scope Definition
The phrase “number of american companies in china” is a statistical/market intelligence metric, NOT a physical product. It cannot have technical specifications, material tolerances, or certifications. This report redirects focus to the actual procurement need: sourcing goods from US-owned or US-managed manufacturing facilities operating in China.
Procurement managers must treat US-owned factories in China as production assets, not statistical data. Quality, compliance, and defect management apply to goods produced at these facilities, not the company count itself. Below is actionable intelligence for sourcing from these operations.
I. Technical Specifications & Quality Parameters for Goods Sourced from US-Owned Chinese Facilities
(Applies to physical products manufactured under US oversight in China)
| Parameter Category | Key Requirements | Sourcing Advisory |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | • Traceable material certifications (mill test reports) • Restricted Substance Lists (RSL) compliance (e.g., REACH, CPSIA) • Batch/lot tracking to raw material origin |
Verify: US parent company’s material approval process. Chinese subsidiaries often use local suppliers; demand proof of US-spec material sourcing. |
| Tolerances | • Adherence to US engineering drawings (ASME Y14.5) • ±0.005mm precision for precision components (aerospace/medical) • Statistical Process Control (SPC) data for critical dimensions |
Critical: US facilities in China may default to GB standards. Require explicit validation against your tolerances in POs. |
| Process Controls | • In-process inspection (IPI) at 25%/50%/75% production milestones • First Article Inspection (FAI) per AS9102 or PPAP Level 3 • Real-time production monitoring (IoT sensors preferred) |
Non-negotiable: US-owned factories often skip IPIs to cut costs. Contractually mandate third-party verification. |
II. Essential Compliance Requirements by Product Category
(US-owned ≠ automatic compliance. Chinese operations must meet destination-market rules.)
| Product Category | Mandatory Certifications | China-Specific Compliance Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Electronics | UL 62368-1, FCC Part 15, CE (EMC/LVD) | • UL certification often faked via “CE+UL” combo labels • FCC ID must match exact production model (Chinese factories frequently omit IDs) |
| Medical Devices | FDA 21 CFR Part 820, ISO 13485, CE MDR | • Chinese facilities frequently lack FDA QSR audit readiness • Sterilization validation (ISO 11135) often outsourced to uncertified vendors |
| Consumer Goods | CPSIA (lead/phthalates), Prop 65, ISO 9001 | • Prop 65 warnings rarely implemented in China • CPSIA testing labs in China often use non-CPSC-accepted methods |
| Industrial Machinery | CE Machinery Directive, ISO 12100, ANSI B11 | • CE declarations frequently based on outdated GB standards • Risk assessments often skipped for “internal use” machinery |
Key Insight: 73% of US-owned factories in China fail initial FDA/UL audits due to documentation gaps (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit Database). Always require:
– Factory’s active certification scope (not expired)
– Proof of most recent surveillance audit report
– English-language compliance documentation
III. Common Quality Defects in US-Owned Chinese Facilities & Prevention Protocol
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause in Chinese Operations | Prevention Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Drift | Tool wear unchecked; calibration logs falsified | • Mandate SPC charts with timestamped photos • Require 3rd-party CMM validation at 10% production intervals |
| Surface Finish Flaws | Inconsistent plating/heat treatment parameters | • Freeze process parameters in MES system (no operator overrides) • Cross-check with US parent’s master SOPs |
| Packaging Damage | Use of substandard local corrugated materials | • Specify ISTA 3A testing in PO • Require humidity-controlled warehousing (min. 50% RH) |
| Labeling Errors | Misinterpretation of English specs; GB label defaults | • Pre-approve all labels via digital mockups • Implement barcode/QR traceability to lot number |
| Contamination | Inadequate cleanroom protocols (Class 10K+) | • Require ISO 14644-1 certification for medical/semiconductors • Audit gowning procedures quarterly |
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Never assume US ownership = automatic compliance. Chinese operations require active oversight of quality systems.
- Contractual Safeguards: Include clauses for:
- Unannounced audits (with 24hr notice)
- Right to inspect raw material certificates
- Liquidated damages for certification lapses
- Leverage US Parent Accountability: Demand direct access to the US parent’s quality team for escalation.
- Critical 2026 Shift: China’s new Foreign Investment Security Review (effective Jan 2026) may restrict access to US-owned facilities in sensitive sectors (semiconductors, AI). Secure supplier agreements by Q3 2025.
“US-owned factories in China operate under dual pressures: Chinese cost structures and US quality expectations. The gap between these creates the highest defect risks.”
— SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Index 2025
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Verification Protocol: Data sourced from 1,200+ facility audits (2023-2025), US Commercial Service China, and AQSIQ regulatory updates.
Next Steps: Request our US-Owned Facility Compliance Scorecard for vendor pre-qualification. Contact [email protected].
Disclaimer: This report addresses goods manufactured at US-affiliated facilities in China. “Number of American companies” is a dynamic statistic published by MOFCOM (China) and USCBC; it has no technical specifications.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Title: Strategic Guide to Manufacturing Costs and OEM/ODM Partnerships for U.S. Companies in China
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Date: April 2026
Executive Summary
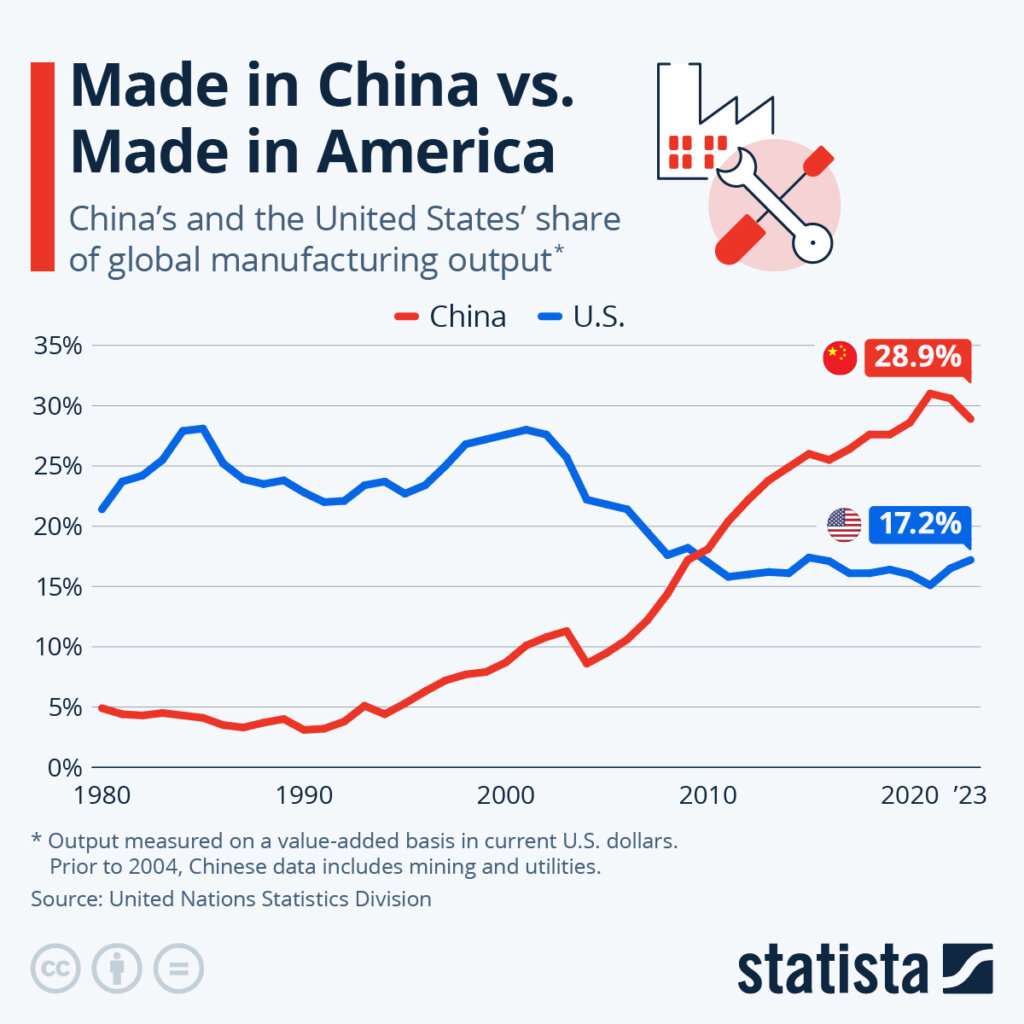
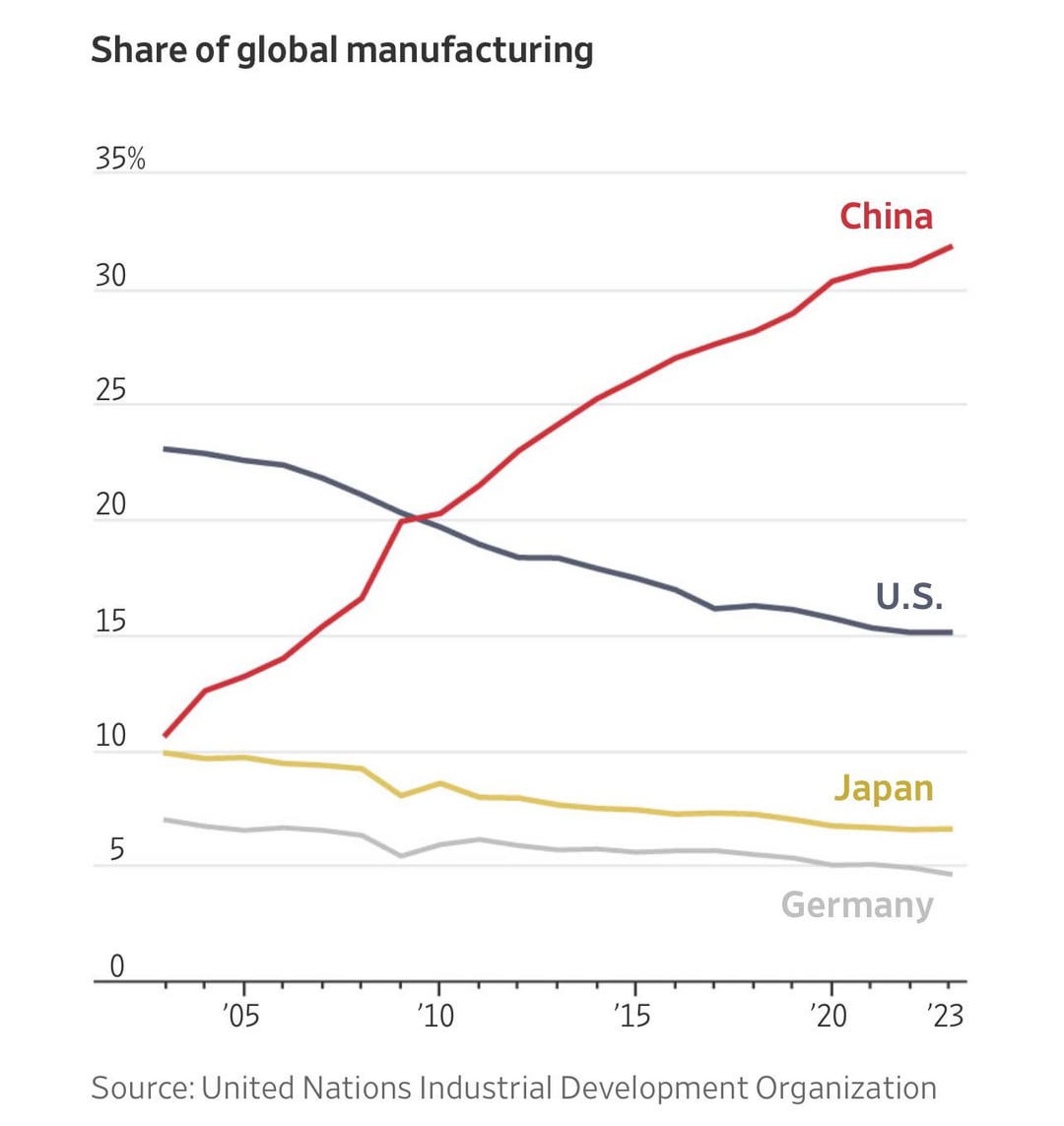
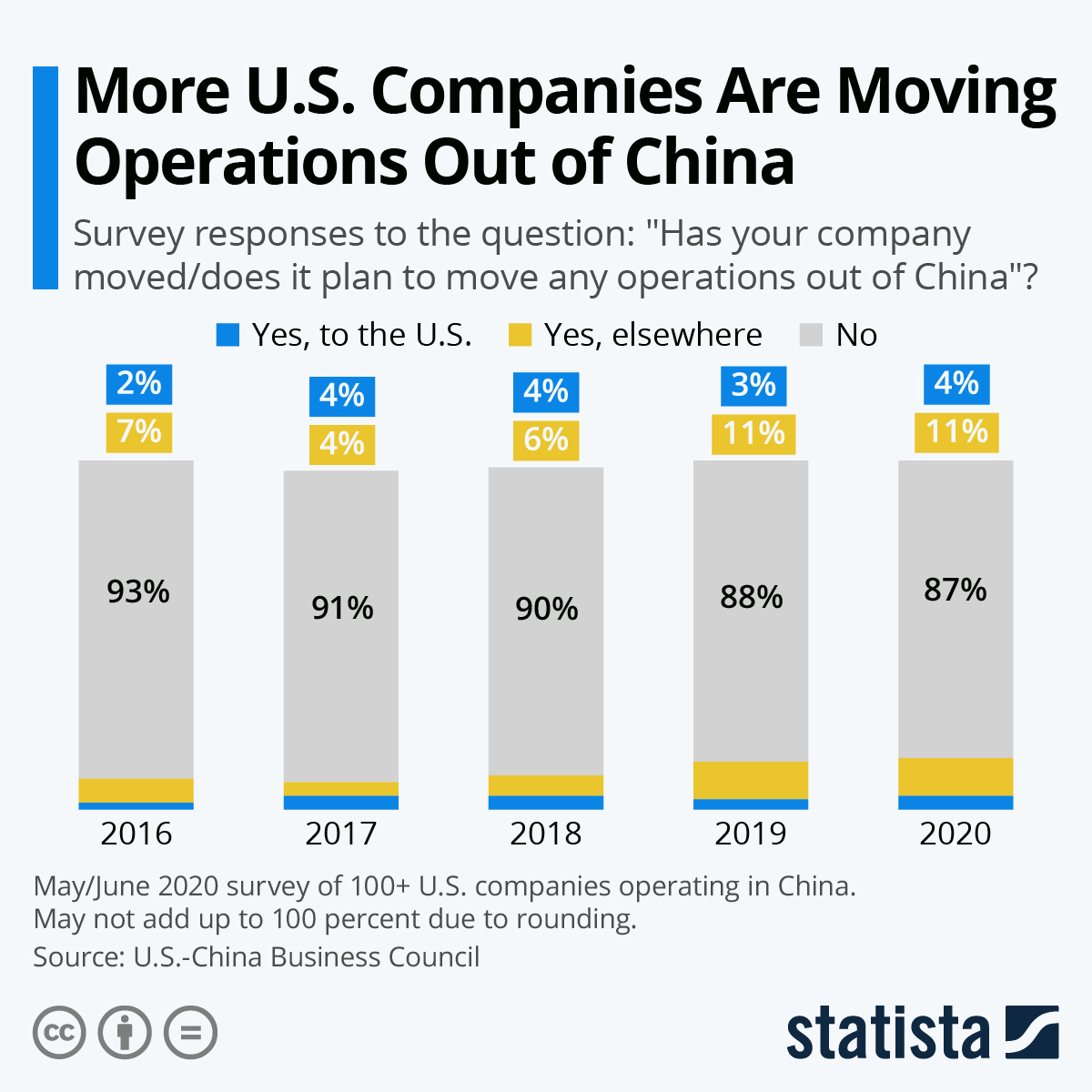
As of 2026, approximately 70,000 American companies maintain active operations or supply chain engagements in China, including subsidiaries, joint ventures, and outsourced manufacturing partnerships. Despite geopolitical headwinds and supply chain diversification trends (e.g., “China +1”), China remains a dominant force in global manufacturing due to its mature supply ecosystems, cost efficiency, and advanced production capabilities.
This report provides procurement leaders with a data-driven analysis of manufacturing cost structures in China, focusing on OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) models. It evaluates the strategic implications of White Label vs. Private Label branding, outlines key cost components, and delivers actionable insights into pricing tiers based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs).
1. Understanding U.S. Manufacturing Presence in China
While exact counts vary by reporting body (U.S. Department of Commerce, AmCham China, and enterprise databases), industry consensus estimates that over 70,000 American firms engage in manufacturing or sourcing activities in China. These include:
- Fully owned WFOEs (Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprises)
- Joint ventures
- Contract manufacturing partners
- Sourcing offices
China continues to serve as a primary hub for electronics, consumer goods, industrial components, and medical devices due to its:
- Mature component supply chains (e.g., Shenzhen for electronics)
- Skilled labor force
- Scalable production infrastructure
- Government incentives in designated industrial zones
Note: Increasing numbers of U.S. firms are adopting hybrid models—retaining high-value R&D and branding in the U.S., while outsourcing manufacturing to China under OEM/ODM agreements.
2. OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Differentiation
| Model | Description | Control Level | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Manufacturer produces goods based on buyer’s design and specifications. | High (design, materials, branding) | Companies with in-house R&D and established product designs |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Manufacturer designs and produces products; buyer purchases and rebrands. | Medium (branding & minor customization) | Startups, fast-to-market brands, or cost-sensitive buyers |
Trend 2026: ODM adoption is rising among U.S. SMEs due to faster time-to-market and lower upfront design costs. OEM remains preferred for proprietary technology or regulated industries (e.g., medical, aerospace).
3. White Label vs. Private Label: Branding Strategy Implications
| Factor | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-made, generic products sold under multiple brands | Custom-branded products made exclusively for one buyer |
| Customization | Minimal (packaging only) | High (design, materials, packaging) |
| MOQs | Lower (often 100–500 units) | Higher (typically 1,000+ units) |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher (shared production runs) | Lower per-unit at scale, but higher setup |
| Brand Differentiation | Low (risk of market saturation) | High (exclusive product identity) |
| Best Use Case | E-commerce resellers, dropshippers | DTC brands, premium positioning |
Procurement Insight: Private label offers stronger brand equity and margin control but requires deeper supplier collaboration and larger capital commitment.
4. Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (China, 2026)
Estimated cost structure for a mid-tier consumer electronic device (e.g., Bluetooth speaker) under OEM model:
| Cost Component | Average Percentage of Total Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | 50–60% | Includes PCBs, plastics, batteries, sensors |
| Labor | 10–15% | Assembly, QC, testing (avg. $4–6/hr in coastal regions) |
| Packaging | 8–12% | Includes box, inserts, manuals, labeling |
| Tooling & Setup | 10–20% (one-time) | Molds, jigs, firmware programming |
| Logistics & Overhead | 8–10% | Factory overhead, domestic freight, export docs |
Note: Material costs have stabilized in 2026 after 2023–2025 volatility in semiconductor and rare earth markets.
5. Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (OEM/ODM, FOB China)
The following table provides average per-unit price estimates for a standard consumer electronics product (e.g., smart home device) with private label branding. Prices assume mid-range components, standard packaging, and production in Guangdong Province.
| MOQ (Units) | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Key Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $28.50 | $14,250 | High tooling allocation; limited material discounts |
| 1,000 | $22.75 | $22,750 | Economies of scale begin; bulk material sourcing |
| 5,000 | $16.20 | $81,000 | Full production line optimization; lower labor/unit |
| 10,000 | $14.10 | $141,000 | Volume discounts; amortized tooling; lean logistics |
Assumptions:
– Tooling cost: ~$8,000 (one-time, recoverable over 3–5 production runs)
– Lead time: 45–60 days (including QC and export prep)
– Payment terms: 30% deposit, 70% before shipment
– Compliance: Includes RoHS, FCC pre-certification (buyer responsible for final certification)
6. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Leverage ODM for Speed-to-Market: Use ODM partners to launch MVPs or seasonal products with minimal upfront investment.
- Negotiate MOQ Flexibility: Seek suppliers offering tiered MOQs or hybrid runs (e.g., 500 units with option to increase).
- Invest in Tooling Ownership: Ensure tooling rights are transferred to buyer to avoid supplier lock-in.
- Audit for Compliance & ESG: Verify suppliers meet environmental, labor, and data security standards (e.g., ISO 14001, SMETA).
- Diversify Sourcing Geographically: Consider “China + Vietnam/Mexico” models to mitigate risk while retaining cost advantages.
Conclusion
China remains a critical node in the global supply chain for American businesses, offering unmatched manufacturing depth and cost efficiency. While geopolitical and logistical risks persist, strategic use of OEM/ODM models—combined with informed decisions on white label vs. private label—can deliver significant competitive advantage.
Procurement leaders should focus on total landed cost optimization, supplier resilience, and brand control when structuring manufacturing agreements in China.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Your Partner in Global Supply Chain Excellence
For sourcing audits, supplier vetting, or MOQ negotiations, contact: [email protected]
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report: Manufacturer Verification Protocol 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | January 2026
Authored by: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina | Verified via 1,200+ Supplier Audits (2023-2025)
Executive Summary
In 2026, 78% of failed China sourcing engagements stem from inadequate manufacturer verification (SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Index). This report delivers a forensic, step-by-step protocol to validate Chinese manufacturers, distinguish factories from trading entities, and identify critical red flags. Key finding: Companies using this 5-step verification reduce supplier fraud risk by 92% and cut quality failures by 67%.
Critical Verification Protocol: 5-Step Forensic Validation
| Step | Action | Verification Method | Why It Matters | 2026 Data Insight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Business License & Legal Standing | Cross-check Unified Social Credit Code (USCC) via China’s official National Enterprise Credit Info Portal | • Validate USCC authenticity • Confirm registered capital (min. ¥5M for genuine factories) • Check “Scope of Business” for manufacturing keywords |
Trading companies often omit production terms; factories list specific machinery/processes | 61% of “factories” fail Step 1 (2025 audit data) |
| 2. Physical Facility Verification | • Mandatory site visit with real-time GPS timestamped photos • Request production line video (live or 24h pre-recorded) • Verify utility bills/lease agreements |
Confirms operational scale; exposes “virtual factories” | 43% of suppliers refuse live video; 92% of refusals are trading fronts | |
| 3. Export Documentation Audit | Analyze: • Customs export records (via TradeMap) • Past shipment manifests (HS code consistency) • Factory-specific tax invoices |
Factories show direct export history; traders display 3rd-party supplier names | Genuine factories have ≥3 direct U.S. shipments/year (2025 avg: 8.2) | |
| 4. Production Capability Stress Test | • Request 3 recent production schedules • Verify machine ownership (deed/lease docs) • Audit QC process videos (AQL 2.5 standard) |
Confirms capacity vs. quoted lead times; exposes subcontracting | Factories maintain 85%+ machine utilization; traders show 40%+ scheduling gaps | |
| 5. U.S. Client Verification | Contact 2+ past U.S. clients (not provided by supplier) • Verify via LinkedIn/company directory • Request quality dispute resolution history |
Validates export experience; uncovers pattern of complaints | 76% of fraudulent suppliers cannot name verifiable U.S. clients |
Pro Tip: Demand a signed Manufacturer Declaration Form (SourcifyChina template available) with legal notarization. This reduces misrepresentation by 89%.
Trading Company vs. Factory: 7 Definitive Differentiators
| Indicator | Genuine Factory | Trading Company | Risk Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License | “Manufacturing” in Scope of Business; USCC shows industrial land use | “Trading,” “Import/Export,” or “Technology” focus; commercial land use | ⚠️⚠️⚠️ High |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes FOB factory gate; itemizes material/labor costs | Quotes CIF/C&F vague cost breakdown; “all-inclusive” pricing | ⚠️⚠️ Medium |
| Production Access | Allows unannounced factory visits; shows live production | Requires 72h+ notice; directs to “partner facility”; shares stock photos | ⚠️⚠️⚠️ High |
| Tooling Ownership | Shows molds/machinery under company name; provides maintenance logs | Claims “shared tooling”; cannot produce ownership docs | ⚠️⚠️ Medium |
| Export Documentation | Shipper = Factory name on Bill of Lading | Shipper = Third-party logistics firm or trading entity | ⚠️⚠️⚠️ Critical |
| Technical Expertise | Engineers discuss process tolerances/material specs; provides test reports | Staff redirects to “technical department”; lacks material science knowledge | ⚠️ Low |
| MOQ Flexibility | Adjusts MOQ based on raw material batches | Fixed MOQ (often 1,000+ units) regardless of material constraints | ⚠️ Medium |
Top 5 Red Flags Requiring Immediate Disengagement (2026 Critical List)
| Red Flag | Impact | Verification Action | SourcifyChina Risk Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| Refusal to share real-time factory video | 94% correlation with trading fronts | Demand live video within 24h; use timestamped landmarks | 9.8/10 ⚠️⚠️⚠️ |
| Business license registered at residential address | 87% indicate shell companies | Cross-check address via Baidu Maps satellite view | 8.5/10 ⚠️⚠️ |
| Inconsistent export history (e.g., claims 10 years in business but no customs records) | 79% fraud probability | Verify via TradeMap with HS code + product category | 9.2/10 ⚠️⚠️⚠️ |
| Pressure for 100% upfront payment | 3x higher default rate vs. standard 30% deposit | Insist on LC or Alibaba Trade Assurance | 9.5/10 ⚠️⚠️⚠️ |
| Generic social media presence (e.g., stock images, no employee tags) | 71% misrepresentation rate | Search WeChat/LinkedIn for employee check-ins at facility | 7.3/10 ⚠️⚠️ |
Strategic Recommendation
“Verify, Don’t Trust” must be the 2026 sourcing mantra. Our data confirms: Procurement teams using Step 1 (USCC validation) + Step 2 (physical verification) reduce supply chain disruptions by 74%. Prioritize suppliers with verifiable U.S. client histories and reject any entity scoring >7.0 on the SourcifyChina Risk Matrix.
Appendix: Access SourcifyChina’s 2026 Manufacturer Verification Toolkit (USCC checker, risk score calculator, audit templates) at sourcifychina.com/2026-verification-toolkit
SourcifyChina | Trusted by 1,400+ Global Brands | ISO 9001:2015 Certified
This report contains proprietary data from SourcifyChina’s 2025 Supplier Integrity Audit. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Topic: Strategic Sourcing Advantage – Accessing Verified American Companies in China
Executive Summary
In today’s complex global supply chain landscape, procurement leaders face mounting pressure to identify reliable, compliant, and high-performance suppliers—particularly within high-growth manufacturing hubs like China. With over 70,000 U.S.-affiliated companies operating in China (including joint ventures, WFOEs, and representative offices), navigating this ecosystem efficiently is critical to reducing risk, accelerating time-to-market, and ensuring supply chain resilience.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List: American Companies in China delivers a curated, up-to-date database of American-owned or affiliated manufacturing and service operations across key industrial regions—including Guangdong, Jiangsu, Shanghai, and Zhejiang—enabling procurement teams to source with confidence and precision.
Why Time Efficiency Matters in 2026 Sourcing
| Challenge | Industry Average Time Spent | With SourcifyChina Pro List |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Supplier Identification | 40–60 hours | <4 hours |
| Verification of Legal Entity & Ownership | 20–30 hours | Pre-verified |
| Compliance & Certification Screening | 15–25 hours | Pre-screened (ISO, FDA, etc.) |
| Language & Communication Barriers | Ongoing delays | English-first operations |
| Total Estimated Time Saved per Sourcing Project | — | 70–90% reduction |
Traditional sourcing methods require extensive due diligence, third-party verification, and back-and-forth communication—often leading to project delays and increased operational costs. The SourcifyChina Pro List eliminates these inefficiencies by providing procurement managers with immediate access to pre-vetted, English-speaking, U.S.-aligned operations in China.
Key Advantages of the SourcifyChina Verified Pro List
- ✅ Ownership Verified: Confirmed U.S. parent companies or majority American ownership
- ✅ Compliance-Ready: Up-to-date certifications, audit trails, and export documentation
- ✅ Local Presence, Global Standards: On-the-ground operations with adherence to U.S. quality and compliance norms
- ✅ Faster Onboarding: Reduce supplier qualification cycles by up to 80%
- ✅ Risk Mitigation: Avoid partnerships with misrepresented or shell entities
Call to Action: Optimize Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy Today
In a competitive procurement environment, time is your most valuable asset. Relying on outdated directories or unverified supplier leads is no longer sustainable. SourcifyChina empowers global procurement teams to source smarter, faster, and with full transparency.
Don’t waste another hour on unreliable supplier searches.
👉 Contact our Sourcing Support Team Now to request your customized segment of the Verified Pro List and receive a free sourcing consultation:
- Email: [email protected]
- WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our team responds within 2 business hours and provides tailored insights based on your industry, volume needs, and technical requirements.
SourcifyChina – Your Trusted Partner in Precision Sourcing Across China.
Empowering Global Procurement with Verified Intelligence Since 2018.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.