The global market for NPS (National Pipe Straight) thread products has experienced steady growth, driven by rising demand across industries such as oil and gas, water treatment, and industrial manufacturing. According to Grand View Research, the global industrial valves market—closely tied to pipe threading components—was valued at USD 78.9 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.6% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is supported by increasing infrastructure investments, stricter safety regulations, and the need for leak-proof, standardized connections in fluid handling systems. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects sustained expansion in the pipeline equipment sector, citing Asia-Pacific’s rapid industrialization and North America’s aging infrastructure upgrades as key drivers. As demand for reliable, standardized pipe connections grows, so does the need for high-quality NPS pipe thread manufacturers capable of delivering precision, durability, and compliance with international standards. The following list highlights the top 10 manufacturers leading innovation and market share in this essential sector.
Top 10 Nps Pipe Thread Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 NPS / NPT
Domain Est. 2016
Website: apporo-cnc.com
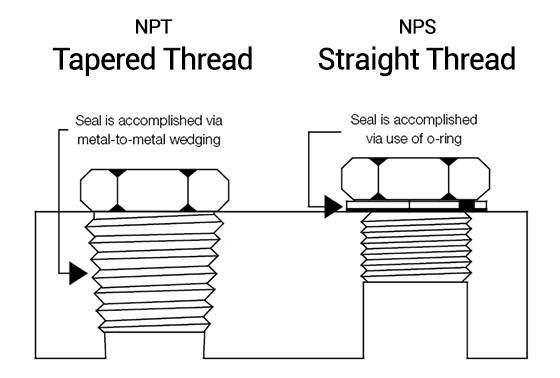
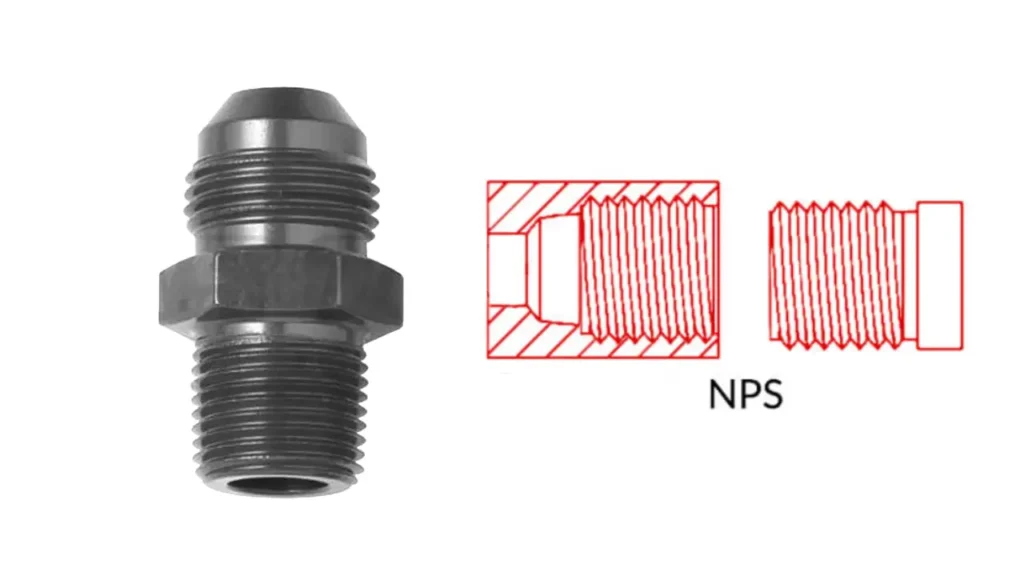
Key Highlights: National Pipe Straight thread (NPS). Both NPT and NPS have the same thread angle 60° included angle and have flat peaks and valleys, and pitch (TPI, thread per ……
#2 ASC Engineered Solutions
Domain Est. 2020
Website: asc-es.com
Key Highlights: Manufacturer and solutions provider of precision-engineered pipe joining products, valves, and related services for the entire construction project ……
#3 Pipes
Domain Est. 1994
Website: webstore.ansi.org
Key Highlights: Free deliveryASME B16.5 Pipe Flanges and Flanged Fittings: NPS 1/2 through NPS 24 Metric/Inch Standard covers pressure-temperature ratings, materials, dimensions, tolerances ……
#4 Pipe Thread Standards
Domain Est. 2009
Website: petersenproducts.com
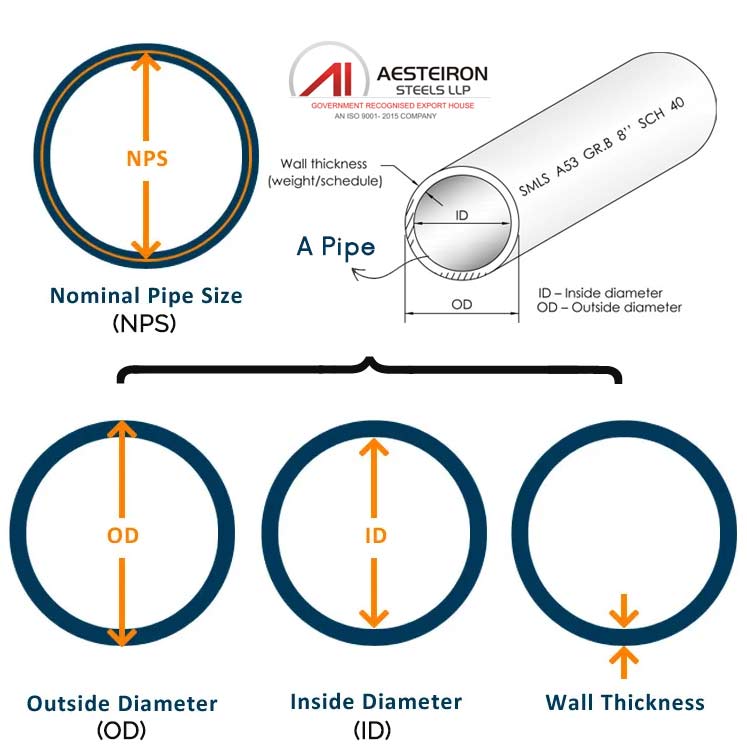
Key Highlights: Pipe Threading Acronyms: NPS: Nominal Pipe Size (Not the pipe ID or OD), NPT: National Pipe Thread (tapered) is a US standard for tapered threads….
#5 NPS Pipe Thread: Uses, Standards, and Applications
Domain Est. 2010
Website: sannke.com
Key Highlights: Discover everything about NPS pipe threads – their specifications, applications, and differences from NPT. Get expert insights on National ……
#6 NP – National Pipe Thread
Domain Est. 2015
Website: tameson.com
Key Highlights: The NP (National pipe) thread standard is used in Canada and the United States. They have tapered threads, which offer a more powerful seal than straight ……
#7 Thread Mills
Domain Est. 2017
Website: titancuttingtools.com
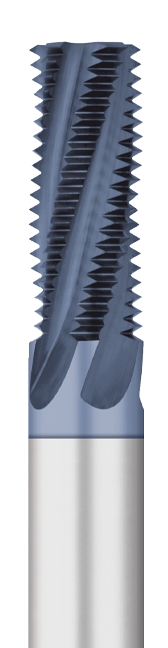
Key Highlights: Engineered to cut internal and external National Pipe Straight (N.P.S.) threads, this solid carbide, fully stocked offering of Multi-Form NPS Pipe Thread ……
#8 NPT & NPS Threads – Ryco Hydraulics
Domain Est. 2022
Website: ryco-hydraulics.com
Key Highlights: National Pipe Thread (NPT) is a family of technical standards for threads that has been adopted internationally for interconnecting hoses and fittings….
#9 Explanation of common threads including BSP & NPT
Website: valvesonline.com.au
Key Highlights: NPT stands for National Pipe Thread and is an American standard thread. It … NPT/NPS threads have a 60° angle and have flattened peaks and valleys ……
#10 Thread types » Info about NPS
Website: gewindebohrer.de
Key Highlights: NPS stands for National Pipe Straight. According to the NPS thread table, this describes the thread as a parallel pipe thread, ie a cylindrical design….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Nps Pipe Thread

H2: 2026 Market Trends for NPS Pipe Thread
The North American Pipe (NPS) thread market is poised for steady growth and transformation by 2026, driven by infrastructure renewal, industrial expansion, and evolving regulatory landscapes. Here’s an analysis of key trends shaping the market:
1. Infrastructure Investment as a Primary Growth Driver:
The U.S. Bipartisan Infrastructure Law and similar regional initiatives will continue to fuel demand for NPS pipe thread components through 2026. Major investments in water and wastewater systems, gas distribution networks, and commercial construction will directly increase the need for standardized threaded piping solutions. Municipalities and utilities are prioritizing the replacement of aging infrastructure, where NPS threads remain a preferred choice for reliability and compatibility.
2. Industrial and Energy Sector Expansion:
Growth in manufacturing, petrochemical processing, and renewable energy projects (such as hydrogen and biogas infrastructure) will sustain demand for NPS threaded fittings. These sectors rely on NPS standards for their durability and ease of maintenance in high-pressure and high-temperature environments. The shift toward modular construction in industrial plants also favors pre-threaded NPS components for faster assembly.
3. Increased Focus on Leak Prevention and Safety Compliance:
Regulatory pressure and safety standards are pushing end-users toward higher-quality, leak-resistant connections. This trend benefits premium NPS thread products, including those with thread sealants, coatings, or enhanced machining tolerances. Standards from organizations like ASME and ANSI B1.20.1 will remain critical, with greater enforcement expected in industrial applications.
4. Supply Chain Resilience and Localization:
Ongoing supply chain volatility has prompted a shift toward regional sourcing. By 2026, North American manufacturers of NPS threaded products are likely to see increased demand as buyers prioritize shorter lead times and supply security. This could accelerate nearshoring and reshoring of production, particularly for critical infrastructure projects.
5. Material and Sustainability Trends:
While carbon steel remains dominant, demand for corrosion-resistant alloys (e.g., stainless steel) in NPS threads will grow in chemical and water treatment applications. Sustainability concerns may drive innovation in recyclability and energy-efficient manufacturing processes, though the impact on thread design itself will be limited.
6. Digitalization and Smart Inventory Management:
Distributors and contractors are increasingly adopting digital platforms for inventory and procurement. This trend favors standardized products like NPS threads, enabling better forecasting, reduced stockouts, and integration with building information modeling (BIM) systems in construction projects.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the NPS pipe thread market will remain robust, anchored in infrastructure and industrial demand. Success will depend on manufacturers’ ability to ensure quality, support compliance, and adapt to regional supply chain dynamics. While alternative connection methods (e.g., grooved or flanged systems) compete in certain applications, NPS threading will maintain a strong foothold due to its standardization, cost-effectiveness, and proven reliability.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing NPS Pipe Thread (Quality, IP)
Sourcing NPS (National Pipe Straight) pipe threads involves several potential pitfalls, particularly concerning quality and intellectual property (IP) issues. Being aware of these challenges helps ensure reliable performance and legal compliance.
Poor Thread Quality and Dimensional Inaccuracy
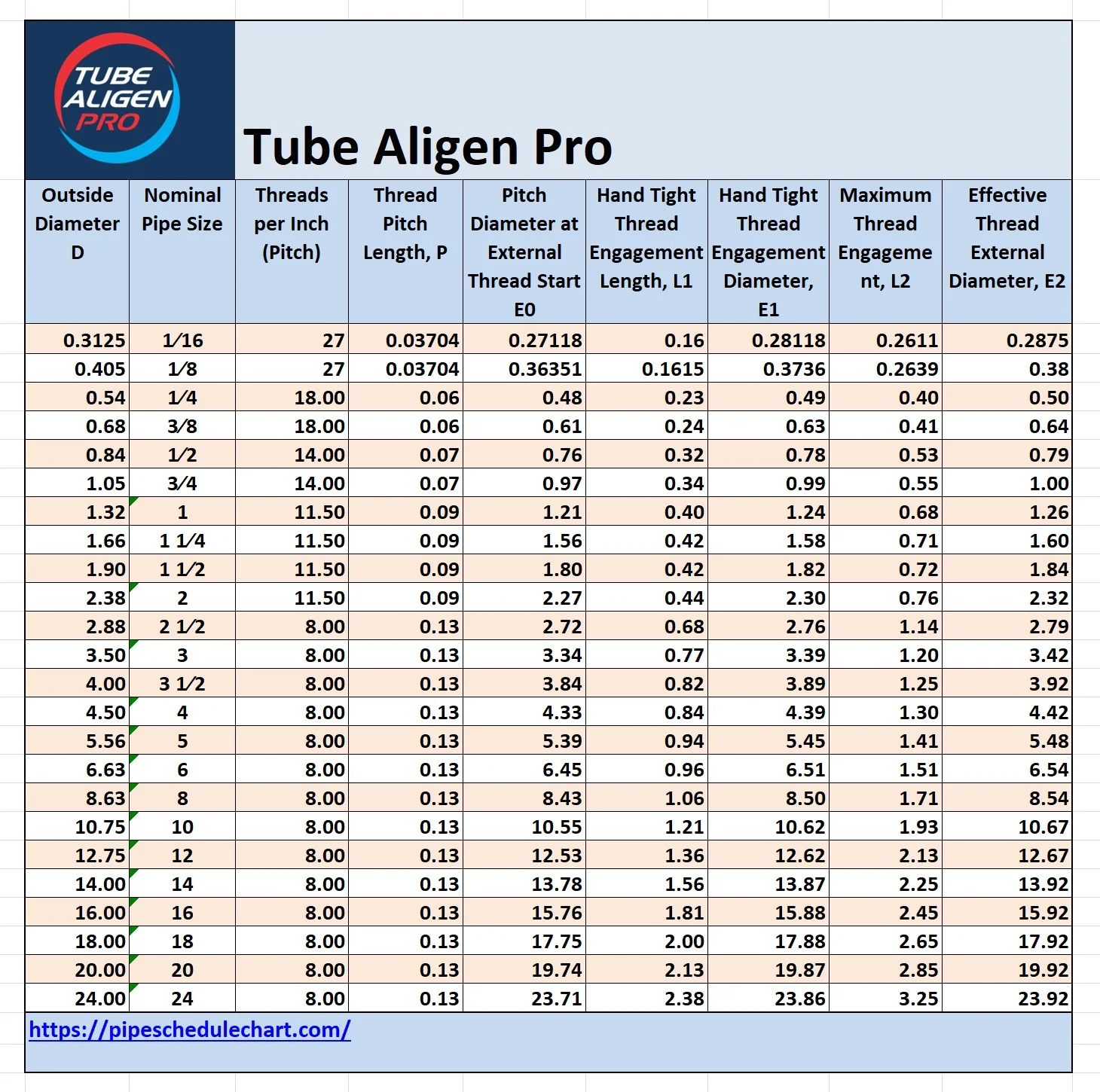
One of the most frequent issues is receiving NPS pipe fittings or components with substandard thread quality. This includes inconsistencies in thread pitch, diameter, or taper (even though NPS is straight, it’s often confused with NPT). Poorly cut threads can lead to leaks, difficulty in assembly, or premature failure under pressure. Sourcing from unverified suppliers, especially in regions with lax manufacturing standards, increases the risk of dimensional inaccuracies that do not conform to ASME B1.20.1 specifications.
Use of Substandard Materials
Low-cost suppliers may use inferior materials—such as low-grade carbon steel or non-compliant alloys—that do not meet required mechanical or corrosion resistance standards. This compromises system integrity, especially in high-pressure or corrosive environments. Without proper material certifications (e.g., mill test reports), verifying compliance becomes difficult, increasing long-term maintenance and safety risks.
Misrepresentation of Thread Type (NPS vs. NPT)
Suppliers may mislabel or confuse NPS (straight) threads with NPT (tapered) threads. Since NPS requires a gasket or O-ring for sealing and NPT relies on thread deformation, using the wrong type results in leaks or joint failure. Inadequate product descriptions or lack of technical clarity exacerbates this issue, especially when sourcing online or through intermediaries.
Lack of Traceability and Certification
Reputable applications require traceable components with proper certifications (e.g., ISO, ASME, API). Many low-cost suppliers fail to provide documentation verifying compliance with industry standards. This lack of traceability creates liability issues and complicates quality assurance processes, particularly in regulated industries like oil and gas or pharmaceuticals.
Intellectual Property Infringement
Sourcing from unauthorized manufacturers can lead to IP violations. Some suppliers replicate branded components (e.g., imitation products from well-known valve or fitting manufacturers) without licensing. Purchasing such items may expose the buyer to legal risks, especially in regions enforcing strict IP laws. Additionally, counterfeit parts often lack performance reliability, posing operational hazards.
Inadequate Testing and Quality Control
Many suppliers, particularly in cost-driven markets, skip essential quality control steps like thread gauging, pressure testing, or visual inspection. Without documented QC procedures, defects may go undetected until installation or operation, resulting in costly downtime and repairs.
Language and Specification Barriers
When sourcing internationally, miscommunication due to language differences or vague specifications can result in incorrect products being delivered. Terms like “NPS thread” may be interpreted differently, leading to mismatched components. Clear technical drawings and standardized callouts are essential but often overlooked.
Supply Chain Transparency Issues
Opaqueness in the supply chain—such as undisclosed subcontractors or multiple sourcing tiers—hinders quality oversight. Buyers may believe they are purchasing from a certified manufacturer, only to receive goods produced by an unqualified third party, increasing the risk of non-compliance and defects.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence: vetting suppliers, demanding certifications, validating samples, and ensuring clear contractual terms around quality and IP compliance.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for NPS Pipe Thread
Overview of NPS Pipe Thread
National Pipe Straight (NPS) thread is a U.S. standard for straight (non-tapered) threads used primarily in low-pressure applications involving piping systems. Unlike NPT (National Pipe Taper) threads, NPS threads require a separate sealing mechanism, such as an O-ring or gasket, to ensure leak-free connections. Understanding the logistics and compliance requirements for NPS pipe thread components is essential for safe, efficient, and legally compliant operations in industries such as oil and gas, plumbing, and industrial manufacturing.
Regulatory Standards and Specifications
NPS pipe thread dimensions and tolerances are governed by American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) standards, particularly ASME B1.20.1. Compliance with these standards ensures interchangeability and safety across systems. Key specifications include thread form, pitch, and diameter tolerances. Always verify that components are certified to relevant standards and accompanied by documentation such as mill test reports or certificates of conformity.
Material and Manufacturing Compliance
NPS threaded components must be manufactured from materials suitable for their intended service conditions (e.g., pressure, temperature, chemical exposure). Common materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, and brass. Manufacturers must adhere to applicable material standards such as ASTM A106 for carbon steel or ASTM A312 for stainless steel. Ensure that material traceability and heat lot records are maintained for compliance and quality assurance.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Proper packaging is critical to prevent damage to NPS threads during shipping and storage. Threaded ends should be protected with plastic or metal caps, and components should be securely bundled or crated to avoid impact and corrosion. Label packages clearly with part number, size, material, and applicable standards. Avoid stacking heavy items on top of threaded components to prevent deformation.
Transportation and Shipping Considerations
Transport NPS pipe components in accordance with international and domestic shipping regulations, including those from the Department of Transportation (DOT) and International Maritime Organization (IMO). For international shipments, comply with Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) to define responsibility for logistics and risk transfer. Use moisture-resistant packaging in humid environments and consider desiccants to prevent rust during transit.
Import/Export Compliance
When shipping NPS pipe thread components across borders, ensure compliance with customs regulations and trade agreements. Provide accurate Harmonized System (HS) codes—typically under 7307 (tube or pipe fittings of iron or steel)—and complete documentation such as commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. Be aware of anti-dumping duties or trade restrictions that may apply to certain countries of origin.
Quality Assurance and Inspection
Implement a quality control process that includes visual inspection, thread gauging, and dimensional verification upon receipt. Use calibrated thread ring or plug gauges to confirm compliance with ASME B1.20.1. Retain inspection records to support quality audits and regulatory compliance. Non-conforming items should be quarantined and reported to the supplier.
Environmental, Health, and Safety (EHS) Compliance
Handle NPS piping materials in accordance with OSHA and EPA guidelines, particularly when dealing with coatings, lubricants, or galvanized surfaces that may contain hazardous substances. Provide appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) during handling and installation. Follow proper disposal procedures for packaging and scrap metal in line with local environmental regulations.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Maintain comprehensive records for traceability and compliance, including purchase orders, inspection reports, material certifications, and shipping documents. Digital record systems can enhance audit readiness and streamline compliance reporting. Retain records for a minimum of seven years, or as required by industry-specific regulations.
Industry-Specific Compliance Needs
Certain industries impose additional requirements. For example:
– Oil & Gas: Compliance with API standards and potentially NORSOK or ISO 15156 for sour service.
– Pharmaceuticals: Adherence to ASME BPE (Bioprocessing Equipment) standards for hygienic applications.
– Water Treatment: Compliance with NSF/ANSI 61 for components in contact with drinking water.
Verify that NPS components meet all applicable sector-specific certifications before deployment.
Conclusion
Adhering to logistics and compliance best practices for NPS pipe thread ensures system integrity, regulatory conformity, and operational efficiency. Regular audits, supplier qualification, and continuous training are essential for maintaining compliance across the supply chain. Always consult relevant standards and legal requirements specific to your region and industry.
Conclusion for Sourcing NPS Pipe Thread Components:
Sourcing NPS (National Pipe Straight) pipe thread components requires careful attention to industry standards, material compatibility, and supplier reliability to ensure system integrity and performance. By adhering to ANSI/ASME B1.20.1 standards, procurement teams can ensure dimensional accuracy and interchangeability across fittings. Evaluating suppliers based on quality certifications, manufacturing capabilities, and traceability is essential for maintaining consistency and compliance, particularly in critical applications such as oil and gas, plumbing, and industrial systems.
Additionally, clear specifications regarding material type (e.g., stainless steel, carbon steel, brass), coating requirements, pressure ratings, and end-use environment will mitigate risks of leakage, corrosion, or system failure. Leveraging long-term supplier relationships and conducting regular quality audits further enhance supply chain resilience.
In summary, successful sourcing of NPS pipe thread components hinges on a strategic balance of technical precision, quality assurance, and supplier collaboration—ensuring safe, reliable, and cost-effective integration into piping systems.