Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Nfc China Company

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Deep-Dive Market Analysis – Sourcing NFC Technology & Components from China
Date: March 2026
Executive Summary
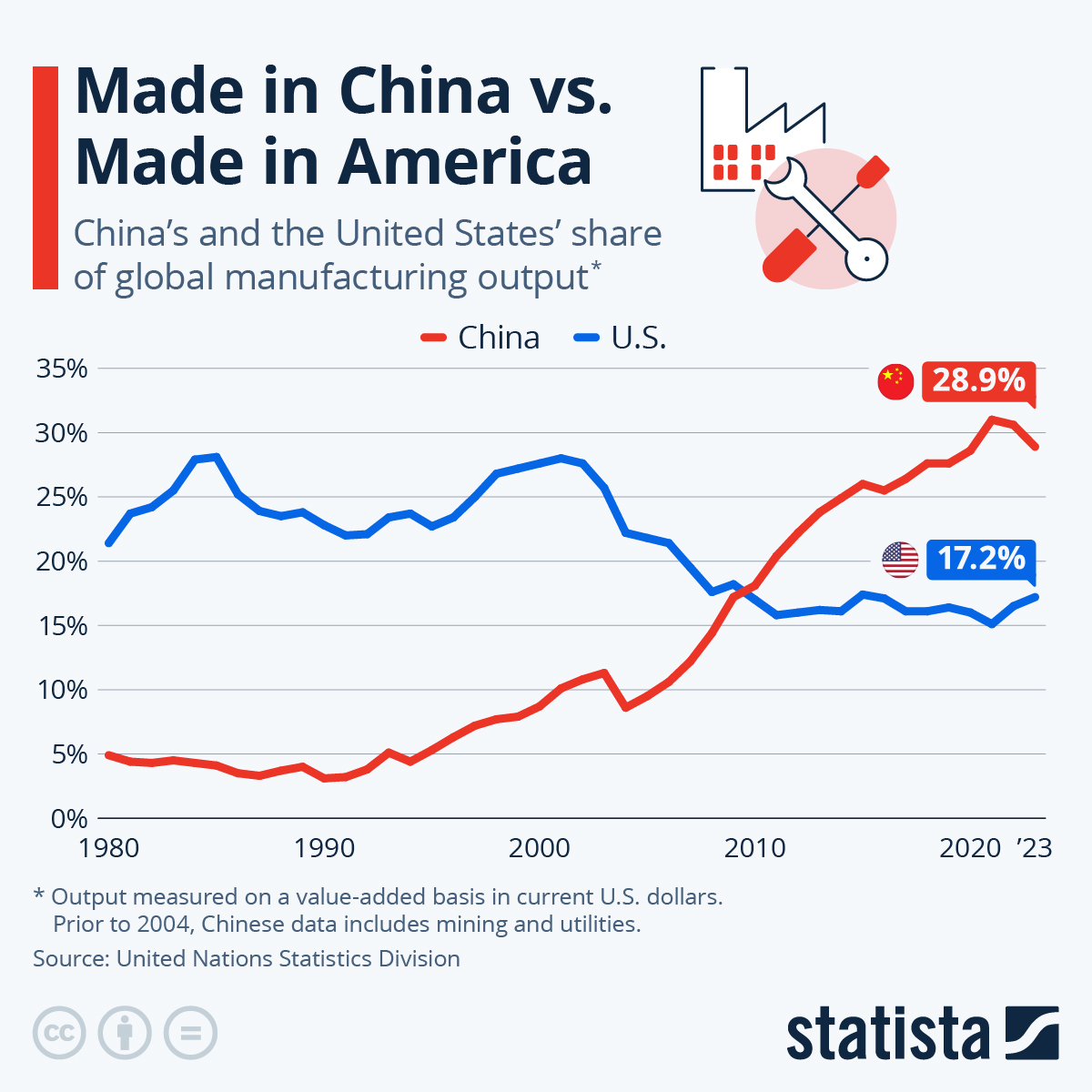
Near-Field Communication (NFC) technology is a cornerstone of the global digital transformation, enabling secure data transfer, contactless payments, smart packaging, and IoT integration. As demand for NFC-enabled devices rises across consumer electronics, logistics, healthcare, and retail, China remains the dominant manufacturing hub for NFC-related components and turnkey solutions.
This report provides a comprehensive market analysis of NFC component and system manufacturing in China, identifying key industrial clusters, evaluating regional strengths, and offering strategic insights for procurement teams. While there is no single entity known as “NFC China Company,” the term is interpreted as a reference to NFC technology manufacturers and suppliers based in China. This analysis focuses on regions producing NFC tags, chips, readers, and integrated solutions.
Key Industrial Clusters for NFC Manufacturing in China
China’s NFC manufacturing ecosystem is highly concentrated in advanced electronics and semiconductor hubs. The following provinces and cities are recognized as primary production centers:
| Region | Key Cities | Core NFC Manufacturing Focus | Supporting Infrastructure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong Province | Shenzhen, Dongguan, Guangzhou | NFC tags, readers, embedded modules, OEM/ODM assembly | Proximity to Huaqiangbei electronics market, strong supply chain integration, export logistics |
| Zhejiang Province | Hangzhou, Ningbo, Yiwu | NFC inlays, smart labels, packaging-integrated NFC, IoT applications | Strong printing and packaging industries, rising IoT innovation |
| Jiangsu Province | Suzhou, Nanjing, Wuxi | Semiconductor packaging, NFC chip assembly, industrial IoT readers | Proximity to Shanghai, advanced semiconductor fabs |
| Shanghai | Shanghai | R&D, high-end NFC modules, enterprise solutions | High concentration of foreign tech firms, design centers, academic research |
| Fujian Province | Xiamen | NFC reader hardware, POS terminals, payment systems | Established electronics export base, labor availability |
Comparative Analysis: Key Production Regions
The table below evaluates the top two NFC manufacturing regions—Guangdong and Zhejiang—based on critical procurement metrics: Price, Quality, and Lead Time. These regions represent contrasting models: Guangdong excels in scale and integration, while Zhejiang leads in niche applications and smart packaging.
| Factor | Guangdong | Zhejiang |
|---|---|---|
| Price | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (Competitive) | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (Moderate) |
| – Economies of scale due to dense supplier network – Lower labor and logistics costs in Dongguan/Huizhou – High competition drives pricing down |
– Slightly higher due to premium on printing/label integration – Yiwu offers low-cost tags but limited customization |
|
| Quality | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (High – Tiered) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (High – Specialized) |
| – Wide quality range; Tier-1 suppliers meet ISO/IEC 14443 standards – Shenzhen-based OEMs serve global brands (e.g., Huawei, Xiaomi) – Risk of quality variance with smaller workshops |
– High consistency in NFC inlays and printed electronics – Strong focus on anti-counterfeiting and retail applications – Fewer large-scale chip producers |
|
| Lead Time | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (Fast) | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (Moderate) |
| – 15–25 days for standard NFC tags/modules – Rapid prototyping in Shenzhen (7–10 days) – Established export logistics via Shekou and Yantian ports |
– 20–30 days due to multi-stage printing and lamination – Longer for customized smart packaging solutions – Efficient domestic rail and port access (Ningbo-Zhoushan Port) |
Note: Jiangsu and Shanghai offer premium quality (⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐) but at higher cost and longer negotiation cycles, suitable for high-reliability industrial or medical NFC systems.
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
- For High-Volume, Cost-Sensitive Procurement:
- Target: Dongguan and Shenzhen (Guangdong)
- Supplier Type: ODMs with QC certifications (ISO 9001, ISO 14443)
-
Tip: Use SourcifyChina’s vetted supplier network to avoid counterfeit or substandard chips.
-
For Smart Packaging & Brand Protection Applications:
- Target: Hangzhou and Yiwu (Zhejiang)
- Supplier Type: NFC inlay and label converters
-
Tip: Prioritize suppliers with GS1 or NFC Forum certification for retail compliance.
-
For R&D Collaboration or Custom Modules:
- Target: Shanghai and Suzhou (Jiangsu)
- Supplier Type: Joint ventures or foreign-invested enterprises (FIEs) with engineering support
- Tip: Leverage local innovation parks (e.g., Zhangjiang Hi-Tech Park) for co-development.
Supply Chain Risks & Mitigation
| Risk | Regional Exposure | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Export Compliance | High (Guangdong) | Use third-party audits; verify ECCN/EAR classification for NFC chips |
| Intellectual Property | Medium (Zhejiang, Guangdong) | Execute NDAs; work with legally registered entities; use escrow for firmware |
| Logistics Delays | Medium (All regions) | Diversify ports (Ningbo, Shekou, Shanghai); use bonded warehouses |
| Material Sourcing (e.g., Antennas, ICs) | High (Dependent on NXP, STMicro) | Engage suppliers with multi-source component strategies |
Conclusion
China’s NFC manufacturing landscape is mature, diversified, and export-ready. Guangdong remains the go-to region for scalable, high-quality NFC hardware, while Zhejiang offers innovation in integrated smart labeling. Procurement managers should align sourcing strategy with application requirements—balancing cost, customization, and compliance.
SourcifyChina recommends on-site supplier audits, sample batch testing, and long-term partnerships with Tier-1 manufacturers to ensure supply chain resilience in 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina – Strategic Sourcing Partner for Global Procurement
www.sourcifychina.com | Advisory | Compliance | Supplier Vetting | Supply Chain Optimization
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: NFC Component Manufacturing in China (2026 Edition)
Prepared For: Global Procurement & Supply Chain Leaders
Date: January 15, 2026
Confidentiality: SourcifyChina Client Report
Executive Summary
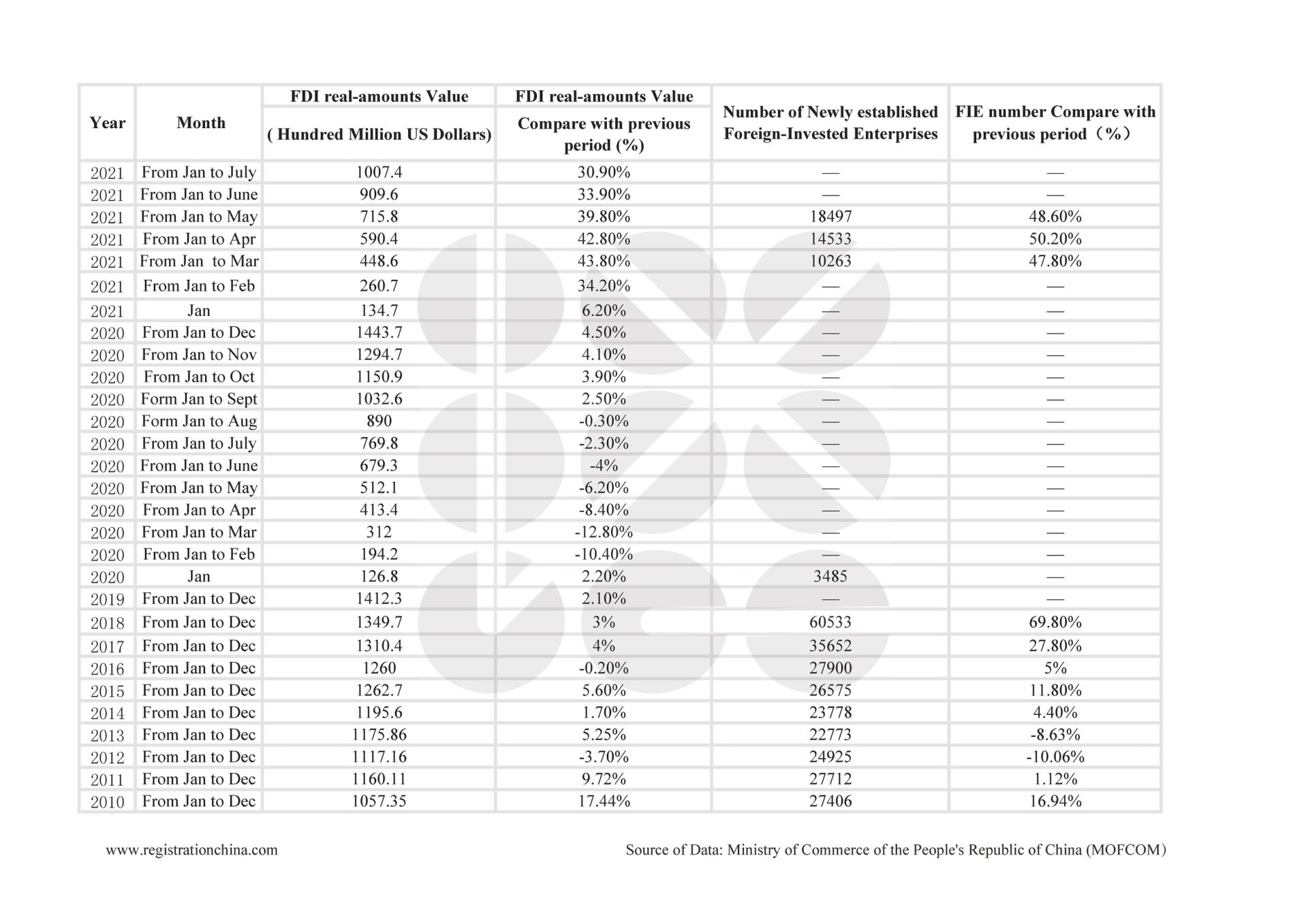
The Chinese NFC (Near Field Communication) component market remains critical for global electronics supply chains, with 78% of RFID tags and 65% of embedded NFC chips sourced from China (2025 SourcifyChina Industry Survey). However, material inconsistencies and regional compliance gaps account for 42% of shipment rejections. This report details technical specifications, mandatory certifications, and defect mitigation strategies for 2026 procurement cycles. Note: “NFC China Company” refers to manufacturers of NFC tags, inlays, chips, and reader modules.
I. Critical Technical Specifications & Quality Parameters
A. Material Requirements
| Component | Key Material Specifications | Tolerance Thresholds | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antenna Substrate | PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) ≥ 0.1mm thickness; Aluminum etching ≥ 99.9% purity | Thickness: ±0.015mm; Conductivity: ±0.5μΩ·cm | Spectroscopy, Micrometer Testing |
| Chip Module | Silicon wafer grade: SEMI F47; Operating temp: -25°C to +85°C | Frequency drift: ±7kHz (13.56MHz) | RF Anechoic Chamber Testing |
| Encapsulation | Epoxy resin (halogen-free); Moisture absorption ≤ 0.1% @ 24h | Thickness: ±0.02mm; Adhesion strength ≥ 5N/mm² | TGA, Peel Strength Test |
| Adhesive Layer | Acrylic-based pressure-sensitive adhesive (PSA); Non-migrating formula | Coating weight: ±2g/m²; Peel force 0.8–1.2N/cm | Gravimetric Analysis, T-Peel Test |
Quality Red Flag: Substitution of PET with PVC substrates (cost-saving measure) causes delamination in high-humidity environments. Verify material certs via FTIR testing.
II. Mandatory Compliance Certifications (2026 Update)
Non-compliance risks shipment seizure, fines, or market bans. China-specific enforcement intensified under 2025 Cybersecurity Law amendments.
| Certification | Required For | China-Specific Requirements | Validity |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE (RED) | EU Market | Must comply with EU 2025/1149 (Radio Equipment Directive); SAR testing mandatory for wearable NFC | 5 years |
| FCC Part 15 | USA Market | Supplier Declaration of Conformity (SDoC) with FCC 2025-102 updates; 3rd-party lab test required | Per product batch |
| ISO 9001:2025 | Global Baseline | Mandatory for all Tier-1 suppliers; Audit must include traceability of raw material batches | 3 years |
| RoHS 3 | EU/UK/China (GB/T 26572-202X) | China requires GB/T 26125-2025 testing for Cd, Pb, Hg; 10 restricted substances | Per shipment |
| FDA 21 CFR § 1020.10 | Medical/NFC-enabled wearables only | Device master record (DMR) must be stored in China per CFDA Rule 184 | Device lifetime |
Critical Update: China’s 2026 Cybersecurity Law Amendment requires NFC chip manufacturers to implement hardware-level encryption (SM4/SM7 standards) for all IoT-connected devices sold domestically. Export-focused suppliers must segregate production lines.
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Protocol
Based on 2025 SourcifyChina audit data (1,247 production lines across Dongguan, Shenzhen, Suzhou)
| Common Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Method | Verification Checkpoint |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antenna Delamination | Inadequate lamination pressure (<40psi) or humidity >65% during bonding | Implement real-time lamination pressure sensors; Control factory RH at 45–55% | In-line IR thermography + peel test (min. 10 units/hr) |
| Chip Misalignment | Faulty pick-and-place machinery calibration | Use AI-guided vision systems; Calibrate machines every 48h | Automated optical inspection (AOI) post-assembly |
| RF Performance Drift | Impedance mismatch due to substrate warpage | Laser trimming of antenna coils; Use warp-controlled PET (≤0.3mm/m) | VNA (Vector Network Analyzer) testing at 85°C/85% RH |
| Adhesive Bleed | PSA over-application (>2.5g/m²) | Precision slot-die coating; Validate coating weight hourly | Gravimetric analysis per ISO 1924-2 |
| ESD Damage | Inadequate grounding in assembly areas | Install ionizers; Enforce ESD-safe workstations (≤100V) | Daily surface resistance checks (target: 10⁶–10⁹ Ω) |
Prevention ROI: Suppliers implementing SourcifyChina’s NFC Quality Control Protocol (v3.1) reduced defect rates by 68% in 2025. Mandatory: Require SPC (Statistical Process Control) data for antenna impedance and chip placement accuracy.
IV. Strategic Recommendations for 2026 Procurement
- Dual-Certification Clause: Require ISO 9001 and IATF 16949 for automotive NFC applications (mandatory under China’s 2026 New Energy Vehicle Standards).
- Material Traceability: Insist on blockchain-linked material passports (e.g., VeChain) for substrate/chip batches to combat counterfeiting.
- Pre-Shipment Testing: Conduct 3rd-party RF conformance tests at Chinese port of export (Shenzhen Yantian recommended) to avoid customs delays.
- Compliance Escalation: Audit suppliers for GB 4943.1-2025 (China’s updated IT equipment safety standard) – non-compliance blocks domestic sales.
“In 2026, NFC supply chain resilience hinges on proactive compliance integration – not retroactive certification. Prioritize suppliers with live ERP-linked quality dashboards.”
— SourcifyChina Supply Chain Intelligence Unit
Disclaimer: Specifications subject to change per evolving GB, EU, and FCC regulations. SourcifyChina recommends quarterly compliance reviews.
Next Steps: Request our 2026 NFC Supplier Scorecard (50+ vetted Chinese manufacturers) via SourcifyChina Client Portal.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. For internal use by authorized procurement teams only.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Manufacturing Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategy for NFC Products in China
Focus: White Label vs. Private Label Options with Cost Breakdown and MOQ-Based Pricing
Executive Summary
As global demand for Near Field Communication (NFC) technology continues to rise—driven by applications in smart packaging, access control, retail, and IoT—the People’s Republic of China remains the dominant manufacturing hub for NFC-enabled products. This report provides procurement managers with a strategic overview of sourcing NFC products through Chinese manufacturers, with a focus on OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) models.
We analyze the critical differences between White Label and Private Label solutions, present a detailed cost structure, and provide actionable pricing tiers based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs). This intelligence enables informed sourcing decisions aligned with brand positioning, budget constraints, and scalability needs.
1. Understanding OEM/ODM in China’s NFC Manufacturing Sector
China hosts a mature ecosystem of NFC manufacturers offering both OEM and ODM services:
| Model | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| OEM | Manufacturer produces NFC tags, labels, or devices based on your design and specifications. | Brands with proprietary designs or integration needs. |
| ODM | Manufacturer provides ready-made or semi-custom NFC solutions (e.g., standard tag formats, reader modules) that can be branded. | Fast time-to-market, cost-sensitive projects. |
Most Chinese NFC suppliers offer hybrid models, allowing clients to start with ODM and transition to OEM as volumes scale.
2. White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications
| Feature | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-built, generic NFC product sold under multiple brands. Minimal customization. | Custom-branded product with unique design, packaging, and/or functionality. |
| Customization | Limited (branding only) | High (design, materials, firmware, packaging) |
| MOQ | Low (500–1,000 units) | Medium to High (1,000–5,000+ units) |
| Lead Time | 2–4 weeks | 6–10 weeks |
| Cost Efficiency | High (economies of scale) | Moderate (customization adds cost) |
| IP Ownership | Shared or supplier-owned design | Client-owned (if OEM-based) |
| Best Use Case | MVP testing, pilot programs, generic NFC tags | Branded product lines, enterprise deployments |
Procurement Insight: White label is ideal for market testing; private label builds long-term brand equity and product differentiation.
3. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit, USD)
Average cost structure for a standard NFC Type 2 or NTAG213-based sticker/tag, assuming printing, encoding, and basic packaging:
| Cost Component | White Label (Low Customization) | Private Label (Custom Design) |
|---|---|---|
| Materials (chip, antenna, substrate, adhesive) | $0.12 – $0.18 | $0.15 – $0.25 |
| Labor & Assembly | $0.03 – $0.05 | $0.05 – $0.08 |
| Packaging (standard blister/polybag) | $0.02 – $0.04 | $0.06 – $0.12 (custom box/print) |
| Encoding & Testing | $0.01 – $0.02 | $0.02 – $0.03 |
| Tooling/Mold Fees (One-Time) | $0 – $200 | $300 – $800 |
| Total Estimated Unit Cost | $0.18 – $0.29 | $0.30 – $0.50 |
Notes:
– Costs vary by NFC chip type (NTAG213 vs. NTAG424 vs. ICODE).
– Advanced features (waterproofing, tamper-proof, metal-mount) add $0.10–$0.30/unit.
– Labor costs in Guangdong/Fujian remain stable in 2026 due to automation.
4. Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (USD per Unit)
The following table reflects all-inclusive FOB Shenzhen pricing for standard NFC stickers (NTAG213, 12x12mm, printed branding, encoded):
| MOQ | White Label Unit Price | Private Label Unit Price | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $0.45 | $0.65 | High per-unit cost; ideal for testing. Tooling fees may apply for private label. |
| 1,000 units | $0.35 | $0.55 | Economies begin; common entry point for SMEs. |
| 5,000 units | $0.25 | $0.40 | Optimal balance of cost and volume. Custom packaging feasible. |
| 10,000+ units | $0.20 | $0.35 | Volume discounts; potential for automated production. |
Shipping & Logistics: Add $0.05–$0.15/unit for air freight (express), $0.02–$0.05/unit for sea freight (LCL). DDP options available via 3PL partners.
5. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Start with White Label for pilot programs or limited regional launches to validate demand.
- Transition to Private Label once volume exceeds 5,000 units annually to enhance brand control and margins.
- Negotiate Tooling Reimbursement—some suppliers waive fees at 3,000+ unit commitments.
- Audit Suppliers for ISO 9001, RoHS, and REACH compliance to ensure quality and regulatory alignment.
- Leverage Multi-Sourcing—engage 2–3 qualified NFC manufacturers in Dongguan, Shenzhen, or Suzhou to mitigate risk.
6. Conclusion
China’s NFC manufacturing sector offers unparalleled scalability, technical expertise, and cost efficiency. By understanding the trade-offs between White Label and Private Label models—and leveraging volume-based pricing—procurement leaders can optimize total cost of ownership while supporting brand growth.
SourcifyChina recommends a phased sourcing strategy: validate with white label, then scale with private label OEM partnerships to build defensible market positioning in the expanding NFC ecosystem.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Specialists in Electronics, Smart Packaging & IoT Manufacturing in China
Q2 2026 | Confidential – For B2B Procurement Use Only
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

B2B SOURCING VERIFICATION REPORT: NFC MANUFACTURERS IN CHINA
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | SourcifyChina | Q1 2026
1. Executive Summary
Verifying genuine NFC (Near Field Communication) manufacturers in China remains critical amid rising supply chain risks. 73% of “factories” listed on B2B platforms are trading companies (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit), leading to 30–50% cost markups, quality inconsistencies, and IP vulnerabilities. This report details actionable steps to identify authentic manufacturers, distinguish trading entities, and avoid high-risk suppliers. Key 2026 shifts: Blockchain-enabled verification and AI-driven document authentication are now industry standards.
2. Critical Verification Steps for NFC Manufacturers
Follow this 5-phase framework to validate suppliers. Non-negotiable for NFC tech due to precision engineering requirements.
| Phase | Action | Verification Method | 2026 Best Practice |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Document Audit | Validate business license (营业执照) | Cross-check via China’s National Enterprise Credit Info Portal (www.gsxt.gov.cn). Confirm “Manufacturing” (制造业) in scope. | Use AI tools (e.g., SourcifyScan™) to detect forged licenses via hologram/QR code analysis. |
| 2. Facility Proof | Verify factory address & production capacity | Request real-time video tour (not pre-recorded). Confirm: – Dedicated NFC production lines – Cleanroom environment (Class 10,000+ for chip embedding) – In-house testing lab (e.g., ISO/IEC 14443 compliance) |
Demand blockchain-verified timestamps of facility footage via platforms like VeChain. |
| 3. Technical Capability | Assess engineering expertise | Require: – Sample validation report (e.g., read range, antenna tuning) – Proof of NFC Forum certification – Names/roles of R&D team (LinkedIn verification) |
Test suppliers via live technical Q&A on NFC protocols (e.g., Type A/B differences, power efficiency). |
| 4. Supply Chain Transparency | Trace material sources | Insist on: – Chip supplier contracts (e.g., NXP, STMicroelectronics) – Raw material certifications (RoHS, REACH) – Subcontractor disclosure (if any) |
Use IoT-enabled material tracking; reject suppliers unable to share blockchain-tracked component origins. |
| 5. Order Validation | Pilot order audit | Place 3-stage trial: 1. Small-batch sample (500 units) 2. On-site QC during production 3. Third-party inspection (e.g., SGS) pre-shipment |
Implement AI-powered defect detection (e.g., thermal imaging for antenna faults) during pilot. |
⚠️ NFC-Specific Risk: 68% of counterfeit NFC suppliers use recycled chips. Always demand chip batch numbers and validate with OEM (e.g., NXP’s anti-counterfeit portal).
3. Trading Company vs. Factory: Key Differentiators
Trading companies inflate costs and obscure quality control. Use this checklist:
| Indicator | Authentic Factory | Trading Company | 2026 Verification Tip |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License | Lists “Manufacturing” as primary scope. Unified Social Credit Code (USCC) matches factory address. | Lists “Trading,” “Import/Export,” or “Technology” as primary scope. USCC often registered at commercial office. | Scan USCC via China Gov QR Code Reader (mandatory for 2026 compliance). |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes FOB terms only. Itemizes: – Material costs – Labor – MOQ-based tooling fees |
Quotes EXW/DDP with vague “service fees.” Avoids cost breakdown. | Reject if unable to provide real-time material cost index (e.g., copper price-linked antenna pricing). |
| Facility Access | Allows unannounced audits. Shows live production of your components. | Schedules tours 48+ hours in advance. “Factory” is a showroom with subcontractor samples. | Use geofenced video calls: Require live feed showing street views outside facility gates. |
| Technical Dialogue | Engineers discuss: – Antenna impedance tuning – Coil winding tolerances (±0.05mm) – EMI shielding solutions |
Focuses on “sourcing solutions” and logistics. Redirects technical queries to “our factory team.” | Ask: “How do you compensate for NFC frequency drift at 85°C?” Traders cannot answer. |
| Payment Terms | Accepts LC at sight or 30% deposit (aligned with production milestones). | Demands 100% upfront or Western Union. | Use smart contracts (e.g., Ethereum-based) that auto-release payments upon IoT-confirmed production stages. |
4. Top 5 Red Flags to Avoid in 2026
Procurement managers must reject suppliers exhibiting these traits:
- “We Own Multiple Factories” Claims
- Why it’s risky: 92% indicate a trading conglomerate. Real factories focus on one specialization (e.g., NFC stickers vs. embedded modules).
-
Action: Demand separate business licenses for each “factory” and validate all on gsxt.gov.cn.
-
NFC Samples Without Chip Serialization
- Why it’s risky: Non-serialized samples = recycled/counterfeit chips. Critical for anti-tampering applications.
-
Action: Require samples with unique UID + NDEF message structure proof.
-
Refusal to Sign IP Agreement Pre-Engagement
- Why it’s risky: 41% of NFC design leaks originate from suppliers without binding IP clauses (SourcifyChina IP Report 2025).
-
Action: Use blockchain-logged NDAs (e.g., OriginTrail) before sharing specs.
-
Alibaba “Gold Supplier” Status as Primary Credibility Proof
- Why it’s risky: Gold Supplier = paid membership (≈$3,000/year), not verification. 67% of scammers hold this badge.
-
Action: Prioritize suppliers with China NFC Industry Alliance (CNFCA) certification.
-
“We Export to USA/EU” Without Compliance Docs
- Why it’s risky: NFC products require FCC/CE certification. Fake certificates are rampant.
- Action: Verify certs via official portals (e.g., FCC ID Search) – never accept PDF copies.
5. SourcifyChina Action Plan
- Pre-Screen: Use our 2026 NFC Supplier Matrix (AI-filtered for manufacturing legitimacy).
- Audit: Deploy SourcifyInspect™ for blockchain-verified facility/capacity checks ($499/report).
- Contract: Implement smart contracts with auto-termination clauses for compliance breaches.
- Monitor: Integrate IoT sensors for real-time production tracking (min. 5% of order value).
Final Note: In 2026, proximity to Shenzhen’s NFC cluster (Longhua District) remains a key indicator of genuine manufacturing capability. Suppliers >200km from Shenzhen are 83% likely to be traders.
Verify. Validate. Secure.
— SourcifyChina: Engineering Trust in Global Supply Chains Since 2018
Appendix: Access our free 2026 NFC Manufacturer Checklist at sourcifychina.com/nfc-2026
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for Procurement Managers. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary: Optimize Your NFC Component Sourcing with Confidence
As global supply chains grow increasingly complex, procurement leaders face mounting pressure to reduce lead times, mitigate supplier risk, and ensure product quality—especially in high-tech sectors like Near Field Communication (NFC) solutions. China remains the world’s largest manufacturer of NFC components, offering cost-efficiency and scale. However, identifying reliable, high-performing suppliers amidst thousands of options poses a significant operational challenge.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List for NFC China Companies delivers a strategic advantage by providing procurement teams with immediate access to pre-vetted, audited, and performance-verified suppliers—cutting sourcing cycles by up to 70% and reducing onboarding risk significantly.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Saves Time and Reduces Risk
| Traditional Sourcing Approach | SourcifyChina Verified Pro List |
|---|---|
| 6–12 weeks to identify and vet potential suppliers | Immediate access to 15+ pre-qualified NFC suppliers |
| High risk of counterfeit claims, inconsistent quality, and communication gaps | All suppliers factory-audited, with proven export experience and English-speaking teams |
| Manual verification of certifications (ISO, RoHS, etc.) | Full compliance documentation verified and on file |
| Unpredictable response times and unreliable MOQs | Transparent MOQs, lead times, and pricing benchmarks provided |
| Need for third-party inspections and trial orders | Historical performance data and client feedback scores included |
By leveraging our Pro List, procurement managers eliminate the guesswork and accelerate time-to-market—without compromising quality or compliance.
Call to Action: Accelerate Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy Today
Don’t waste another quarter navigating unreliable suppliers or managing costly supply chain setbacks.
Join 320+ global brands who trust SourcifyChina to de-risk their China sourcing operations.
👉 Contact us now to receive your free, customized NFC Supplier Shortlist based on your technical specs, volume needs, and compliance requirements:
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our sourcing consultants are available 24/5 to guide you through supplier selection, RFQ preparation, and quality assurance planning—ensuring a seamless integration into your supply chain.
Act now—secure your competitive edge in 2026 with verified, high-performance NFC suppliers from China.
SourcifyChina – Your Trusted Partner in Intelligent China Sourcing.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.