The global gemstone market, fueled by rising demand for ethically sourced and natural stones in jewelry and luxury accessories, is experiencing steady expansion. According to Grand View Research, the global gemstone market size was valued at USD 29.7 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.3% from 2023 to 2030. Natural opal, renowned for its iridescent play-of-color and unique geological formation, represents a niche yet high-value segment within this market. Mordor Intelligence projects continued growth in demand for premium and transparently sourced gemstones, with Australia—the leading producer of natural opal—accounting for over 90% of the world’s supply. This surge in consumer interest, particularly in sustainable and traceable gem materials, has elevated the prominence of reputable opal manufacturers and suppliers. As buyers increasingly prioritize authenticity and quality, identifying the top natural opal stone manufacturers becomes critical for retailers and designers seeking reliable, high-grade inventory.
Top 10 Natural Opal Stone Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Spencer Opal Mines
Domain Est. 2000
Website: spenceropalmines.com
Key Highlights: 30-day returnsPrecious Spencer Opal Stone Free-form. Buy Now. Precious Spencer Opal Stone Free-form. SKU 00698. $500.00.Missing: natural manufacturer…
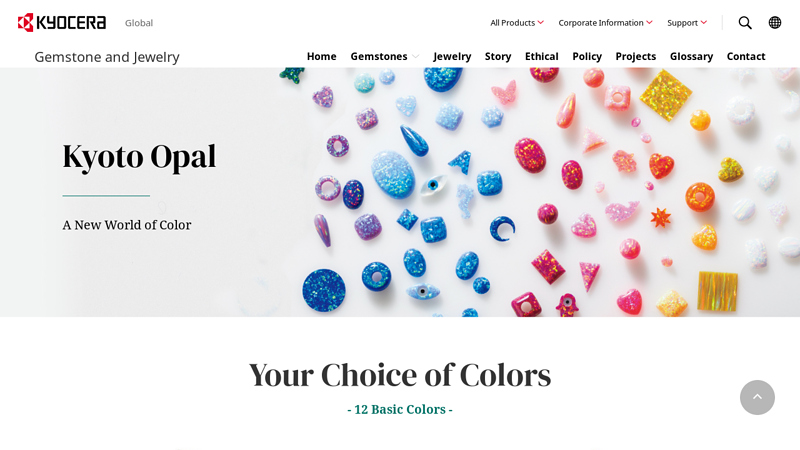
#2 Kyoto Opal
Domain Est. 1993
Website: global.kyocera.com
Key Highlights: An innovative synthetic opal impregnated with polymer for added strength. The company’s Kyoto headquarters inspires the Kyoto Opal colors….
#3 Opal Gemstones
Domain Est. 1998
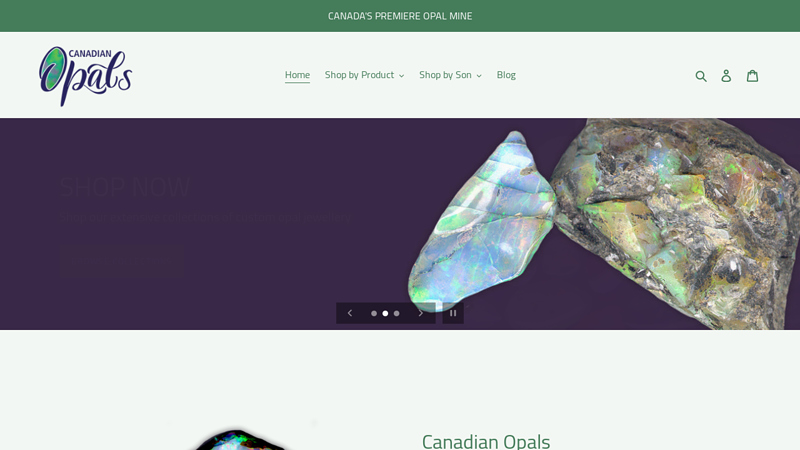
#4 Canadian Opals
Domain Est. 1998
Website: opalscanada.com
Key Highlights: Opal Resources Canada designs, creates and sells the finest of opal products. Each opal stone is a unique one-of-a-kind piece of nature that only you will own….
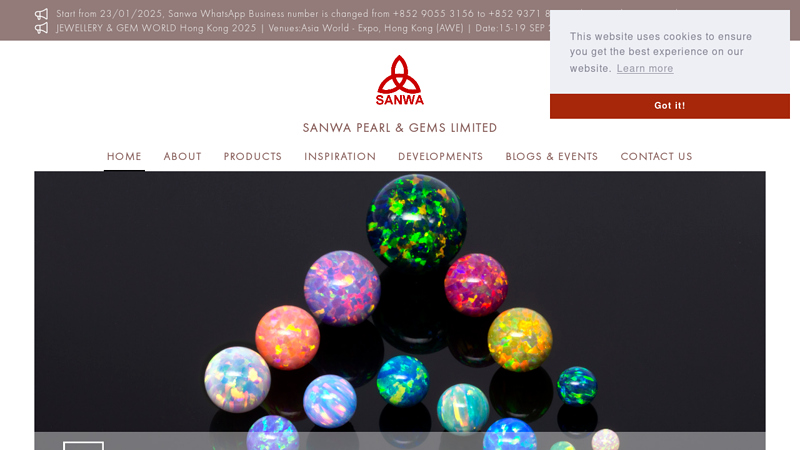
#5 Synthetic Opal
Domain Est. 1999
Website: sanwapearl.com.hk
Key Highlights: Sanwa Pearl & Gems Ltd is the market leader for synthetic opal products. Click here for more information about Sanwa!…
#6 Opal Minded Australia
Domain Est. 2002
Website: opalminded.com
Key Highlights: Opal Minded is Australia’s premier opal jewellery store, offering handcrafted designs and lifelong opal care services. Call us today at 02 9247 9885….
#7 Buy Australian Black Opal
Domain Est. 2008
#8 Opal Ring Collection
Domain Est. 2014
Website: blackstaropal.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery 30-day returnsShop genuine Australian opal rings in gold and silver. Authentic, natural opals and expertly crafted, one-of-a-kind ring designs. Free worldwide shippin…
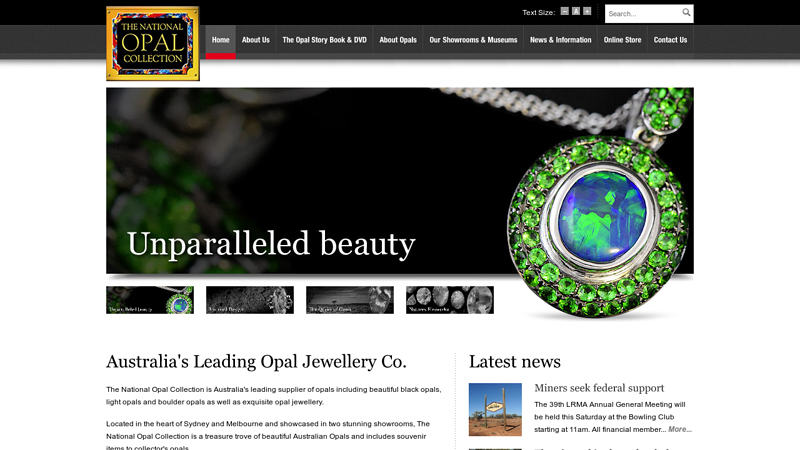
#9 The National Opal Collection
Website: nationalopal.com
Key Highlights: The National Opal Collection is Australia’s leading supplier of opals including beautiful black opals, light opals and boulder opals as well as exquisite opal ……
#10 Australian Opal Shop
Website: australianopalshop.com.au
Key Highlights: We are a family run Business, with over 20+ years of cutting and polishing Australian Opal. Making unique gold, silver and beaded one of a kind Opal pieces….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Natural Opal Stone

2026 Market Trends for Natural Opal Stone
The natural opal stone market is poised for notable shifts by 2026, influenced by evolving consumer preferences, technological advancements, sustainability concerns, and global economic dynamics. Below is an analysis of the key trends expected to shape the industry in the coming years.
Rising Demand for Ethically Sourced and Traceable Opals
Consumers in 2026 are increasingly prioritizing transparency and ethical sourcing in their gemstone purchases. With heightened awareness of environmental and social issues in mining, there will be strong demand for opals with verifiable origins, especially those certified by third-party organizations. Australian opals, particularly from Lightning Ridge and Coober Pedy, will maintain premium status due to established mining regulations and provenance tracking. Blockchain technology is expected to play a growing role in providing digital certificates of authenticity and ethical sourcing, enhancing consumer trust.
Growth of the Lab-Grown Opal Market and Its Impact
While natural opals remain highly valued for their uniqueness, lab-created opals are gaining traction due to their affordability and consistent quality. However, this trend will push the natural opal market to emphasize its rarity, iridescence, and geological authenticity. By 2026, marketing strategies for natural opals will likely focus on storytelling—highlighting the stone’s formation over millions of years and its status as a natural wonder—differentiating it from synthetic alternatives.
Influence of Jewelry Design and Fashion Trends
Natural opals are expected to feature prominently in high-end and artisanal jewelry collections in 2026. Designers are increasingly incorporating opals into modern, minimalist settings that highlight the stone’s play-of-color, appealing to younger, style-conscious consumers. The popularity of birthstone jewelry and personalized pieces will also bolster opal demand, as October’s official birthstone. Additionally, opals may see increased use in men’s luxury accessories, such as cufflinks and signet rings, expanding their market beyond traditional uses.
Market Expansion in Emerging Economies
Asia-Pacific, particularly China and India, will continue to emerge as key growth markets for natural opals. Rising disposable incomes, expanding middle classes, and growing appreciation for gemstone jewelry will drive demand. E-commerce platforms and social media marketing will play a crucial role in reaching these consumers, with influencers and digital showrooms showcasing opal collections to a global audience.
Price Volatility and Supply Constraints
Natural opal supply remains limited due to the finite nature of opal fields and environmental restrictions on mining. By 2026, premium-quality black opals and boulder opals are expected to see price increases, driven by scarcity and collector interest. Climate change impacts, particularly in Australia, may also affect mining operations, further tightening supply. This scarcity will reinforce the investment appeal of high-grade natural opals, attracting collectors and investors.
Sustainability and Environmental Responsibility
Sustainable mining practices will become a competitive advantage. Opal producers and suppliers who adopt eco-friendly extraction methods, reduce water usage, and support local communities will gain favor among environmentally conscious buyers. Certifications related to responsible mining and carbon footprint reduction will likely become standard expectations in premium market segments.
In conclusion, the 2026 market for natural opal stone will be defined by a blend of tradition and innovation. While challenges such as supply constraints and competition from lab-grown alternatives persist, the intrinsic beauty, rarity, and emotional appeal of natural opals position them well for continued relevance and growth—especially when paired with ethical practices and digital transparency.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Natural Opal Stone (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing natural opal stone can be rewarding, but it comes with significant challenges related to quality assessment and intellectual property concerns. Being aware of these pitfalls is crucial for buyers, designers, and retailers.
Misjudging Opal Quality and Authenticity
One of the most frequent issues in sourcing natural opal is accurately assessing its quality and ensuring it is genuinely natural. Buyers may fall into traps such as:
- Confusing synthetic or treated opals with natural ones: Lab-created opals or doublets/triplets (composites with thin layers of natural opal glued to backing material) are often passed off as solid natural opal. These lack the value and durability of genuine stones.
- Overlooking play-of-color inconsistencies: High-quality natural opal exhibits vibrant, shifting colors. Dull, static, or patchy color patterns may indicate lower quality or imitation.
- Ignoring inclusions and fractures: Natural opals often contain internal flaws. Excessive cracks or inclusions can compromise durability and appearance, especially in black or boulder opal.
- Inadequate understanding of body tone and transparency: The base color (body tone) significantly affects value—black opal is rarer and more valuable than white opal. Transparency and clarity also impact desirability.
Supply Chain Transparency and Provenance Risks
Lack of traceability in the opal supply chain raises concerns about ethical sourcing and authenticity:
- Unclear mining origins: Opals from regions like Lightning Ridge (Australia) carry premium value, but unverified claims about origin are common. Without proper documentation, buyers cannot confirm ethical mining practices or geographic authenticity.
- Mixing of treated and untreated stones: Some suppliers may blend heat-treated or sugar-treated opals with natural ones without disclosure, misleading buyers about the stone’s true nature.
Intellectual Property and Design Copying
In the jewelry and decorative arts sectors, sourcing opals also presents IP-related risks:
- Replication of signature designs: Unique opal cuts or arrangements used by renowned designers or brands can be copied by third parties using similar-looking stones. Buyers may inadvertently source items that infringe on protected designs.
- Misrepresentation of artisanal origin: Handcrafted pieces from Indigenous Australian communities (e.g., Aboriginal artists) may be imitated or falsely attributed, raising ethical and legal concerns under cultural IP frameworks.
- Lack of design protection in sourcing regions: In some countries, weak enforcement of design patents allows generic manufacturers to replicate distinctive opal settings or patterns without consequence.
Inadequate Certification and Documentation
Many suppliers fail to provide verifiable certification, leading to disputes over quality and origin:
- Absence of gemological reports: Reputable labs (e.g., GIA, AGL) rarely issue reports for opals, but independent appraisals or supplier certifications should detail treatment status and origin. Their absence increases risk.
- Vague or misleading labeling: Terms like “natural,” “genuine,” or “Australian opal” may be used deceptively without substantiation.
Price vs. Value Mismatch
Buyers often face inflated prices for low-grade material due to:
- Emotional appeal over objective evaluation: Opals’ iridescence can cloud judgment, leading to overpayment for stones with poor durability or unstable color.
- Market speculation and scarcity claims: Suppliers may exaggerate rarity, especially with boulder or black opal, to justify premium pricing without factual basis.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence, expert consultation, clear sourcing agreements, and, where possible, third-party verification of both quality and provenance.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Natural Opal Stone
Natural opal stones, prized for their iridescent play-of-color, are subject to specific logistics and compliance considerations due to their value, fragility, and international trade regulations. Adhering to these guidelines ensures legal compliance, safe handling, and smooth cross-border transactions.
Regulatory Compliance
Natural opal is classified as a gemstone, and its trade is governed by national and international regulations. Key compliance areas include:
- CITES (Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species): While opal itself is not regulated under CITES, verify that any accompanying materials (e.g., coral or endangered wood in jewelry settings) are not restricted.
- Country of Origin Declarations: Many countries, including the U.S. (via the FTC Jewelry Guides) and the EU, require accurate disclosure of the gemstone’s origin. Misrepresentation of provenance (e.g., labeling non-Australian opal as “Australian”) can result in penalties.
- Import/Export Licenses: Check destination country requirements. Some nations require permits or declarations for precious stones, especially above certain values or weights.
- Customs Valuation: Provide accurate invoices with fair market value. Undervaluation may lead to fines or shipment seizure.
- HS Code Classification: Use the correct Harmonized System code. For rough or unworked opal, this is typically 7103.10. For worked or cut opal, use 7103.99, depending on processing level.
Mining & Environmental Regulations
- Ethical Sourcing: Ensure opals are sourced from mines complying with local labor and environmental laws. Australia (e.g., Lightning Ridge, Coober Pedy), Ethiopia, and Mexico are major producers with varying regulatory frameworks.
- Artisanal and Small-Scale Mining (ASM): If sourcing from ASM operations, confirm adherence to responsible mining practices and consider certification programs promoting ethical sourcing.
Packaging & Handling
Due to opal’s relative softness (Mohs hardness 5.5–6.5) and sensitivity to moisture and temperature, proper packaging is crucial:
- Protective Wrapping: Wrap each stone in acid-free tissue or soft foam to prevent scratches and chipping.
- Secure Cushioning: Use rigid containers with shock-absorbent materials (e.g., bubble wrap, foam inserts) to prevent movement during transit.
- Moisture Control: Include desiccants in packaging, especially for hydrophane opals (e.g., Ethiopian opal), which can absorb water and crack.
- Temperature Stability: Avoid extreme temperatures; never ship via cargo holds prone to freezing or excessive heat.
Transportation & Logistics
- Courier Selection: Use reputable, insured couriers experienced in handling high-value, fragile goods (e.g., FedEx, DHL, Brinks).
- Tracking & Insurance: Always declare full value and purchase all-risk insurance covering theft, loss, and damage.
- Air vs. Ground: Air freight is preferred for international shipments due to speed and reduced handling. Ensure proper documentation for air cargo security.
- Chain of Custody: Maintain records of handlers and transit points, especially for high-value consignments.
Documentation Requirements
Accurate and complete documentation is essential for customs clearance:
- Commercial Invoice: Include seller/buyer details, description (“natural opal stone, unworked/rough/cut”), weight, quantity, unit value, total value, and country of origin.
- Packing List: Detail contents per package, weights, and dimensions.
- Certificate of Origin: May be required by importing country.
- Gemological Report (Optional but Recommended): For high-value stones, include a report from a recognized lab (e.g., GIA, IGS) confirming natural origin and treatment status.
Import Duties & Taxes
- Duty Rates: Vary by country. In the U.S., natural uncut opals may enter duty-free under HTS 7103.10.00, while cut/opal cabochons may incur duties.
- VAT/GST: Most countries apply value-added or goods and services tax on imported opals. Ensure compliance with local tax laws.
- De Minimis Thresholds: Shipments under certain values may be exempt from duties/taxes—check destination country rules.
Prohibited & Restricted Imports
- Conflict Minerals Regulations: While opal is not a conflict mineral under laws like the U.S. Dodd-Frank Act, due diligence is advised if sourcing from politically sensitive regions.
- Cultural Heritage Laws: Some countries restrict export of gemstones considered national heritage. For example, Ethiopia has imposed temporary export bans on raw opal in the past—verify current regulations.
Best Practices
- Due Diligence: Vet suppliers for legal and ethical compliance.
- Labeling: Clearly mark packages as “Fragile” and “Valuable Contents.”
- Record Keeping: Maintain all transaction documents for at least 5–7 years for audit purposes.
- Consult Experts: Work with customs brokers or legal advisors familiar with gemstone trade regulations in relevant jurisdictions.
By following this guide, traders, importers, and exporters of natural opal can ensure compliance, minimize risk, and support ethical and sustainable trade practices.
In conclusion, sourcing natural opal stones requires careful consideration of origin, quality, ethical practices, and market reliability. Natural opals, prized for their unique play-of-color and rarity, are primarily sourced from regions such as Australia, Ethiopia, and Mexico, each offering distinct characteristics. When sourcing, it is essential to establish relationships with reputable suppliers, verify authenticity through gemological certification, and ensure ethical mining practices that support environmental sustainability and fair labor conditions. Additionally, understanding market trends and price fluctuations helps in making informed purchasing decisions. By prioritizing transparency, quality, and responsibility, buyers can secure genuine natural opal stones that meet both aesthetic and ethical standards, ensuring long-term value and customer satisfaction.