The global motorbike chassis manufacturing industry is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising motorcycle production, increasing demand for lightweight and high-performance materials, and advancements in vehicle dynamics. According to Grand View Research, the global motorcycle market was valued at USD 87.5 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030, indirectly boosting demand for high-precision chassis systems. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence reports that increased urbanization, rising disposable incomes in emerging economies, and a growing preference for premium and electric motorcycles are key factors fueling investment in advanced chassis technologies. As manufacturers prioritize stability, handling, and safety, the role of the chassis has evolved from a structural backbone to a performance-critical component — placing leading chassis producers at the forefront of innovation. This growing demand has intensified competition among key players, resulting in a landscape defined by engineering excellence and technological integration. The following list highlights the top 10 motorbike chassis manufacturers shaping the future of two-wheeled mobility.
Top 10 Motorbike Chassis Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 BBR Motorsports, Inc
Domain Est. 1998
Website: bbrmotorsports.com
Key Highlights: BBR Motorsports is the industry’s premier adult four-stroke playbike performance technology company. Engineering from the minds of racers, coupled with the ……
#2 Thompson Choppers
Domain Est. 2003
Website: thompsonchoppers.com
Key Highlights: Custom bagger, motorcycle & chopper frame manufacturer offering bagger, rigid, softail, and swingarm motorcycle chassis. Specializing in chopper frames,…
#3 alpha Racing Chassis Anbau
Domain Est. 2004
Website: alpharacing.com
Key Highlights: 14-day returnsalpha Racing also offers accessories for chassis and motorsport motorcycles from renowned manufacturers such as Ilmberger Carbon, Brembo and Renthal….
#4 Bike Frames For Trails & MTB
Domain Est. 1998
Website: dmrbikes.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over £2,500For over 30 years, we have dedicated ourselves to creating some of the finest mountain bikes, dirt jump bikes, pedals, frames, and components in the indust…
#5 Indian Motorcycle
Domain Est. 1999 | Founded: 1901
Website: indianmotorcycle.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $99 · 30-day returnsFounded in 1901, Indian Motorcycle is an American brand of motorcycles manufactured in Spirit Lake, Iowa. Designed to embody Indian Motorcyc…
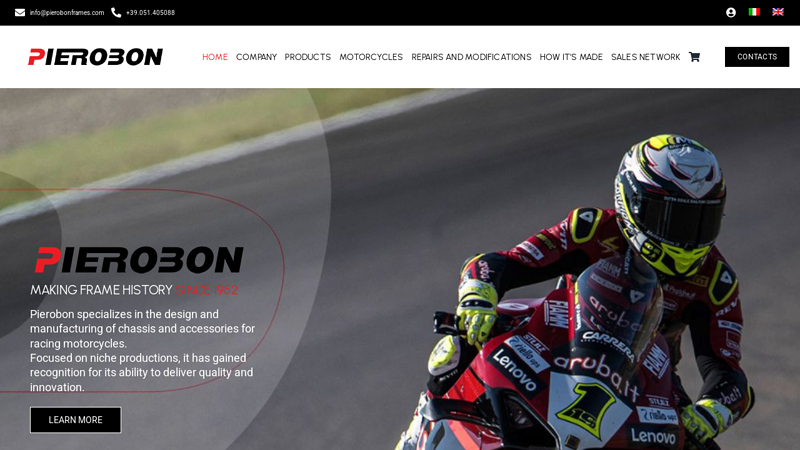
#6
Domain Est. 2001 | Founded: 1952
Website: pierobonframes.com
Key Highlights: MAKING FRAME HISTORY SINCE 1952. Pierobon specializes in the design and manufacturing of chassis and accessories for racing motorcycles….
#7 Voodoo Vintage Fabrication
Domain Est. 2010
Website: voodoovintage.com
Key Highlights: Custom motorcycle frames for your Metric or Harley motorcycle. Many popular sizes and options. Frames for custom Yamaha XS650, Honda CB350 and Honda CB360, ……
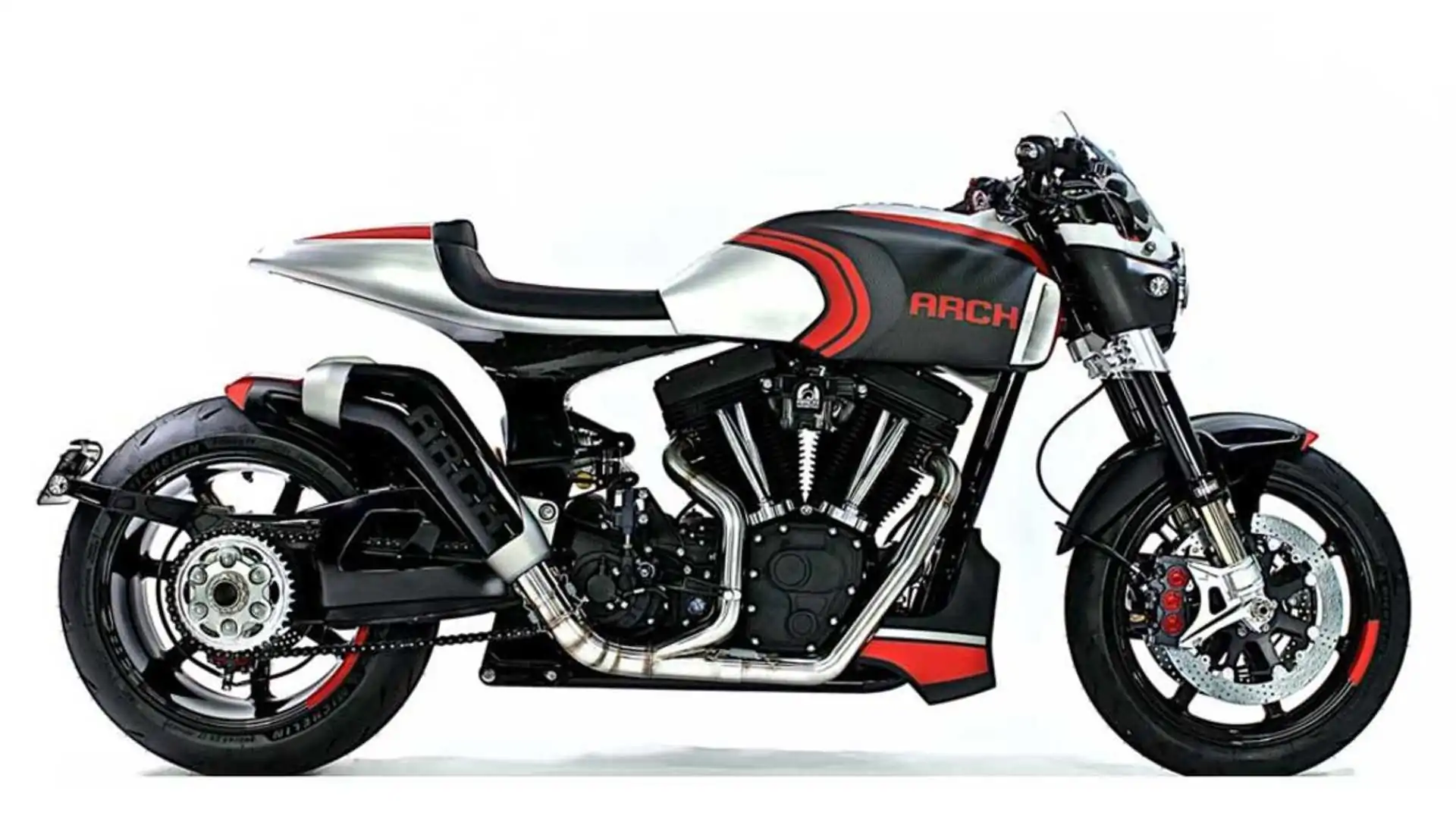
#8 ARCH 1s
Domain Est. 2011
Website: archmotorcycle.com
Key Highlights: The ARCH 1s draws influence from both cruiser and street sport riding to create a motorcycle that defies industry categorization….
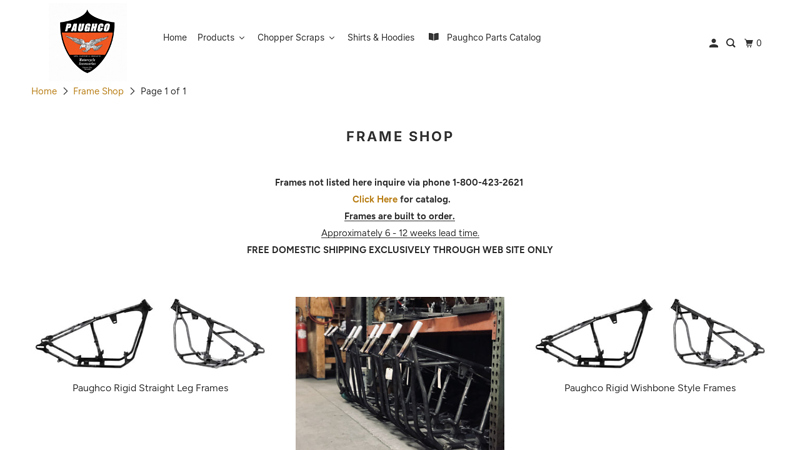
#9 Frame Shop
Domain Est. 2019
Website: paughcoparts.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $199 90-day returnsFrames are built to order. Approximately 6 – 12 weeks lead time. FREE DOMESTIC SHIPPING EXCLUSIVELY THROUGH WEB SITE ONLY…
#10 Chassis
Website: wimoto.eu
Key Highlights: WiMoto is specialized in engineering of tubular frames. Whether it is a racing bike, a café racer, a scrambler or other custom bike, the principle stays the ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Motorbike Chassis

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Motorbike Chassis
The motorbike chassis market in 2026 is poised for transformation, driven by evolving consumer demands, technological advancements, and regulatory pressures. While chassis design remains fundamentally critical to performance, handling, and safety, several key trends are reshaping materials, architecture, and integration strategies.
1. Accelerated Adoption of Lightweight Materials
The pursuit of performance and efficiency is pushing widespread use of advanced materials:
– Increased Aluminum Usage: High-strength aluminum alloys will dominate mid-to-high-end segments, offering an optimal balance of weight reduction, cost, and manufacturability. Twin-spar and perimeter frames will increasingly use forged or extruded aluminum.
– Carbon Fiber for Premium Segments: Carbon fiber-reinforced polymer (CFRP) chassis components—especially subframes and full monocoques in superbikes and limited-edition models—will grow, driven by falling production costs and improved molding technologies.
– Hybrid Structures: Combining materials (e.g., steel backbone with aluminum subframes or magnesium engine mounts) will gain traction to optimize cost, weight, and stiffness.
2. Modular and Scalable Platform Designs
Manufacturers are shifting toward modular chassis platforms to reduce R&D costs and streamline production:
– Family Platforms: Shared chassis architectures across different models (e.g., sport, naked, adventure) will become standard, enabling faster time-to-market and cost efficiency.
– Electric Motorbike Influence: As electric motorcycles grow, dedicated EV platforms with centralized mass and integrated battery protection will redefine chassis geometry, influencing even ICE (internal combustion engine) designs.
3. Integration of Electronics and Connectivity
Chassis are evolving into “smart” structures:
– Sensor Integration: Chassis will increasingly house or interface with inertial measurement units (IMUs), suspension position sensors, and ABS components.
– Active Suspension Systems: More high-end models will feature electronically controlled suspensions (e.g., Öhlins Smart EC), requiring chassis designs that accommodate complex linkages and actuators.
– Data-Driven Tuning: Real-time feedback from chassis-mounted sensors will enable adaptive handling, enhancing safety and rider experience.
4. Focus on Sustainability and Circular Design
Environmental regulations and ESG goals are influencing materials and lifecycle considerations:
– Recyclable Materials: Greater emphasis on using recyclable aluminum and bio-based composites to reduce carbon footprint.
– Design for Disassembly: Chassis will be engineered for easier separation of materials at end-of-life, supporting circular economy principles.
– Reduced Manufacturing Waste: Adoption of precision manufacturing (e.g., hydroforming, additive manufacturing for prototyping) will minimize material waste.
5. Rise of Performance-Oriented and Custom Chassis Solutions
- Aftermarket and Custom Builds: Demand for bespoke chassis in the custom and racing segments will grow, supported by advanced CAD/CAM and CNC fabrication.
- Adventure and Dual-Sport Dominance: The popularity of adventure bikes will drive demand for robust, long-travel chassis with high ground clearance and torsional rigidity.
6. Regional Market Dynamics
- Asia-Pacific: Dominates production and innovation, especially in lightweight engineering (Japan, India, China). Cost-effective steel-tube chassis will persist in entry-level segments.
- Europe and North America: Focus on premium, high-performance, and electric models will drive innovation in advanced materials and electronics integration.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the motorbike chassis will no longer be a passive structural component but an intelligent, integrated system central to performance, safety, and sustainability. Innovation will be driven by material science, digital integration, and platform scalability, with a clear bifurcation between mass-market cost-optimized designs and high-end, technologically advanced solutions. OEMs that embrace modular engineering and sustainable practices will lead the evolving landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Motorbike Chassis: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing motorbike chassis, especially from third-party or overseas suppliers, involves significant risks related to both quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Failing to address these pitfalls can lead to safety issues, legal disputes, brand damage, and financial losses.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Material Specifications
Suppliers may use substandard or non-compliant materials (e.g., low-grade steel or aluminum alloys) to reduce costs. This compromises structural integrity, increases the risk of fatigue failure, and can lead to catastrophic safety issues under stress or impact.
Poor Welding and Manufacturing Practices
Inadequate welding techniques—such as inconsistent penetration, porosity, or improper joint preparation—can severely weaken the chassis. Without rigorous quality control, defects may go undetected, leading to premature failure during use.
Lack of Traceability and Certification
Many suppliers fail to provide material test reports (MTRs), weld certifications, or compliance documentation (e.g., ISO 3834, EN 15085). This lack of traceability makes it difficult to verify quality standards and poses challenges during audits or liability investigations.
Inadequate Testing and Validation
Sourced chassis may not undergo proper testing for torsional rigidity, impact resistance, or fatigue life. Relying solely on visual inspection or dimensional checks without structural validation increases the risk of field failures.
Insufficient Quality Control Processes
Suppliers with weak QC systems may deliver inconsistent products across batches. Without defined inspection protocols or statistical process control, deviations in tolerances and fitment can disrupt downstream assembly.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
Design Infringement and Copying
Sourcing from unverified manufacturers increases the risk of inadvertently using chassis designs that infringe on existing patents or registered designs. This exposes the buyer to legal action, product recalls, and reputational damage.
Loss of Design Ownership
Contracts that fail to specify IP ownership can result in disputes. If a supplier contributes to design modifications or reverse-engineers a chassis, they may claim partial or full rights, limiting the buyer’s ability to manufacture or modify the design independently.
Reverse Engineering and Unauthorized Replication
Suppliers with access to engineering drawings or physical samples may reproduce and sell the chassis to competitors. This is especially prevalent in regions with weak IP enforcement, leading to market dilution and revenue loss.
Inadequate Legal Agreements
Absence of strong Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs), IP assignment clauses, or export controls in supplier contracts leaves designs vulnerable. Verbal agreements or informal arrangements offer little legal recourse in case of IP theft.
Jurisdictional Challenges in IP Enforcement
Disputes involving international suppliers can be difficult and costly to resolve, particularly in countries where IP laws are poorly enforced. Legal action may be impractical, allowing counterfeit or cloned products to proliferate.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should:
– Conduct thorough supplier audits and factory assessments.
– Require material certifications and third-party testing reports.
– Implement strict quality inspection protocols (e.g., NDT for welds).
– Secure comprehensive legal agreements that assign IP ownership and restrict unauthorized use.
– Register designs and patents in key markets.
– Work with legal counsel experienced in international IP law.
Proactively addressing quality and IP risks ensures safer products, protects innovation, and safeguards long-term business interests.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Motorbike Chassis
Overview
This guide outlines key logistics considerations and compliance requirements for the international transportation and handling of motorbike chassis. Whether shipping raw chassis components or completed frames, adherence to regulations ensures timely delivery and avoids legal or financial penalties.
Classification & Harmonized System (HS) Code
Identify the correct HS code to determine import duties, taxes, and regulatory controls. Motorbike chassis typically fall under:
– HS 8714.10: Parts and accessories of motorcycles or cycles fitted with an auxiliary motor, specifically frames and forks.
Verify the exact code with local customs authorities, as classifications may vary by country and chassis type (e.g., racing vs. standard).
Packaging & Handling
Proper packaging is critical to prevent damage during transit:
– Use sturdy wooden crates or steel-reinforced containers.
– Apply rust-inhibitive coatings or VCI (Vapor Corrosion Inhibitor) paper.
– Securely fasten chassis to prevent movement; use corner protectors and padding.
– Label packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and handling instructions.
Transportation Modes
Choose the appropriate shipping method based on volume, urgency, and cost:
– Air Freight: Fast but expensive; suitable for urgent or low-volume shipments.
– Ocean Freight (FCL/LCL): Cost-effective for bulk shipments; plan for longer lead times.
– Road/Rail: Ideal for regional or continental transport within compliant regions (e.g., EU or NAFTA).
Documentation Requirements
Ensure all required documentation is accurate and complete:
– Commercial Invoice
– Packing List
– Bill of Lading (B/L) or Air Waybill (AWB)
– Certificate of Origin
– Import/Export Licenses (if applicable)
– Customs Declaration Forms
Regulatory Compliance
Adhere to destination country regulations:
– Emissions & Safety Standards: While the chassis itself may not be emission-regulated, it must support compliance with final vehicle standards (e.g., EU Whole Vehicle Type Approval, U.S. FMVSS).
– Material Restrictions: Comply with REACH (EU), RoHS, or other chemical/material regulations if applicable (e.g., coatings, adhesives).
– Product Certification: Some markets may require proof of conformity to structural safety or crash standards.
Import Duties & Taxes
Calculate and prepare for:
– Customs duties based on HS code and trade agreements.
– Value Added Tax (VAT) or Goods and Services Tax (GST).
– Anti-dumping or countervailing duties, if applicable (check trade status with exporting country).
Special Considerations
- Free Trade Zones (FTZ): Consider using FTZs to defer duties and streamline re-export.
- Incoterms: Clearly define responsibilities using appropriate Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF, DDP).
- Insurance: Obtain comprehensive cargo insurance covering loss, damage, and delays.
Environmental & Sustainability Compliance
- Adhere to waste and recycling regulations for packaging materials.
- Maintain records for end-of-life vehicle (ELV) directives if supplying to markets like the EU.
Conclusion
Successful logistics and compliance for motorbike chassis require attention to classification, packaging, documentation, and regional regulations. Partner with experienced freight forwarders and customs brokers to ensure smooth cross-border operations and avoid disruptions.
Conclusion for Sourcing Motorbike Chassis
Sourcing a motorbike chassis requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, availability, and compatibility with performance requirements. Whether for manufacturing, customization, or repair purposes, selecting the right chassis is critical to the safety, durability, and overall functionality of the motorcycle. A thorough evaluation of suppliers—considering factors such as material specifications, manufacturing standards, lead times, and certifications—ensures reliability and long-term value.
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) chassis offer guaranteed compatibility and quality but often come at a higher price point, while aftermarket or recycled options can provide cost savings if sourced from reputable suppliers with proper inspection and testing protocols. Additionally, emerging trends such as lightweight materials (e.g., aluminum or carbon fiber), modular designs, and advancements in EV motorcycle chassis present new opportunities for innovation and efficiency.
Ultimately, successful sourcing hinges on a clear understanding of technical requirements, market options, and supply chain dynamics. By establishing strong relationships with trusted suppliers and conducting due diligence, businesses and individuals can secure motorbike chassis that meet both performance expectations and budgetary constraints, supporting the development of safe, high-quality motorcycles.