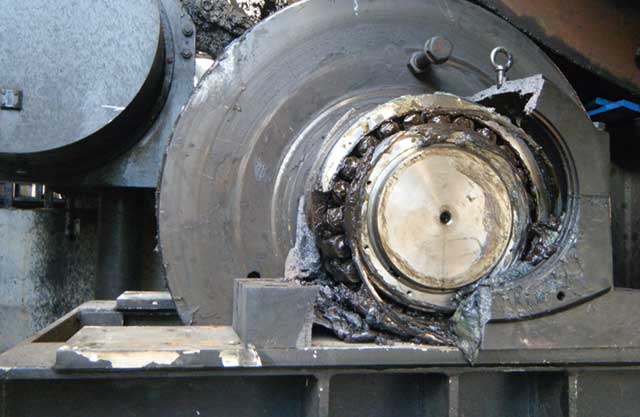
The global lubricants market, driven by increasing industrial automation and demand for high-performance machinery maintenance, is projected to grow at a CAGR of 3.8% from 2023 to 2028, according to Mordor Intelligence. Within this sector, motor bearing grease—a critical component for reducing friction, preventing wear, and extending equipment lifespan—has gained substantial traction. With rising output in industries such as automotive, manufacturing, and renewable energy, the demand for specialized greases that ensure reliable motor performance continues to climb. This growth is further amplified by the shift toward energy-efficient electric motors, which require premium-grade lubricants to maintain optimal efficiency under variable loads and temperatures. As the market expands, a select group of manufacturers has emerged as leaders, combining advanced formulation expertise, rigorous quality standards, and global supply chains to dominate the motor bearing grease landscape. Based on market presence, product innovation, and technical performance, we spotlight the top 9 motor bearing grease manufacturers shaping the industry’s future.
Top 9 Motor Bearing Grease Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Nye Lubricants
Domain Est. 1996
Website: nyelubricants.com
Key Highlights: Nye’s mission is to partner with innovative companies to develop high-performance solutions using our lubricant technology and engineering expertise….
#2 TotalEnergies special lubricants and greases for automotive industry
Domain Est. 2014
Website: lubricants.totalenergies.com
Key Highlights: TotalEnergies Lubrifiants is a major producer of greases worldwide, with 8 plants located in each continent to better serve our customers….
#3 Mobil Polyrex™ EM Series
Domain Est. 1991
Website: mobil.com
Key Highlights: Our Mobil Polyrex™ EM grease is designed for electric motor bearings. Specially formulated to improve bearing performance and protection for long electric ……
#4 Bearing lubrication
Domain Est. 1996
Website: skf.com
Key Highlights: SKF lubricants are designed for your needs and tested for performance in real applications. Our experience with bearings, lubricants and applications…
#5 Sta-Lube Products
Domain Est. 1996
Website: crcindustries.com
Key Highlights: Professional automotive lubrication with Sta-Lube products from CRC. Premium greases, gear oils, transmission fluids & specialty lubricants for pros….
#6 Maintenance Products
Domain Est. 1996
Website: nsk.com
Key Highlights: Avoid unexpected downtime with NSK’s proven bearing grease and user-friendly bearing heaters….
#7 AMALIE Motor Oil
Domain Est. 1996 | Founded: 1903
Website: amalie.com
Key Highlights: Our families and quality are at the heart of everything we do. After all, we’ve been delivering premium motor oils and lubricants since 1903….
#8 Schaeffer Oil
Domain Est. 1998
Website: schaefferoil.com
Key Highlights: From synthetic engine oils, hydraulic fluids, greases and gear lubes, our products help you own equipment longer, operate more efficiently and reduce hassles….
#9 Trusted Choice of Automakers Worldwide
Domain Est. 2017
Website: idemitsulubricants.com
Key Highlights: ️⚠️ Warning: Fraudulent Idemitsu Website Alert ⚠️ Idemitsu Lubricants America has identified a scam website targeting U.S. customers. This site is not ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Motor Bearing Grease

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Motor Bearing Grease
The global motor bearing grease market is poised for steady growth through 2026, driven by increasing industrial automation, expansion in electric motor applications, and rising demand for high-performance lubricants across key sectors such as automotive, manufacturing, and renewable energy. Several strategic trends are expected to shape the market landscape in the coming years:
-
Growing Demand in Electric Vehicles (EVs)
As the automotive industry accelerates the shift toward electrification, motor bearing grease applications in electric traction motors are gaining prominence. EVs require specialized greases that offer thermal stability, electrical insulation, and low noise performance. By 2026, demand for electric motor-compatible greases is anticipated to rise significantly, particularly in regions with strong EV adoption policies such as Europe, China, and North America. -
Advancements in Synthetic and Long-Life Greases
The push for reduced maintenance and extended equipment life is fueling demand for high-performance synthetic greases. These formulations, based on PAO (Polyalphaolefin) or ester base oils with advanced thickeners like lithium complex or polyurea, are expected to dominate the premium segment. OEMs and industrial users are increasingly adopting greases with longer re-lubrication intervals, supporting sustainability and operational efficiency goals. -
Expansion in Renewable Energy Sector
Wind turbines represent a critical application for motor bearing greases, especially in generator and pitch control systems. With global investments in wind energy projected to grow through 2026, demand for high-reliability, temperature-resistant greases capable of withstanding harsh environmental conditions will rise. Grease manufacturers are tailoring products to meet the durability and performance standards required in offshore and onshore wind farms. -
Focus on Sustainability and Biodegradability
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability initiatives are driving innovation in eco-friendly lubricants. By 2026, there will be greater adoption of biodegradable and low-toxicity motor bearing greases, particularly in environmentally sensitive regions and applications. Formulators are exploring bio-based thickeners and ester oils to meet growing demand for greener alternatives without compromising performance. -
Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific is expected to remain the largest and fastest-growing market due to rapid industrialization, expanding manufacturing bases, and strong automotive production in countries like China, India, and South Korea. Meanwhile, North America and Europe will see steady growth supported by stringent energy efficiency standards and modernization of industrial infrastructure. -
Digitalization and Condition Monitoring Integration
The rise of Industry 4.0 and predictive maintenance technologies is influencing grease development. By 2026, smart greases with embedded sensors or compatibility with condition monitoring systems may begin emerging, enabling real-time assessment of lubricant health and bearing performance. This trend supports proactive maintenance and reduces unplanned downtime.
In conclusion, the 2026 motor bearing grease market will be characterized by technological innovation, sustainability-driven formulation changes, and strong growth in high-tech applications such as electric mobility and renewable energy. Companies that invest in R&D, expand their synthetic and eco-friendly product portfolios, and align with digital maintenance trends are likely to gain a competitive advantage.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Motor Bearing Grease: Quality and IP Risks
Sourcing the right motor bearing grease is critical for ensuring equipment reliability and longevity. However, organizations often encounter significant pitfalls related to quality inconsistencies and intellectual property (IP) concerns, especially when dealing with suppliers in competitive or less-regulated markets. Being aware of these challenges helps mitigate operational risks and protect business interests.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
-
Inconsistent Product Formulation
Some suppliers—particularly lower-tier or generic manufacturers—may alter grease formulations without notice to reduce costs. This can lead to variations in base oil viscosity, thickener type, or additive packages, resulting in poor performance, accelerated bearing wear, or premature failure. -
Misrepresentation of Performance Specifications
Suppliers may falsely claim compliance with industry standards (e.g., ISO, ASTM, NLGI grades) or overstate performance metrics such as temperature range, oxidation stability, or water resistance. Without independent verification, buyers risk using grease unsuitable for their application. -
Counterfeit or Substandard Materials
In global supply chains, counterfeit greases or those made with recycled or inferior base oils are a growing concern. These products often fail under load or high temperatures, leading to unplanned downtime and costly repairs. -
Lack of Traceability and Testing Data
Reputable suppliers provide batch-specific test reports and material traceability. Sourcing from vendors who cannot produce verifiable quality documentation increases the risk of receiving inconsistent or non-compliant products. -
Inadequate Packaging and Contamination Risks
Poor packaging (e.g., non-sealed containers, improper labeling) can lead to contamination with moisture, dust, or other particulates during transport and storage. This compromises grease integrity before it’s even used.
Intellectual Property (IP) and Compliance Risks
-
Unauthorized Use of Branded Formulations
Some manufacturers produce “copycat” greases that mimic well-known branded products (e.g., mimicking Mobil, Shell, or Klüber formulations) without licensing. This not only violates IP rights but may also result in inconsistent quality since the replica may not meet the original performance benchmarks. -
Reverse Engineering Without Licensing
While analyzing competitors’ products is common, producing and selling grease based on reverse-engineered formulations without proper IP clearance can expose buyers and suppliers to legal action, especially in regions with strong IP enforcement. -
OEM Specification Misuse
Some suppliers claim their grease meets OEM specifications (e.g., Siemens, ABB, GE) without formal approval or testing. Using such grease may void equipment warranties and expose the end-user to liability in case of failure. -
Lack of IP Agreements in Custom Formulations
When developing custom grease formulations with a supplier, failing to establish clear IP ownership in contracts can result in disputes. The supplier may claim rights to the formula or resell it to competitors, undermining competitive advantage. -
Export Compliance and Regulatory Risks
Certain grease additives or base oils may be subject to international trade controls or environmental regulations (e.g., REACH, RoHS). Sourcing from suppliers unaware of these requirements can lead to shipment delays, fines, or IP complications due to restricted technology transfers.
Best Practices to Avoid Pitfalls
- Audit Suppliers: Conduct on-site audits to verify manufacturing processes, quality control, and IP compliance.
- Require Certifications: Insist on test reports, ISO certifications, and OEM approvals.
- Use NDAs and IP Clauses: When co-developing formulations, ensure contracts define IP ownership and confidentiality.
- Conduct Independent Testing: Validate grease performance through third-party labs before full-scale procurement.
- Build Long-Term Partnerships: Work with trusted, transparent suppliers who prioritize compliance and quality over cost-cutting.
By proactively addressing quality and IP risks, organizations can ensure reliable motor performance, avoid legal exposure, and protect their operational and competitive integrity.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Motor Bearing Grease
Overview
This guide outlines the logistics and compliance requirements for the safe handling, storage, transportation, and regulatory compliance of Motor Bearing Grease. Adherence to these guidelines ensures product integrity, personnel safety, and compliance with international and local regulations.
Product Identification
- Product Name: Motor Bearing Grease
- Chemical Type: Typically lithium-based, calcium-based, or synthetic grease (formulation varies by product)
- CAS Number(s): Varies by formulation (e.g., Lithium 1: 7439-93-2; Mineral Base Oil: 64742-52-5)
- UN Number: UN 3082 (if environmentally hazardous) or UN 1263 (flammable liquid, if applicable)
- Classification: Non-hazardous or hazardous depending on base oil and additives; consult SDS
Safety Data Sheet (SDS) Compliance
- Maintain up-to-date Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for each grease variant in accordance with GHS (Globally Harmonized System).
- Ensure SDS is accessible to all handlers, transporters, and emergency responders.
- SDS must include:
- Hazard identification
- Composition/information on ingredients
- First-aid and firefighting measures
- Accidental release measures
- Handling and storage guidance
- Exposure controls/personal protection
- Physical and chemical properties
- Stability and reactivity
- Toxicological and ecological information
- Disposal considerations
- Transport information
- Regulatory information
Storage Requirements
- Temperature: Store between 10°C and 30°C (50°F to 86°F). Avoid extreme heat or freezing.
- Environment: Dry, well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight and moisture.
- Containers: Keep in original, sealed containers to prevent contamination.
- Shelving: Store off the ground on pallets or shelves to avoid floor moisture.
- Segregation: Keep away from strong oxidizers, acids, and incompatible chemicals.
- Labeling: Ensure all containers are clearly labeled with product name, batch number, and hazard warnings.
Handling Procedures
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
- Nitrile or chemical-resistant gloves
- Safety goggles or face shield
- Protective clothing/apron to prevent skin contact
- Avoid prolonged or repeated skin contact; wash hands thoroughly after handling.
- Use in well-ventilated areas to prevent vapor buildup (especially if heated).
- Do not consume, inhale, or allow contact with eyes.
- Use dedicated tools to prevent cross-contamination.
Transportation Guidelines
- Domestic (e.g., US DOT):
- Classify according to 49 CFR; typically non-hazardous unless flash point < 60°C (140°F).
- If flammable: Class 3, PG III; proper labeling and documentation required.
- International (IMDG, IATA, ADR):
- Check flash point and environmental hazards.
- If environmentally hazardous: UN 3082, Class 9, PG III (marine transport).
- Proper packaging, marking, labeling, and transport documents (e.g., Dangerous Goods Declaration) must be used if applicable.
- Packaging: Use UN-certified containers if transporting hazardous variants. Drums and pails must be secured to prevent leakage.
- Vehicle Requirements: Ensure vehicles are clean, dry, and compatible with grease residues.
Environmental & Disposal Compliance
- Spill Response:
- Contain spill with absorbent materials (e.g., oil socks, clay absorbents).
- Do not wash into drains or waterways.
- Collect waste and dispose of as hazardous or non-hazardous waste per local regulations.
- Waste Disposal:
- Used grease and contaminated absorbents may be classified as hazardous waste.
- Dispose through licensed waste handlers in compliance with EPA (USA), Environment Agency (UK), or equivalent.
- Follow RCRA (Resource Conservation and Recovery Act) guidelines if applicable.
- Environmental Impact: Prevent soil and water contamination; report significant spills to authorities as required.
Regulatory Compliance
- OSHA (USA): Comply with Hazard Communication Standard (HazCom 2012), including SDS availability and employee training.
- REACH (EU): Ensure registration, evaluation, and authorization of chemicals; provide SVHC (Substances of Very High Concern) information if applicable.
- CLP Regulation (EU): Proper classification, labeling, and packaging per GHS.
- TSCA (USA): Confirm all chemical substances are listed or exempt under the Toxic Substances Control Act.
- Local Regulations: Comply with country-specific rules (e.g., WHMIS in Canada, NICNAS in Australia).
Training & Documentation
- Train all personnel involved in handling, storage, and transportation on:
- SDS interpretation
- Spill response
- PPE use
- Emergency procedures
- Maintain records of training, SDS versions, shipping manifests, and incident reports.
- Conduct periodic audits to ensure compliance with all regulatory standards.
Emergency Response
- Fire: Use CO₂, dry chemical, or foam extinguishers. Water may be ineffective.
- Inhalation: Move to fresh air; seek medical attention if symptoms occur.
- Skin Contact: Wash with soap and water; remove contaminated clothing.
- Eye Contact: Rinse thoroughly with water for at least 15 minutes; seek medical help.
- Ingestion: Rinse mouth; do not induce vomiting; seek immediate medical attention.
- Emergency Contacts: Post local emergency numbers and poison control centers.
Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance management of Motor Bearing Grease minimizes risks to health, safety, and the environment. Always refer to the specific product’s SDS and stay updated with evolving regulatory requirements in all regions of operation.
Conclusion for Sourcing Motor Bearing Grease
In conclusion, sourcing the appropriate motor bearing grease is a critical step in ensuring the longevity, efficiency, and reliability of electric motors and rotating equipment. The selection process must take into account several key factors, including operating temperature, speed, load conditions, environmental exposure, and compatibility with existing lubricants and materials.
After evaluating various suppliers, product specifications, and performance data, it is evident that high-quality, industry-approved greases—such as those based on lithium complex or polyurea thickeners with synthetic base oils—offer superior performance in most motor applications. These formulations provide excellent thermal stability, oxidation resistance, and water resistance, which are essential for minimizing wear and preventing premature bearing failure.
Furthermore, partnering with reputable lubricant suppliers that offer technical support, consistent product quality, and certification to standards (e.g., ISO, NLGI grades, and OEM approvals) is crucial. A strategic sourcing approach should balance cost-effectiveness with long-term performance, favoring reliable products that reduce downtime and maintenance costs.
Ultimately, the right motor bearing grease—properly specified, applied, and maintained—contributes significantly to improved operational efficiency and equipment lifespan. Therefore, continuous monitoring, staff training, and periodic review of grease performance will ensure that the selected solution remains optimal over time.