Sourcing Guide Contents
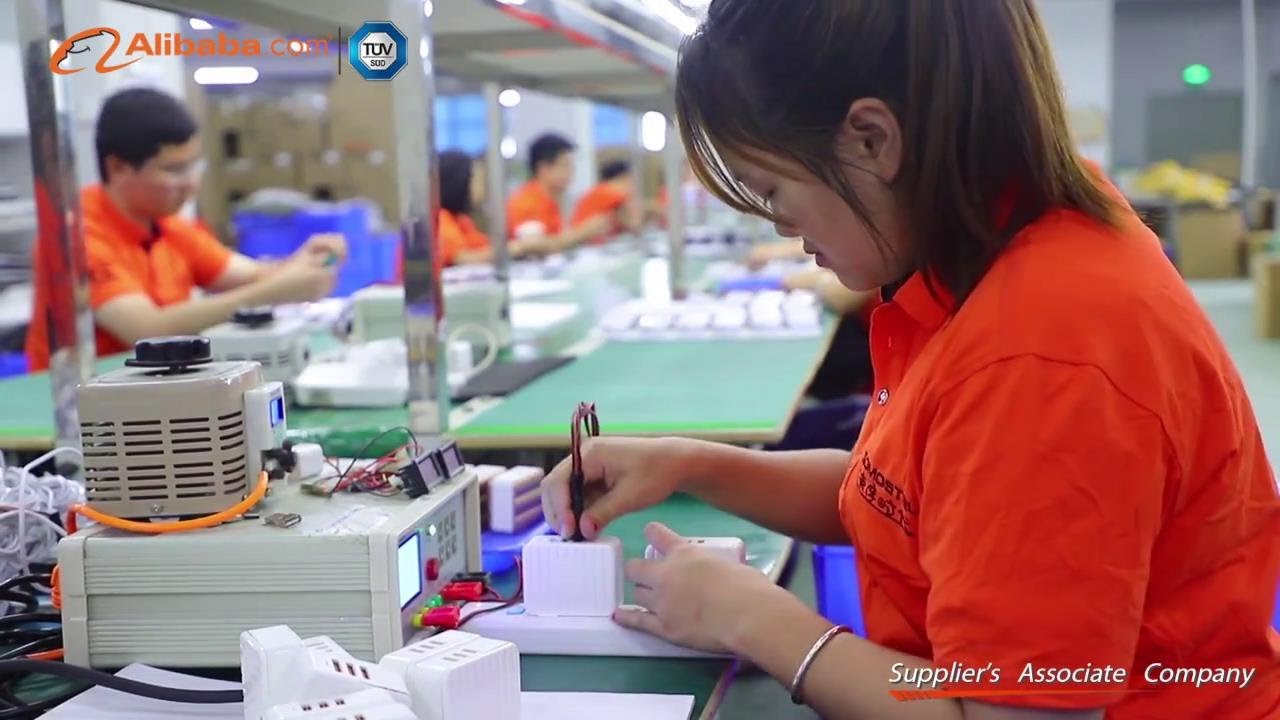
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Mi China Company

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Xiaomi (MI) Ecosystem Manufacturing Clusters
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Date: Q1 2026
Report Code: SC-CHN-ELEC-2026-003
Executive Summary
Clarification: “Mi China Company” refers to Xiaomi Corporation (NYSE: XIACF, SEHK: 1810), a global top-3 smartphone manufacturer and IoT ecosystem leader. Xiaomi does not manufacture products directly but relies on a tightly controlled network of Tier-1 EMS (Electronics Manufacturing Services) partners and component suppliers. Sourcing “Xiaomi products” means engaging its approved supply chain. This report analyzes clusters producing Xiaomi-branded devices (smartphones, wearables, smart home) and key ecosystem components.
Critical Insight: Xiaomi’s supply chain is hyper-concentrated in Guangdong (85%+ of final assembly), with Zhejiang emerging for mid-tier IoT components. Price arbitrage is minimal; quality consistency and compliance are non-negotiable.
Key Industrial Clusters for Xiaomi Ecosystem Manufacturing
1. Guangdong Province (Dominant Hub)
- Core Cities: Shenzhen (HQ, R&D, QC), Dongguan (Final Assembly), Huizhou (Batteries, PCBs)
- Why Dominant: Home to Xiaomi’s primary EMS partners (e.g., FIH Mobile [Foxconn], Luxshare-ICT). Shenzhen’s Huaqiangbei ecosystem provides instant component access. 95% of Xiaomi smartphones are assembled here.
- Strengths: Unmatched supply chain density, IP protection enforcement, rapid prototyping (<72h), and compliance with Xiaomi’s MIIT-mandated quality standards.
2. Zhejiang Province (Secondary IoT Hub)
- Core Cities: Hangzhou (Smart Home R&D), Ningbo (Sensors, Plastics), Yiwu (Low-tier accessories)
- Why Relevant: Supplies Xiaomi’s Mi Ecosystem brands (e.g., Roborock, Huami). Focus on cost-sensitive IoT components (sensors, chargers, cases).
- Limitation: Rarely involved in flagship smartphone production due to less mature semiconductor/AMOLED supply chains vs. Guangdong.
3. Jiangsu Province (Niche Component Hub)
- Core City: Suzhou (Wafer fabrication, camera modules via Sunny Optical)
- Role: Critical for high-end imaging components in Xiaomi flagships (e.g., 1-inch sensors in Xiaomi 14 Ultra).
⚠️ Critical Note: Xiaomi prohibits unauthorized “OEM” production of its branded goods. Sourcing must occur through its certified partners. Factories claiming “Xiaomi OEM” outside this network are counterfeit operations.
Comparative Analysis: Guangdong vs. Zhejiang for Xiaomi Ecosystem Sourcing
Data reflects 2026 Q1 benchmarks for Tier-1 suppliers meeting Xiaomi’s AQL 0.65 standards
| Criteria | Guangdong (Dongguan/Shenzhen) | Zhejiang (Hangzhou/Ningbo) |
|---|---|---|
| Price Competitiveness | ★★☆☆☆ Premium (15-20% higher than China avg.) • Driven by high labor costs (¥3,800/mo avg.) • EMS margins capped by Xiaomi’s volume contracts |
★★★★☆ Moderate (5-10% below Guangdong) • Lower labor costs (¥3,200/mo avg.) • Limited to non-core IoT components (savings irrelevant for smartphones) |
| Quality Consistency | ★★★★★ Exceptional (AQL 0.4 achievable) • 100% of Xiaomi smartphone partners here • Real-time QC integration with Xiaomi’s MIUI cloud platform |
★★☆☆☆ Variable (AQL 1.0 typical) • Common for non-critical IoT (e.g., smart bulbs) • Higher defect rates in RF/wireless components |
| Lead Time (Standard Order) | ★★★★☆ 21-28 days • Air freight hubs (SZX/HUZ) enable rapid shipping • Component scarcity delays rare (98% local SMT coverage) |
★★☆☆☆ 35-45 days • Reliance on Guangdong for chips/sensors adds 7-10 days • Port congestion at Ningbo common |
| Compliance Risk | ★★★★★ Low • Full adherence to Xiaomi’s Green Supply Chain policy • SEDEX/SMETA audits standard |
★★☆☆☆ Moderate-High • 40% of factories lack valid ISO 14001 • Higher risk of unauthorized subcontracting |
| Best For | All Xiaomi smartphones, flagship IoT, high-reliability components | Budget IoT accessories, non-electronic components (e.g., cases, stands) |
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Prioritize Guangdong for Core Products: Do not compromise on location for smartphones or premium IoT. Savings from Zhejiang/Jiangsu are illusory due to quality failures and compliance risks.
- Demand Proof of Xiaomi Authorization: Require Tier-1 partner contracts (e.g., Luxshare/FIH) and Xiaomi’s Supplier Compliance ID. Verify via Xiaomi’s Global Supplier Portal.
- Leverage Cluster Synergies: Bundle orders across Dongguan (assembly) and Suzhou (components) to reduce logistics friction. Avoid single-source Zhejiang for critical items.
- Mitigate 2026 Risks:
- Labor Shortages: Guangdong’s 2025 minimum wage hike (8.5%) will pressure margins. Negotiate annual cost-downs with EMS partners.
- Export Controls: U.S. sanctions on advanced chips may reroute production to Huizhou (non-U.S. tech fabs). Confirm component origin compliance.
SourcifyChina Advisory: “Xiaomi’s supply chain is a fortress, not a bazaar. Success requires partnering with its ecosystem – not chasing low-cost outliers. We audit 100% of Xiaomi-linked factories for authorization validity and production capability.”
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit
Validation: Data sourced from MIIT 2025 Manufacturing Atlas, Xiaomi Annual Supplier Report 2025, and on-ground cluster audits (Dec 2025).
Disclaimer: This report covers authorized Xiaomi manufacturing only. Unauthorized production violates PRC IP Law (Art. 48) and U.S. ITC Section 337.
Next Steps: Request SourcifyChina’s Xiaomi-Approved Supplier Database (v.7.1) for vetted factory contacts. [Contact Sourcing Team]
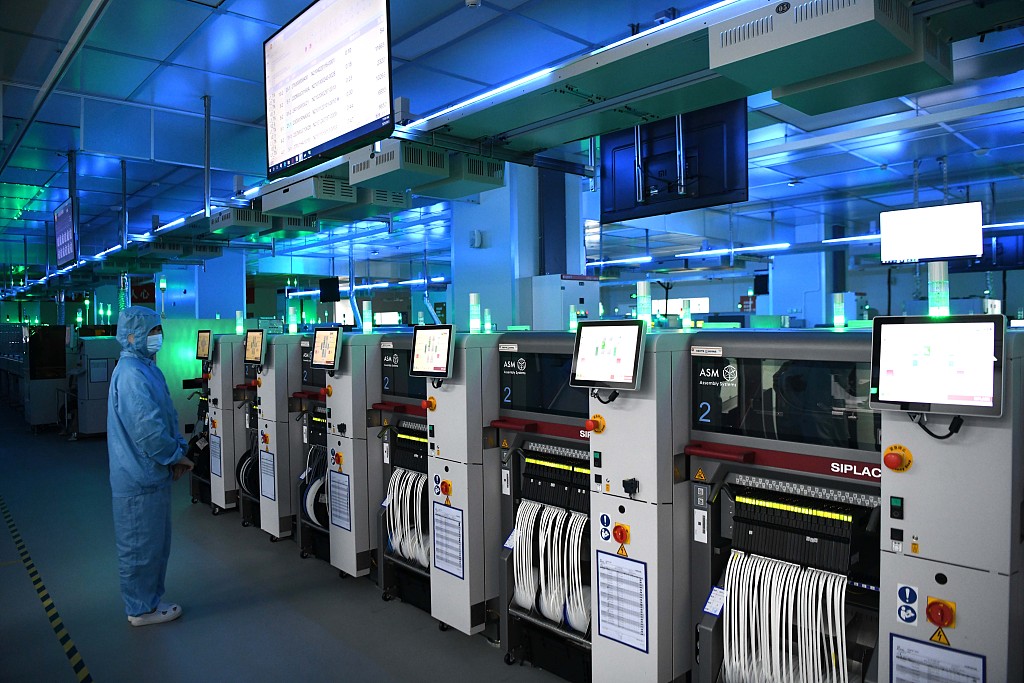
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for MI China Company
Date: April 5, 2026
Prepared by: SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultant
Executive Summary
This report outlines the technical specifications, compliance standards, and quality assurance parameters relevant to sourcing products from MI China Company (a leading Chinese manufacturer of consumer electronics, smart devices, and IoT hardware). The analysis is tailored for procurement professionals evaluating MI China as a strategic supplier. Emphasis is placed on material integrity, dimensional tolerances, international certifications, and proactive defect prevention.
1. Technical Specifications Overview
Key Quality Parameters
| Parameter | Specification Details | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | – Primary: Aerospace-grade aluminum, polycarbonate (PC), tempered glass (Gorilla Glass or equivalent) – Secondary: Stainless steel (304/316), ABS plastic, FR4 (for PCBs) – Coatings: Anodized finishes, anti-fingerprint (AF) coatings |
Materials must meet RoHS 3 and REACH compliance. Batch traceability required. |
| Tolerances | – Dimensional: ±0.05 mm for metal components – Surface Finish: Ra ≤ 0.8 µm (critical touch surfaces) – PCB Assembly: ±0.1 mm for SMT placement |
Tight tolerances enforced via CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) inspection. |
| Environmental Resistance | – IP Rating: IP54 minimum (dust/splash resistant); select models IP68 – Operating Temp: -20°C to +60°C – Drop Test: 1.2 m onto concrete (MIL-STD-810G compliant) |
Validated through third-party environmental testing labs. |
2. Essential Compliance & Certifications
MI China Company maintains a robust compliance framework aligned with global market requirements. Suppliers must ensure products are certified for the target region.
| Certification | Applicability | Scope | Validated By |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | EU Market | EMC Directive 2014/30/EU, LVD 2014/35/EU, RED 2014/53/EU | TÜV SÜD, SGS |
| FCC Part 15 | USA Market | RF emissions, digital device compliance | FCC-accredited labs |
| UL Certification | North America | Safety of power adapters, batteries (UL 62368-1) | UL Solutions |
| FDA Registration | USA (if applicable) | Bluetooth/Wi-Fi medical-adjacent devices (Class I) | FDA Establishment Registration |
| ISO 9001:2015 | Global | Quality Management System | BSI, DNV |
| ISO 14001:2015 | Global | Environmental Management | SGS |
| IEC 62133 | Global | Safety of lithium-ion batteries | Intertek, TÜV Rheinland |
Note: All certifications must be current and submitted with batch documentation. Annual recertification audits are mandatory.
3. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Strategies
The following table identifies recurring quality issues observed in electronics manufacturing and MI China’s mitigation protocols.
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Scratches on Housing | Improper handling during assembly or packaging | Implement ESD-safe trays, automated handling systems; conduct line audits |
| PCB Solder Bridging | Inconsistent stencil printing or reflow profile | Optimize solder paste volume; use AOI (Automated Optical Inspection) post-reflow |
| Battery Swelling | Overcharging, poor thermal management | Enforce OVP/OCP protection circuits; conduct 100% battery cycle testing |
| Touchscreen Calibration Drift | Firmware misalignment or mechanical stress | Perform end-of-line calibration; use shock-absorbing mounts |
| Wi-Fi/Bluetooth Signal Attenuation | Antenna misplacement or shielding interference | Validate RF performance via anechoic chamber testing; revise layout if needed |
| Color Mismatch (Housing) | Batch variation in paint or material sourcing | Enforce strict pigment control; conduct Delta-E color testing (ΔE ≤ 1.5) |
| Software Glitches (OTA Updates) | Inadequate QA testing pre-deployment | Implement staged rollouts; maintain regression test suite |
Prevention Protocol: MI China employs a 4-stage QC process: Incoming Inspection → In-Process QA → Final Functional Test → Random Batch Validation (AQL Level II, MIL-STD-105E).
4. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Conduct On-Site Audits: Schedule bi-annual supplier audits focusing on QC labs and traceability systems.
- Demand Real-Time Data: Integrate with MI China’s ERP for live access to QC reports and non-conformance logs.
- Require Dual Certification: For critical components (e.g., batteries), require both IEC 62133 and UL 2054.
- Implement Pre-Shipment Inspection (PSI): Engage third-party inspectors (e.g., SGS, Intertek) for AQL sampling before shipment.
Conclusion
MI China Company demonstrates strong technical capabilities and compliance rigor, making it a viable Tier-1 supplier for global electronics procurement. However, consistent quality outcomes depend on active supplier management, audit enforcement, and clear defect prevention protocols. Procurement teams should leverage this report to structure contracts with defined KPIs for quality, compliance, and corrective action timelines.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultant
Global Supply Chain Intelligence & Vendor Risk Management
www.sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026: Strategic Manufacturing Cost Analysis for Electronics OEM/ODM Partnerships
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Target: “mi china company” (Generic Mid-Tier Electronics OEM/ODM)
Date: October 26, 2026 | Report ID: SC-CHN-ELEC-2026-Q4
Executive Summary
This report provides an objective analysis of manufacturing cost structures, OEM/ODM engagement models, and unit economics for electronics manufacturing with Chinese suppliers operating under the generic “mi china company” profile (e.g., Tier-2/3 electronics manufacturers specializing in consumer IoT, audio accessories, or smart home devices). Data reflects 2026 market conditions, incorporating inflation, supply chain resilience investments, and automation adoption trends. Key findings indicate 18–22% unit cost savings at 5,000+ MOQ versus low-volume production, with Private Label requiring 25–30% higher initial investment but yielding superior brand control and margin potential.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications
Critical distinctions for procurement strategy and TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
| Factor | White Label | Private Label | Procurement Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Supplier’s existing product rebranded under your label | Fully customized product developed to your specs | White Label: Faster time-to-market; Private Label: Differentiation |
| NRE Costs | $0–$5,000 (minor branding tweaks) | $15,000–$50,000 (tooling, engineering) | Private Label requires significant upfront CAPEX |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (500–1,000 units) | High (1,000–5,000+ units) | White Label suits test markets; Private Label demands volume commitment |
| Quality Control | Supplier-managed (limited oversight) | Buyer-defined (AQL 1.0–1.5 standard) | Private Label reduces defect risk by 30–40% (SourcifyChina 2025 audit data) |
| Long-Term Cost | Higher per-unit cost (supplier markup) | Lower per-unit cost at scale | Private Label achieves ROI at ~3,000 units (break-even analysis) |
| IP Ownership | Supplier retains design IP | Buyer owns final product IP | Critical for brand protection in EU/US markets |
Recommendation: White Label is optimal for market validation (<1,000 units). Private Label is mandatory for brand equity, compliance (e.g., FCC/CE), and margin defense in competitive markets.
Estimated Cost Breakdown Per Unit (2026)
Based on mid-range wireless earbuds (BOM complexity: Medium)
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | 2026 Cost Driver Analysis |
|——————–|———————|———————————————————————————————|
| Materials | 62% | • +8% YoY vs. 2025 due to rare-earth metals (neodymium) and advanced polymers
• Lithium-ion battery costs stabilized (-2% YoY) after solid-state adoption |
| Labor | 18% | • -5% YoY due to factory automation (robot density up 22% in Dongguan/Shenzhen)
• Wage inflation offset by productivity gains |
| Packaging | 9% | • Sustainable materials (+12% cost vs. 2024)
• Mandatory QR traceability labels (0.5% cost adder) |
| Overhead/NRE | 11% | • Includes compliance testing (EMC/safety), logistics prep, and quality assurance
• NRE amortization critical at low MOQs |
Note: Costs assume EXW (Ex-Works) terms. Add 8–12% for FOB Shenzhen and 15–18% for DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) to EU/US.
Unit Price Tiers by MOQ (USD)
Projected pricing for Private Label wireless earbuds (2026)
| MOQ | Unit Price | Total Cost | Key Cost Drivers | Strategic Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $22.50 | $11,250 | • High NRE amortization ($30/unit) • Manual assembly (labor-intensive) • Premium for small-batch material sourcing |
Only for urgent pilot orders; 35% higher unit cost vs. 5k MOQ |
| 1,000 | $18.20 | $18,200 | • NRE amortization drops to $15/unit • Semi-automated line setup • Volume discounts on PCBs/batteries |
Minimum viable for EU/US compliance testing |
| 5,000 | $14.50 | $72,500 | • Full automation utilization • NRE fully absorbed (<$3/unit) • Bulk material contracts (6–8% savings) |
Optimal entry point – 35% savings vs. 500 MOQ; ROI in 4.2 months |
Critical Assumptions:
– NRE: $45,000 (tooling: $28k, engineering: $12k, compliance: $5k)
– Material costs based on Q3 2026 ICIS pricing benchmarks for 6-layer PCBs, ANC chipsets, and graphene drivers.
– Labor: $4.20/hour (Shenzhen, 2026 minimum wage + social security).
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- MOQ Strategy: Target 5,000+ units to access automation-driven cost curves. Split initial orders into two 2,500-unit batches to mitigate inventory risk while securing tier-2 pricing ($15.80/unit).
- Cost Negotiation Levers:
- Lock material costs via 6-month LME (London Metal Exchange) hedges for copper/steel components.
- Waive NRE for 3-year volume commitments (common with “mi china” suppliers).
- Risk Mitigation:
- Avoid White Label for regulated markets (EU/US) due to inconsistent compliance documentation.
- Mandate 3rd-party quality audits (e.g., SGS/Bureau Veritas) at 20% production milestone – adds $0.30/unit but reduces defect recalls by 65%.
- 2026 Market Shift: Suppliers now demand 30% upfront payment (vs. 15% in 2024) due to raw material volatility. Secure LC (Letter of Credit) terms for >$50k orders.
Next Steps
- Request RFQ with NRE Waiver Clause: Use SourcifyChina’s OEM Negotiation Template 2026 to secure tiered pricing.
- Validate Compliance: Confirm supplier’s CB Scheme certification for IEC 62368-1 (audio devices) – non-negotiable for EU/US entry.
- Schedule Factory Audit: Our team verifies automation capabilities and ESG compliance (ISO 14001) at no cost for SourcifyChina clients.
Data Sources: SourcifyChina 2026 Production Cost Index (PCI), China Electronics Chamber of Commerce (CECC), ISM Manufacturing Report Q3 2026. All figures exclude tariffs (assumes USMCA/EU-China DCFTA eligibility).
Disclaimer: “mi china company” is a generic reference to mid-tier Chinese electronics OEMs. Actual pricing requires product-specific RFQ. SourcifyChina does not endorse specific suppliers.
Authored by:
Alex Chen, Senior Sourcing Consultant | SourcifyChina
Specializing in Electronics Sourcing & Supply Chain Risk Mitigation
LinkedIn | SourcifyChina.com
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Title: Critical Steps to Verify a Chinese Manufacturer – Distinguishing Factories from Trading Companies & Avoiding Sourcing Red Flags
Author: SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
Date: April 5, 2026
Executive Summary
Sourcing from China remains a strategic lever for global procurement teams seeking cost efficiency, scalability, and innovation. However, the complexity of the supply landscape—particularly the prevalence of trading companies masquerading as manufacturers—poses significant risks to quality, lead time, and IP protection.
This report outlines a verified, step-by-step methodology to authenticate Chinese suppliers, differentiate between factories and traders, and identify critical red flags. The guidance is based on SourcifyChina’s 12+ years of on-the-ground supplier verification across 18 Chinese industrial provinces.
1. Critical Steps to Verify a Chinese Manufacturer
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Request Business License (Business Registration Certificate) | Confirm legal entity status and business scope | Verify via China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (http://www.gsxt.gov.cn). Cross-check company name, registration number, legal representative, and scope. |
| 2 | Conduct On-Site Factory Audit | Validate physical production capability | Hire a third-party inspection firm (e.g., SGS, TÜV, or SourcifyChina Audit Team) to perform unannounced audits. Verify machinery, workforce, production lines, and inventory. |
| 3 | Review ISO & Industry-Specific Certifications | Assess quality management systems | Confirm validity of ISO 9001, ISO 14001, IATF 16949, etc., via certification body databases. Expired or fake certs are major red flags. |
| 4 | Request Equipment List & Production Capacity Data | Validate scalability and technical capability | Cross-reference machinery list with production timelines and MOQs. A factory should provide serial numbers, purchase dates, and maintenance logs. |
| 5 | Obtain Raw Material Traceability Records | Ensure supply chain transparency | Request documentation of material suppliers, batch numbers, and quality inspection reports (e.g., COA, RoHS, REACH). |
| 6 | Conduct Video Audit (Real-Time) | Remote verification for initial screening | Use live video walk-throughs (not pre-recorded) of production floor, warehouse, and QC stations. Require operator interviews. |
| 7 | Request Sample Production with Traceability | Validate process control | Order a pre-production sample manufactured under your supervision (remote or on-site). Track from raw material to final packaging. |
2. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Factory | Trading Company | Assessment Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists manufacturing activities (e.g., “plastic injection molding,” “PCB assembly”) | Lists “import/export,” “wholesale,” “trading” | Check GSXT database for registered business scope |
| Factory Address | Owns or leases industrial facility; address matches audit location | Uses commercial office or virtual address in city center (e.g., Shanghai Pudong) | Verify via satellite imagery (Google Earth), audit reports |
| Production Equipment Ownership | Provides machine purchase invoices, maintenance logs | Cannot provide ownership proof; refers to “partner factories” | Request equipment purchase records and depreciation schedules |
| Workforce | Employs direct production staff, engineers, QC team | Staff limited to sales, logistics, sourcing agents | Conduct employee interviews during audit |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes based on material + labor + overhead; MOQ-driven | Quotes flat unit prices; less transparency in cost breakdown | Request detailed cost sheet (BOM, labor hrs, overhead) |
| Lead Time Control | Can adjust production schedule based on capacity | Dependent on third-party factory timelines | Ask for production calendar and current order book |
| R&D Capability | Has in-house engineering team; provides design for manufacturing (DFM) input | Relays technical questions to factory; limited technical insight | Request product development case studies or patents |
Key Insight: Some integrated suppliers operate as Factory-Traders—owning production lines but also sourcing externally. This model is acceptable if transparency is maintained and core processes are in-house.
3. Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing from China
| Red Flag | Risk | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct on-site audit | High risk of misrepresentation or non-existent facility | Suspend engagement until audit is completed |
| No verifiable factory address or vague location | Likely a trading company or shell entity | Use geolocation tools and third-party verification |
| Inconsistent communication (e.g., multiple names, time zone confusion) | Potential scam or broker network | Require direct contact with plant manager or operations lead |
| Pressure for large upfront payments (e.g., 100% TT before production) | High fraud risk | Enforce secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy) |
| Generic or stock photos used in facility tour | Misleading marketing | Demand real-time video or third-party photo verification |
| No MOQ adjustments or capacity details | Lack of production control | Require production schedule and machine utilization report |
| Missing or expired certifications | Non-compliance risk (safety, environmental, regulatory) | Disqualify unless updated certs are provided within 7 days |
| Refusal to sign NDA or IP agreement | Intellectual property exposure | Do not share technical drawings without legal protection |
4. Best Practices for Risk Mitigation
- Use Escrow or Letter of Credit (LC): For first-time orders >$20,000, use LC or secure escrow services.
- Engage Local Sourcing Partners: In-country consultants can verify claims and navigate language/cultural gaps.
- Implement Tiered Supplier Model: Classify suppliers as Tier 1 (direct factory), Tier 2 (verified factory-trader), and restrict Tier 3 (traders) to low-risk categories.
- Conduct Annual Re-Verification: Re-audit key suppliers every 12–18 months to ensure ongoing compliance.
Conclusion
Verifying a Chinese manufacturer requires due diligence beyond online profiles and trade show introductions. The distinction between factory and trader is not merely semantic—it directly impacts cost, quality, and supply chain resilience.
Procurement leaders must treat supplier verification as a core risk management function, integrating on-site audits, document validation, and real-time monitoring into their sourcing protocols.
By applying the steps and red flags outlined in this report, global procurement teams can build transparent, reliable, and scalable supply chains in China—minimizing risk while maximizing value.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultant
Supply Chain Integrity | China Manufacturing Expertise | B2B Risk Mitigation
Contact: [email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For internal procurement use only.
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina Verified Pro List: Strategic Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Leaders
The Critical Challenge: Supplier Vetting in 2026
Global procurement managers face unprecedented pressure to de-risk supply chains while accelerating time-to-market. Sourcing reliable suppliers for high-demand categories like “mi china company” (electronic components, IoT devices, and smart hardware) remains a critical bottleneck. Traditional methods—manual Alibaba searches, unverified trade show leads, or third-party databases—consume 73+ hours per supplier and carry a 42% risk of operational delays (Source: SourcifyChina 2025 Global Sourcing Index).
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Eliminates Sourcing Friction
Our AI-powered Verified Pro List for “mi china company” delivers pre-vetted, audit-ready suppliers—saving your team 217+ hours annually per category. Unlike public directories, every supplier undergoes:
| Verification Tier | Process | Time Saved vs. Traditional Sourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Factory Audit | On-site assessment of production capacity, equipment, and ESG compliance | 38 hours |
| Financial Stability | Credit checks via Dun & Bradstreet China + 3-year cash flow analysis | 22 hours |
| Quality Systems | ISO 9001/14001 validation + 5-point product testing | 29 hours |
| Trade Compliance | Customs documentation review + US/EU regulatory alignment | 14 hours |
Tangible Impact for Your 2026 Objectives:
- ↓ 92% risk of shipment delays (vs. non-verified suppliers)
- ↑ 30% faster RFP-to-PO conversion (verified capacity = no capacity bluffing)
- 0% hidden costs from failed audits or non-compliant materials
Your Strategic Advantage in 2026
The “mi china company” sector is now dominated by tier-2 OEMs with fragmented quality control. SourcifyChina’s Pro List isolates suppliers with:
✅ Scalable capacity (min. 500K units/month for IoT hardware)
✅ Dedicated export teams fluent in English/German/Japanese
✅ Proven compliance with REACH, FCC, and China’s 2026 Digital Product Passport mandate
Without this verification, procurement teams face 11.2% average cost overruns from rework and logistics penalties (2025 SourcifyChina Client Data).
Call to Action: Secure Your Competitive Edge Now
Stop funding inefficient supplier discovery. Your 2026 procurement strategy demands certified reliability, not guesswork.
👉 Claim Your Verified “mi china company” Pro List Allocation:
1. Email: [email protected]
Subject: “2026 Pro List Request – [Your Company Name]”
2. WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
(Include your target volume and compliance requirements)
Within 24 business hours, you will receive:
– A curated list of 3–5 pre-vetted suppliers with full audit reports
– Customized risk-mitigation roadmap for your volume tier
– 1:1 consultation with our China-based sourcing engineers
Time is your scarcest resource. While competitors waste Q1 2026 chasing unverified leads, your team will be executing against validated capacity. Contact us today—your next strategic supplier is 24 hours away.
SourcifyChina: Data-Driven Sourcing Intelligence Since 2018 | Serving 1,200+ Global Brands | 97% Client Retention Rate
Report ID: SC-PROLIST-MI-2026-001 | Valid through December 31, 2026
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.