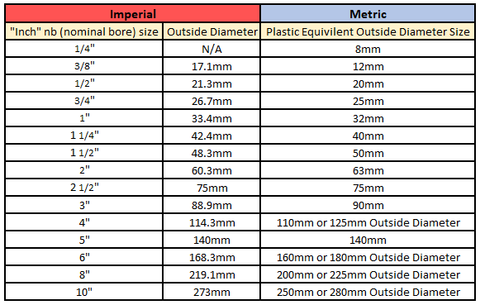
The global market for metric pipe sizes is experiencing steady expansion, driven by increasing demand across industries such as oil and gas, construction, automotive, and industrial manufacturing. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global steel pipes market was valued at USD 127.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.2% from 2024 to 2029, with metric-sized pipes representing a significant share—particularly in European and Asian markets where ISO and DIN standards prevail. Similarly, Grand View Research highlights that the rising infrastructure investments and pipeline modernization projects are accelerating the need for standardized, high-quality metric tubing solutions. As regional and international standards continue to emphasize compatibility and efficiency, manufacturers that specialize in precise metric pipe dimensions are gaining competitive advantage. In this evolving landscape, the following six companies have emerged as leading producers of metric pipe sizes, combining technical precision, global reach, and consistent adherence to international standards.
Top 6 Metric Pipe Sizes Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Industrial, Maritime & Fluid Power Tubing
Domain Est. 1996
Website: worldwidemetric.com
Key Highlights: World Wide Metric is a premier resource for tubing, offering a comprehensive selection of sizes and materials that include: carbon steel, stainless steel, ……
#2 Pipe Chart
Domain Est. 1997
Website: amerpipe.com
Key Highlights: Use our ANSI Pipe Chart to determine the nominal pipe size, wall thickness, weight and schedule designations. For easy reference, print out this up-to-date …Missing: metric manu…
#3 Metric Metal
Domain Est. 1996
Website: metricmetal.com
Key Highlights: Browse America’s largest inventory of metric-sized metals at Metric Metal. Find high-quality materials with on-time delivery and exceptional service….
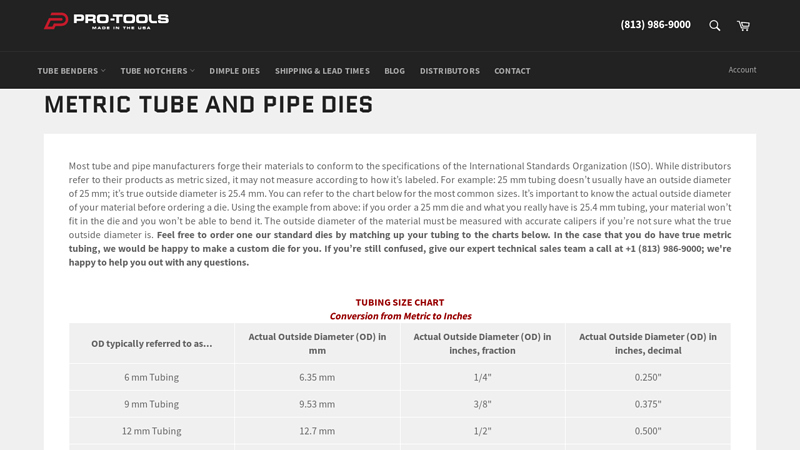
#4 Metric Tube and Pipe Dies
Domain Est. 1998
Website: pro-tools.com
Key Highlights: Need a die for metric-sized tube or pipe die? No problem! Pro-Tools makes dies for almost any material up to 63.5 mm outside diameter….
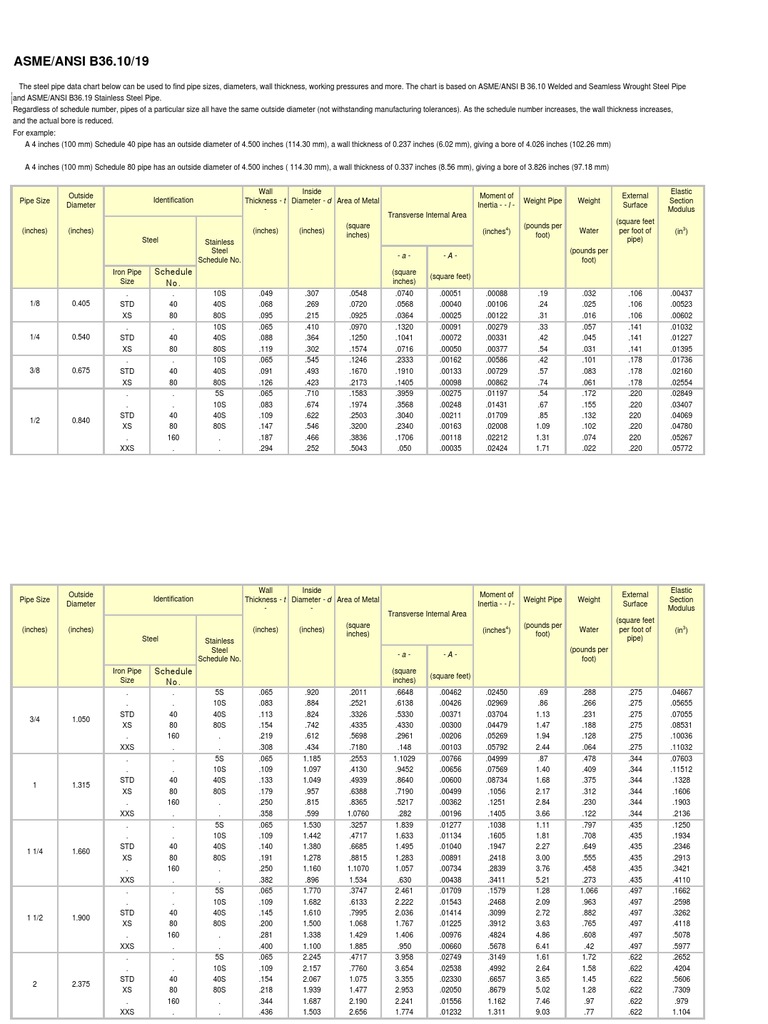
#5 ASME/ANSI B36.10/19
Domain Est. 2000
Website: engineeringtoolbox.com
Key Highlights: The steel pipe data chart below can be used to find pipe sizes, diameters, wall thickness, working pressures and more…
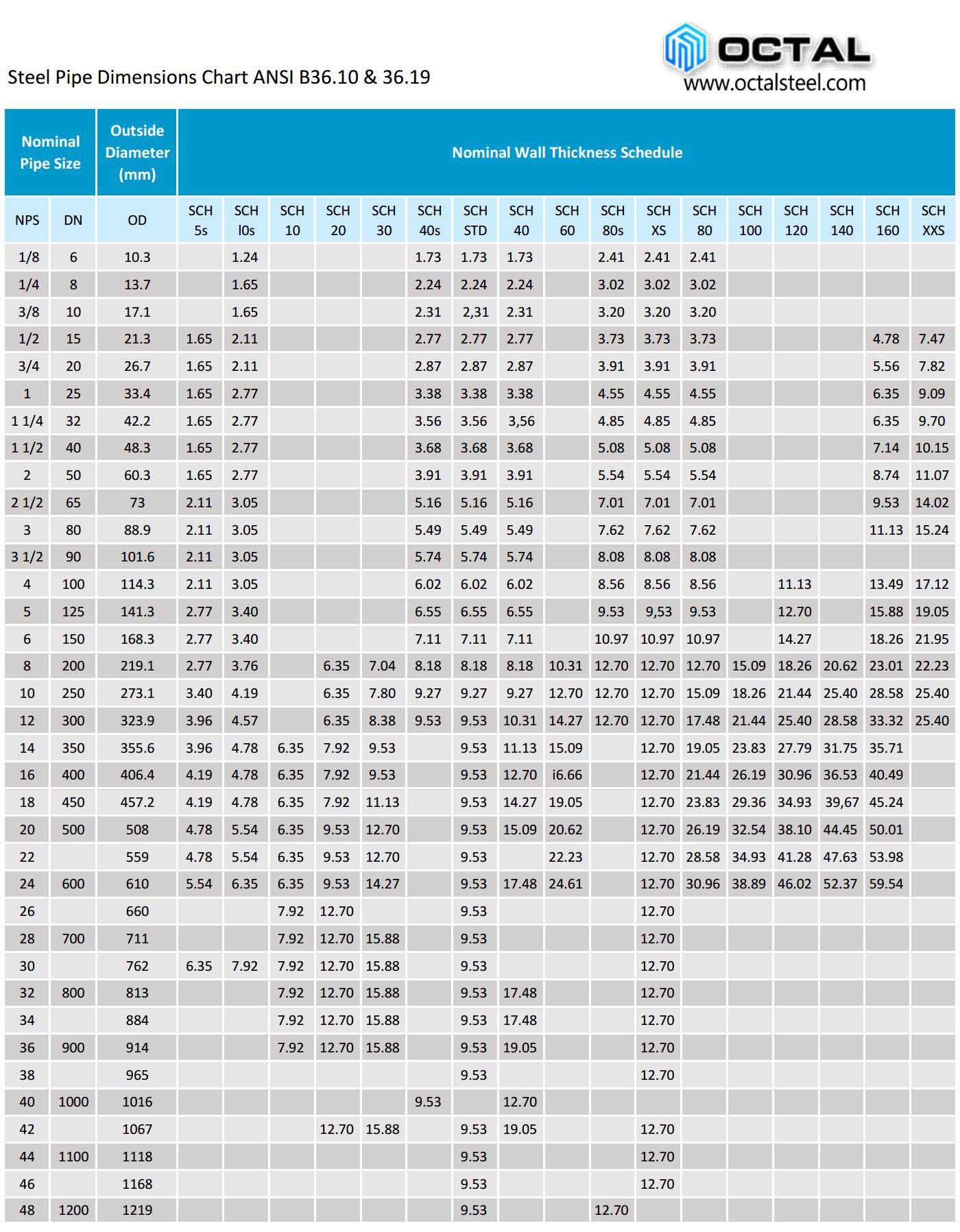
#6 Standard Pipe Schedules and Sizes Chart Table Data
Domain Est. 2000
Website: engineersedge.com
Key Highlights: The following chart gives standard pipe schedule or pipes sizes as given by ANSI / ASME B36.10M and API 5L. Data given in based on the NPS Tables….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Metric Pipe Sizes
2026 Market Trends for Metric Pipe Sizes
The global market for metric pipe sizes is poised for continued growth and transformation by 2026, driven by infrastructure development, industrial modernization, and sustainability initiatives. While traditional imperial standards persist in certain regions, the adoption of metric pipe sizes is accelerating due to standardization benefits, international project alignment, and regulatory shifts. Key trends shaping the market include:
Increasing Adoption in Emerging Economies
Developing regions in Asia-Pacific, Africa, and Latin America are prioritizing infrastructure expansion in water supply, energy transportation, and urban construction. These projects often follow international engineering standards, favoring metric pipe sizes (e.g., DN – Diameter Nominal) for compatibility with globally sourced materials and equipment. Countries investing heavily in smart cities and sustainable utilities are standardizing on metric systems to streamline procurement and ensure long-term interoperability.
Growth in Renewable Energy and Water Infrastructure
The push toward carbon neutrality is fueling investments in renewable energy projects such as solar thermal plants, geothermal systems, and green hydrogen pipelines—all of which increasingly rely on metric-based design specifications. Similarly, aging water infrastructure in both developed and developing nations is being replaced or upgraded using metric-sized pipes, especially in desalination plants and wastewater treatment facilities where precision and corrosion resistance are critical.
Standardization and Compliance Pressures
Global standards organizations such as ISO and CEN continue to promote metric pipe dimensions (e.g., ISO 6708 for DN designations), pushing industries toward harmonization. Regulatory frameworks in the European Union, Middle East, and parts of Asia mandate metric compliance for public tenders and construction codes. By 2026, multinational engineering firms are expected to standardize their design libraries on metric systems, further driving market demand.
Material Innovation and Lightweight Solutions
Advancements in polymer-based piping (e.g., PP-R, PEX, HDPE) in metric sizes are gaining market share over traditional steel and copper, particularly in plumbing and district heating. These materials offer corrosion resistance, ease of installation, and lower lifecycle costs—attributes that align with the goals of sustainable construction. Manufacturers are expanding their metric product lines to meet rising demand in residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
Digitalization and BIM Integration
Building Information Modeling (BIM) and digital twin technologies are becoming standard in engineering and construction. Metric pipe sizes are inherently compatible with international BIM libraries and CAD software, facilitating seamless design, logistics, and asset management. As digital workflows become the norm, the efficiency of using metric systems will further entrench their dominance in new projects.
Regional Challenges and Transition Dynamics
Despite the global trend, North America remains a stronghold for NPS (Nominal Pipe Size) standards. However, cross-border projects, supply chain integration, and the presence of multinational corporations are increasing the need for metric-compatible components. Dual-marking (metric/imperial) and adapter solutions will remain prevalent, but long-term industry forecasts suggest gradual metrication, especially in export-oriented manufacturing sectors.
In summary, by 2026, the metric pipe size market will be characterized by stronger growth in non-residential and utility sectors, driven by globalization, sustainability mandates, and technological integration. Stakeholders—including manufacturers, distributors, and engineering firms—should prioritize metric product development and compliance to remain competitive in an increasingly standardized and interconnected global marketplace.
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Metric Pipe Sizes (Quality, IP)
Sourcing metric pipe sizes with the correct quality standards and International Protection (IP) ratings involves several potential pitfalls. Avoiding these ensures reliability, safety, and compliance in industrial, commercial, or infrastructure applications.
Confusing Metric Pipe Standards Across Regions
Different countries and industries use varying metric pipe standards (e.g., ISO, DIN, JIS, BS), which may have similar outer diameters but differ in wall thickness, tolerances, or material grades. Misidentifying the applicable standard can lead to incompatibility with fittings or flanges, resulting in leaks or system failure.
Overlooking Material Quality and Certification Requirements
Sourcing pipes without verifying material certifications (e.g., EN 10204 3.1 or 3.2) can compromise system integrity. Using substandard materials—especially in high-pressure, high-temperature, or corrosive environments—can lead to premature failure. Always confirm chemical composition, mechanical properties, and compliance with international quality standards like ISO 9001.
Misinterpreting IP Ratings for Pipe Enclosures or Fittings
IP (Ingress Protection) ratings apply to enclosures, not the pipe itself, but are critical for electrical conduit systems or junction boxes connected to piping. A common mistake is assuming the pipe’s IP rating matches system requirements. For example, IP66 ensures dust-tight and powerful water jet resistance—essential in outdoor or washdown environments—but this must be verified for associated components, not assumed.
Assuming Metric Pipe Sizes Are Universally Interchangeable
Even within metric systems, nominal diameters (e.g., DN25) may not directly correspond to actual outer diameters across standards. Assuming interchangeability without cross-referencing dimensional tables can result in misalignment during installation and costly rework.
Neglecting Corrosion Resistance and Environmental Compatibility
Selecting a pipe based solely on size and pressure rating while ignoring environmental factors—such as humidity, chemical exposure, or UV radiation—can lead to rapid degradation. For example, stainless steel grades (e.g., 304 vs. 316) offer different corrosion resistance; choosing incorrectly compromises longevity.
Failing to Verify Traceability and Supplier Reliability
Sourcing from unreliable suppliers may result in counterfeit or uncertified products. Lack of traceability makes it difficult to validate quality during audits or failure investigations. Always work with reputable suppliers who provide full documentation and batch traceability.
Ignoring Installation and Maintenance Constraints
Even with correct sizing and IP-rated components, poor installation practices—such as improper sealing or unqualified welding—can negate quality efforts. Ensure compatibility with installation methods and maintenance access, especially in confined or hazardous areas.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires thorough specification review, supplier vetting, and attention to both dimensional and performance standards—ensuring that metric pipe systems meet operational and safety expectations.
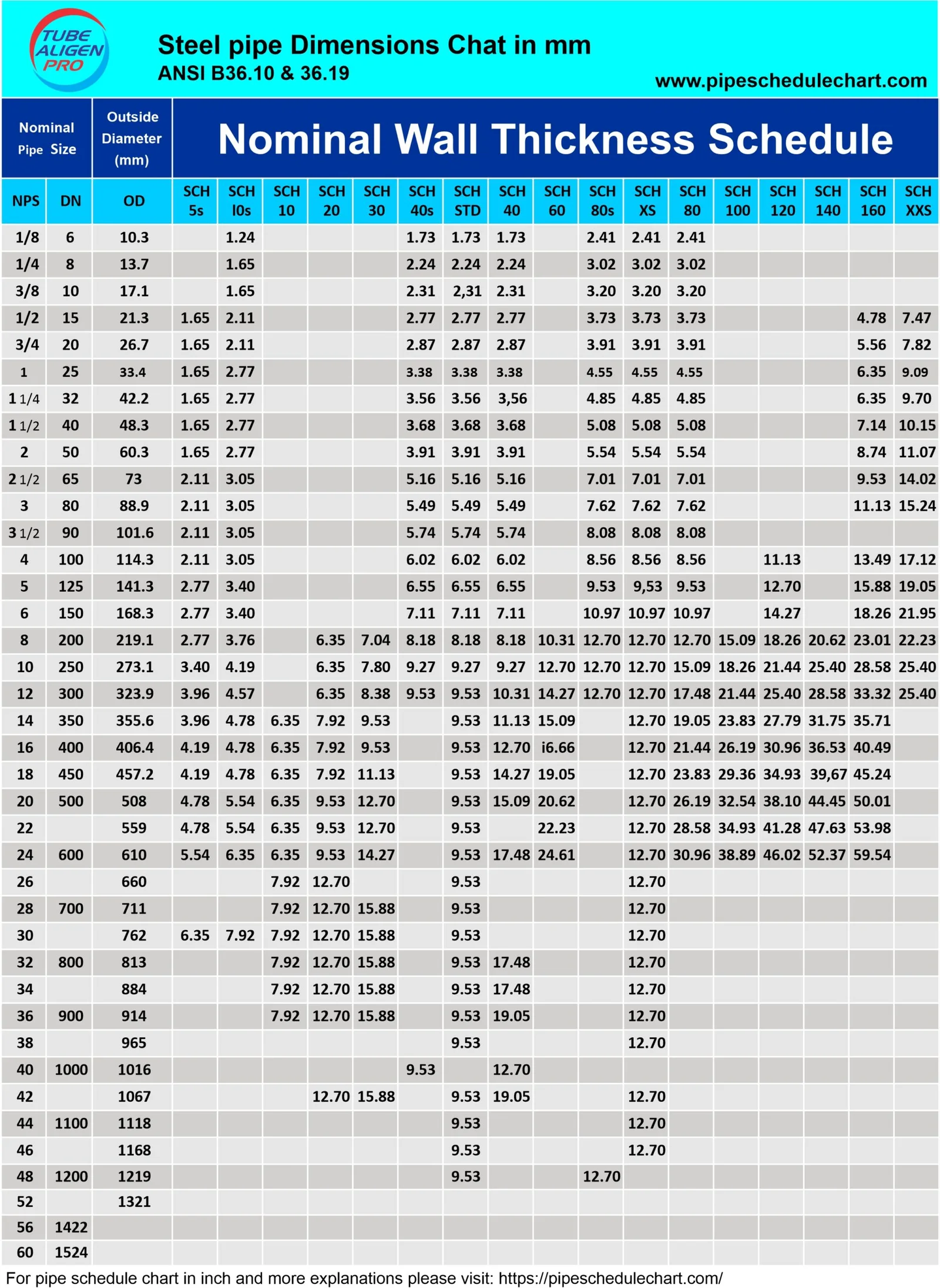
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Metric Pipe Sizes
Understanding and adhering to standards for metric pipe sizes is essential for efficient logistics, international trade, and regulatory compliance. This guide outlines key considerations for handling, transporting, and ensuring compliance of metric-sized piping systems.
Standardization and Specifications
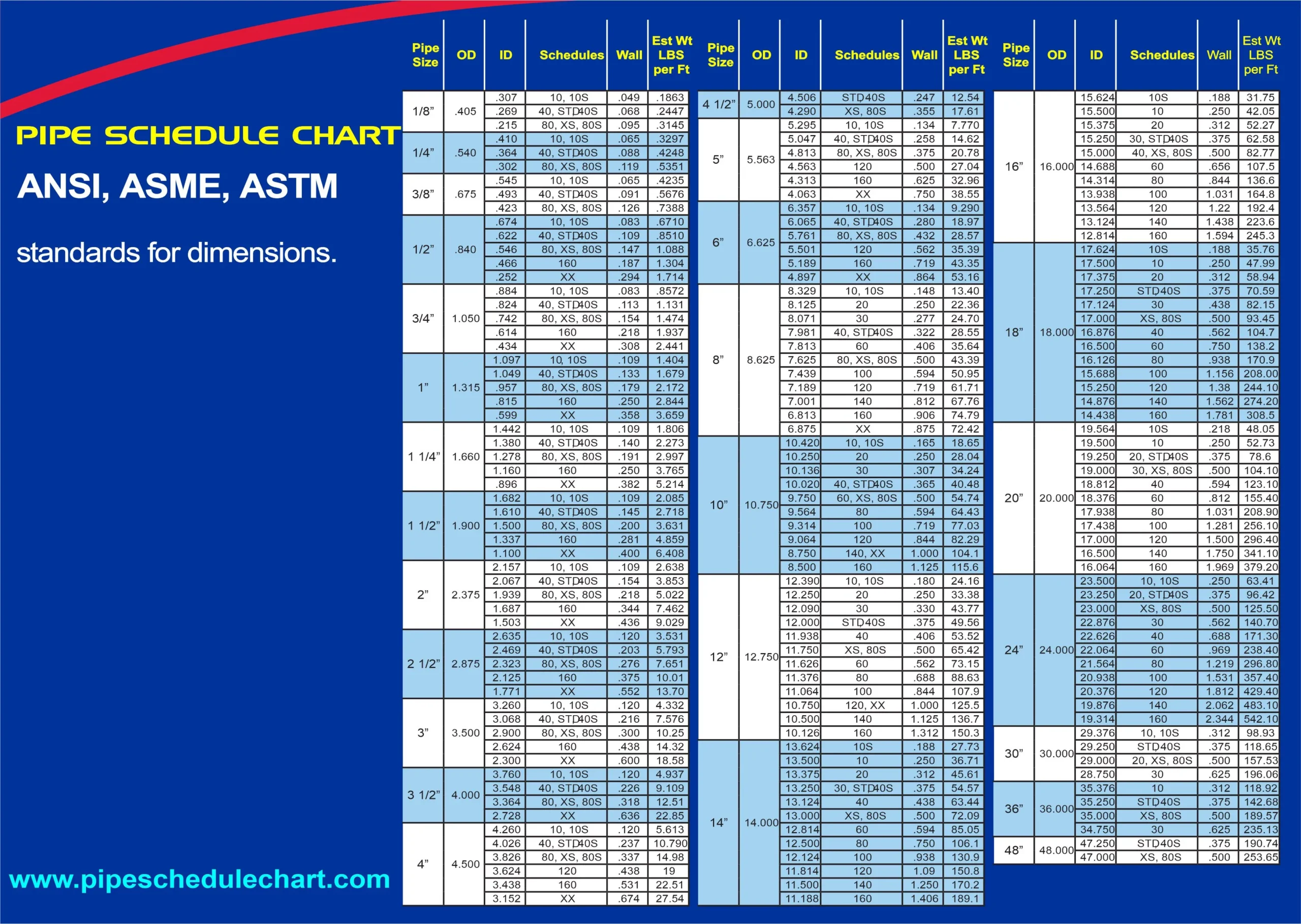
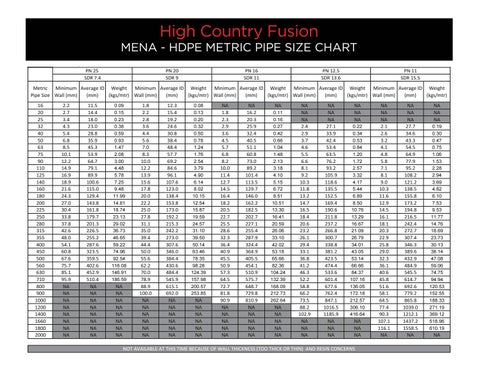
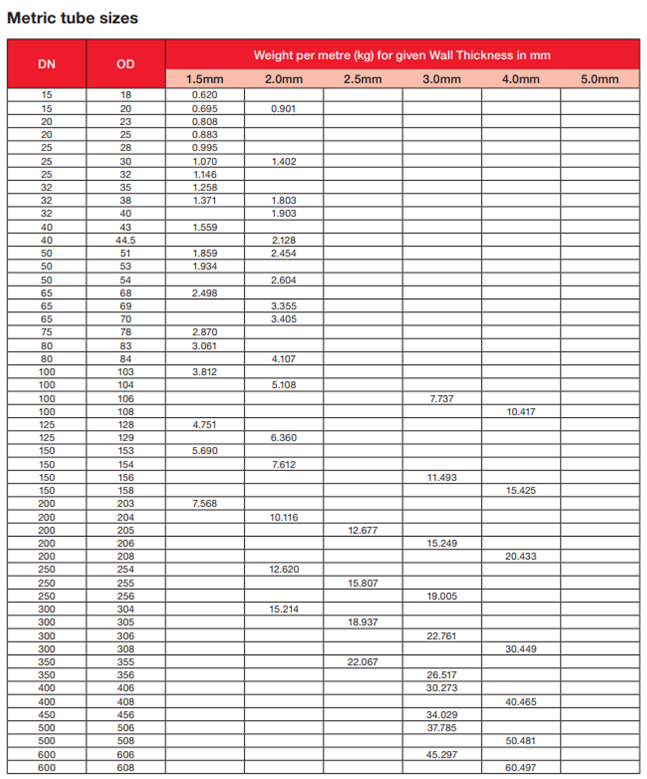
Metric pipe sizes are primarily defined by international standards such as ISO (International Organization for Standardization) and regional standards like EN (European Norm). The most common designation is DN (Diamètre Nominal or Nominal Diameter), which represents the approximate internal diameter in millimeters. For example, DN50 corresponds to a nominal pipe size of approximately 50 mm.
Key standards include:
– ISO 6708: Defines DN (Nominal Diameter) for pipes, fittings, and valves.
– ISO 4200: Specifies dimensions for seamless and welded steel tubes.
– EN 10255: Details requirements for non-alloy steel tubes suitable for welding and threading.
Adherence to these standards ensures interchangeability and compatibility across global supply chains.
Material and Dimensional Compliance
Ensure that all pipes and fittings meet relevant material specifications (e.g., stainless steel, carbon steel, PVC) and dimensional tolerances. Compliance with ISO or EN standards is often a legal requirement in many countries, especially within the European Union under the Construction Products Regulation (CPR) or Pressure Equipment Directive (PED).
Important checks:
– Verify DN and wall thickness (e.g., Schedule or metric series like SDR for plastic pipes).
– Confirm material grade and certification (e.g., EN 10204 3.1 for material test reports).
– Validate surface finish and coating (e.g., galvanization) for corrosion resistance during transport.
Packaging and Handling
Proper packaging prevents damage during transit and ensures compliance with shipping regulations:
- Steel and metal pipes: Bundled with protective end caps, secured with steel straps, and placed on wooden skids. Use moisture-resistant wrapping to prevent rust.
- Plastic pipes (e.g., HDPE, PVC): Stored in dry environments, shielded from UV exposure, and stacked appropriately to avoid deformation.
- Labeling must include DN, material type, standard (e.g., ISO 4200), heat/lot number, and manufacturer information.
Transportation and Storage
Logistics planning must account for:
– Weight and dimensions: Metric pipes often come in 6m or 12m lengths; verify load limits and vehicle compatibility.
– International shipping: Comply with IMDG Code (for sea freight) or ADR (for road in Europe) if transporting hazardous materials or coated pipes with chemical treatments.
– Warehousing: Store pipes horizontally on flat, level surfaces with adequate support to prevent sagging. Segregate materials to avoid galvanic corrosion (e.g., steel and aluminum).
Customs and Documentation
For cross-border shipments:
– Provide accurate Harmonized System (HS) codes (e.g., 7306 for iron or steel pipe).
– Include certificates of conformity, CE marking (if applicable), and test reports.
– Ensure language compliance—technical documents may need translation (e.g., into French, German, or local language).
Quality Assurance and Traceability
Maintain full traceability from manufacturer to end user:
– Implement a documented quality management system (e.g., ISO 9001).
– Retain mill test certificates and inspection reports.
– Conduct periodic audits and dimensional checks upon receipt.
Environmental and Safety Compliance
- Follow REACH and RoHS regulations if pipes contain restricted substances.
- Ensure worker safety during handling using proper PPE and lifting equipment.
- Dispose of damaged or obsolete pipes in accordance with local environmental regulations.
By following this guide, organizations can ensure that metric pipe size logistics are efficient, compliant, and aligned with global industry best practices.
Conclusion on Sourcing Metric Pipe Sizes:
Sourcing metric pipe sizes requires careful attention to international standards, compatibility with existing systems, and supplier reliability. Unlike imperial (NPT or IPS) sizing, metric pipes are designated by their outer diameter (OD) in millimeters (e.g., DN or Ø) and wall thickness, often governed by standards such as ISO 4200, DIN 2391, or EN 10255. Ensuring alignment with these specifications is essential for system integrity and interchangeability.
When sourcing, consider regional availability—metric pipes are widely adopted in Europe, Asia, and many industrial sectors globally, but may require longer lead times or custom orders in regions dominated by imperial standards. Working with certified suppliers who adhere to recognized quality standards helps mitigate risks related to material consistency, tolerances, and performance.
In summary, successfully sourcing metric pipe sizes involves understanding technical specifications, selecting reliable suppliers familiar with international standards, and verifying compatibility with connectors, fittings, and system requirements. Proactive planning and clear communication with vendors will ensure efficient procurement, reduce downtime, and support the long-term reliability of piping systems.