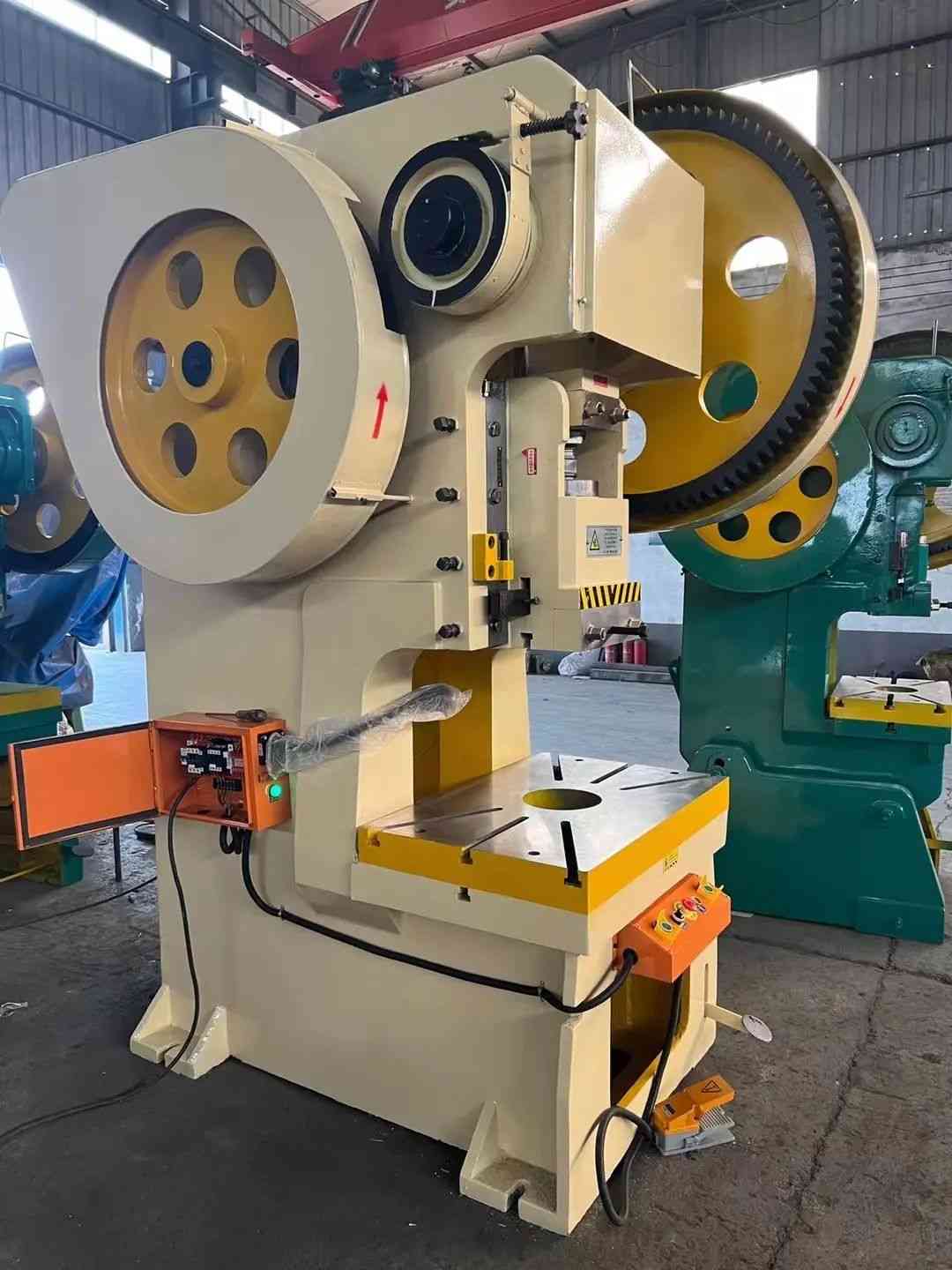
The global mechanical presses market is witnessing steady expansion, driven by increasing demand from the automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing sectors for high-precision metal forming solutions. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the mechanical press market was valued at USD 4.3 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.2% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2029. This growth is fueled by advancements in automation, rising adoption of servo-driven mechanical presses, and the ongoing trend toward lean manufacturing processes. Additionally, Grand View Research highlights that innovations in press technology—particularly energy efficiency and integration with Industry 4.0 systems—are key factors shaping competitive dynamics. As manufacturers seek higher throughput, accuracy, and flexibility, the role of leading mechanical press producers becomes increasingly pivotal. The following list presents the top 10 mechanical press manufacturers shaping the industry through technological innovation, global reach, and robust product portfolios.
Top 10 Mechanical Presses Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 SEYI Machinery The leading servo and mechanical press …
Domain Est. 1998
Website: seyi.com
Key Highlights: Shieh Yih Machinery Industry Co., Ltd (SEYI Machinery) is a leading manufacturer of medium-large servo presses. Main customers are manufacturers in various ……
#2 Industrial Stamping Press Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2014
Website: sangiacomo-presses.com
Key Highlights: Sangiacomo Presses stands as a leader among mechanical press manufacturers. We utilize our expertise from over 65 years of experience and 17,000 stamping ……
#3 Presses
Domain Est. 1998
Website: chinfong.com
Key Highlights: We are a leading Mechanical Press and Hot Forging Press manufacturer in Taiwan specialized in Mechanical Press, Hot Forging Press, Fine Blanking Press, ……
#4 Mechanical Presses
Domain Est. 1998 | Founded: 1969
Website: eaglepresses.com
Key Highlights: Leading North American mechanical press manufacturer since 1969. Committed to manufacturing innovative, high quality mechanical presses….
#5 Mechanical presses
Domain Est. 1999
Website: mossini.com
Key Highlights: Founded by Mario Mossini in 1970, Mossini SpA started its own business as a manufacturer of mechanical presses….
#6 Stamping Presses
Domain Est. 2004
Website: aida-global.com
Key Highlights: AIDA stamping presses, servo and mechanically driven, with advanced metal forming technology, provide reliable, powerful manufacturing solutions….
#7 Mechanical stamping and metal forming presses
Domain Est. 1995
Website: andritz.com
Key Highlights: ANDRITZ Kaiser produces highly precise presses, thus increasing productivity, quality, and lifetime and decreasing overall operating costs….
#8 Mechanical Press Solutions
Domain Est. 1997
Website: stamtec.com
Key Highlights: Find your ideal mechanical press at Stamtec! Our presses deliver superior strength and resistance to deflection, perfect for your specific applications….
#9 Mechanical Presses Archives
Domain Est. 2000
Website: mecolpress.com
Key Highlights: Mecolpress manufactures mechanical presses, hydraulic presses, used mechanical presses and used hydraulic presses, carefully revised, ……
#10 Stamping press machine, Mechanical press machine, Hydraulic …
Domain Est. 2021
Website: yanglipress.com
Key Highlights: YangLi CNC mainly produces high-tech products that integrate optics, electronics, electronics, and hydraulics, including CNC turret punch presses, ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Mechanical Presses
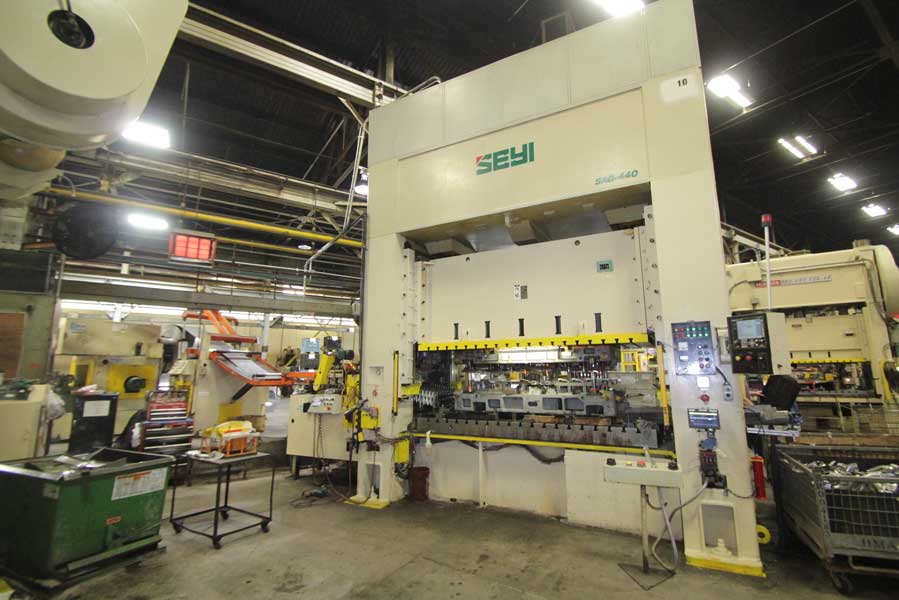

2026 Market Trends for Mechanical Presses
The mechanical press market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, shifting industrial demands, and sustainability imperatives. While traditional mechanical presses remain vital in high-volume manufacturing, emerging trends are reshaping their design, application, and competitiveness against alternative technologies.
Increased Integration of Smart Manufacturing and Industry 4.0
By 2026, mechanical presses will increasingly feature embedded sensors, real-time monitoring systems, and Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity. This enables predictive maintenance, remote diagnostics, and seamless integration into digital factory ecosystems. Manufacturers will leverage data analytics to optimize press performance, reduce downtime, and improve quality control—making mechanical presses more adaptive and efficient in smart production environments.
Rise of Hybrid and Servo-Driven Mechanical Presses
Although fully hydraulic or servo-electric presses offer flexibility, hybrid mechanical presses—combining mechanical drive systems with servo technology—are gaining traction. These systems deliver the high-speed precision of mechanical presses with enhanced control over stroke length, speed, and forming force. By 2026, servo-mechanical presses are expected to dominate new installations in industries like automotive and aerospace, where precision and energy efficiency are critical.
Focus on Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
With global emphasis on reducing carbon footprints, mechanical press manufacturers are optimizing energy use through regenerative braking, improved motor efficiency, and lightweight structural designs. Regulatory pressures and corporate sustainability goals will drive demand for energy-certified presses. Additionally, recyclability of press components and reduced lubricant usage will become key differentiators in the market.
Demand from Electric Vehicle (EV) Manufacturing
The rapid expansion of the EV industry is creating new opportunities for mechanical presses, particularly in stamping battery enclosures, motor components, and lightweight chassis parts. High-strength steel and aluminum forming require robust, high-speed presses, reinforcing the relevance of advanced mechanical systems. By 2026, press suppliers will increasingly tailor solutions to EV-specific production needs.
Regional Shifts and Automation Integration
Asia-Pacific, led by China and India, will remain the largest market for mechanical presses due to expanding manufacturing bases. However, North America and Europe will see growth driven by reshoring initiatives and automation upgrades. Mechanical presses will be increasingly integrated with robotic feeding, part handling, and vision systems, enabling lights-out manufacturing and reducing labor dependency.
Competitive Pressure from Alternative Technologies
Despite advancements, mechanical presses face competition from servo-hydraulic and multi-axis servo presses, which offer greater flexibility for low-volume, high-mix production. By 2026, mechanical press vendors will need to emphasize their advantages in speed, durability, and cost-effectiveness for high-volume applications to maintain market share.
In conclusion, the 2026 mechanical press market will be characterized by smarter, greener, and more adaptable machines. Success will depend on embracing digitalization, meeting the demands of evolving industries like EVs, and differentiating through performance and sustainability.
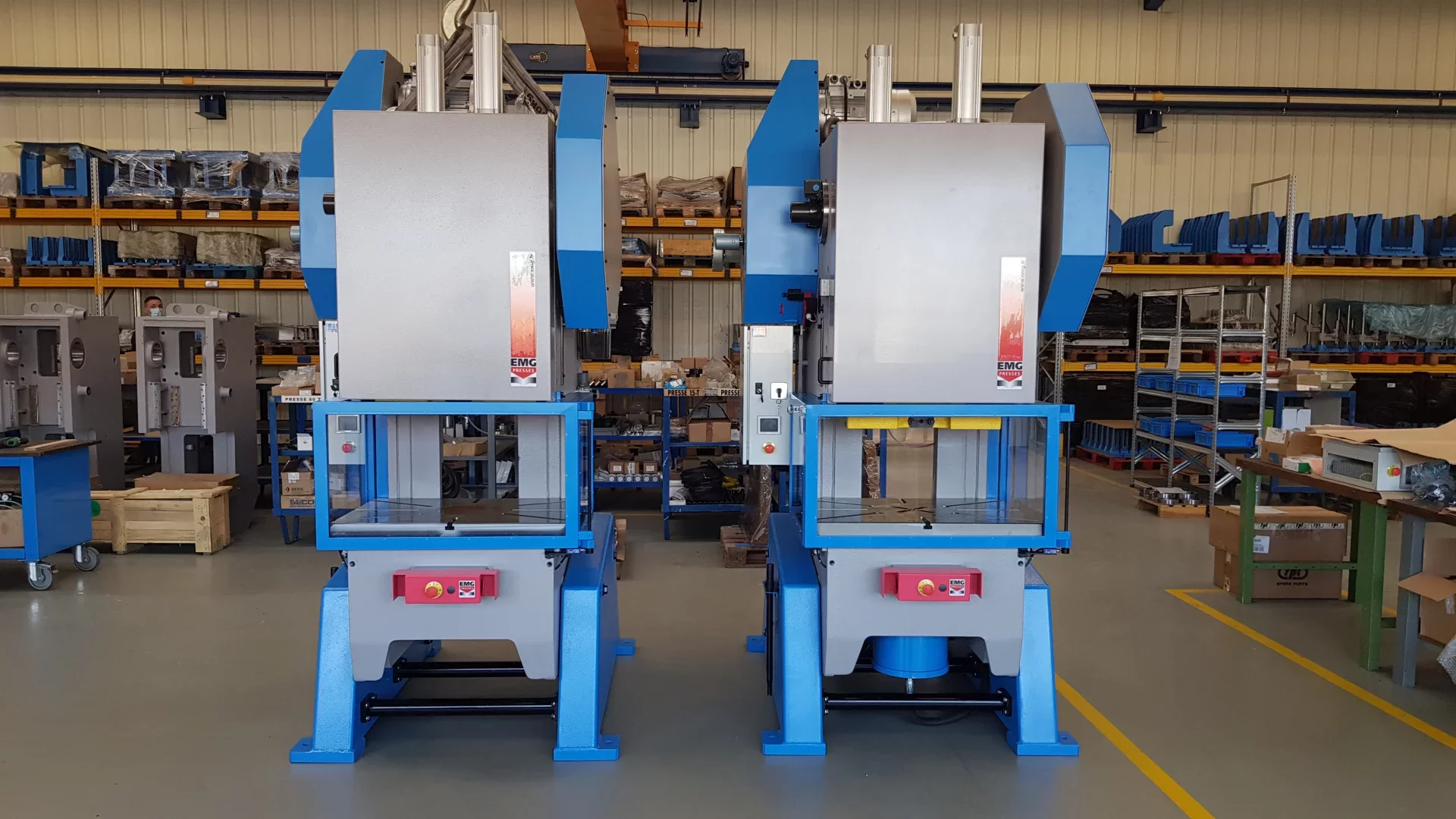

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Mechanical Presses: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing mechanical presses—especially from international or new suppliers—can expose companies to significant risks related to product quality and intellectual property (IP) infringement. Being aware of these common pitfalls helps mitigate financial loss, operational downtime, and legal exposure.
Poor Build Quality and Substandard Materials
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing mechanical presses is receiving equipment built with inferior materials or lacking proper engineering standards. Some suppliers may cut corners by using low-grade steel, undersized components, or outdated manufacturing techniques, resulting in presses that fail prematurely or underperform. These issues often surface only after installation, leading to costly repairs, production delays, and safety hazards.
Inadequate Quality Control Processes
Suppliers may lack robust quality assurance systems such as ISO certifications or in-process inspections. Without documented quality controls, there’s a higher risk of inconsistent welding, misaligned parts, or improper assembly, all of which compromise the reliability and safety of the press. Buyers may not discover these defects until after the equipment is operational, by which time it’s difficult and expensive to enforce warranties or returns.
Misrepresentation of Technical Specifications
Some suppliers exaggerate performance claims, such as tonnage capacity, stroke rate, or precision tolerances, to win contracts. Presses that don’t meet advertised specs can damage tooling, produce defective parts, or pose safety risks. It’s essential to validate claims through third-party testing or factory acceptance tests (FAT) before shipment.
Lack of Compliance with Safety Standards
Mechanical presses must comply with regional safety regulations such as OSHA (U.S.), CE (EU), or ISO 12100. Some imported presses may lack required safety features like dual palm buttons, light curtains, or emergency stops. Non-compliant equipment can lead to workplace injuries, regulatory fines, and liability issues.
Intellectual Property Infringement
A major hidden risk is purchasing presses that infringe on patented designs or technologies. Some manufacturers clone well-known press models without licensing, replicating gear systems, clutch mechanisms, or control architectures that are protected by IP laws. If caught, buyers may be held liable for using or distributing infringing equipment, facing legal action or forced decommissioning.
Insufficient Documentation and Lack of Traceability
Suppliers may fail to provide complete technical documentation, including schematics, maintenance manuals, or material certifications. This complicates maintenance, training, and regulatory compliance. In IP disputes, missing documentation also makes it harder to prove the legitimacy or origin of the equipment.
Weak Warranty and After-Sales Support
Even if a press meets initial quality expectations, poor supplier support can undermine long-term performance. Limited warranty coverage, unavailability of spare parts, or unresponsive service teams can lead to extended downtime. This is especially problematic with overseas suppliers where language barriers and time zones add complexity.
How to Mitigate These Risks
- Conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, including site audits and reference checks.
- Require third-party inspections and factory acceptance testing.
- Verify compliance with relevant safety and technical standards.
- Consult legal experts to assess IP risks, especially when sourcing from regions with weak IP enforcement.
- Insist on complete technical documentation and clear warranty terms.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls, companies can source mechanical presses that are safe, reliable, and free from hidden legal and operational risks.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Mechanical Presses
Overview
Mechanical presses are essential in manufacturing processes such as stamping, forming, and punching. Due to their size, weight, and safety-critical nature, shipping, handling, installation, and operation must follow strict logistics and regulatory compliance standards. This guide outlines key considerations for the safe and compliant management of mechanical presses throughout their lifecycle.
Transportation & Shipping
Packaging & Crating
- Ensure presses are securely mounted on skids or in custom crates to prevent movement during transit.
- Use weather-resistant, industrial-grade packaging to protect against moisture, dust, and corrosion.
- Include lifting points and load distribution markings on the crate or base for safe handling.
Mode of Transport
- Heavy-Duty Trucking: Most common; requires route planning to avoid weight-restricted bridges and low-clearance areas.
- Flatbed Trailers: Ideal for large presses; require proper blocking, bracing, and tarping.
- Intermodal Shipping: For international shipments; ensure compliance with container weight limits and International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code if applicable.
Handling Equipment
- Use forklifts, cranes, or telehandlers with adequate lifting capacity (refer to press weight specifications).
- Always use slings rated for the load and attach to designated lifting points only.
- Never lift a press by its components (e.g., flywheel, clutch, or die area).
Import/Export Compliance
Documentation
- Prepare accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, and bills of lading.
- Include Harmonized System (HS) Code for mechanical presses (typically 8462.21 or 8462.29, depending on function).
- Provide a detailed technical description, including tonnage, stroke length, and drive type.
Regulatory Requirements
- Comply with destination country’s import regulations (e.g., CE marking for EU, UL/CSA for North America).
- Obtain necessary permits for oversized or overweight shipments where required.
- Adhere to export control regulations (e.g., U.S. EAR or EU Dual-Use Regulations) if technology involves controlled components.
Installation & Site Preparation
Facility Requirements
- Verify floor load capacity (typically 500–1,000 psf depending on press size).
- Ensure adequate clearance for operation, maintenance, and die changes.
- Provide proper utility connections: electrical (voltage, phase, amperage), compressed air, and hydraulic lines if applicable.
Anchoring & Alignment
- Secure press to foundation using manufacturer-specified anchor bolts.
- Perform precision leveling to prevent vibration and misalignment.
- Confirm alignment with feed systems, conveyors, or automation equipment.
Safety & Operational Compliance
Regulatory Standards
- Comply with OSHA 29 CFR 1910.211–217 (U.S.) for mechanical power presses.
- Adhere to ANSI B11.1–2023 (Safety of Mechanical Power Presses).
- In the EU, ensure conformity with Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC and EN 692 standards.
Safety Devices & Controls
- Install and certify presence-sensing devices (e.g., light curtains, dual palm buttons).
- Implement proper guarding (fixed, interlocked, or movable) around point of operation.
- Test emergency stop systems and ensure accessibility from all operator positions.
Risk Assessment & Documentation
- Conduct a hazard analysis and risk assessment (per ISO 12100).
- Maintain a Technical File or Declaration of Conformity for regulatory audits.
- Keep logs of safety inspections, maintenance, and operator training.
Maintenance & Recordkeeping
Preventive Maintenance
- Follow manufacturer-recommended maintenance schedules.
- Regularly inspect clutch/brake systems, gears, bearings, and structural components.
- Lubricate moving parts per specifications to prevent premature wear.
Compliance Records
- Maintain logs of:
- Safety device testing (monthly/annual)
- Operator training and certifications
- Mechanical inspections and repairs
- Regulatory audits and updates
Disposal & Decommissioning
Environmental Compliance
- Recycle hydraulic fluids, oils, and metal components in accordance with EPA or local regulations.
- Properly dispose of electrical components containing hazardous materials (e.g., capacitors).
Data & Security
- Remove or securely wipe any programmable logic controllers (PLCs) or data storage devices.
- Document decommissioning for compliance and asset management purposes.
Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance management of mechanical presses ensures operational safety, regulatory adherence, and equipment longevity. Always consult manufacturer guidelines and local regulations when planning transportation, installation, or maintenance activities. Regular training and documentation are critical to maintaining a compliant and safe press operation.
Conclusion for Sourcing Mechanical Presses
In conclusion, sourcing mechanical presses requires a strategic approach that balances performance, reliability, cost-efficiency, and long-term support. A thorough evaluation of suppliers based on technical specifications, build quality, service and maintenance support, delivery timelines, and total cost of ownership is essential to make an informed decision. It is important to align the press specifications with the specific production requirements, including tonnage, speed, safety features, and automation compatibility.
Additionally, partnering with reputable manufacturers or suppliers who demonstrate proven industry experience and strong customer service can significantly reduce downtime and operational risks. Conducting site visits, reviewing customer testimonials, and analyzing after-sales support capabilities further enhance sourcing success.
Ultimately, the right mechanical press not only improves manufacturing efficiency and product quality but also contributes to operational safety and scalability. A well-executed sourcing process ensures long-term value, supporting sustainable growth and competitiveness in the manufacturing landscape.