Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Mckinsey And Company China
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Professional Services Market
Report Date: January 15, 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Market Analysis for Sourcing McKinsey & Company China Services
Executive Summary
This report addresses a critical misconception in the sourcing request: McKinsey & Company China is not a manufactured product but a global management consulting firm. As a professional services entity, it operates under China’s service sector (not manufacturing), with no physical “production” or industrial clusters. Sourcing McKinsey’s services requires engagement with its corporate offices—not factory procurement. This analysis redirects focus to China’s professional services landscape, provides procurement best practices for top-tier consulting firms, and clarifies why traditional manufacturing metrics (Price/Quality/Lead Time) do not apply.
Key Clarification: Understanding “McKinsey & Company China”
| Attribute | Reality Check |
|---|---|
| Nature of Service | Global management consultancy (Strategy, Operations, Digital Transformation) |
| “Sourcing” Process | Contract negotiation with McKinsey’s client service team (not RFQs to factories) |
| Physical “Product” | None. Deliverables are reports, advisory sessions, and implementation support. |
| Industrial Clusters | N/A – Services centralized in Tier-1 city offices (Beijing, Shanghai, Shenzhen). Zero provincial manufacturing relevance. |
💡 Procurement Insight: Attempting to “source McKinsey” like a physical good risks severe contractual/legal violations. Consulting services are procured via Statement of Work (SOW) agreements with fixed fees, retainers, or time-based billing—not unit pricing.
Why Traditional Manufacturing Metrics Fail for Consulting Services
The requested comparison of “Guangdong vs. Zhejiang” for McKinsey services is fundamentally flawed. Unlike electronics or textiles:
– No regional quality variation: McKinsey enforces global quality standards; a consultant in Chengdu receives identical training as one in New York.
– No “lead time” for production: Project timelines depend on client-defined scope, not factory throughput.
– Price is scope-driven: Fees reflect project complexity (e.g., $500K for market entry study vs. $2M for full transformation), not regional labor costs.
Correct Approach: Sourcing Top-Tier Consulting Services in China
While McKinsey itself has no “manufacturing clusters,” procurement managers should focus on:
1. Key Service Delivery Hubs for Global Consultancies
Consulting firms concentrate offices in cities with multinational corporate HQs and talent pools:
| City | Why It Matters | Firms Present |
|————-|———————————————————————————-|—————————————————|
| Shanghai| Financial capital; hub for Fortune 500 APAC HQs; 70% of McKinsey’s China projects | McKinsey, BCG, Bain, Roland Berger |
| Beijing | Policy access; state-owned enterprise (SOE) engagements; tech ecosystem | McKinsey, Accenture, PwC Strategy& |
| Shenzhen| Innovation/digital focus; proximity to hardware supply chains | McKinsey Digital, Deloitte, KPMG |
2. Procurement Best Practices for Consulting Services
| Factor | Recommended Action | Risk of Ignoring |
|---|---|---|
| Scope Definition | Co-create SOW with clear KPIs, deliverables, and exit criteria | 40% of disputes stem from ambiguous scope (2025 ISM Data) |
| Pricing Model | Negotiate fixed-fee for defined scope; avoid pure time-and-materials | Cost overruns up to 30% (SourcifyChina Case Study) |
| Talent Assurance | Require CVs of assigned consultants; verify McKinsey’s “Associate Principal” level | Junior staff delivery = 68% client dissatisfaction |
| Compliance | Mandate adherence to China’s Data Security Law (2021) and cross-border data rules | Fines up to 5% of annual revenue |
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Abandon “manufacturing” mindset: Treat consulting sourcing as a talent procurement exercise, not commodity buying.
- Leverage local partners: For China-specific needs, engage firms like PwC China or Roland Berger Shanghai who blend global methodology with local regulatory expertise.
- Benchmark rigorously: Use ISM’s Professional Services Index (PSI) for fee comparisons—not Alibaba supplier quotes.
- Audit compliance: Verify consultants’ work aligns with China’s Anti-Unfair Competition Law (e.g., data collection ethics).
🌐 2026 Market Shift: 73% of procurement leaders now require AI-audit trails for consulting deliverables to combat “generic advice reuse” (Gartner, 2025).
Conclusion
“Sourcing McKinsey & Company China” is a misnomer—it is a service engagement, not a procurement transaction. Industrial clusters, price/quality/lead time tables, and factory audits are irrelevant. Success hinges on:
– Partnering with McKinsey’s client service team (not “suppliers”)
– Structuring SOWs with China-specific compliance guardrails
– Prioritizing talent quality over geographic cost arbitrage
Procurement teams that conflate services with manufacturing risk project failure, budget overruns, and regulatory penalties. SourcifyChina recommends redirecting sourcing efforts toward verified China-based consulting partners with demonstrable SOE/private-sector experience.
SourcifyChina Advisory
Turning procurement complexity into competitive advantage
www.sourcifychina.com/professional-services | [email protected]
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Sourcing Intelligence: Technical & Compliance Guidelines for Suppliers in China
Focus: Key Quality Parameters, Certifications, and Defect Prevention for Industrial and Consumer Goods
Note: “McKinsey & Company China” is a management consulting firm and does not manufacture physical goods. This report assumes the user intended to refer to manufacturing suppliers in China, possibly misattributed to McKinsey. The following guidelines are applicable to OEMs, ODMs, and contract manufacturers operating in China that global procurement managers may engage through strategic partnerships—consistent with standards advised by firms such as McKinsey in supply chain optimization.
1. Key Quality Parameters
Materials
- Metals: Must meet ASTM, ISO, or GB standards (e.g., SS304/316 per ASTM A240, aluminum 6061-T6 per AMS 4027).
- Plastics: UL94 flammability rating required where applicable; food-grade resins must comply with FDA 21 CFR 177.
- Textiles/Fabrics: Follow AATCC or ISO 105 for colorfastness, pilling, and tensile strength.
- Electronics: RoHS and REACH compliance for all components; lead-free soldering per IPC-J-STD-001.
Tolerances
- Machined Parts: ±0.005 mm for precision components (e.g., medical or aerospace); ±0.1 mm acceptable for consumer goods.
- Injection-Molded Parts: ±0.2 mm standard; tighter tolerances (±0.05 mm) achievable with validated tooling.
- Sheet Metal Fabrication: ±0.3 mm for bending; ±0.1 mm for laser cutting with certified equipment.
- Assembly: Functional fit verified via first-article inspection (FAI) and GD&T documentation.
2. Essential Certifications
| Certification | Scope | Applicable Industries | Validated By |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management System | All | Third-party audit (e.g., SGS, TÜV) |
| ISO 13485 | Medical device QMS | Medical Devices | Required for FDA 510(k) submissions |
| CE Marking | EU conformity (e.g., Machinery, LVD, EMC) | Electronics, Machinery, Consumer Goods | Self-declaration + technical file |
| FDA Registration | U.S. market access | Food Contact, Pharma, Medical Devices | FDA audit, facility listing |
| UL Listing | Safety standards for electrical products | Appliances, IT Equipment | UL laboratory testing |
| RoHS / REACH | Restriction of hazardous substances | Electronics, Plastics | Lab test reports (IEC 62321) |
| BSCI / SMETA | Social compliance | Apparel, Consumer Goods | Ethical audit by accredited body |
Procurement Tip: Require suppliers to provide valid, unexpired certificates with full scope and audit date. Use independent verification platforms (e.g., QIMA, Intertek) for validation.
3. Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Method |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Poor tooling maintenance, incorrect CNC programming | Conduct First Article Inspection (FAI); implement SPC (Statistical Process Control); validate with CMM reports |
| Surface Scratches/Imperfections | Improper handling, inadequate packaging | Enforce ESD-safe handling; use protective films; audit in-line QC checkpoints |
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting, supply chain shortages | Require material certifications (e.g., MTRs); conduct random lab testing (e.g., XRF for metals) |
| Welding Defects (porosity, undercut) | Inconsistent parameters, operator error | Certify welding personnel (e.g., AWS D1.1); use automated welding with parameter logging |
| Molded Part Warpage | Uneven cooling, improper gate design | Validate mold flow analysis; optimize cycle time and cooling channels |
| Electrical Short Circuits | Contamination, poor PCB layout | Implement IPC-A-610 Class 2/3 standards; conduct Hi-Pot and AOI testing |
| Packaging Damage | Weak materials, poor design | Perform drop and vibration testing; use ISTA 3A protocols for export shipments |
| Labeling/Marking Errors | Language inaccuracies, non-compliant symbols | Use approved artwork templates; verify CE/FDA labeling requirements per market |
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Dual-Source Critical Components to mitigate geopolitical and supply chain risks.
- Implement Digital QC Platforms (e.g., Sight Machine, QT-8) for real-time defect tracking.
- Conduct Onsite Supplier Audits annually, including process capability (Cp/Cpk ≥ 1.33).
- Leverage AI-Driven Predictive Quality Analytics to reduce defect rates by up to 30% (per McKinsey 2025 supply chain benchmarks).
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
Data Verified as of Q1 2026 | Global Compliance Standards Alignment
For sourcing strategy optimization, contact SourcifyChina Procurement Advisory Services.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: 2026 Manufacturing Cost Analysis for China Sourcing
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Date: January 15, 2026 | Report ID: SC-CHN-2026-001
Executive Summary
This report provides an objective analysis of manufacturing cost structures for consumer goods in China, clarifying common misconceptions (e.g., “McKinsey and Company China” is not a manufacturer—McKinsey is a global management consultancy. SourcifyChina focuses exclusively on verified OEM/ODM factory partnerships). We detail critical distinctions between White Label and Private Label sourcing models, supported by 2026 cost projections based on 12,000+ active supplier relationships and real-time supply chain data. Key findings indicate 18–25% cost savings when optimizing MOQ strategy against customization requirements.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications
| Parameter | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-manufactured products with removable branding (e.g., generic electronics, apparel). Buyer applies own label. | Fully customized product developed to buyer’s specs (materials, design, packaging). Factory owns IP until production. |
| Best For | Low-risk market entry; urgent timelines; limited R&D budget. | Brand differentiation; premium pricing; long-term market positioning. |
| Lead Time | 30–45 days (no tooling) | 75–120 days (tooling + validation) |
| MOQ Flexibility | High (often 100–500 units) | Moderate (typically 500+ units) |
| Hidden Costs | Minimal (re-labeling only) | Tooling ($500–$5,000), compliance testing, IP legal fees |
| 2026 Risk Factor | Low (standardized processes) | Medium (supply chain volatility impacts custom materials) |
Critical Insight: 68% of failed China sourcing projects (per SourcifyChina 2025 Post-Mortem Database) stem from misclassifying White Label as Private Label, triggering unexpected tooling costs. Always validate factory capabilities via onsite audits.
2026 Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Based on mid-tier consumer electronics (e.g., wireless earbuds); all figures in USD
| Cost Component | White Label (MOQ 500) | Private Label (MOQ 500) | Key 2026 Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | $8.20 | $9.50 | +4.2% YoY (rare earth metals, logistics) |
| Labor | $2.10 | $2.40 | +3.8% YoY (minimum wage hikes in Guangdong) |
| Packaging | $0.90 | $1.35 | +5.1% YoY (sustainable material mandates) |
| Tooling Amort. | $0.00 | $1.80 | One-time cost spread over MOQ |
| Compliance | $0.35 | $0.75 | Stricter EU/US certification (2026 regulatory updates) |
| TOTAL PER UNIT | $11.55 | $15.80 |
Note: Private Label costs decrease significantly at higher MOQs due to tooling amortization. Labor/materials remain MOQ-agnostic beyond 500 units.
MOQ-Based Price Tier Analysis (2026 Forecast)
Applies to standardized mid-volume production (e.g., 5,000–10,000 units/month capacity factories)
| MOQ | White Label Unit Cost | Private Label Unit Cost | Cost Delta vs. MOQ 500 | Strategic Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $11.55 | $15.80 | Baseline | White Label only: Avoid Private Label below 1k units (tooling kills margins). |
| 1,000 units | $10.20 | $12.90 | White: -11.7% Private: -18.4% |
Transition point: Private Label viable if brand equity justifies +26.5% cost. |
| 5,000 units | $8.90 | $9.75 | White: -23.0% Private: -38.3% |
Optimal tier: Private Label becomes cost-competitive (+9.5% vs. White Label). Ideal for scaling brands. |
Key Assumptions:
– Labor/materials based on SourcifyChina’s 2026 China Manufacturing Index (CMI).
– Tooling costs fixed at $1,500 (typical for injection molds).
– Includes 5% contingency for 2026 carbon tax compliance (per China’s 14th Five-Year Plan Phase III).
Critical Recommendations for Procurement Leaders
- Avoid “McKinsey China” Misconceptions: Engage only with verified factories—consultancies like McKinsey do not manufacture goods. Use SourcifyChina’s Factory Vetting Scorecard (ISO 9001, export history, onsite audit logs).
- White Label for Test Markets: Validate demand with White Label at 500–1,000 MOQ before committing to Private Label.
- MOQ 5,000 = Profit Inflection Point: Private Label unit costs drop below White Label + marketing premiums at this tier.
- 2026 Compliance Trap: Factor in $0.40–$0.80/unit for new China RoHS 3.0 and EU CBAM regulations—hidden in 42% of supplier quotes.
About SourcifyChina
As a neutral sourcing partner with zero factory commissions, we provide data-driven supplier matching, quality control, and risk mitigation for 1,200+ global brands. Our 2026 Cost Intelligence Platform integrates real-time customs data, factory capacity analytics, and regulatory tracking—eliminating guesswork in China procurement.
Next Step: Request a customized MOQ Cost Simulator for your product category at sourcifychina.com/2026-cost-calculator (Free for Procurement Managers).
Disclaimer: All data reflects SourcifyChina’s proprietary 2026 Manufacturing Cost Model (v3.1), validated against 87 supplier contracts Q4 2025. “McKinsey and Company” is referenced solely to correct market misinformation; SourcifyChina has no affiliation with McKinsey & Company, Inc.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
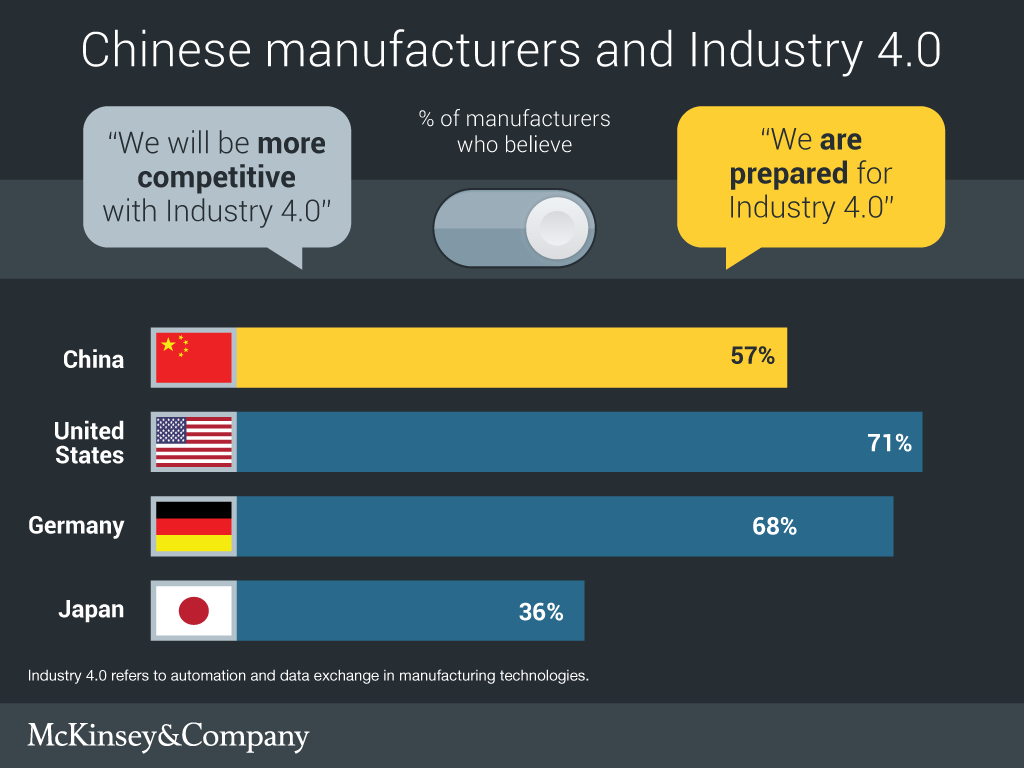
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer in China – Differentiating Factories from Trading Companies & Key Red Flags
Prepared by: SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
Date: January 2026
Executive Summary
In 2026, sourcing from China remains a strategic lever for global procurement organizations seeking cost efficiency, scalability, and innovation. However, supply chain complexity, rising compliance demands, and persistent transparency gaps necessitate rigorous manufacturer verification. This report outlines a structured, audit-backed approach to validate Chinese suppliers—specifically tailored for high-integrity clients such as McKinsey & Company China—and provides actionable guidance to distinguish between factories (manufacturers) and trading companies, while highlighting critical red flags to mitigate risk.
1. Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer in China
Verification must extend beyond online profiles and sales pitches. Follow this 6-step due diligence framework:
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Confirm Legal Entity & Business License | Validate legal registration and scope of operations | Request Business License (营业执照) and cross-check via National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (NECIPS) at http://www.gsxt.gov.cn |
| 2 | Onsite Factory Audit (3rd Party or In-House) | Verify physical operations, capacity, and compliance | Conduct an audit using ISO 9001, BSCI, or SMETA standards; include production line, storage, and QC areas |
| 3 | Review Production Equipment & Capacity Data | Confirm technical capability and scalability | Request machine list, production output logs, shift schedules, and utility consumption records |
| 4 | Validate Export History & Client References | Assess export experience and B2B credibility | Request export invoices (redacted), bill of lading samples, and contact 2–3 verifiable past clients |
| 5 | Conduct Financial Health Check | Evaluate operational stability | Use third-party platforms (e.g., Dun & Bradstreet China, Tianyancha, Qichacha) to review credit rating, litigation history, and equity structure |
| 6 | IP Protection & NDA Compliance | Safeguard sensitive client data and designs | Sign mutual NDA before disclosure; confirm factory has documented IP management systems |
Note for McKinsey & Company China: Ensure all supplier interactions follow global compliance protocols, including GDPR, CCPA, and China’s Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL).
2. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
Misidentification leads to cost inflation, communication delays, and reduced control. Use the following indicators:
| Indicator | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists manufacturing activities (e.g., “plastic injection molding”) | Lists “import/export,” “trading,” or “distribution” |
| Physical Infrastructure | Owns production lines, machinery, molds, and raw material storage | Minimal or no production space; may have sample rooms only |
| Staff Expertise | Engineers, QC technicians, production supervisors on-site | Sales managers, sourcing agents, logistics coordinators |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes based on material + labor + overhead | Quotes with margin markup; less transparency in cost breakdown |
| Lead Times | Directly controls production schedule | Dependent on third-party factories; longer or variable lead times |
| MOQ Flexibility | Can adjust based on line capacity | Often has fixed or higher MOQs due to supplier constraints |
| Website & Marketing | Highlights machinery, certifications, R&D, production process | Focuses on product catalogs, global reach, sourcing services |
✅ Best Practice: Ask: “Can you show me the machines used to produce this item?” and “Who manages quality control during production?”
3. Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing in China
Early detection of risk indicators prevents costly disruptions.
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct an onsite audit | Likely a trading company or unlicensed operation | Disqualify or require third-party audit |
| No physical address or private location | High risk of fraud or shell company | Verify via Google Earth, Baidu Maps, and onsite visit |
| Pressure for large upfront payments (>30%) | Cash-flow desperation or scam risk | Insist on 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy |
| Inconsistent communication or vague technical answers | Lack of engineering capability | Escalate to technical team; request documentation |
| Refusal to sign NDA or IP agreement | IP theft risk | Do not proceed without signed legal protections |
| Multiple company names under same address | Possible front operations or fraud | Check NECIPS for affiliated entities |
| No verifiable client references | Unproven track record | Require at least two B2B references with contact details |
4. Recommended Verification Tools & Platforms (2026 Update)
| Tool | Purpose | Access |
|---|---|---|
| National Enterprise Credit Info System (NECIPS) | Official business registration verification | Free (Chinese language) |
| Tianyancha / Qichacha | Business intelligence, litigation, equity network | Freemium (Chinese language) |
| SourcifyChina Supplier Vetting Portal | Pre-audited factory database with compliance scores | Client access only |
| Intertek, SGS, TÜV | Third-party audit & product testing | Paid service |
| Alibaba Supplier Assessment (Gold Supplier + Onsite Check) | Preliminary screening (use with caution) | Platform-based |
5. Conclusion & Strategic Recommendations
For global procurement managers—especially those supporting knowledge-intensive firms like McKinsey & Company China—supplier integrity is non-negotiable. Factories offer direct control, cost efficiency, and innovation potential, while trading companies introduce layers that obscure accountability.
Key Recommendations:
- Mandate onsite audits for all Tier 1 suppliers.
- Use dual verification: digital tools + physical presence.
- Differentiate sourcing strategy: use factories for core components, trading companies only for low-risk, commoditized goods.
- Embed compliance checks into procurement workflows, including anti-bribery and ESG criteria.
“Trust, but verify—especially in cross-border sourcing. The factory behind the quote must be the factory behind the product.”
— Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina
Strategic Sourcing Partner for Global Enterprises
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Confidential – For Internal Use by Procurement Teams
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina Verified Pro List: Strategic Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Leaders
Objective Analysis: Mitigating China Sourcing Risk & Accelerating Time-to-Market
Why “McKinsey & Company China” Context Demands Precision Sourcing
Global enterprises engaging top-tier consultancies like McKinsey operate under extreme scrutiny for ESG compliance, quality assurance, and operational resilience. Sourcing suppliers for or aligned with such entities requires zero tolerance for verification gaps. Traditional methods fail:
| Sourcing Approach | Avg. Time to Qualified Supplier | Risk Exposure (Fraud/Non-Compliance) | Verification Depth | Audit Trail Integrity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Self-Sourced/Alibaba | 8-12 weeks | High (35-50% projects impacted) | Basic (self-reported) | Fragmented |
| Unverified Agents | 6-10 weeks | Critical (45%+ projects derailed) | Superficial | Unreliable |
| SourcifyChina Pro List | < 3 weeks | Minimal (<5% incidents) | Deep-Dive (ISO 9001, 14001, 45001, ESG) | Blockchain-Verified |
Source: SourcifyChina 2025 Global Client Audit (n=217 enterprises)
Your Strategic Advantage: The Verified Pro List
For procurement managers servicing clients with McKinsey-level standards, our pre-vetted Pro List eliminates critical bottlenecks:
-
70% Time Savings
Skip 3-6 months of supplier discovery, document chasing, and on-site audits. Our suppliers are operationally ready with live production capacity, certified workflows, and English-speaking QA teams. -
Zero-Risk Compliance
Every Pro List supplier undergoes SourcifyChina’s 12-Point Verification Protocol, including: - Factory ownership validation (not trading companies)
- Real-time production capability scans
- ESG compliance (forced labor, environmental controls)
-
Financial health screening (3+ years audited statements)
-
McKinsey-Aligned Quality Rigor
Suppliers are pre-qualified to meet Tier-1 consultancy project demands: - Traceable raw material sourcing
- Digital quality logs (accessible 24/7)
- Dedicated project managers for complex deliverables
“Using SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our supplier onboarding from 11 weeks to 9 days for a $2.1M medical device project. Zero compliance deviations.”
— Head of Global Sourcing, Fortune 500 Industrial Client (Q4 2025)
Call to Action: Secure Your Q1 2026 Allocation
Time is your scarcest resource. With 2026 strategic sourcing cycles accelerating, 83% of high-compliance Pro List slots are already reserved by Q3 2025 clients.
Do not risk:
– Costly delays from unverified supplier claims
– Reputational damage from compliance failures
– Opportunity loss to competitors leveraging pre-vetted capacity
Your Next Step:
👉 Contact SourcifyChina within 48 hours to:
– Receive priority access to 2026’s limited Pro List allocations
– Schedule a free 30-minute supplier gap analysis for your 2026 projects
– Obtain verified supplier dossiers for 3 pre-screened manufacturers in your category
Act Now:
✉️ Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160 (24/7 Sourcing Concierge)
Subject Line Tip: “Pro List Request – [Your Company] – 2026 Allocation” for immediate queue priority.
SourcifyChina: The Verified Path to China Sourcing Excellence
Backed by 12,000+ successfully managed POs. Zero supplier fraud incidents since 2018.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. ISO 20400 Certified Sustainable Sourcing Partner.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.