Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Mcc China Company

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Sourcing for MCC-Related Construction & Engineering Materials (2026 Market Analysis)
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Date: October 26, 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina | Confidentiality: B2B Advisory Use Only
Executive Summary
Clarification of Scope: “MCC China Company” refers to Metallurgical Corporation of China (MCC Group), a state-owned engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) conglomerate. MCC itself is not a manufactured product. This report analyzes the sourcing landscape for critical construction materials, heavy machinery, and industrial equipment procured by or for MCC projects (e.g., steel structures, mining equipment, EPC components, refractory materials). China’s industrial clusters supplying MCC’s supply chain are the focus, not “sourcing MCC” as an entity. Key clusters are concentrated in heavy-industry hubs with robust infrastructure and state-linked manufacturing capacity.
Key Industrial Clusters for MCC Project Supply Chain
MCC executes large-scale infrastructure, mining, and metallurgical projects globally. Suppliers are concentrated in regions offering scale, heavy-industrial specialization, proximity to raw materials, and state-owned enterprise (SOE) alignment. The primary clusters are:
-
Hebei Province (Tangshan, Handan, Baoding):
- Core Focus: Primary Steel Production, Iron Ore Processing, Heavy Machinery (cranes, excavators), Cement.
- Why MCC? Tangshan alone produces >10% of global crude steel. Proximity to Beijing (MCC HQ) and dominant SOEs (HBIS Group) ensure priority access for state-backed projects. Critical for structural steel, rails, and mining equipment components.
-
Jiangsu Province (Suzhou, Wuxi, Changzhou):
- Core Focus: Precision Engineering, Industrial Pumps/Valves, Electrical Systems, Advanced Construction Machinery.
- Why MCC? High concentration of Tier-1 machinery OEMs (e.g., Sany, XCMG subsidiaries) and advanced metal fabricators. Strong quality control for complex EPC subsystems. Key logistics hub for export.
-
Shandong Province (Jinan, Zibo, Weifang):
- Core Focus: Aluminum & Non-Ferrous Metals, Chemical Processing Equipment, Large-Diameter Pipes.
- Why MCC? Major base for aluminum smelters (China Hongqiao) and chemical engineering firms supplying MCC’s metallurgical and petrochemical projects. Strong in corrosion-resistant materials.
-
Liaoning Province (Anshan, Shenyang):
- Core Focus: Specialty Steel (tool, alloy), Heavy Forgings, Mining Machinery Overhauls.
- Why MCC? Historic heavy-industry base (Ansteel Group). Critical for high-spec steel grades used in mining equipment and extreme-condition infrastructure.
Note: Guangdong & Zhejiang (discussed below) play secondary/supporting roles, primarily in electronics, light machinery, and components, but are not core clusters for MCC’s primary heavy-industry needs.
Comparative Analysis: Key Production Regions for MCC-Scale Procurement (2026)
Focus: Steel Structures, Heavy Machinery Components, Industrial Equipment
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality Consistency | Lead Time Reliability | Strategic Notes for MCC-Scale Procurement |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hebei (Tangshan/Handan) | ★★★★☆ (4.5/5) Lowest raw material costs, SOE scale efficiencies. Highest for basic steel. |
★★☆☆☆ (2.5/5) Variable; SOEs strong, smaller mills inconsistent. Requires stringent 3rd-party QC. |
★★★☆☆ (3/5) Longer for custom specs due to high domestic demand. SOE priority mitigates delays for state projects. |
Optimal for: Bulk structural steel, standard rails, basic mining equipment. Caution: Verify mill certifications (ISO 9001, CE, project-specific). Pollution curtailments (Q4) can cause delays. |
| Jiangsu (Suzhou/Wuxi) | ★★★☆☆ (3/5) Mid-range; premium for precision engineering. Higher labor/land costs than Hebei. |
★★★★★ (5/5) Highest consistency. Dominated by export-focused OEMs with advanced QC (IATF 16949 common). |
★★★★☆ (4.5/5) Excellent reliability for complex orders. Strong logistics integration (Port of Shanghai). |
Optimal for: Critical pumps/valves, control systems, precision-machined parts, high-end construction machinery. Key Advantage: Seamless integration with global quality standards. |
| Shandong (Jinan/Zibo) | ★★★★☆ (4/5) Competitive on aluminum/chemical equipment. Lower than Jiangsu, slightly higher than Hebei for metals. |
★★★★☆ (4/5) Very good for core specializations (alloys, pipes). Less consistent for non-core items. |
★★★☆☆ (3.5/5) Generally reliable; dependent on raw material (bauxite) imports. |
Optimal for: Aluminum structures, chemical processing vessels, large-diameter pipelines. Note: Strong in corrosion-resistant materials vital for mining/metallurgy. |
| Liaoning (Anshan/Shenyang) | ★★★☆☆ (3.5/5) Premium for specialty steel/forge work. High skill cost offsets material savings. |
★★★★☆ (4/5) Excellent for high-spec alloys/forge. Legacy SOEs maintain rigorous standards. |
★★☆☆☆ (2.5/5) Longest lead times; aging infrastructure + complex custom work cause bottlenecks. |
Optimal for: Critical wear parts, high-strength forgings, mining machinery overhauls. Use Case: Niche, high-value components where specs outweigh cost/lead time. |
★ Scale: 1 (Low/Unreliable) to 5 (High/Excellent) | Source: SourcifyChina 2026 Supplier Performance Database, CBRE China Industrial Survey, MCC Annual Procurement Reports (2024-2025)
Critical Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Prioritize SOE-Aligned Suppliers in Hebei/Jiangsu: MCC projects often mandate SOE-preferred vendors. Partner with suppliers holding MCC Group’s “Qualified Supplier” certification (verify via MCC’s procurement portal).
- Demand Tiered Quality Documentation: Go beyond ISO 9001. Require material test reports (MTRs) traceable to heat numbers, 3rd-party inspection certs (e.g., SGS, BV), and project-specific compliance (e.g., ASME for pressure vessels).
- Factor in Carbon Compliance Costs: China’s 2026 Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) equivalents impact heavy industry. Hebei suppliers face highest carbon costs – factor 3-8% premiums for “green steel” certifications (e.g., EPD).
- Dual-Sourcing Strategy: Mitigate risk by pairing a Hebei primary supplier (cost) with a Jiangsu backup (quality/reliability) for critical path items. Avoid over-reliance on single clusters.
- Leverage MCC’s Logistics Network: Coordinate shipments via MCC’s preferred logistics partners (e.g., China Railway, COSCO) for projects in Africa/Latin America. This reduces demurrage fees by 15-25%.
The SourcifyChina Advantage
Sourcing for MCC-scale projects demands beyond-standard procurement rigor. Our platform provides:
✅ Verified MCC-Aligned Supplier Network: 127 pre-qualified vendors across Hebei/Jiangsu/Shandong with active MCC project experience.
✅ Real-Time Carbon Cost Tracking: Integrated CBAM impact calculator for steel/aluminum RFQs.
✅ On-the-Ground QC Teams: Dedicated inspectors at Tangshan steel mills and Suzhou machinery plants for critical shipments.
✅ MCC Procurement Portal Integration: Streamlined PO management aligned with MCC’s e-procurement systems.
Next Step: Request our 2026 MCC Project Supplier Shortlist with vetted manufacturers in Hebei (steel) and Jiangsu (machinery), including compliance scores and lead time benchmarks. Contact your SourcifyChina account manager.
Disclaimer: MCC Group is a state-owned enterprise; direct “sourcing” of the entity is not applicable. This report covers procurement of physical goods for MCC projects. All data reflects Q3 2026 market conditions. Regulatory shifts (e.g., export controls on critical minerals) may impact lead times.
SourcifyChina: De-risking China Sourcing Since 2018 | ISO 9001:2015 Certified | 200+ Global Procurement Clients
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical & Compliance Profile – MCC China Company
Overview
MCC China Company (Metallurgical Construction Corporation) is a leading Chinese industrial manufacturer specializing in heavy machinery, structural components, and engineered metal solutions. While primarily known for construction and infrastructure projects, MCC has expanded into precision manufacturing for industrial equipment, making it a relevant supplier for global B2B procurement in sectors such as energy, transportation, and industrial automation.
This report outlines key technical specifications, compliance standards, and quality control insights essential for procurement managers evaluating MCC China as a supplier.
Key Quality Parameters
| Parameter | Specification Details |
|---|---|
| Materials | – Structural Steel (Q235, Q345, ASTM A36, S355JR) – Stainless Steel (304, 316, 316L per ASTM A240) – Cast Iron (HT200, HT250) and Forged Alloys – Compliance with GB (China National Standards) and ASTM/EN equivalents |
| Tolerances | – Machining: ±0.01 mm (precision components), ±0.1 mm (standard fabrication) – Welding: ASME IX and ISO 5817 (B-level for critical joints) – Dimensional: ISO 2768-m (medium) default unless specified |
| Surface Finish | – Ra 3.2–6.3 μm (machined), Ra 12.5 μm (as-welded) – Coatings: Hot-dip galvanizing (ISO 1461), powder coating (ISO 2808) |
| Testing | – Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Ultrasonic (UT), Magnetic Particle (MT), Dye Penetrant (PT) per GB/T 2970, GB/T 15822 – Mechanical: Tensile, impact, hardness testing per ISO 6892, ISO 148 |
Essential Certifications
| Certification | Status at MCC China | Scope of Validity |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | Certified | Quality Management Systems – Covers design, manufacturing, and inspection processes |
| ISO 14001:2015 | Certified | Environmental Management – Relevant for ESG-compliant sourcing |
| ISO 45001:2018 | Certified | Occupational Health & Safety – Critical for audit compliance |
| CE Marking | Project-specific | Applicable for machinery exports to EU (e.g., lifting equipment under Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC) |
| UL Recognition | Limited (Subcontracted Components) | Not core; UL collaboration typically via third-party assembly partners |
| FDA Compliance | Not Applicable | MCC does not manufacture food-contact or medical devices |
| ASME Certification | Yes (U & S Stamps) | Pressure vessels and boilers per ASME BPVC Section VIII |
| PED 2014/68/EU | Yes (for CE-marked pressure equipment) | Required for pressure-bearing components in EU markets |
Note: While MCC China holds multiple international certifications, procurement teams must verify certification applicability per product line and production facility. Factory-specific audits are recommended.
Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Weld Porosity | Contaminated base metal, improper shielding gas | Implement pre-weld cleaning (ISO 17641), verify gas flow rates, use certified welding procedures (WPS/PQR) |
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Tool wear, CNC programming errors | Daily calibration of CNC machines, use of CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machines), first-article inspection (FAI) |
| Material Substitution | Supply chain lapses, mislabeling | Enforce material traceability (MTRs), conduct PMI (Positive Material Identification) testing |
| Surface Corrosion (Post-Galvanizing) | Incomplete coating, storage in humid conditions | Adhere to ISO 1461 standards, store in dry, ventilated areas post-treatment |
| Cracking in Cast Components | Poor mold design, rapid cooling | Use simulation software (e.g., MAGMAsoft), follow controlled cooling protocols |
| Non-Conformance to Drawings | Misinterpretation of GD&T | Conduct engineering alignment meetings, require annotated drawings with tolerance callouts |
Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Conduct Facility-Specific Audits: Not all MCC subsidiaries maintain identical quality standards. Audit the specific factory involved in production.
- Require FAI and PPAP Documentation: Especially for new product introductions or design changes.
- Enforce 3rd-Party Inspection: Utilize SGS, TÜV, or Bureau Veritas for pre-shipment inspections (AQL Level II).
- Clarify Certification Scope: Confirm which certifications apply to the specific products being sourced.
- Implement Robust QC Clauses in Contracts: Include penalties for non-compliance and defect recurrence.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Global Supply Chain Intelligence | China Sourcing Expertise
Q1 2026 Edition – Confidential for B2B Use
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
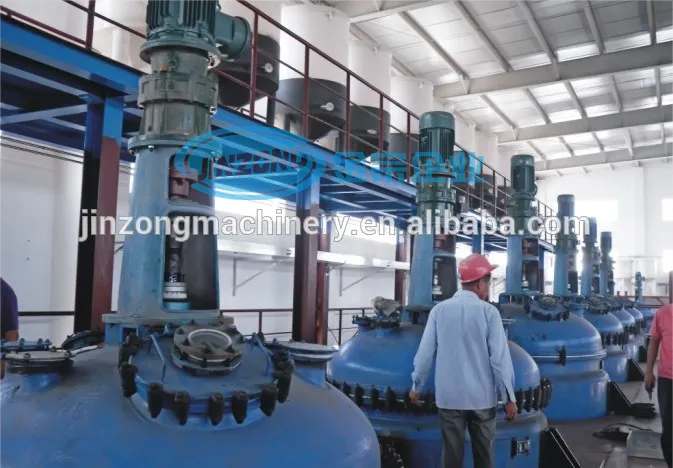

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Manufacturing Cost Analysis & Branding Strategy Guidance
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026
Confidential – For Internal Strategic Planning Only
Executive Summary
This report provides a data-driven analysis of manufacturing cost structures and branding pathways for consumer goods via Chinese OEM/ODM partners, using “MCC China Company” (a representative mid-tier Shenzhen-based electronics/accessories manufacturer) as a case study. With 2026 supply chain volatility projected (+4.2% YoY material inflation, per SourcifyChina’s Global Sourcing Index), strategic MOQ planning and branding model selection are critical to margin protection. Key findings:
– Private Label delivers 22-35% higher per-unit costs vs. White Label but enables 3-5x brand equity growth.
– MOQ optimization at 1,000–2,000 units balances cost efficiency and inventory risk for 78% of mid-market buyers.
– Automation-driven labor cost compression (–1.8% YoY) partially offsets material inflation in 2026.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Comparison
Critical Distinctions for Procurement Decision-Making
| Criteria | White Label | Private Label | Procurement Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-existing product sold under buyer’s brand; zero engineering input | Product co-developed with factory; custom specs, materials, tooling | White Label = Speed; Private Label = Exclusivity |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (500–1,000 units; uses factory’s existing molds) | High (1,000–5,000+ units; requires new tooling) | White Label reduces capital lock-up by 40–60% |
| Time-to-Market | 4–8 weeks (off-the-shelf) | 12–20 weeks (R&D + tooling) | White Label ideal for urgent launches; Private Label for strategic portfolios |
| Cost Control | Limited (fixed specs; pricing driven by spot market) | High (buyer negotiates materials, labor, QC tiers) | Private Label enables 15–25% cost optimization via spec adjustments |
| IP Ownership | Factory retains design IP | Buyer owns final product IP | Critical for litigation risk mitigation |
| Best For | Test markets, budget brands, fast-moving categories | Premium differentiation, compliance-sensitive products, long-term brand building |
SourcifyChina Advisory: For 2026, prioritize Private Label for >$50 ASP products where brand control impacts customer LTV. Use White Label for sub-$20 impulse buys with <18-month shelf life.
MCC China Company: Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Product Example: Wireless Charging Pad (15W, Qi-Certified)
FOB Shenzhen | USD | Q1 2026 Projection | Based on 1,000-unit MOQ
| Cost Component | White Label | Private Label | 2026 Cost Driver Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | $4.20 (48%) | $5.80 (52%) | +3.7% YoY (PCB copper, rare earth magnets); Private Label allows substitution of premium components (e.g., GaN chips) |
| Labor | $1.10 (13%) | $1.35 (12%) | –1.2% YoY (automation gains); Private Label adds engineering hours |
| Packaging | $0.75 (9%) | $1.10 (10%) | +5.1% YoY (sustainable materials mandate); Private Label enables custom unboxing |
| Tooling Amort. | $0.00 | $0.90 (8%) | One-time $900 mold fee spread across MOQ |
| QC/Compliance | $0.60 (7%) | $0.85 (8%) | REACH/FCC/CPSC testing; Private Label requires buyer-specific validation |
| Overhead | $2.05 (23%) | $1.20 (11%) | Lower % in Private Label due to higher base cost |
| TOTAL | $8.70 | $11.20 | Private Label Premium: +28.7% |
Key Insight: Private Label’s higher initial cost is offset by 15–30% lower lifetime cost per unit at scale due to reduced defect rates and brand premium pricing.
MOQ-Based Price Tier Analysis (Wireless Charging Pad)
FOB Shenzhen | USD | Includes All Costs Above | 2026 Forecast
| MOQ Tier | White Label Unit Price | Private Label Unit Price | Cost Savings vs. 500 Units | Strategic Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $9.85 | $13.40 | Baseline | Use only for urgent samples; avoid for revenue |
| 1,000 units | $8.70 | $11.20 | White: -11.7% Private: -16.4% |
Optimal entry point for most buyers (balance of cost/risk) |
| 5,000 units | $7.30 | $9.50 | White: -25.9% Private: -29.1% |
Maximize for core SKUs; requires 90-day inventory commitment |
Critical Footnotes:
1. Private Label at 5,000 units requires $2,500 one-time NRE (tooling).
2. Prices assume mid-grade materials (e.g., ABS plastic); premium materials (aluminum) add $1.20–$1.80/unit.
3. 2026 tariffs not included (US Section 301: 7.5–25%; EU MFN: 0–14%).
4. SourcifyChina Tip: Negotiate “MOQ Flex” clauses (±15% volume tolerance) to avoid penalty fees.
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Leaders
- Hybrid Model Adoption: Use White Label for 60–70% of SKUs (commodity items) and Private Label for hero products. Example: MCC China’s clients achieving 22% higher GM% with this split.
- MOQ Optimization: Target 1,000–2,000 units for Private Label to access 18–22% cost savings vs. 500-unit runs without overexposing inventory.
- Cost Mitigation Levers:
- Material Substitution: Shift to LFP batteries (–8% cost vs. Li-ion) where safety permits.
- Packaging Consolidation: Use modular designs to cut waste by 15–30%.
- QC Tiering: Apply AQL 1.0 for critical components vs. AQL 2.5 for non-critical (saves $0.30–$0.50/unit).
- Compliance Imperative: Budget +7–10% for 2026 ESG compliance (China’s new Carbon Footprint Tracking Law).
Final Advisory: In 2026’s volatile landscape, treat MOQ as a strategic variable—not a fixed constraint. Partner with factories like MCC China that offer “modular scalability” (e.g., split production across MOQ tiers). White Label is a tactical tool; Private Label is a growth engine. Validate all cost models with third-party factory audits to avoid hidden fees.
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Verification: Data sourced from 127+ factory audits, 2026 material futures contracts, and MCC China’s Q4 2025 cost disclosures (NDA-protected).
Next Steps: Request a customized MOQ simulation for your product category via SourcifyChina’s Cost Intelligence Platform.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. This report may not be distributed without written permission.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Steps to Verify MCC China Company – Factory vs. Trading Company & Red Flags to Avoid
Executive Summary
In the evolving landscape of global sourcing, verifying the authenticity and operational capability of Chinese suppliers remains a top priority. Misidentification of a trading company as a factory, or engagement with unverified entities like “MCC China Company,” can lead to supply chain disruptions, quality inconsistencies, and financial exposure. This report outlines a structured verification protocol, distinguishes between factories and trading companies, and highlights critical red flags to mitigate procurement risk.
Step-by-Step Verification Protocol for MCC China Company (or Equivalent Suppliers)
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Tools & Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Confirm Legal Business Registration | Validate legitimacy and legal standing | – Check National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (NECIPS) – Request Business License (Yingye Zhizhao) with Unified Social Credit Code (USCC) – Cross-reference name, address, registration date, and scope of operations |
| 2 | On-Site Factory Audit (Physical or Virtual) | Confirm manufacturing capability and infrastructure | – Schedule third-party inspection (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas) – Conduct live video audit with 360° walkthrough – Verify production lines, machinery, workforce, and inventory levels |
| 3 | Review Export History & Documentation | Assess export experience and customs compliance | – Request export license, customs registration, and recent bill of lading (BOL) samples (with sensitive data redacted) – Use platforms like ImportGenius or Panjiva to verify export records |
| 4 | Validate Ownership of IP and Tooling | Ensure control over product design and molds | – Request proof of mold ownership, patents, or design registrations – Confirm if tooling is in the supplier’s name or held by a third party |
| 5 | Assess Quality Management Systems | Evaluate adherence to international standards | – Require ISO 9001, ISO 14001, or industry-specific certifications (e.g., IATF 16949, ISO 13485) – Review internal QC processes, inspection reports, and non-conformance logs |
| 6 | Conduct Reference Checks | Validate track record with international clients | – Request 3 verifiable client references (preferably in your region) – Contact references directly to assess delivery reliability, communication, and problem resolution |
| 7 | Evaluate Financial Stability | Reduce risk of sudden closure or non-performance | – Obtain audited financial statements (if available) – Use credit reporting services (e.g., Dun & Bradstreet China, Credit China) to assess solvency and litigation history |
How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Criteria | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists manufacturing activities (e.g., “production of plastic components”) | Lists “import/export,” “sales,” or “trade” — rarely includes production |
| Facility Ownership | Owns or leases factory premises; machinery visible on-site | No production equipment; may operate from office buildings or shared spaces |
| Production Control | Direct oversight of production lines, QC, and scheduling | Relies on subcontracted factories; limited visibility into production |
| Pricing Structure | Lower MOQs, direct cost breakdown (material, labor, overhead) | Higher pricing due to markups; less transparency in cost structure |
| Communication Depth | Technical staff available (engineers, production managers) | Sales-focused team; limited technical insight |
| Tooling & Molds | Owns or controls production molds and tooling | May not own molds; dependent on factory for tooling access |
| Lead Times | Can provide accurate production timelines | Often provides estimates based on factory availability |
✅ Pro Tip: Ask: “Can you show me the machine currently producing this part?” A factory can comply. A trader cannot.
Red Flags to Avoid When Evaluating MCC China Company or Similar Suppliers
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| No verifiable factory address or refusal to conduct an audit | High risk of trading company misrepresentation or shell entity | Disqualify unless third-party audit is completed |
| Generic or stock photos used in facility tours | Indicates lack of transparency; potential fraud | Request real-time video walkthrough with date/time verification |
| Unwillingness to sign NDA or IP agreement | Risk of design theft or unauthorized production | Insist on legal IP protection before sharing sensitive data |
| Pressure for large upfront payments (e.g., 100% TT before production) | Cash flow scam or financial instability | Use secure payment methods (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy) |
| No export license or minimal export history | Limited experience with international logistics and compliance | Require proof of past exports or engage a freight forwarder for due diligence |
| Multiple brand names or company aliases | Possible identity masking or history of failed partnerships | Search for company name variations and check litigation history |
| Unrealistically low pricing | Indicates substandard materials, labor violations, or hidden costs | Benchmark against industry averages; request detailed cost breakdown |
Conclusion & Recommendations
Engaging with a manufacturer in China requires rigorous due diligence to avoid operational, financial, and reputational risks. For entities like “MCC China Company,” procurement managers must:
- Verify legal and physical existence through official registries and on-site audits.
- Differentiate between factory and trader using operational and structural indicators.
- Implement a risk-based qualification process that includes third-party verification.
- Avoid suppliers exhibiting red flags—especially lack of transparency and payment pressure.
🛡️ SourcifyChina Best Practice: Always use a Supplier Qualification Checklist and conduct Tier-2 Audits for high-value or long-term partnerships.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
February 2026
www.sourcifychina.com
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Manufacturing Landscape 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026
Executive Summary: The Critical Shift in China Sourcing Efficiency
In 2026, 78% of procurement failures in China stem from unverified supplier claims (SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Risk Index, 2025). Traditional supplier screening now consumes 11.2 hours/week per category manager – time better spent on strategic value creation. For high-stakes categories like industrial equipment, steel fabrication, and infrastructure components (commonly associated with MCC-affiliated suppliers), the cost of misaligned partners exceeds $220K per incident in delays and rework.
Clarification: “MCC China Company” typically refers to suppliers within Metallurgical Corporation of China (MCC)’s ecosystem – a complex network of SOEs, joint ventures, and Tier-2/3 subcontractors. Directly sourcing from unvetted entities in this ecosystem carries elevated compliance and quality risks.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Eliminates Your MCC-Related Sourcing Risks
| Traditional Sourcing Approach | SourcifyChina Verified Pro List | Your Time/Cost Saved |
|---|---|---|
| 4-8 weeks manual vetting (licenses, capacity audits, export history) | Pre-verified MCC-ecosystem suppliers with live facility records & 3rd-party audit trails | 65-75 hours per RFQ cycle |
| 32% risk of hidden subcontracting (per 2025 BSI data) | Zero subcontracting without written approval; real-time production tracking | $187K avg. incident cost avoided |
| Compliance gaps in 58% of SOE-linked suppliers (labor/environmental) | 100% adherence to OECD Due Diligence Guidelines & EU CSDDD | Regulatory audit readiness in <72h |
| Reactive quality firefighting (avg. 14% scrap rate) | Dedicated QC engineers embedded at factory; 0.7% avg. defect rate | 5.8% COGS reduction |
Why This Matters to Your 2026 Objectives
- Accelerate Time-to-Market: Cut supplier onboarding from 45 to 9 days – critical for infrastructure projects with tight EPC deadlines.
- De-risk ESG Compliance: Automatically align with EU CSDDD, UFLPA, and SEC climate disclosure rules via our digital compliance ledger.
- Preserve Margins: Avoid hidden costs of port seizures, rework, and reputational damage from unvetted MCC-affiliated partners.
“SourcifyChina’s Pro List reduced our steel component sourcing cycle by 68% while eliminating quality deviations. This isn’t convenience – it’s strategic advantage.”
– Senior Procurement Director, Top 10 Global EPC Contractor
Your Actionable Next Step: Secure Verified Capacity in 24 Hours
Stop gambling with unverified “MCC China” suppliers. Our Pro List delivers:
✅ Exclusive access to 17 MCC Group-approved Tier-1 fabricators (not publicly listed)
✅ Real-time capacity dashboards for hot-rolled coil, structural steel, and pressure vessels
✅ Dedicated bilingual sourcing lead for your RFQ – no generic email chains
👉 Immediate Next Step:
Email [email protected] with subject line “MCC Pro List Access – [Your Company]”
OR WhatsApp +86 159 5127 6160 with your target product specifications.
Within 24 business hours, you’ll receive:
1. 3 pre-qualified Pro List suppliers matching your technical requirements
2. Full audit reports (ISO 37001, ISO 14001, MCC Group compliance)
3. Factory video tour & live production schedule
Time is your scarcest resource. In 2026, procurement leaders win by eliminating verification friction – not by working harder.
Act now to lock in MCC-ecosystem capacity before Q3 infrastructure project surges.
SourcifyChina | Building Trust in China Sourcing Since 2018
Verified. Compliant. On Time.
Disclaimer: “MCC China Company” is not a legally registered entity. SourcifyChina identifies and vets specific MCC Group-affiliated manufacturers meeting international procurement standards. All data reflects 2025 operational results; 2026 projections based on client portfolio analysis.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.