The global mass flow rate controller market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision flow control in industries such as semiconductor manufacturing, chemical processing, oil & gas, and pharmaceuticals. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at approximately USD 4.2 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.8% from 2023 to 2028. Similarly, Grand View Research estimates that the market will expand at a CAGR of 6.1% during the forecast period of 2023–2030, underpinned by advancements in automation and process optimization technologies. This sustained growth trajectory reflects rising investments in industrial automation and stringent regulatory standards requiring accurate gas and liquid flow measurement. As demand intensifies, several manufacturers have emerged as leaders in innovation, reliability, and global market reach. Below is a data-driven overview of the top 10 mass flow rate controller manufacturers shaping the future of process control across high-tech industries.
Top 10 Mass Flow Rate Controller Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Flow Control & Measurement
Domain Est. 1996
Website: brooksinstrument.com
Key Highlights: As the leading global mass flow control and flow meter manufacturer, Brooks Instrument offers the world’s most comprehensive line of precision flow control and ……
#2 Aalborg, Manufacturer of High Quality Flow Instrumentation
Domain Est. 1996
Website: aalborg.com
Key Highlights: Mass Flow Controllers, Variable Area Meters & Valves · Product Overviews · Product Configurator · Catalog in PDF · Select product configurations available in 24 ……
#3 Mass Flow Controllers
Domain Est. 1989
Website: mks.com
Key Highlights: Find the Perfect Mass Flow Controller with MKS. Wide range of MFCs for diverse flow rates and gases. Reliable flow measurement & control….
#4 Mass Flow Controller and Module
Domain Est. 1994
Website: horiba.com
Key Highlights: HORIBA is the recognised leader of high performance mass flow meters, mass flow controllers, automatic pressure controllers and liquid vaporization systems….
#5 Mass Flow Controllers
Domain Est. 1995
Website: parrinst.com
Key Highlights: Mass Flow Controllers add an automated control valve to the mass flow meter to provide gas flows that are proportional to an electronic set point….
#6 Sierra Instruments
Domain Est. 1997
Website: sierrainstruments.com
Key Highlights: We design and manufacture high-performance thermal mass flow controllers, immersible thermal mass flowmeters, vortex flow meters and transit-time ultrasonic ……
#7 Our mass flow controllers
Domain Est. 1998
Website: bronkhorst.com
Key Highlights: A mass flow controller precisely controls the flow rate of gas or liquid within a system. Acting as a regulator, an MFC ensures that the correct amount of gas ……
#8 Alicat Scientific
Domain Est. 2000
Website: alicat.com
Key Highlights: High performance gas flow, liquid flow and pressure meters and controllers. Custom-built, tuned, and calibrated all on short lead times….
#9 Rheonik
Domain Est. 2001
Website: rheonik.com
Key Highlights: Worldwide unmatched design and performance Coriolis Mass Flow Meter. Flow rates from 0.002 to 30000 kg/min, very high pressure rates and exotic materials….
#10 Mass Flow Online web shop for Gas & Liquids meters
Domain Est. 2004
Website: massflow-online.com
Key Highlights: We offer online cost effective, high quality flow measurement and control instruments, not requiring customer specific advice or a quotation….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Mass Flow Rate Controller
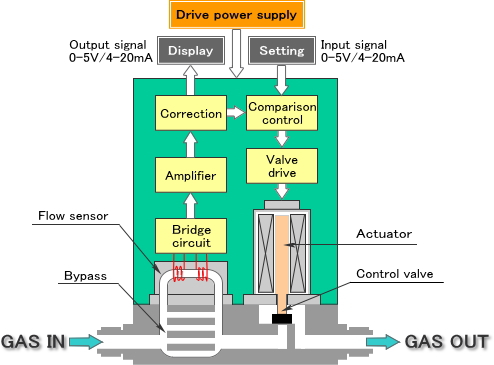
H2: Projected Market Trends for Mass Flow Rate Controllers in 2026
The global market for Mass Flow Rate Controllers (MFCs) is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, expanding industrial applications, and increasing demand for precision in automation and process control. Below are the key market trends expected to shape the MFC landscape in 2026:
-
Growth in Semiconductor and Electronics Manufacturing
The semiconductor industry remains a dominant end-user of MFCs due to the critical need for precise gas delivery in deposition, etching, and doping processes. With continued expansion in semiconductor fabrication facilities (fabs), especially in Asia-Pacific and North America, demand for high-accuracy and fast-response MFCs is expected to rise. Advancements in 3D NAND and EUV lithography will further drive the need for next-generation MFCs capable of handling ultra-pure gases with minimal contamination. -
Adoption of Digital and Smart MFCs
By 2026, digital MFCs with integrated communication protocols (e.g., EtherCAT, Modbus, and PROFINET) will gain market share over traditional analog models. The integration of IoT and Industry 4.0 technologies enables real-time monitoring, remote diagnostics, and predictive maintenance. Smart MFCs with embedded sensors and self-calibration features will enhance process efficiency and reduce downtime in industrial settings. -
Expansion in Renewable Energy and Green Technologies
The growing focus on clean energy is fostering new applications for MFCs in hydrogen fuel cell production, electrolysis, and carbon capture systems. As green hydrogen gains traction globally, MFCs will play a vital role in controlling hydrogen and oxygen flow with high precision, supporting the scalability and safety of these systems. -
Increased Demand in Life Sciences and Biopharmaceuticals
The biopharmaceutical sector is increasingly utilizing MFCs in bioreactors, fermentation processes, and lab automation. The push for personalized medicine and advanced cell therapies will require highly reliable and sterile-compatible MFCs, accelerating innovation in materials (e.g., corrosion-resistant alloys) and sealing technologies. -
Regional Market Shifts and Supply Chain Localization
While North America and Europe maintain strong demand due to advanced manufacturing and R&D activities, the Asia-Pacific region—particularly China, South Korea, and Taiwan—is expected to lead market growth. Localized production and reduced dependency on Western suppliers will drive regional MFC manufacturing, encouraging partnerships between global suppliers and local players. -
Miniaturization and Customization Trends
There is a growing need for compact, low-flow MFCs in portable medical devices, analytical instruments, and microfluidic systems. Manufacturers are focusing on modular designs and customizable solutions to meet specific client requirements across diverse industries, enhancing product differentiation. -
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Focus
Regulatory pressures and corporate sustainability goals are pushing MFC manufacturers to develop energy-efficient models with lower power consumption and reduced environmental impact. Emphasis on recyclable materials and longer product lifecycles will become key selling points.
In summary, the 2026 mass flow rate controller market will be characterized by innovation in digitalization, increased adoption across emerging industries, and geographic diversification. Companies that invest in smart technologies, sustainability, and application-specific solutions are likely to gain a competitive edge in this evolving landscape.
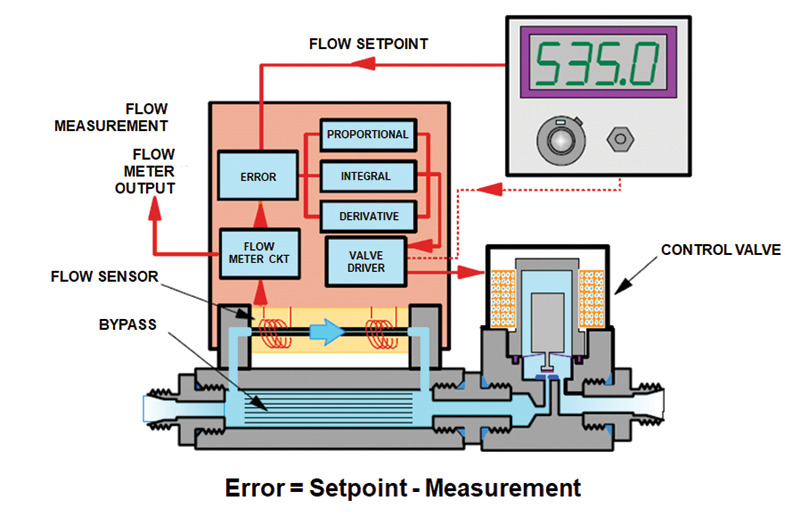
When sourcing Mass Flow Rate Controllers (MFCs) for hydrogen (H₂) service, several common pitfalls can compromise safety, performance, and long-term reliability. Hydrogen’s unique properties—small molecular size, high diffusivity, flammability, and potential for embrittlement—make it especially challenging. Below are key pitfalls related to quality and Ingress Protection (IP) rating, with specific emphasis on H₂ applications:
1. Poor Material Compatibility (Quality Issue)
Pitfall: Using MFCs with materials not rated for hydrogen service.
- Hydrogen Embrittlement: H₂ can diffuse into certain metals (e.g., carbon steel, some stainless steels), causing embrittlement and catastrophic failure over time.
- Seal Degradation: Common elastomers (e.g., NBR, EPDM) swell, crack, or degrade in H₂ environments.
✅ Solution:
– Use hydrogen-compatible materials: 316L stainless steel, Monel, or Hastelloy wetted parts.
– Select seals made from perfluoroelastomers (FFKM) or PTFE-based materials.
– Verify material certifications (e.g., ASTM G174, NACE MR0175/ISO 15156 for H₂ environments).
2. Inadequate Leak Integrity (Quality Issue)
Pitfall: MFCs not tested or certified for low-leak performance with H₂.
- Hydrogen molecules are the smallest and most prone to leakage, even through microscopic gaps.
- Poor sealing or substandard manufacturing can result in dangerous H₂ leaks (flammability range: 4–75% in air).
✅ Solution:
– Specify MFCs with helium leak testing (e.g., <1×10⁻⁹ atm·cm³/s He).
– Look for ISO 10942 or CGA G-9.1 compliance for hydrogen equipment.
– Prefer welded or metal-sealed designs over O-ring or elastomer-based seals.
3. Incorrect IP Rating for Environment (IP Issue)
Pitfall: Selecting MFCs with insufficient Ingress Protection (IP) for the operating environment.
- H₂ systems are often used in outdoor, industrial, or washdown environments where dust and moisture are present.
- An IP65-rated MFC may be insufficient if exposed to high-pressure water jets or heavy dust.
✅ Solution:
– Choose IP66 or IP67 for harsh environments (e.g., outdoor H₂ refueling stations, chemical plants).
– For washdown or marine applications, consider IP69K if high-pressure/temperature cleaning is used.
– Ensure conduit entries and cable glands also meet the same IP rating.
4. Lack of H₂-Specific Calibration and Certification (Quality Issue)
Pitfall: Using MFCs calibrated for air or N₂, not H₂.
- MFCs are typically calibrated for specific gases. Using an N₂-calibrated MFC for H₂ without correction leads to significant flow measurement errors due to differences in thermal conductivity and viscosity.
✅ Solution:
– Source MFCs specifically calibrated for hydrogen.
– Verify NIST-traceable certification and request calibration certificates for H₂.
– Consider MFCs with multi-gas capability and built-in H₂ correction factors.
5. Ignoring Safety Standards and Certifications (Quality & Compliance)
Pitfall: Selecting non-certified MFCs for hazardous (ATEX, IECEx) or high-pressure H₂ zones.
- H₂ is classified as a Zone 1 or Zone 2 hazardous area in many installations.
✅ Solution:
– Ensure MFCs have ATEX, IECEx, or UL/CSA hazardous location certifications if used in explosive atmospheres.
– Confirm pressure rating compatibility with system requirements (H₂ systems often operate at 350–700 bar).
6. Overlooking Long-Term Stability and Drift (Quality Issue)
Pitfall: Choosing low-cost MFCs with poor long-term stability in H₂ environments.
- H₂ can affect sensor performance over time, especially in thermal-based MFCs (e.g., thermal dispersion sensors).
✅ Solution:
– Opt for MFCs with long-term drift specifications <1% per year.
– Select models with auto-zeroing or in-situ calibration features.
– Prefer Coriolis-based MFCs for highest accuracy and stability with H₂ (though more expensive).
Summary Checklist When Sourcing H₂ MFCs:
| Criteria | Recommendation |
|——–|—————-|
| Wetted Materials | 316L SS, Monel, FFKM/PTFE seals |
| Leak Rate | <1×10⁻⁹ atm·cm³/s He (helium tested) |
| Calibration | H₂-specific, NIST-traceable |
| IP Rating | IP66/IP67 minimum (IP69K for washdown) |
| Certifications | ATEX/IECEx (if in hazardous area), CGA G-9.1 |
| Sensor Type | Thermal (H₂-calibrated) or Coriolis for precision |
Final Note:
Never compromise on quality when handling hydrogen. The cost of failure—due to leaks, inaccurate dosing, or component degradation—far exceeds the upfront cost of a properly specified MFC. Always consult with manufacturers experienced in hydrogen service and request application-specific validation data.
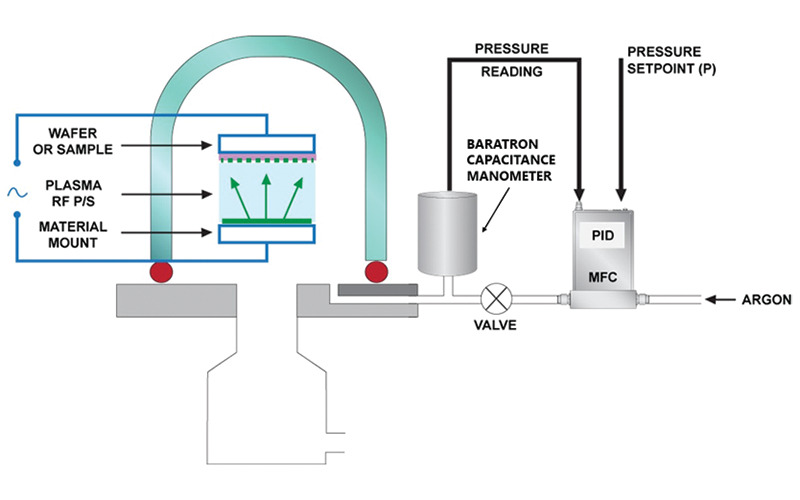
Hydrogen (H₂) Mass Flow Rate Controller: Logistics & Compliance Guide
1. Introduction
This guide outlines essential logistics and compliance considerations for the safe handling, transportation, installation, and operation of Mass Flow Rate Controllers (MFCs) used with hydrogen (H₂) gas. Hydrogen is a highly flammable, low-density, and diffusive gas, requiring strict adherence to safety, regulatory, and technical standards.
2. Regulatory & Compliance Framework
Compliance with international, national, and local regulations is mandatory. Key standards include:
International Standards
- ISO 16111: Transportable gas storage devices – Hydrogen absorbed in reversible metal hydrides.
- ISO 26042: Safety of hydrogen fuel systems for road vehicles.
- IEC 60079 Series: Explosive atmospheres – Equipment and protection for hazardous areas.
- ISO 15869: Gaseous hydrogen and hydrogen blends – Land vehicle fuel containers.
United States
- DOT 49 CFR: Hazardous materials transportation regulations, including H₂ classification (UN 1049, Hazard Class 2.1).
- OSHA 29 CFR 1910.103: Hydrogen safety in the workplace.
- NFPA 2: Hydrogen Technologies Code (storage, piping, ventilation, MFC placement).
- CGA G-5.5: Commodity specification for hydrogen.
European Union
- ADR/RID/ADN: European regulations for road, rail, and inland waterway transport of dangerous goods (Class 2.1 – Flammable Gas).
- ATEX Directive 2014/34/EU: Equipment used in explosive atmospheres.
- PED 2014/68/EU: Pressure Equipment Directive – applies to H₂ MFCs operating above threshold pressures.
- REACH & RoHS: Material compliance for components.
Other Regions
- Canada: TDG Regulations (Transportation of Dangerous Goods).
- China: GB/T 34542.2-2018 (Hydrogen safety guidelines).
- Japan: High Pressure Gas Safety Act.
3. Logistics & Transportation
Packaging & Labeling
- MFCs must be shipped clean, dry, and with protective caps on all ports.
- Use packaging compliant with UN-certified containers if residual H₂ is present.
- Label with:
- UN 1049 (Hydrogen, compressed)
- Class 2.1 Flammable Gas hazard label
- “Keep Away from Heat/Ignition Sources”
- Proper shipping name: “Hydrogen, compressed”
Transport Modes
- Ground (Truck/Rail): Follow ADR or DOT regulations. Use ventilated vehicles; avoid passenger transport.
- Air: Restricted; requires special approval (IATA DGR – Special Provision A150). Often prohibited unless non-hazardous residual content.
- Sea (IMDG Code): Allowed with proper classification, stowage, and segregation from oxidizers.
Pre-Shipment Procedures
- Purge MFCs with inert gas (e.g., N₂) before shipment if previously used with H₂.
- Ensure valves are closed and secured.
- Provide Safety Data Sheet (SDS) and transport documentation.
4. Installation & Handling
Location & Environment
- Install in well-ventilated areas or explosion-proof enclosures.
- Avoid confined spaces; ensure hydrogen can disperse upward (H₂ is lighter than air).
- Maintain safe distance from ignition sources, electrical equipment, and oxidizers.
Piping & Connections
- Use hydrogen-compatible materials (e.g., 316L stainless steel, specific elastomers like Kalrez or Viton).
- Avoid copper or carbon steel (risk of embrittlement).
- Ensure leak-tight connections (VCR, face-seal fittings recommended).
- Install check valves and pressure relief devices upstream.
Grounding & Bonding
- Ground MFC and associated equipment to prevent static discharge.
- Use conductive tubing and fittings in flammable environments.
5. Operational Safety & Monitoring
Leak Detection
- Use hydrogen-specific sensors (catalytic or semiconductor-based) near MFCs.
- Perform bubble testing or helium leak testing during commissioning.
Pressure & Flow Limits
- Operate within MFC manufacturer’s specifications:
- Max inlet pressure (typically 10–30 bar for H₂)
- Flow range and accuracy
- Temperature range (–10°C to +50°C typical)
- Use pressure regulators upstream to avoid over-pressurization.
Ventilation
- Maintain air exchange rates per NFPA 2 (minimum 1 ft/min upward velocity in enclosed spaces).
- Install forced ventilation with interlocks if H₂ concentration exceeds 25% LEL.
6. Maintenance & Calibration
Routine Checks
- Inspect for leaks, corrosion, or mechanical damage monthly.
- Check calibration every 6–12 months or per process requirements.
- Replace seals and filters as per manufacturer schedule.
Calibration Gas
- Use certified hydrogen/nitrogen calibration mixtures.
- Ensure traceability to NIST or equivalent standards.
Decommissioning
- Purge system with inert gas (N₂) before disassembly.
- Cap all ports and store in dry, ventilated area.
- Dispose of components according to local e-waste and hazardous material rules.
7. Training & Documentation
Personnel Training
- Train staff on:
- H₂ hazards (flammability, embrittlement, asphyxiation in confined spaces)
- Emergency shutdown procedures
- Leak response (evacuate, ventilate, eliminate ignition sources)
- PPE (flame-resistant clothing, face shield, gloves)
Required Documentation
- Equipment manuals and certifications (ATEX, PED, CE, etc.)
- Risk assessment and Safe Work Procedure (SWP)
- Leak test records
- Maintenance and calibration logs
- SDS for hydrogen and MFC components
8. Emergency Procedures
In Case of Leak
- Shut off hydrogen supply at source.
- Ventilate the area – do not use electrical switches.
- Evacuate and alert emergency personnel.
- Eliminate ignition sources (no smoking, spark-producing tools).
- Use H₂-compatible fire extinguishers (Class B) if fire occurs.
Fire Involving H₂
- Do not extinguish flame unless gas flow can be stopped (risk of explosion if reignited).
- Cool surrounding equipment with water from a safe distance.
- Evacuate and call emergency services.
9. Conclusion
The use of Mass Flow Controllers with hydrogen demands rigorous attention to logistics, safety, and compliance. By adhering to recognized standards, implementing proper handling procedures, and training personnel, risks can be minimized while ensuring reliable and efficient operation in hydrogen-based applications (e.g., fuel cells, semiconductor manufacturing, laboratory research).
Prepared by: [Your Organization]
Revision Date: [Insert Date]
Contact: [Safety Officer / Engineering Lead]
References: NFPA 2, ISO 16111, IEC 60079, DOT 49 CFR, ATEX, CGA G-5.5
Note: Always consult the MFC manufacturer and local authorities for site-specific compliance requirements.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sourcing a mass flow rate controller requires careful consideration of several key factors including accuracy, repeatability, compatibility with the process media, required flow range, response time, and environmental conditions. It is essential to select a controller from a reputable supplier that offers reliable calibration, technical support, and compliance with relevant industry standards. Evaluating both initial investment and long-term operational costs will contribute to optimal performance and cost-efficiency. By aligning technical specifications with application requirements and ensuring proper integration and maintenance, the selected mass flow rate controller will provide precise and stable flow control, enhancing process reliability and product quality.