The global magnetron market is witnessing steady expansion, driven by rising demand in microwave ovens, industrial heating, radar systems, and medical applications. According to Grand View Research, the global microwave oven market—where magnetrons are a core component—was valued at USD 12.4 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.3% from 2023 to 2030. This growth trajectory directly fuels the needs of magnetron manufacturers, who are scaling production and investing in R&D to meet performance, efficiency, and durability demands across consumer and industrial sectors. Additionally, advancements in radar and defense technologies, particularly in aerospace and automotive applications, are opening new avenues for high-power magnetron adoption. With sustained demand and technological innovation shaping the competitive landscape, we examine the top 9 magnetron manufacturers leading the charge in quality, output, and global market influence.
Top 9 Magnetron Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Magnetron Tubes For Sale
Domain Est. 1997
Website: pentalabs.com
Key Highlights: For industrial heating, radar, and medical systems, here you can find magnetron tubes for sale from leading magnetron manufacturers, Penta Labs….
#2 Vacuum Coating Company
Domain Est. 1997
Website: gencoa.com
Key Highlights: Gencoa is a vacuum coating company providing vacuum technology and vacuum coating solutions. Learn about our range of magnetrons and process control ……
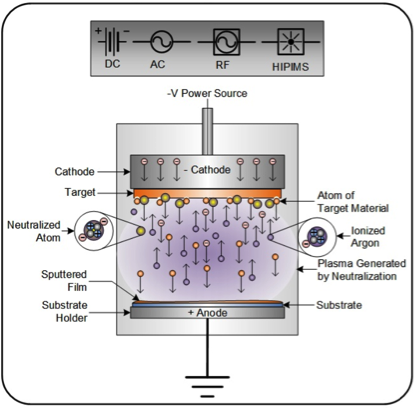
#3 PVD Magnetron Sputtering Systems, Thermal Evaporation …
Domain Est. 1998
Website: semicore.com
Key Highlights: Semicore is a manufacturer and worldwide supplier of PVD or Physical Vapor Deposition equipment and Custom Vacuum Systems for the electronics, academics ……
#4
Domain Est. 1999
Website: magnetron.com.co
Key Highlights: MAGNETRON SAS provides its customers a product built according to the most advanced manufacturing technology, using new materials of the highest quality….
#5 Microwave Power Products
Domain Est. 2014
Website: mppinc.com
Key Highlights: We are a global manufacturer of electronic components and subsystems serving primarily the aerospace and defense markets. … Power Grid and Magnetron Products ……
#6 Richardson Electronics
Domain Est. 1993
Website: rell.com
Key Highlights: Richardson Electronics, Ltd. is a leading global provider of engineered solutions, power grid and microwave tubes and related consumables….
#7 Communications & Power Industries
Domain Est. 1995
Website: cpii.com
Key Highlights: Communications & Power Industries (CPI) provides microwave, radio frequency (RF), power and control solutions for defense, communications, medical, ……
#8 Magnetrons (VED’s)
Domain Est. 2000
Website: mpdcomponents.com
Key Highlights: MPD offers magnetrons to meet requirements of various different aerospace applications. We build strap & vane and coaxial magnetrons….
#9 Magnetron Tube Products : Hitachi High
Domain Est. 2001
Website: hitachi-hightech.com
Key Highlights: Magnetrons main components are the filament, magnets, yoke, anode core, cooling fins, vane, and the output antenna. It is typically used on microwave ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Magnetron

H2: Market Trends Analysis for Magnetron in 2026
As we approach 2026, the global magnetron market is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by technological advancements, shifting industrial demands, and evolving regulatory environments. Magnetrons—vacuum tubes that generate microwave frequencies—remain pivotal in a range of applications, from consumer appliances to industrial heating and medical technologies. This analysis outlines the key market trends expected to shape the magnetron industry in 2026, with a focus on innovation, regional dynamics, competitive landscape, and emerging applications.
-
Decline in Consumer Appliance Demand, Growth in Industrial and Scientific Applications
The traditional demand for magnetrons in household microwave ovens is slowing due to market saturation in mature economies and a shift toward solid-state RF (radio frequency) technologies, which offer greater control, efficiency, and longevity. However, this decline is being offset by rising adoption in industrial heating, plasma generation, and scientific instrumentation. In 2026, industrial applications such as microwave-assisted drying, sintering, and chemical processing are projected to represent over 45% of magnetron demand, particularly in the food processing, ceramics, and waste treatment sectors. -
Advancements in High-Power and Frequency-Stable Magnetrons
Research and development efforts are focusing on improving magnetron efficiency, power output, and frequency stability. High-power magnetrons (5–100 kW range) are seeing increased use in defense (e.g., radar systems) and fusion energy research. Innovations in phase-locked and frequency-tunable magnetrons are enhancing their integration with digital control systems, improving reliability in critical applications. Companies like Toshiba, Panasonic, and Communications & Power Industries (CPI) are leading in next-generation designs. -
Expansion in Emerging Markets
Asia-Pacific, particularly India, Southeast Asia, and parts of Africa, is emerging as a key growth region for magnetron applications. Rising urbanization, infrastructure development, and government support for industrial modernization are increasing demand for microwave-based processing technologies. Local manufacturing initiatives and cost-effective production are enabling regional players to capture market share, especially in mid-range industrial magnetrons. -
Competition from Solid-State RF Technology
A major long-term trend affecting the magnetron market is the growing adoption of solid-state RF amplifiers. These semiconductor-based systems offer precise frequency control, scalability, and longer operational lifespans, making them attractive in applications such as microwave plasma and advanced radar. While solid-state systems currently remain cost-prohibitive for high-power applications, their prices are expected to decline by 2026, increasing competitive pressure on magnetron manufacturers to innovate or differentiate. -
Sustainability and Regulatory Pressures
Environmental regulations targeting energy efficiency and e-waste are influencing magnetron design and deployment. In the EU and North America, stricter energy standards are pushing manufacturers to develop more efficient magnetrons and improve end-of-life recyclability. Additionally, efforts to reduce hazardous materials (e.g., beryllium oxide in insulators) are driving material innovation and supply chain adjustments. -
Integration with IoT and Smart Systems
In industrial settings, magnetrons are increasingly being integrated into IoT-enabled platforms for remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and process optimization. Smart magnetron systems with embedded sensors and communication modules allow real-time performance tracking, reducing downtime and improving energy efficiency. This trend is particularly evident in food processing and pharmaceutical manufacturing. -
Defense and Aerospace Resurgence
Geopolitical tensions and modernization of military systems are boosting demand for high-reliability magnetrons in radar and electronic warfare. The U.S., China, and several NATO countries are investing in next-generation radar systems that rely on high-efficiency magnetrons. This sector is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.8% through 2026, providing a stable revenue stream for specialized magnetron producers.
Conclusion
By 2026, the magnetron market will be characterized by a bifurcation: declining relevance in consumer electronics but sustained and growing importance in industrial, scientific, and defense applications. Success for manufacturers will depend on their ability to innovate in performance and reliability, adapt to regional market dynamics, and navigate the competitive threat posed by solid-state RF technologies. Companies that invest in hybrid solutions—such as magnetron-solid-state hybrid systems—or niche high-power applications are likely to maintain a competitive edge in this evolving landscape.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Magnetrons: Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
Sourcing magnetrons—particularly for applications like microwave ovens, radar systems, or industrial heating—can present significant challenges, especially when balancing cost, performance, and legal compliance. Two major areas of risk are quality inconsistencies and intellectual property (IP) infringement. Being aware of these pitfalls is essential for manufacturers and integrators to avoid operational failures, legal disputes, and reputational damage.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
-
Inconsistent Performance and Reliability
Low-cost magnetrons from unverified suppliers often suffer from poor manufacturing standards, leading to inconsistent frequency output, power levels, and shortened operational lifespans. This variability can result in system inefficiencies or premature failures in end products. -
Substandard Materials and Construction
Inferior cathodes, anodes, or vacuum seals can compromise magnetron durability. Using low-grade materials increases the risk of arcing, overheating, and leakage, which not only reduces performance but also poses safety hazards. -
Lack of Certification and Testing Data
Many suppliers—especially in less-regulated markets—fail to provide proper certifications (e.g., ISO, RoHS, or IEC standards) or verifiable test reports. Without independent validation, it is difficult to assess real-world performance under operational stress. -
Poor Thermal and Frequency Stability
Lower-quality magnetrons may not maintain stable frequency or output power under varying load or temperature conditions, leading to inefficient energy use and potential interference with other electronic systems. -
Inadequate Quality Control Processes
Suppliers without robust QC protocols may ship units with undetected defects. Batch-to-batch inconsistency is common, making it difficult to ensure uniformity in mass production.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
-
Counterfeit or Reverse-Engineered Products
Some suppliers offer “compatible” or “generic” magnetrons that closely mimic patented designs from established brands (e.g., Panasonic, Toshiba, or LG). These may be unauthorized copies, infringing on design patents, utility models, or even trade secrets. -
Unlicensed Use of Proprietary Technology
Key innovations in magnetron design—such as mode stirrers, cooling systems, or cathode configurations—are often protected. Sourcing from manufacturers that use such technology without licensing exposes buyers to secondary liability for IP infringement. -
Ambiguous or Missing IP Documentation
Suppliers may not provide clear documentation regarding the origin of their designs or IP clearance. This lack of transparency increases legal risk, especially in regulated markets or when products are exported. -
Difficulty Enforcing Warranty or Recourse
If a magnetron is found to be infringing on third-party IP, the supplier may not stand behind the product legally. This leaves the buyer exposed to litigation, product recalls, or customs seizures. -
Grey Market and Unauthorized Distribution
Purchasing from unauthorized distributors or grey market channels increases the likelihood of receiving non-compliant, re-marked, or stolen IP-based components, undermining both quality and legal standing.
Mitigation Strategies
- Source from Reputable, Verified Suppliers: Prioritize manufacturers with a proven track record, industry certifications, and transparent production practices.
- Conduct Technical Audits and Sample Testing: Evaluate performance, durability, and consistency through independent lab testing.
- Verify IP Ownership and Licensing: Request documentation proving the supplier’s right to manufacture and sell the magnetron design.
- Include IP Indemnification Clauses in Contracts: Ensure suppliers legally assume responsibility for any IP infringement claims.
- Engage Legal and Technical Experts: Involve IP attorneys and engineering teams during the sourcing process to assess risks thoroughly.
By proactively addressing both quality and IP concerns, companies can ensure reliable performance, regulatory compliance, and long-term supply chain integrity when sourcing magnetrons.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Magnetron
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance procedures for Magnetron to ensure efficient operations, regulatory adherence, and smooth movement of goods across supply chains.
Supply Chain Overview
Magnetron’s supply chain involves sourcing raw materials, manufacturing components, distribution to partners and customers, and reverse logistics for returns or recycling. Key stakeholders include suppliers, freight carriers, customs brokers, and internal departments such as procurement, manufacturing, and quality assurance.
Regulatory Compliance
Magnetron must comply with international, national, and regional regulations related to manufacturing, transportation, and product safety. Key compliance areas include:
- Export Controls: Adherence to EAR (Export Administration Regulations) and ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations) when applicable, especially for technology with dual-use potential.
- Product Safety Standards: Compliance with CE marking (EU), FCC (USA), RoHS, REACH, and other environmental and safety directives.
- HS Code Classification: Accurate Harmonized System code assignment for all products to ensure correct tariffs and customs treatment.
- Country of Origin Requirements: Maintaining documentation to verify origin for trade agreements and import regulations.
Transportation & Freight Management
Efficient transportation planning is critical for cost control and on-time delivery.
- Carrier Selection: Choose carriers based on reliability, cost, and compliance history. Maintain approved vendor lists.
- Incoterms Usage: Clearly define responsibilities using standard Incoterms (e.g., FOB, EXW, DDP) in all contracts.
- Freight Documentation: Ensure all shipments include commercial invoices, packing lists, bills of lading, and certificates of origin as required.
- Insurance Coverage: Maintain cargo insurance for all high-value shipments, especially for international transit.
Customs Clearance Procedures
Smooth customs clearance minimizes delays and avoids penalties.
- Pre-Shipment Verification: Validate documentation accuracy and completeness prior to dispatch.
- Duties & Tariffs: Calculate and plan for applicable duties, VAT, or GST based on destination country regulations.
- Customs Brokers: Partner with licensed brokers in key markets to facilitate clearance and respond to customs inquiries.
- Automated Systems: Utilize electronic data interchange (EDI) and customs management platforms where possible.
Inventory & Warehouse Compliance
Warehousing operations must meet safety, traceability, and regulatory standards.
- Storage Conditions: Maintain appropriate environmental controls (temperature, humidity) for sensitive components.
- Labeling & Tracking: Use barcode/RFID systems for real-time inventory tracking. Labels must include lot numbers, expiry dates (if applicable), and handling instructions.
- Security Protocols: Implement access controls, surveillance, and inventory audits to prevent theft or loss.
- Hazardous Materials: If handling hazardous goods, comply with OSHA, DOT, and ADR regulations including proper storage, labeling, and spill response plans.
Trade Compliance Program
Magnetron must maintain a robust trade compliance program to mitigate risk.
- Screening: Conduct regular screening of customers, suppliers, and destinations against denied party lists (e.g., OFAC, BIS).
- Licensing: Obtain required export licenses or authorizations prior to shipment of controlled items.
- Internal Audits: Perform periodic compliance audits and staff training to reinforce policies.
- Recordkeeping: Retain all logistics and compliance documentation for a minimum of five years (or as required by jurisdiction).
Sustainability & Environmental Compliance
Magnetron is committed to environmentally responsible logistics practices.
- Packaging: Use recyclable or reusable packaging materials and minimize waste.
- Carbon Reporting: Monitor and report logistics-related carbon emissions as part of corporate sustainability goals.
- Waste Management: Partner with certified recyclers for electronic waste and non-reusable materials.
Incident Response & Contingency Planning
Prepare for disruptions with clear response protocols.
- Shipment Delays: Establish communication plans with customers and internal teams in case of delays.
- Customs Holds: Designate a compliance officer to resolve customs issues promptly.
- Alternative Routes/Carriers: Identify backup logistics options for high-priority shipments.
Training & Responsibilities
All personnel involved in logistics and compliance must receive regular training.
- Roles & Responsibilities: Clearly define duties for procurement, logistics coordinators, compliance officers, and warehouse staff.
- Training Schedule: Conduct annual compliance training and refreshers for new regulations or procedures.
Continuous Improvement
Regularly review and optimize logistics and compliance processes.
- KPI Tracking: Monitor on-time delivery, customs clearance time, freight costs, and compliance incident rates.
- Feedback Loops: Gather input from carriers, customers, and internal teams to identify improvement opportunities.
- Technology Upgrades: Invest in logistics management systems (TMS, WMS) and compliance software to enhance visibility and control.
By adhering to this guide, Magnetron ensures reliable, compliant, and sustainable logistics operations across its global footprint.
Conclusion for Sourcing Magnetron:
Sourcing magnetrons requires a strategic approach that balances cost, quality, reliability, and technical compatibility. Given their critical role in applications such as microwave ovens, radar systems, and industrial heating, selecting the right supplier is essential to ensure product performance and longevity. Key considerations include technical specifications (e.g., frequency, power output, efficiency), compliance with international standards (such as RoHS and REACH), supply chain stability, and after-sales support. Engaging with reputable manufacturers—whether established OEMs or qualified alternatives—while conducting rigorous due diligence helps mitigate risks related to counterfeit components and supply disruptions. Ultimately, a well-structured sourcing strategy that incorporates supplier audits, long-term partnerships, and regular performance evaluations ensures a reliable magnetron supply, supports operational efficiency, and contributes to overall product success in the market.