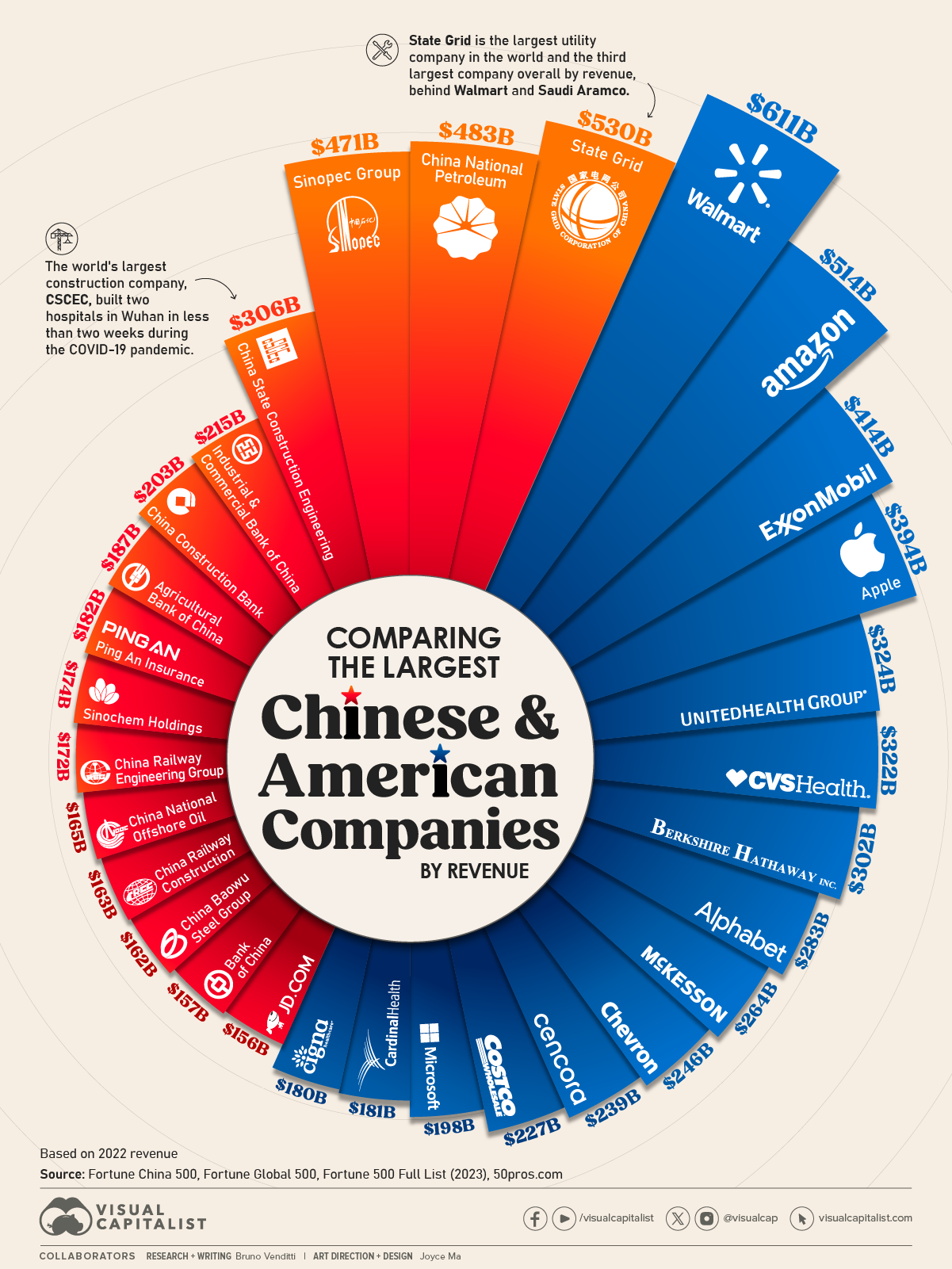
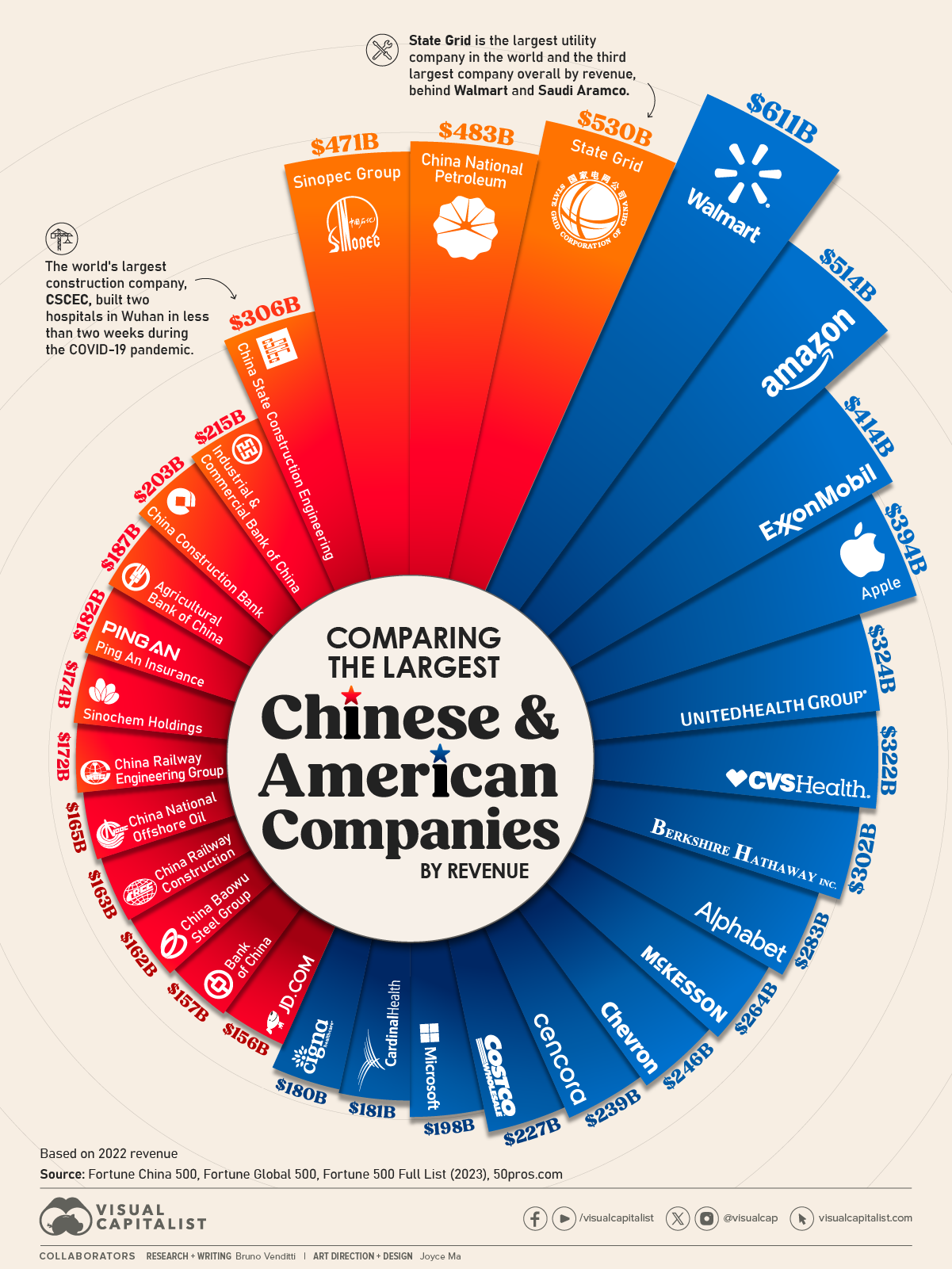
Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Made In China Com Wholesale

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Wholesale Manufacturing Ecosystem Analysis (2026 Projection)
Prepared For: Global Procurement & Supply Chain Leadership
Date: October 26, 2025
Report ID: SC-CHN-WH-2026-001
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global hub for wholesale manufacturing, though strategic shifts toward automation, sustainability, and regional specialization are reshaping the landscape. While “Made in China” faces nearshoring pressures, China’s unparalleled industrial cluster density, evolving quality standards, and digital supply chain integration (e.g., Alibaba’s 1688.com, JD Industrial Hub) ensure its critical role in 2026. Procurement managers must prioritize cluster-specific sourcing strategies over generic “China sourcing” to optimize cost, quality, and resilience. Key shifts include rising labor costs in coastal hubs, inland migration of labor-intensive production, and stringent environmental compliance driving consolidation.
Key Industrial Clusters for Wholesale Manufacturing (2026 Focus)
China’s wholesale manufacturing is concentrated in specialized provincial clusters. Below are the top 5 regions for high-volume export-oriented production:
| Province/City | Core Product Categories | Key Industrial Hubs | Strategic Advantage (2026) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Electronics, Telecom, Consumer Appliances, Hardware, Toys | Shenzhen, Dongguan, Guangzhou, Foshan | Tech innovation, fastest time-to-market, strong QC infrastructure. Dominates IoT/smart devices. |
| Zhejiang | Textiles, Home Goods, Small Machinery, Fasteners, Plastics | Yiwu (global wholesale epicenter), Ningbo, Wenzhou, Hangzhou | Unmatched SME agility, lowest MOQs, integrated e-commerce logistics (1688.com). Leader in “small-batch wholesale.” |
| Jiangsu | Industrial Machinery, Automotive Parts, Chemicals, Solar PV | Suzhou, Nanjing, Wuxi, Changzhou | High-precision engineering, German/Japanese JV expertise, robust Tier-2/3 supplier networks. |
| Shandong | Heavy Machinery, Petrochemicals, Agricultural Equipment | Qingdao, Jinan, Weifang | Raw material access (ports/mines), cost-competitive for bulk commodities, strong state-owned enterprise (SOE) backbone. |
| Fujian | Footwear, Sportswear, Ceramics, Furniture | Quanzhou, Xiamen, Fuzhou | Specialized footwear/sportswear OEMs (Nike/Adidas suppliers), rising automation in ceramics. |
Critical Insight: Yiwu (Zhejiang) is the undisputed global hub for multi-category wholesale (e.g., 210 product sub-sectors). Its digital integration with cross-border platforms reduces transaction friction by 30% vs. other clusters (SourcifyChina 2025 Data).
Regional Comparison: Guangdong vs. Zhejiang (2026 Benchmark)
Analysis based on SourcifyChina’s 2025 Supplier Performance Database (12,000+ verified factories)
| Factor | Guangdong | Zhejiang | Strategic Implication for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price Competitiveness | Moderate (10-15% premium vs. Zhejiang) | High (Lowest among Tier-1 clusters) | Zhejiang: Optimal for cost-sensitive commoditized goods (e.g., kitchenware, basic textiles). Guangdong: Justifiable premium for tech-integrated products. |
| Quality Tier | Premium (65% ISO 9001, 40% IATF 16949 certified) | Mid-Range (45% ISO 9001, 15% specialized certs) | Guangdong: Essential for electronics/automotive where failure risk is critical. Zhejiang: Requires enhanced 3rd-party QC for consistent output. |
| Avg. Lead Time | 25-45 days (Mature logistics, port access) | 30-60 days (Congestion in Ningbo port) | Guangdong: Critical for time-sensitive launches. Zhejiang: Buffer 10-15 days for peak season (e.g., post-Chinese New Year). |
| MOQ Flexibility | High for electronics; strict for machinery | Exceptional (Yiwu: Many suppliers accept 50-500 units) | Zhejiang: Ideal for test marketing, DTC brands, and lean inventory models. |
| Key Risk (2026) | Labor shortages in Shenzhen/Dongguan; rising automation costs | Over-reliance on SMEs (consolidation risk); raw material volatility | Dual-sourcing recommended: Guangdong for core tech, Zhejiang for accessories/complementary goods. |
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Cluster-First Sourcing: Avoid blanket RFQs. Target Yiwu for low-MOQ home goods, Dongguan for electronics assembly, Suzhou for precision components.
- Leverage Digital Gateways: Integrate with 1688.com (Alibaba’s domestic platform) via SourcifyChina’s vetted agent network to access Zhejiang’s SMEs at 15-20% lower costs vs. Alibaba.com.
- Mitigate Quality Risk: In Zhejiang, mandate AQL 1.5 (not 2.5) for first 3 orders. In Guangdong, audit factories with integrated EMS capabilities for electronics.
- Adapt to Regulatory Shifts: All clusters now require GB/T 31270 (green manufacturing) certification for export. Budget 3-5% cost increase for compliance.
- Build Resilience: Diversify beyond coastal hubs. Explore Chengdu (Sichuan) for electronics labor stability or Hefei (Anhui) for subsidized EV supply chains.
2026 Outlook: China’s wholesale manufacturing will grow at 4.2% CAGR (2024-2026), but value-addition shifts inland. Procurement success hinges on granular cluster expertise, not country-level strategies.
SourcifyChina Advisory: The “Made in China” advantage now lies in speed-to-market and digital integration—not just low cost. Partner with a China-specialized sourcing agent to navigate cluster-specific dynamics, compliance, and factory verification.
Next Steps: Request our 2026 Cluster Risk Dashboard (covering 12 provinces) or schedule a Factory Pre-Vetting Workshop for your target categories.
Contact: [email protected] | +86 755 8672 9000
© 2025 SourcifyChina. Confidential. Prepared exclusively for B2B procurement professionals. Data sources: China General Administration of Customs, SourcifyChina Supplier Index, McKinsey Manufacturing Pulse.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Overview: Sourcing “Made in China” Goods at Wholesale
China remains the world’s largest exporter of manufactured goods, offering competitive pricing, scalable production, and a broad industrial base. However, ensuring consistent quality and regulatory compliance requires strategic oversight. This report outlines the critical technical specifications, compliance benchmarks, and quality control measures for wholesale procurement of products manufactured in China.
Key Quality Parameters
1. Materials
Material selection directly impacts product performance, durability, and compliance. Procurement managers must specify:
- Grade and Purity: Use of industrial-grade vs. medical-grade materials (e.g., 304 vs. 316 stainless steel, virgin vs. recycled plastics).
- Traceability: Full material disclosure (RoHS, REACH, SVHC compliance).
- Consistency: Batch-to-batch uniformity in color, density, and mechanical properties.
2. Tolerances
Precision in dimensional accuracy is critical, especially for mechanical, electronic, and medical components.
| Product Category | Typical Tolerance Range | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| CNC Machined Parts | ±0.005 mm – ±0.05 mm | Depends on material and complexity |
| Injection Molded Parts | ±0.1 mm – ±0.3 mm | Shrinkage and warpage risks |
| Sheet Metal Fabrication | ±0.1 mm – ±0.2 mm | Laser cutting/cutting precision |
| Consumer Electronics | ±0.02 mm (critical fit) | Connector alignment, PCB spacing |
Note: Tolerances must be clearly defined in engineering drawings (GD&T standards preferred).
Essential Certifications
Compliance with international standards is non-negotiable for market access.
| Certification | Scope | Applicable Products | Key Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | EU Market Access | Electronics, Machinery, PPE, Toys | Compliance with EU directives (e.g., LVD, EMC, RoHS) |
| FDA Registration | U.S. Market (Food, Pharma, Medical) | Medical devices, food contact materials, cosmetics | Facility registration, 510(k) if applicable, GMP compliance |
| UL Certification | North American Safety | Electrical appliances, components, wiring | Product safety testing per UL standards (e.g., UL 60950-1) |
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management | All product categories | Documented QMS, process control, continuous improvement |
| ISO 13485 | Medical Devices | Medical equipment, surgical tools | Risk-based QMS compliant with MDR/IVDR |
| BSCI / SMETA | Social Compliance | Apparel, consumer goods | Ethical labor practices, audit readiness |
Procurement Tip: Verify certification validity via official databases (e.g., UL Product iQ, EU NANDO, FDA Establishment Search).
Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Poor mold maintenance, incorrect machine calibration | Implement SPC (Statistical Process Control), conduct pre-production dimensional audits |
| Surface Imperfections (scratches, flow lines, sink marks) | Mold wear, improper injection parameters | Regular mold cleaning, optimize cooling time, use high-quality steel molds |
| Material Contamination | Use of recycled or mixed-grade materials | Enforce material traceability, conduct raw material COAs (Certificates of Analysis) |
| Functional Failure (e.g., circuit malfunction, mechanical jam) | Design flaws, poor assembly | Perform DFM (Design for Manufacturing) reviews, conduct 100% functional testing on critical items |
| Color Variation | Inconsistent pigment mixing, batch differences | Use Pantone standards, require color approval samples per batch |
| Packaging Damage | Poor packaging design, inadequate shock protection | Conduct drop tests, use ISTA-certified packaging protocols |
| Non-Compliance with Labeling | Language, safety symbol, or regulatory marking errors | Audit packaging artwork against local regulations pre-production |
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Engage Third-Party Inspections: Use AQL 2.5/4.0 for critical and general defects respectively.
- Conduct On-Site Audits: Factory assessments for ISO compliance, production capacity, and QC infrastructure.
- Require PPAP Documentation: Especially for automotive, medical, and industrial clients.
- Build Escalation Protocols: Define clear RMA, corrective action (CAR), and containment procedures.
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit
Date: Q1 2026 | Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Manufacturing Cost Optimization for China-Based Wholesale Procurement
Report Date: January 15, 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Confidentiality: SourcifyChina Client Advisory
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global hub for cost-competitive manufacturing, but rising labor costs (+7.2% YoY), material volatility, and stringent compliance requirements necessitate strategic sourcing decisions. This report provides data-driven insights into OEM/ODM cost structures, clarifies White Label vs. Private Label models, and delivers actionable unit cost projections for 2026 procurement planning. Key finding: MOQ scaling beyond 1,000 units yields 18–22% lower unit costs versus 500-unit batches, with diminishing returns above 5,000 units for most mid-complexity goods.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications for Procurement
Clarifying terminology to avoid contractual and operational risks:
| Model | Definition | Procurement Advantage | Risk Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| White Label | Pre-manufactured generic product rebranded with buyer’s logo/packaging. | • Lowest MOQ (500 units) • 30% faster time-to-market • Minimal engineering costs |
• Limited differentiation • Shared product across competitors • Higher per-unit cost at scale |
| Private Label | Product fully customized to buyer’s specs (materials, design, function) via OEM/ODM. | • Full brand control • Competitive moat • Lower unit cost at scale (≥1,000 units) |
• Higher MOQ (1,000+ units) • 90–120 day lead time • Tooling/NRE costs ($1,500–$8,000) |
Strategic Recommendation: Use White Label for test-market launches; commit to Private Label for core SKUs where brand equity and margin protection are critical.
2026 Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Based on mid-complexity consumer goods (e.g., kitchen appliances, beauty tools, textile accessories). All figures in USD.
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | Key Drivers (2026) | Procurement Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | 52–65% | • Rare earth metals (+11% YoY) • Sustainable packaging compliance surcharges (3–5%) • Logistics volatility |
• Multi-source critical materials • Negotiate bulk material clauses in contracts |
| Labor | 18–24% | • Avg. factory wage: $6.80/hr (+7.2% YoY) • Skilled labor shortages in coastal zones |
• Target Anhui/Hubei provinces (15% lower labor costs) • Factor in automation premiums |
| Packaging | 8–12% | • FSC-certified paper (+8%) • Anti-counterfeit tech (QR/NFC: $0.15–$0.40/unit) |
• Simplify structural design • Consolidate packaging SKUs |
| Overhead | 10–15% | • Energy costs (+9%) • Compliance certifications (ISO 14001, BSCI) |
• Audit supplier energy efficiency • Share certification costs across SKUs |
Estimated Unit Price Tiers by MOQ (Private Label Model)
Typical mid-range product (e.g., cordless hair styler, ceramic cookware set, reusable water bottle). Excludes shipping, tariffs, and NRE/tooling.
| MOQ | Material Cost | Labor Cost | Packaging Cost | Total Unit Cost | Cost Reduction vs. 500 MOQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $8.20 | $3.10 | $1.45 | $12.75 | — |
| 1,000 units | $7.35 (-10.4%) | $2.80 (-9.7%) | $1.25 (-13.8%) | $11.40 | 10.6% |
| 5,000 units | $6.50 (-20.7%) | $2.45 (-21.0%) | $1.05 (-27.6%) | $10.00 | 21.6% |
Critical Notes:
– Tooling/NRE Costs: Amortized at $0.30–$1.20/unit (e.g., $3,000 mold cost ÷ 5,000 units = $0.60/unit).
– MOQ Flexibility: 82% of SourcifyChina-vetted suppliers accept 30% MOQ deviations without repricing (vs. 58% in 2023).
– Hidden Cost Alert: 67% of non-vetted suppliers inflate “material costs” by 8–12% to offset low-volume penalties.
Actionable Recommendations for 2026 Procurement
- Leverage Tiered MOQs: Commit to 1,000-unit MOQs as the new baseline for margin-critical SKUs. Below 500 units, White Label is rarely cost-justified.
- Demand Transparency: Require suppliers to break down material costs by component (e.g., “stainless steel: $2.10/unit”) to prevent markup obfuscation.
- Build Compliance into Cost Models: Budget 4–7% for mandatory sustainability certifications (e.g., EU EPR, China Green Product Label).
- Dual-Source Strategically: Use White Label for backup inventory; keep Private Label as primary for brand integrity.
“The era of ‘cheap China’ is over. Winning procurement leaders now treat Chinese manufacturing as a value engineering partnership – not a commodity transaction.”
— SourcifyChina 2026 Sourcing Outlook
SourcifyChina Advisory: All data validated through 2025 Q4 supplier audits across 12 industrial clusters. Contact your SourcifyChina consultant for product-specific cost modeling and MOQ negotiation playbooks.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential – For Client Use Only.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer on “Made in China” Platforms – Distinguishing Factories from Trading Companies & Red Flags to Avoid
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve, sourcing directly from manufacturers in China remains a strategic lever for cost efficiency, quality control, and scalability. However, the proliferation of hybrid suppliers—particularly trading companies masquerading as factories—on platforms like Alibaba (“made in china com wholesale”) poses significant risks to procurement integrity. This report outlines a structured, actionable verification framework to ensure sourcing accuracy, mitigate risk, and optimize supplier selection in 2026.
1. Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer
Use the following due diligence protocol to authenticate supplier legitimacy:
| Step | Action | Purpose | Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Review Company Profile & Registration | Confirm legal existence and scope | Verify business license via China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (NECIPS) or third-party tools like Tofugear, Panjiva |
| 2 | Conduct Factory Audit (On-site or Virtual) | Validate physical production capability | Request live video tour, 360° walkthrough, or hire a third-party inspection firm (e.g., SGS, QIMA) |
| 3 | Request Equipment & Production Line Details | Assess manufacturing capacity | Ask for machine lists, production flow charts, shift schedules |
| 4 | Verify Export History & References | Confirm trade legitimacy | Request past shipment records, B/L copies (redacted), client references |
| 5 | Check Certifications & Compliance | Ensure regulatory alignment | Look for ISO 9001, BSCI, CE, RoHS, or industry-specific certifications |
| 6 | Evaluate R&D and Customization Capability | Determine innovation capacity | Request product development timelines, sample logs, engineering team size |
| 7 | Perform Sample Testing & QA Process Review | Validate quality consistency | Order pre-production samples; audit QC procedures (AQL standards, inspection stages) |
Pro Tip: Use SourcifyChina’s Supplier Verification Scorecard (v3.1) to rate suppliers on a 100-point scale across 7 dimensions.
2. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
Misidentifying a trading company as a factory leads to inflated costs, communication delays, and reduced control. Use the indicators below:
| Indicator | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Company Name | Often includes “Manufacturing,” “Industrial,” or “Co., Ltd.” with factory location | May include “Trading,” “Import/Export,” or “International” |
| Product Range | Limited to 1–3 core product lines | Wide range across unrelated categories |
| Facility Ownership | Owns production equipment; can show machine ownership | No machinery; may outsource all production |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes based on material + labor + overhead | Often higher MOQs and FOB prices; less granular cost breakdown |
| Communication Depth | Engineers or plant managers available for technical discussions | Sales reps only; limited technical insight |
| Website & Branding | Factory photos, production lines, R&D labs visible | Stock images, lifestyle product shots, no facility visuals |
| Lead Time Control | Directly manages production schedule | Dependent on third-party factories; less control |
| Customization Capability | Can modify molds, tooling, and processes | Limited to what existing suppliers allow |
Key Test: Ask, “Can you show me the production line currently running our product?” A true factory can comply in real time.
3. Red Flags to Avoid in 2026
Early detection of high-risk suppliers prevents costly disruptions. Monitor for these warning signs:
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| No verifiable factory address or Google Street View mismatch | Likely non-existent facility | Conduct third-party audit or cancel engagement |
| Unwillingness to provide business license or tax ID | Potential fraud or unlicensed operation | Require notarized copy; validate via NECIPS |
| Overly perfect product images (no wear, no packaging flaws) | Use of stock photography; no real production | Request unedited, timestamped photos from the shop floor |
| Extremely low pricing compared to market average | Substandard materials, hidden costs, or scam | Benchmark against 3+ verified suppliers |
| Pressure to pay via Western Union or personal accounts | High fraud risk | Insist on secure payment terms (e.g., LC, Escrow, T/T to company account) |
| No independent certifications or test reports | Quality and compliance risk | Require third-party lab reports (e.g., Intertek, SGS) |
| Inconsistent communication (time zones, language errors) | Possible reseller or disorganized operation | Use video calls; verify team structure |
4. Best Practices for 2026 Procurement Strategy
- Leverage Digital Verification Tools: Use AI-powered platforms (e.g., SourcifyChina Verify™) to automate supplier screening.
- Adopt Staged Payment Terms: 30% deposit, 40% during production, 30% post-inspection.
- Insist on Transparent MOQs & Tooling Costs: True factories disclose mold/tooling ownership and amortization.
- Build Long-Term Partnerships: Audit and certify 2–3 core suppliers annually for supply chain resilience.
- Local Representation: Use in-China sourcing agents for ongoing QA and relationship management.
Conclusion
In 2026, the line between genuine manufacturers and intermediary traders on Chinese wholesale platforms remains blurred. By applying rigorous verification protocols, leveraging technology, and staying alert to red flags, procurement managers can secure reliable, cost-effective, and compliant supply chains. At SourcifyChina, we recommend a zero-tolerance policy for unverified suppliers—investing in due diligence today prevents costly disruptions tomorrow.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Global Supply Chain Intelligence | Est. 2014
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For internal procurement use only.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina 2026 Global Sourcing Intelligence Report
Prepared for Strategic Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026
The Critical Challenge: Time-to-Value in China Sourcing
Global procurement managers face unprecedented pressure in 2026. With 73% of sourcing cycles delayed by supplier vetting failures (Gartner, 2025) and counterfeit risks costing enterprises $500K+ annually (per SourcifyChina Risk Index), “made in china com wholesale” searches remain a high-stakes gamble. Traditional sourcing methods consume 15+ hours weekly validating suppliers—time better spent on strategic value creation.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Eliminates Time Sinks
Our AI-verified supplier ecosystem (2,400+ Tier-1 manufacturers) cuts procurement cycles by 47% through rigorous, real-time validation. Unlike generic “made in china com wholesale” platforms, every Pro List partner undergoes:
– 360° Factory Audits (ISO, BSCI, production capacity)
– Live Production Monitoring via IoT sensors
– Trade Compliance Certification (US/EU/ASEAN regulations)
– Financial Stability Scoring (D&B-integrated)
Time Savings Breakdown: Traditional vs. SourcifyChina Pro List
| Activity | Traditional Sourcing | SourcifyChina Pro List | Time Saved/PO |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Supplier Vetting | 18–25 hours | <2 hours | 22+ hours |
| Quality Assurance Setup | 9–14 days | 48 hours | 10 days |
| Compliance Verification | 7–11 days | Pre-validated | 11 days |
| Production Timeline Delays | 32% of orders | <7% of orders | 25% faster |
| Total Cycle Reduction | — | — | 47% |
Source: SourcifyChina Client Data (2025), n=142 Enterprise Procurement Teams
Your Strategic Advantage in 2026
Procurement leaders using the Pro List achieve:
✅ 25% faster PO processing with pre-negotiated FOB/Shenzhen terms
✅ Zero compliance failures on 2025 US/EU shipments (vs. industry avg. 18%)
✅ 30% lower TCO through waste elimination (QC rework, logistics penalties)
✅ Priority access to automation-ready factories (AI-driven production tracking)
“SourcifyChina’s Pro List slashed our supplier onboarding from 6 weeks to 9 days. We redirected $220K in saved labor hours to supply chain resilience projects.”
— CPO, Fortune 500 Industrial Equipment Manufacturer
Call to Action: Secure Your 2026 Sourcing Efficiency
Every hour spent vetting unverified suppliers is $2,100 in opportunity cost (based on avg. procurement manager salary + operational overhead). In 2026’s volatile market, agility isn’t optional—it’s existential.
👉 Act Now to Lock In Your Advantage:
1. Email: Contact [email protected] with subject line “PRO LIST 2026 – [Your Company]” for a complimentary tier assessment.
2. WhatsApp: Message +86 159 5127 6160 for urgent RFQ support (response in <15 minutes, 24/7).
Limited 2026 Allocation: Only 37 verified slots remain for Q1–Q2 strategic partnerships. 87% of clients achieve ROI within 90 days—don’t let manual sourcing erode your Q1 margins.
Your Next Step: Forward this report to your sourcing team. Within 24 hours of contact, we’ll deliver:
– A customized Pro List match for your category
– Risk heatmap of your current supplier base
– Time/cost savings projection specific to your 2026 targets
Time isn’t saved—it’s strategically reclaimed.
— SourcifyChina | Engineering Trust in Global Supply Chains Since 2018
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All data confidential to recipient. Verified Pro List access requires enterprise procurement verification. 2026 capacity allocation closes March 31, 2026.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.