The global machine parts manufacturing industry is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising industrial automation, increased demand for precision components, and expanding applications across automotive, aerospace, and machinery sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global industrial machinery market size was valued at USD 524.2 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects steady expansion in machine parts demand, fueled by advancements in smart manufacturing and increasing investments in predictive maintenance technologies. As industries worldwide prioritize efficiency and reliability, the role of high-quality machine parts manufacturers becomes increasingly critical. In this evolving landscape, a select group of industry leaders stands out for their innovation, global reach, and commitment to engineering excellence—shaping the future of industrial performance.
Top 10 Machine Parts Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
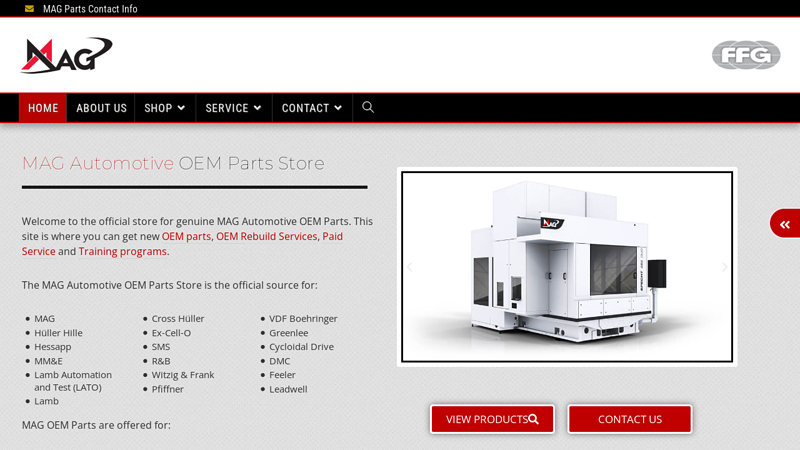
#1 MAG Automotive OEM Parts Store
Domain Est. 2005
Website: service.mag-ias.com
Key Highlights: Welcome to the official store for genuine MAG Automotive OEM Parts. This site is where you can get new OEM parts, OEM Rebuild Services, Paid Service and ……
#2 PAI Industries, Inc.
Domain Est. 1993
Website: pai.com
Key Highlights: PAI Industries manufactures and distributes quality service parts to the heavy-duty truck industry. For over 40 years we’ve been supplying distributors ……
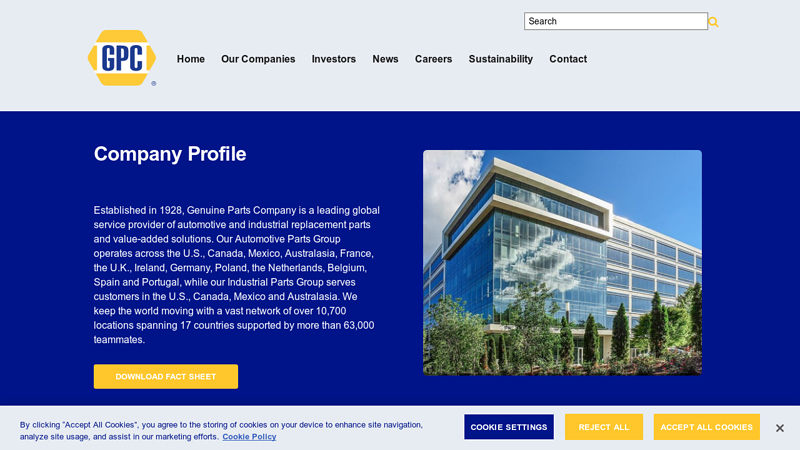
#3 Genuine Parts Company
Domain Est. 1995 | Founded: 1928
Website: genpt.com
Key Highlights: Established in 1928, Genuine Parts Company is a leading global service provider of automotive and industrial replacement parts and value-added solutions….
#4 Precision Manufacturing Machine Parts
Domain Est. 1997 | Founded: 1927
Website: famcomachine.com
Key Highlights: Empowering industries with precision machine parts since 1927. Famco: leading manufacturer of mechanical shears, squaring shears, presses, cutters, ……
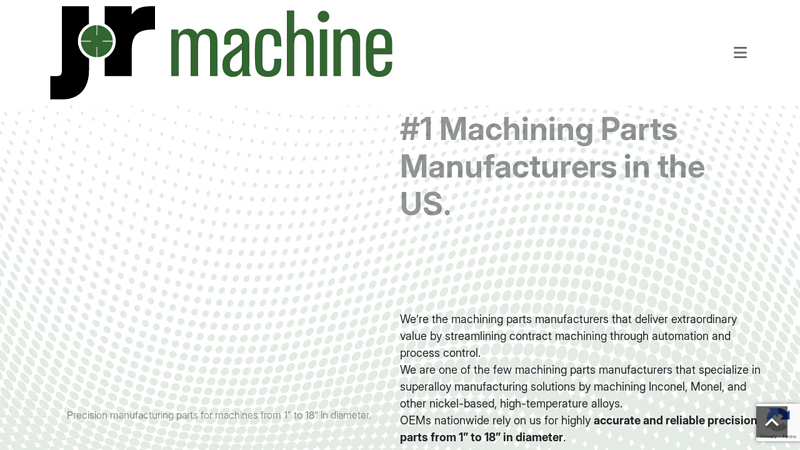
#5 #1 Machining Parts Manufacturers in the US
Domain Est. 1998
Website: jrmachine.com
Key Highlights: We’re the machining parts manufacturers that deliver extraordinary value by streamlining contract machining through automation and process control….
#6 Industrial Machine Parts & Equipment Services
Domain Est. 1999
Website: generalkinematics.com
Key Highlights: Our machine parts department has a huge inventory of replacement springs, stabilizers, motors, and other vibratory equipment parts and accessories in stock….
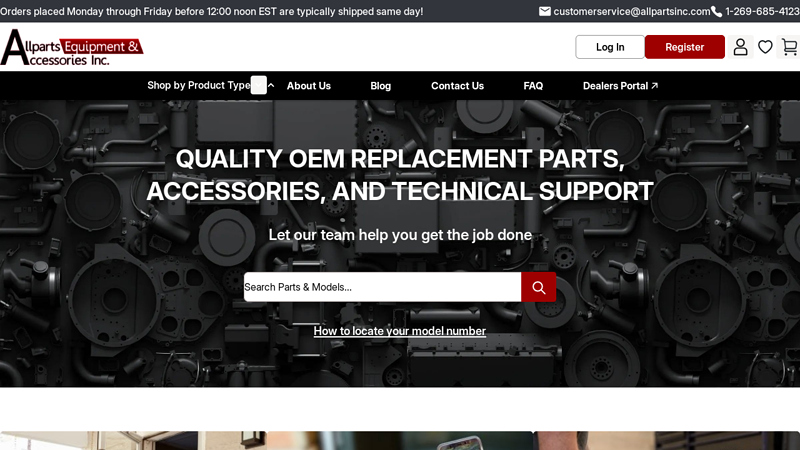
#7 OEM Parts Online
Domain Est. 2010
Website: allpartsinc.com
Key Highlights: 2-day deliveryTrusted OEM replacement parts supplier for 60+ years. Shop Allparts Equipment & Accessories for all industries. Fast shipping across US & Canada….
#8 PartsForMachines
Domain Est. 2019
Website: partsformachines.com
Key Highlights: Partsformachines is the largest online spare parts store in UK for all construction, agriculture, and industrial machinery. Get hassle-free delivery at the ……
#9 All World Machinery
Domain Est. 2002
Website: allworldmachinery.com
Key Highlights: All World is your one-stop shop solutions provider for aftermarket machine tool spare parts, services, repairs, and custom-engineered applications….
#10 H&W Machine Repair & Rebuilding
Domain Est. 2005
Website: machinerypartsdepot.com
Key Highlights: What We Do! As a one-stop-shop for the metalworking industry, our company provides new and used machines, high-quality replacement parts, and accessories….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Machine Parts

2026 Market Trends for Machine Parts
Global Demand and Industrial Growth
The machine parts market is expected to experience steady growth by 2026, driven by the expansion of advanced manufacturing, automation, and infrastructure development worldwide. Key industries such as automotive, aerospace, industrial machinery, and renewable energy are projected to increase their demand for precision machine components. Emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, particularly India and Southeast Asia, will play a significant role in driving demand due to rising industrialization and government-led manufacturing initiatives.
Advancements in Smart Manufacturing and Industry 4.0
By 2026, the integration of Industry 4.0 technologies will continue to reshape the machine parts sector. Smart sensors, IoT-enabled components, and predictive maintenance systems are becoming standard in industrial equipment. Machine parts with embedded monitoring capabilities will allow for real-time performance tracking, reducing downtime and improving operational efficiency. This shift is encouraging manufacturers to invest in intelligent components that support data-driven decision-making.
Sustainability and Green Manufacturing
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals will influence machine parts production and design. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting eco-friendly materials, energy-efficient production processes, and recyclable components. By 2026, demand is expected to grow for machine parts made from lightweight alloys, biodegradable composites, and recycled metals, particularly in the EU and North America where green manufacturing standards are tightening.
Supply Chain Resilience and Localization
Ongoing geopolitical tensions and past disruptions have prompted a reevaluation of global supply chains. By 2026, there will be a stronger emphasis on regionalization and nearshoring of machine parts production. Companies are investing in localized manufacturing hubs to reduce dependency on single-source suppliers and mitigate risks. This trend supports the growth of regional machine parts suppliers and encourages vertical integration within industrial supply chains.
Technological Innovation and Material Science
Advances in additive manufacturing (3D printing), nanotechnology, and advanced coatings are enabling the production of more durable, efficient, and complex machine parts. Customization and rapid prototyping will become more accessible, allowing for faster innovation cycles. High-performance materials such as ceramics, superalloys, and self-lubricating composites will gain traction in high-stress applications, especially in aerospace and energy sectors.
Workforce and Skills Transformation
As machine parts systems become more sophisticated, there is a growing need for skilled technicians and engineers capable of working with advanced machinery. The labor market will see increased demand for expertise in mechatronics, robotics, and digital twin technologies. Training programs and partnerships between industry and educational institutions will be critical to addressing the skills gap by 2026.
Conclusion
The machine parts market in 2026 will be characterized by technological sophistication, sustainability focus, and resilient supply networks. Companies that embrace digital transformation, invest in R&D, and adapt to regional market dynamics will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities in this evolving industrial landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Machine Parts: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Supplier Vetting
Failing to thoroughly assess a supplier’s manufacturing capabilities, quality control processes, and certifications (e.g., ISO 9001) often leads to inconsistent or substandard parts. Relying solely on price without evaluating technical expertise can result in parts that fail under operational conditions.
Poor Material Specifications
Ambiguous or incomplete material requirements (e.g., grade, hardness, heat treatment) increase the risk of receiving parts made from inferior or non-compliant materials, compromising durability and safety.
Lack of Dimensional and Tolerance Control
Machine parts often require tight tolerances and precise geometries. Without clear engineering drawings and inspection protocols, suppliers may deliver components that do not fit or function as intended, leading to assembly delays or equipment failure.
Insufficient Testing and Inspection
Skipping third-party inspections or in-house quality checks allows defects such as surface flaws, dimensional inaccuracies, or structural weaknesses to go undetected until after integration, increasing rework costs and downtime.
Inconsistent Batch-to-Batch Quality
Even if initial samples meet standards, ongoing production may drift due to changes in raw materials, tooling, or processes. Without robust quality assurance agreements and regular audits, long-term reliability suffers.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
Unprotected Design Disclosure
Sharing detailed CAD files or technical specifications without non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) or other legal safeguards exposes proprietary designs to misuse, reverse engineering, or unauthorized replication.
Unauthorized Manufacturing and Counterfeiting
Suppliers in certain regions may produce and sell copies of your parts without permission. This not only erodes market share but can also damage brand reputation if counterfeit parts fail in the field.
Grey Market Diversion
Suppliers may divert legitimately produced parts to unauthorized markets or resellers, undermining pricing strategies and distribution agreements.
Lack of IP Clauses in Contracts
Failing to include clear IP ownership terms in procurement contracts can result in disputes over design rights, especially when custom tooling or modifications are involved.
Weak Supply Chain Oversight
Without visibility into sub-tier suppliers and manufacturing locations, companies risk unknowingly sourcing from facilities that have previously engaged in IP infringement or lack IP compliance policies.
Addressing these pitfalls requires proactive due diligence, strong contractual protections, continuous quality monitoring, and a clear IP strategy throughout the sourcing process.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Machine Parts
Overview
Transporting machine parts globally involves navigating complex logistics and compliance requirements. This guide provides essential information to ensure the safe, efficient, and legally compliant movement of machine components across domestic and international supply chains.
Classification and Documentation
Correctly classifying machine parts is critical for customs clearance and regulatory compliance. Use the Harmonized System (HS) code to identify each part, ensuring accurate tariff classification. Common HS codes for machine parts range from 84.31 (parts of machinery for various industrial applications) to 85.03 (parts of electrical machinery). Maintain accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, and bills of lading. For international shipments, include detailed descriptions, part numbers, weights, and values.
Packaging and Handling
Machine parts require robust packaging to prevent damage during transit. Use wooden crates, reinforced cardboard, or custom-fitted containers based on part size and fragility. Clearly label packages with handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” “Do Not Stack”). Include internal cushioning and moisture barriers where necessary. For heavy or oversized parts, ensure proper lifting points and secure crating to meet freight carrier requirements.
Transportation Modes and Considerations
Choose the appropriate transportation mode based on lead time, cost, and part characteristics:
– Air Freight: Best for urgent, high-value, or lightweight components.
– Ocean Freight: Cost-effective for heavy or large-volume shipments; use FCL (Full Container Load) or LCL (Less than Container Load).
– Road/Rail: Ideal for regional or cross-border land transport; ensure compliance with weight and dimension regulations.
For oversized or heavy machinery parts, coordinate with freight forwarders for special permits and route planning.
Import/Export Regulations
Comply with export control laws such as the U.S. Export Administration Regulations (EAR) or EU Dual-Use Regulation, especially if parts contain controlled technologies. Obtain necessary export licenses when required. For imports, verify country-specific regulations, including safety, environmental, and technical standards (e.g., CE marking in the EU, CCC in China). Be aware of trade sanctions, embargoes, and restricted party screening requirements.
Customs Clearance
Ensure all required documentation is complete and consistent to avoid delays. This includes:
– Commercial invoice
– Packing list
– Bill of lading or airway bill
– Certificate of origin (if claiming preferential tariffs under trade agreements)
– Import/export licenses (if applicable)
Work with a licensed customs broker to facilitate smooth clearance and address duty assessments.
Product Compliance and Standards
Verify that machine parts meet destination market requirements. Key standards may include:
– ISO standards for quality and safety
– RoHS and REACH compliance for hazardous substances (EU)
– UL, CSA, or ETL certification for electrical components
– Pressure Equipment Directive (PED) for parts used in pressure systems
Ensure technical documentation and conformity assessments are available upon request.
Risk Management and Insurance
Insure shipments against loss, damage, or theft. Choose coverage that reflects the full replacement value and includes risks specific to machine parts (e.g., shock, moisture, rust). Conduct regular risk assessments of suppliers, logistics partners, and transportation routes. Implement traceability systems using barcodes or RFID to monitor parts throughout the supply chain.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Adopt sustainable packaging materials and optimize load efficiency to reduce carbon footprint. Comply with environmental regulations regarding the disposal of packaging materials and hazardous components. Consider recycling programs for scrap or obsolete machine parts.
Conclusion
Successful logistics and compliance for machine parts depend on accurate classification, proper documentation, secure packaging, and adherence to international regulations. Partnering with experienced freight forwarders, customs brokers, and compliance experts ensures efficient, lawful, and timely delivery worldwide. Regular training and audits help maintain ongoing compliance and operational excellence.
In conclusion, sourcing machine parts effectively requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, reliability, and timeliness. It is essential to evaluate suppliers based on their reputation, certifications, production capabilities, and ability to meet specifications and delivery schedules. Leveraging both local and global supply chains can provide competitive advantages, while building strong supplier relationships ensures long-term success and supply chain resilience. Additionally, incorporating sustainable and ethical sourcing practices contributes to operational integrity and corporate responsibility. With careful planning, thorough due diligence, and ongoing supplier management, organizations can secure high-quality machine parts that support efficient operations, reduce downtime, and enhance overall productivity.