The global fastener market, valued at USD 116.1 billion in 2023, is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% through 2030, driven by expanding demand across automotive, aerospace, electronics, and construction sectors (Grand View Research, 2023). Within this landscape, precision screws such as M3.5 variants have emerged as critical components in high-tolerance applications—ranging from consumer electronics to medical devices—where reliability and standardization are paramount. As automation and miniaturization trends accelerate, especially in Asia-Pacific and North America, the need for high-quality, ISO-compliant M3.5 screws continues to rise. This growing demand has elevated the importance of manufacturers capable of delivering consistency, scalability, and materials innovation. Based on production capacity, global reach, quality certifications, and industry reputation, the following nine companies stand out as leading M3.5 screw manufacturers shaping the future of precision fastening.
Top 9 M3.5 Screw Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 M3.5 Screws
Domain Est. 1998
Website: globalspec.com
Key Highlights: 45-day returnsList of M3.5 Screws Product Specs, Datasheets, Manufacturers & Suppliers….
#2 Screw (m3.5 X 7 Mm) 661037001
Domain Est. 2004
Website: ereplacementparts.com
Key Highlights: 1–2 day delivery 365-day returnsBuy the official Ridgid Screw (m3.5 X 7 Mm) 661037001 replacement – Use our model diagrams, repair help, and video tutorials to help get the job don…
#3 M3.5 Stainless Steel Self Tapping Screws Cross Round Pan Head …
Domain Est. 2009
Website: taydaelectronics.com
Key Highlights: In stock 30-day returnsM3.5 Stainless Steel Self Tapping Screws Cross Round Pan Head 3x8mm ; Thread Length · 8mm ; Manufacturer · Tayda Electronics ; Menufacturer Part No. · Stainl…
#4 M3.5 Machine Screws
Domain Est. 1994
Website: newark.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $150 · 60-day returnsFind a huge range of M3.5 Machine Screws at Newark Electronics. We stock a wide range of Machine Screws, such as M4, M3, M5 & M6 Machine Sc…
#5 M3.5 Screws & Fasteners
Domain Est. 1995
Website: mouser.com
Key Highlights: $4.99 deliveryM3.5 Screws & Fasteners are available at Mouser Electronics. Mouser offers inventory, pricing, & datasheets for M3.5 Screws & Fasteners….
#6 M3.5X5MM PH-FL-MS-SS-ISO7046
Domain Est. 1996
Website: pencomsf.com
Key Highlights: Metric. Product Type, Machine screw. Head Type, 90 degree flat head. Thread, M3.5 x 0.6. Length (L), 5 mm. Length Range (L), 5.24/4.76. Recess, Cross-recess….
#7 Metric Machine Screws
Domain Est. 2004
Website: mfsupply.com
Key Highlights: 8–13 day deliveryLooking for metric sized machine screws? We carry metric machine screws per Din 965, ISO 14581, JIS B1111, ISO 7045, Din 7985A, and ISO 14583 specifications….
#8 M3.5
Domain Est. 2004
Website: fastenersuperstore.com
Key Highlights: In stock $18.17 deliveryM3.5-1.65 x 10 mm Thread Forming Screws for Plastics 45 / Six-Lobe (Torx®) / Pan Head / Steel / Zinc ; Part Number: 547376 ; Carton Quantity: 10,000 pcs ; C…
#9 M3 Flat Head Cap Machine Screws (FHCS)
Domain Est. 2019
Website: us.store.bambulab.com
Key Highlights: In stock Free deliveryM3 Flat Head Cap Machine Screws (FHCS) 1. Stainless steel grade 4.8 countersunk hex socket full-thread screws. 2. The countersunk head can be concealed ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for M3.5 Screw

H2: 2026 Market Trends for M3.5 Screws
The global market for M3.5 screws is projected to experience steady growth and notable shifts by 2026, driven by advancements in manufacturing, rising demand across key industries, and evolving supply chain dynamics. As a specialized fastener with a 3.5 mm nominal diameter, the M3.5 screw serves niche but critical applications in electronics, automotive systems, medical devices, and precision machinery. The following analysis outlines the key trends expected to shape the M3.5 screw market in 2026:
-
Increased Demand from Electronics and Consumer Devices
The proliferation of compact electronic devices—such as wearables, smartphones, drones, and IoT hardware—continues to drive demand for small, reliable fasteners like the M3.5 screw. As product designs become more miniaturized and modular, manufacturers favor standardized yet robust screws that offer high durability in tight spaces. This trend is expected to accelerate through 2026, particularly in Asia-Pacific electronics manufacturing hubs. -
Growth in Electric Vehicles (EVs) and Automotive Electrification
The automotive sector, especially the EV market, is adopting more electronic control units (ECUs), battery management systems, and sensor arrays—all of which use M3.5 screws for internal assembly. With global EV production expected to surge by 2026, demand for precision fasteners will rise correspondingly, enhancing the role of M3.5 screws in automotive applications. -
Shift Toward High-Performance Materials
Market demand is pushing manufacturers to produce M3.5 screws from advanced materials such as stainless steel (A2 and A4 grades), titanium, and specialized alloys that offer superior corrosion resistance, strength-to-weight ratio, and thermal stability. This shift is particularly evident in aerospace, medical, and marine applications, where reliability under extreme conditions is critical. -
Sustainability and Circular Economy Pressures
By 2026, sustainability regulations and corporate ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals are expected to influence fastener production. Recyclable materials, energy-efficient manufacturing (e.g., cold forging), and reduced packaging waste will become competitive differentiators. Some producers may offer take-back programs or reusable fastener solutions, especially in industrial equipment sectors. -
Supply Chain Localization and Resilience
Ongoing geopolitical tensions and post-pandemic supply chain reevaluations are prompting companies to diversify sourcing. While China remains a dominant producer of small screws, regional manufacturing in Southeast Asia, Eastern Europe, and North America is expected to grow. This trend supports shorter lead times and reduced import dependency, benefiting industries requiring just-in-time delivery of M3.5 screws. -
Automation and Smart Manufacturing Integration
The rise of Industry 4.0 technologies is transforming fastener production and usage. Automated screw feeding systems, robotic assembly lines, and smart inventory management (e.g., RFID-tagged fasteners) are increasing efficiency in end-user operations. M3.5 screws compatible with automated handling are likely to gain market share, especially in high-volume electronics and automotive plants. -
Standardization and Quality Certification
As global trade continues, adherence to international standards (e.g., ISO, DIN, ANSI) becomes more critical. By 2026, buyers are expected to prioritize suppliers with certifications such as ISO 9001, IATF 16949 (for automotive), or medical-grade compliance (e.g., ISO 13485). This trend will elevate quality expectations and may consolidate the market around fewer, more capable producers.
Conclusion
By 2026, the M3.5 screw market will be shaped by technological innovation, sector-specific demands, and sustainability imperatives. While still a small component in broader industrial systems, its role in enabling precision engineering and product reliability ensures sustained relevance. Companies that invest in material innovation, automation compatibility, and supply chain resilience are best positioned to capture growth in this specialized fastener segment.
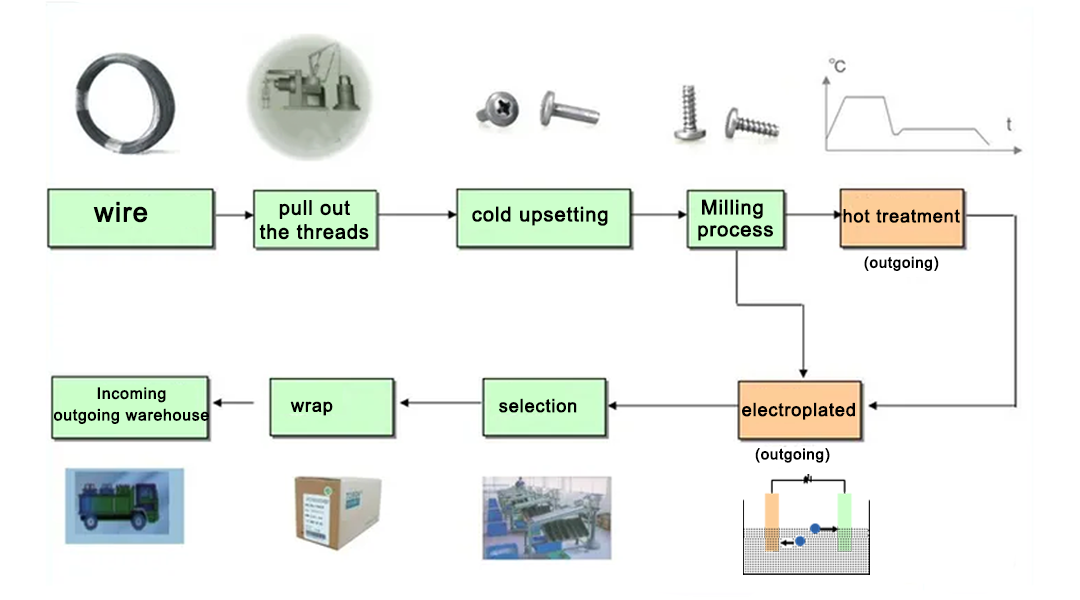
H2: Common Pitfalls When Sourcing M3.5 Screws (Quality and IP Considerations)
Sourcing M3.5 screws may seem straightforward, but several pitfalls can compromise product quality, performance, and compliance—especially when quality standards and intellectual property (IP) are not carefully managed. Below are key challenges to watch for:
1. Inconsistent Material Quality
Many suppliers—particularly low-cost manufacturers—use substandard materials (e.g., low-grade stainless steel or unverified alloys) that fail to meet required mechanical or corrosion resistance specifications. This can lead to thread stripping, breakage, or premature rusting, especially in demanding environments.
2. Poor Thread Precision and Tolerances
M3.5 is a less common metric size compared to M3 or M4, increasing the risk of non-standard thread profiles or incorrect pitch (typically 0.6 mm). Inaccurate threading leads to assembly issues, cross-threading, or reduced clamping force.
3. Inadequate or Misrepresented IP (Intellectual Property) Compliance
Some suppliers may offer screws that mimic proprietary designs (e.g., Torx Plus, Pentalobe) protected by IP rights. Sourcing such items without proper licensing exposes buyers to legal risks, including infringement claims and shipment seizures.
4. Lack of Certification and Traceability
Critical applications (e.g., medical, aerospace, automotive) require screws with full material certifications (e.g., RoHS, REACH, ISO 898). Many generic suppliers lack proper documentation or falsify certifications, undermining quality assurance and regulatory compliance.
5. Inconsistent Surface Treatments and Coatings
Poorly applied or unverified coatings (e.g., zinc plating, Dacromet) may not deliver the specified corrosion protection or torque performance. This is especially problematic in humid or saline environments.
6. Supply Chain Transparency Issues
OEMs often face challenges tracing the origin of screws, particularly when sourced through intermediaries. Opaque supply chains increase risks of counterfeit parts, ethical sourcing violations, and quality deviations.
7. Overlooking Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) and Customization Limits
Some manufacturers resist small-batch or custom orders for non-standard sizes like M3.5, pushing buyers toward off-spec alternatives that compromise design integrity.
Best Practices to Avoid Pitfalls
– Partner with certified, audited suppliers experienced with precision fasteners.
– Request material test reports (MTRs) and dimensional inspection reports.
– Verify IP rights for specialty drive types before production.
– Conduct pre-production sampling and in-house testing.
– Use procurement contracts that specify compliance, liability, and audit rights.
By addressing these pitfalls proactively, businesses can ensure reliable performance, legal compliance, and long-term cost efficiency when sourcing M3.5 screws.
H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for M3.5 Screw
Overview
The M3.5 screw, while not part of the standard ISO metric screw thread series (which includes M3 and M4), is occasionally used in specialized applications such as precision instruments, electronics, and custom machinery. Due to its non-standard nature, logistics and compliance considerations require careful attention to specification, sourcing, and regulatory alignment.
1. Technical Specifications & Standardization
- Thread Type: M3.5 refers to a nominal diameter of 3.5 mm. Confirm thread pitch (e.g., M3.5×0.6 is common) and whether it follows a recognized standard (e.g., ISO, DIN, or proprietary).
- Standard Compliance: Since M3.5 is not ISO-standardized, ensure full documentation of:
- Thread pitch
- Head type (e.g., pan, flat, socket cap)
- Drive type (e.g., Phillips, slotted, hex)
- Material (e.g., steel, stainless steel, brass)
- Surface finish (e.g., zinc plating, passivation)
- Documentation: Require detailed technical drawings and material certifications (e.g., RoHS, REACH) from suppliers.
2. Sourcing & Procurement
- Supplier Qualification: Source from manufacturers or distributors with capabilities for non-standard threads. Verify traceability and quality control systems.
- Custom Tooling: Be aware that custom taps and dies may be required, affecting lead times and costs.
- Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs): Non-standard parts often have higher MOQs; plan inventory accordingly.
- Dual Sourcing: Consider dual sourcing to mitigate supply chain risk due to limited availability.
3. Packaging & Labeling
- Packaging: Use ESD-safe packaging if used in electronics. Ensure protection from corrosion (e.g., VCI bags for steel screws).
- Labeling:
- Clearly mark part number, material, finish, and compliance certifications.
- Include lot/batch numbers for traceability.
- Follow customer-specific labeling requirements (e.g., barcode, QR code).
4. Regulatory Compliance
- RoHS (EU): Ensure compliance with Restriction of Hazardous Substances, especially if used in electrical/electronic equipment.
- REACH (EU): Confirm no SVHCs (Substances of Very High Concern) in materials or plating.
- Conflict Minerals (US Dodd-Frank Act): If applicable, document origin of tin, tantalum, tungsten, and gold (3TG).
- Packaging Regulations (e.g., EU Directive 94/62/EC): Ensure packaging is compliant with recyclability and heavy metal limits.
5. Shipping & Customs
- HS Code Classification: Use appropriate HS code (e.g., 7318.15 for threaded fasteners of iron/steel). Confirm with customs broker.
- Export Controls: Verify if screws fall under export control regulations (e.g., EAR in the US), especially if made from controlled materials or used in sensitive applications.
- Documentation: Include commercial invoice, packing list, and certificates of compliance (material, RoHS, etc.).
- Country-Specific Requirements:
- UKCA marking may be required for screws supplied in the UK.
- China RoHS requires labeling if used in electronic information products.
6. Inventory & Handling
- Storage: Store in dry, temperature-controlled environments to prevent rust or degradation.
- First Expired, First Out (FEFO): Apply if coatings or materials have shelf-life limitations.
- Traceability: Maintain batch-level tracking for quality and recall purposes.
7. Quality Assurance
- Incoming Inspection: Verify thread dimensions, torque performance, and visual defects.
- Testing: Perform salt spray testing for corrosion resistance if required.
- Certification: Request mill test reports (MTRs) and compliance declarations from suppliers.
Summary
Due to its non-standard nature, the M3.5 screw demands rigorous technical documentation, careful supplier management, and strict adherence to compliance regulations. Proactive planning in sourcing, labeling, and customs clearance is essential to ensure smooth logistics and regulatory alignment across global markets.
Conclusion on Sourcing M3.5 Screws:
After evaluating various sourcing options for M3.5 screws, it is evident that while this size is less standardized than common metric threads like M3 or M4, reliable supply channels do exist. Sourcing M3.5 screws requires careful consideration of application requirements, material specifications (e.g., stainless steel, steel with plating), head type (e.g., pan, flat, hex), and drive style (e.g., Phillips, slotted, Torx).
Specialty fastener suppliers, industrial distributors, and precision hardware manufacturers offer M3.5 screws, though availability may vary by region and quantity. For high-volume or custom needs, direct engagement with manufacturers—particularly in regions with strong fastener industries such as Germany, Japan, or China—can provide cost-effective and consistent supply. Additionally, 3D printing or thread rolling may be viable alternatives for low-volume or prototyping scenarios.
In conclusion, while M3.5 screws are not as readily available as more common sizes, they can be successfully sourced through niche suppliers or custom manufacturing, provided that lead times, quality standards, and minimum order quantities are properly managed. Establishing relationships with reliable vendors and maintaining accurate specifications will ensure long-term supply stability.