The global steel pipe market continues to expand, driven by rising demand in the oil & gas, construction, and infrastructure sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global steel pipes market was valued at USD 75.6 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is further supported by increasing investments in energy transportation networks and water supply systems, particularly in emerging economies. As large-diameter line pipes become critical for major pipeline projects, LSAW (Longitudinal Submerged Arc Welded) steel pipes—known for their strength, durability, and suitability for high-pressure applications—have emerged as a preferred choice in long-distance oil and gas transmission. With market competition intensifying, a select group of manufacturers have risen to prominence through advanced production capabilities, stringent quality compliance, and global supply reach. Below, we present the top 10 LSAW steel pipe manufacturers shaping the industry’s future, based on production capacity, market presence, technological investment, and project track record.
Top 10 Lsaw Steel Pipe Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 China LSAW Steel Pipe Manufacturer, Supplier, and Factory
Domain Est. 2023
Website: zssteelpipes.com
Key Highlights: As a reliable LSAW steel pipe manufacturer, supplier, and factory in China, we offer high-quality products, timely delivery, and excellent customer service….
#2 The world’s leading manufacturer of LSAW pipes
Domain Est. 2008
Website: eew-group.com
Key Highlights: EEW Group is one of the leading global manufacturers of longitudinally welded pipes, with a long and proud history dating back to 1936….
#3 LSAW Steel Pipe, LSAW Pipes Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2015
Website: hebeileading.com
Key Highlights: Hebei Leading offers high-quality LSAW steel pipe. Featuring excellent ductility, weld toughness, uniformity, plasticity and great sealing, ……
#4 Seamless steel pipe
Domain Est. 2017
Website: united-steel.com
Key Highlights: As a professional manufacturer,UNITED STEEL INDUSTRY CO.,LTD offer you the best steel pipes,such as Carbon pipes,seamless steel pipe,stainless steel pipe ……
#5 China Steel Pipe Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2017
Website: tuspipe.com
Key Highlights: TUSPIPE produces LSAW steel pipes (Longitudinally Submerged Arc Welded steel pipes) in strict compliance with standards such as ASTM A252, ……
#6 LSAW Steel Pipe
Domain Est. 2018
Website: winsteelpipes.com
Key Highlights: Our main products are SMLS, ERW, SSAW and LSAW steel pipe and pipe fittings, used in Oil & Gas, Construction & Shipping, Marine & Offshore, Environment & ……
#7 Eastern Steel Manufacturing Co.,Ltd
Domain Est. 2021
Website: eastern-steels.com
Key Highlights: Eastern Steel Manufacturing Co.,Ltd is a leading manufacturer and distributor of seamless steel pipe, welded steel pipe, OCTG products and fittings….
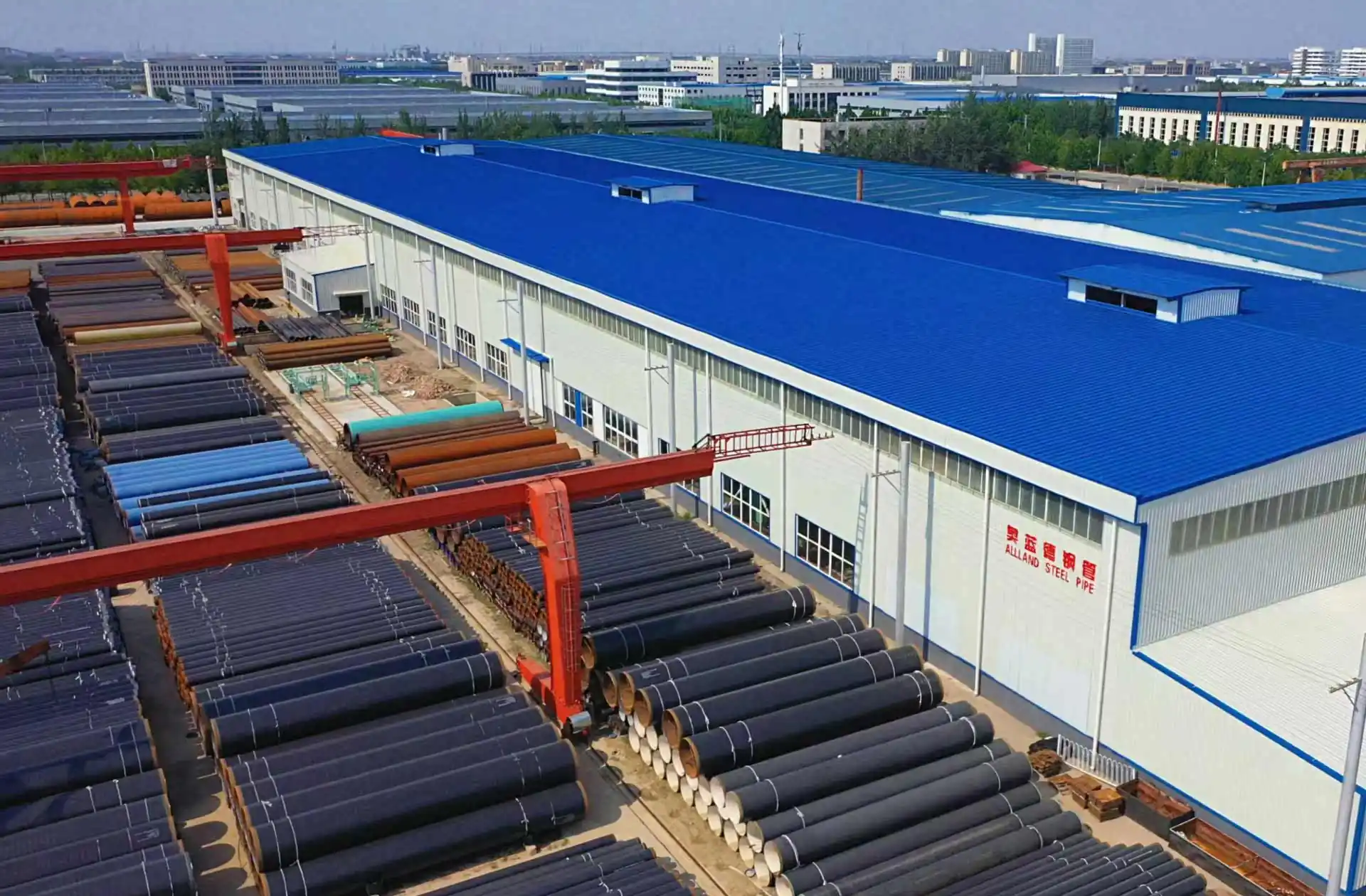
#8 Allland Steel Pipe
Website: alllandpipes.com
Key Highlights: Thick-walled LSAW pipe manufacturer with 200000-ton capacity & JCOE tech. API certified global supplier. Get your reliable steel pipe quote today!…
#9 Onshore large
Domain Est. 2002
Website: severstal.com
Key Highlights: Rating 5.0 (1) Pipes are manufactured from 508 to 1422 mm in diameter, with steel grades reaching up to X100, and lengths from 12 to 18.3 m….
#10 Large
Domain Est. 2003
Website: sms-group.com
Key Highlights: LSAW (Longitudinal Submerged Arc Welding) pipes are usually the most economical solution. These pipes are characterized by diameters from 16 to 64 inches and ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Lsaw Steel Pipe
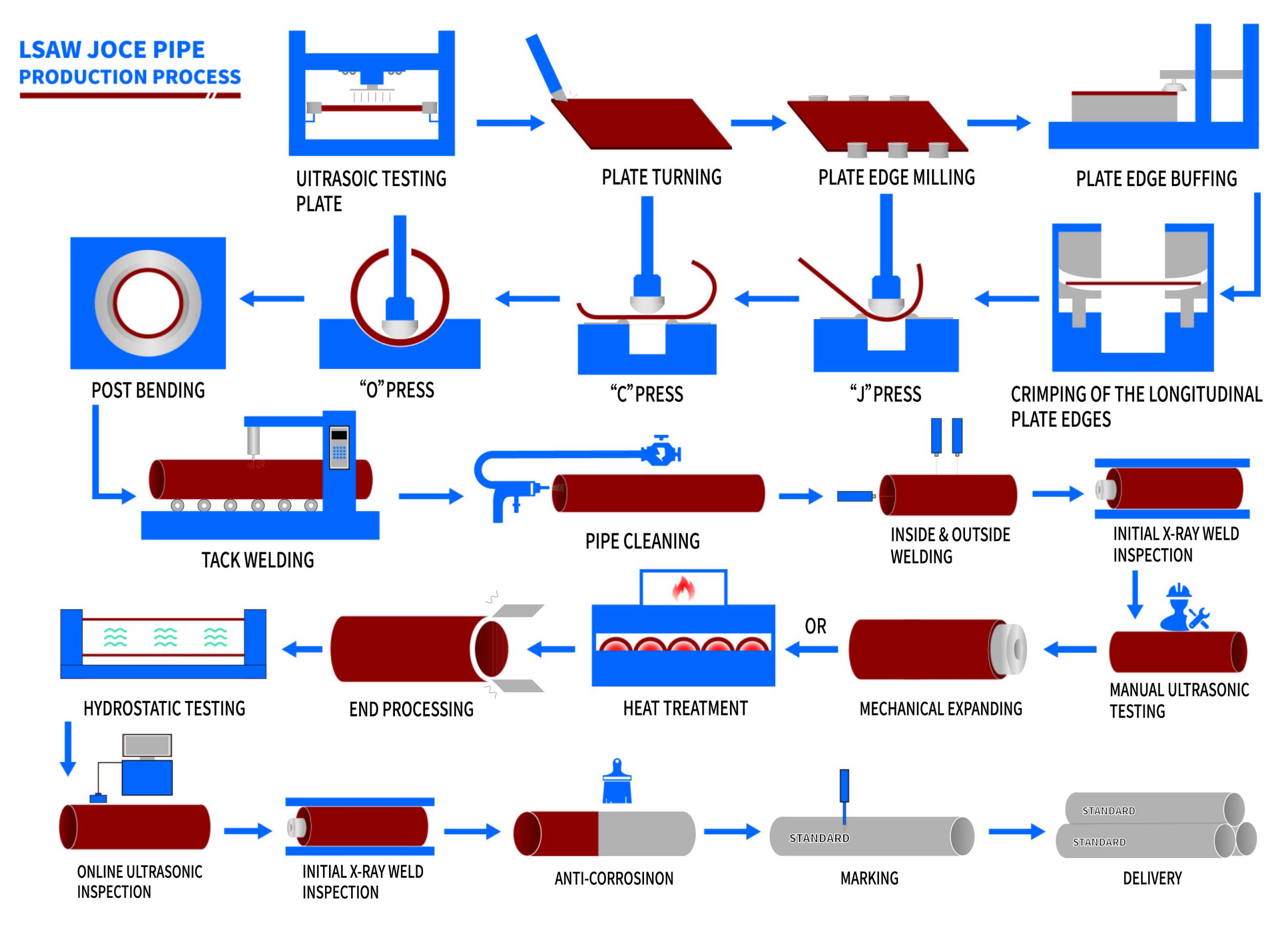
H2: Projected Market Trends for LSAW Steel Pipes in 2026
The Longitudinal Submerged Arc Welded (LSAW) steel pipe market is expected to experience steady growth by 2026, driven by increasing demand across key infrastructure and energy sectors. Several macroeconomic, technological, and regional factors are shaping the trajectory of this market.
-
Rising Infrastructure and Energy Investments
A major driver for LSAW steel pipe demand in 2026 will be the global push for energy security and infrastructure modernization. Governments in North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific are investing heavily in oil and gas pipeline networks, particularly for natural gas transportation as a transitional fuel in the energy mix. LSAW pipes, known for their high strength and suitability for high-pressure applications, are favored for onshore and offshore pipeline projects. -
Growth in Renewable Energy and Hydrogen Infrastructure
While the energy transition is reducing reliance on fossil fuels, LSAW pipes are finding new applications in emerging sectors. By 2026, pilot and large-scale hydrogen transport projects are expected to adopt LSAW technology due to its durability and leak-resistant weld quality. Retrofitting existing natural gas pipelines with LSAW components for hydrogen compatibility is also anticipated to create new market opportunities. -
Technological Advancements and Automation
Manufacturers are increasingly adopting automation and digital monitoring in LSAW production lines to enhance precision, reduce waste, and improve weld integrity. By 2026, smart factories using IoT-enabled quality control systems are expected to dominate leading production hubs in China, India, and Eastern Europe, improving competitiveness and reducing lead times. -
Regional Market Dynamics
- Asia-Pacific will remain the largest consumer and producer of LSAW steel pipes, led by China and India’s urbanization and pipeline expansion programs.
- North America is expected to see moderate growth, supported by shale gas development and aging pipeline replacements under U.S. infrastructure initiatives.
- The Middle East and Africa will witness increased demand due to new oil and gas exploration projects, particularly in the Eastern Mediterranean and Sub-Saharan Africa.
-
Europe’s market will be shaped by regulatory standards and the shift toward low-carbon infrastructure, with niche demand for hydrogen-ready LSAW systems.
-
Raw Material and Cost Volatility
Steel prices and supply chain stability will continue to influence LSAW pipe costs in 2026. Fluctuations in iron ore and scrap metal markets, along with trade policies (e.g., tariffs and anti-dumping measures), may impact profit margins. However, vertical integration and recycling initiatives among key producers are expected to mitigate some cost pressures. -
Sustainability and Regulatory Pressures
Environmental regulations will play a larger role in shaping production standards. By 2026, manufacturers may face stricter emissions guidelines, pushing investment in cleaner production technologies. Additionally, demand for certified, low-carbon steel in LSAW pipes is expected to rise, especially in ESG-driven markets.
Conclusion
The LSAW steel pipe market in 2026 will be characterized by resilient demand from energy and infrastructure sectors, adaptation to new energy vectors like hydrogen, and increased efficiency through digital manufacturing. While challenges related to raw materials and regulation persist, the industry is poised for targeted growth, particularly in emerging economies and next-generation energy projects.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing LSAW Steel Pipes: Quality and Inspection Plan (IP) Issues
Sourcing Longitudinally Submerged Arc Welded (LSAW) steel pipes requires careful attention to quality standards and inspection protocols. Buyers often encounter challenges that can lead to project delays, safety risks, or cost overruns. Below are common pitfalls related to quality and the Inspection Plan (IP) when sourcing LSAW pipes.
Inadequate Material Certification and Traceability
One of the most frequent issues is the lack of proper material test reports (MTRs) and traceability. Some suppliers provide incomplete or falsified documentation, making it difficult to verify compliance with standards like API 5L, ASTM A53, or ISO 3183. Without full traceability from heat number to final product, ensuring consistent quality becomes nearly impossible.
Poor Weld Quality and Inconsistent NDT Coverage
The longitudinal weld is a critical area in LSAW pipes. Inadequate submerged arc welding practices or insufficient non-destructive testing (NDT)—such as ultrasonic testing (UT) or radiographic testing (RT)—can lead to undetected defects like lack of fusion, porosity, or cracks. A weak or poorly inspected weld compromises the structural integrity, especially in high-pressure applications.
Deviations from Specified Wall Thickness and Dimensional Tolerances
LSAW pipes must adhere to strict dimensional tolerances for outer diameter, wall thickness, and straightness. Some manufacturers cut costs by producing pipes with under-thickness walls or inconsistent diameters. This not only affects performance but may also cause fitting and installation issues in the field.
Incomplete or Non-Compliant Inspection Plans (IP)
An effective Inspection and Test Plan (ITP) is essential to validate quality at every production stage. However, many suppliers either skip key inspection points (e.g., pre-weld material checks, post-weld heat treatment verification) or fail to involve third-party inspectors (TPIs) as required by project specifications. Relying solely on supplier-conducted inspections increases the risk of oversight.
Insufficient Mechanical and Chemical Testing
Comprehensive mechanical testing—including tensile, impact (Charpy V-notch), and hardness tests—is often overlooked or inadequately performed. Similarly, chemical composition analysis must confirm that the steel meets specified grades (e.g., API 5L X52, X60, X70). Skipping these tests or accepting batch averages without individual verification can result in substandard material entering the supply chain.
Coating and Surface Treatment Deficiencies
External and internal coatings (e.g., FBE, 3LPE, or epoxy) are vital for corrosion protection. Poor coating application—such as inadequate surface preparation, incorrect curing, or thin spots—reduces pipe lifespan. Without rigorous inspection of coating thickness, adhesion, and holiday detection, long-term reliability is compromised.
Lack of Qualified Manufacturing Oversight
Not all LSAW pipe mills are created equal. Sourcing from mills without proper certifications (e.g., API 5L Monogram, ISO 9001) or experienced quality control teams increases the likelihood of defects. Buyers should verify the mill’s track record and ensure qualified personnel oversee welding, heat treatment, and inspection processes.
Inconsistent Hydrostatic Testing Procedures
Hydrostatic testing is a critical final check to ensure pipe integrity under pressure. However, some suppliers reduce test duration, use incorrect pressures, or fail to document results properly. Skipping or shortening this step can allow weak or flawed pipes to pass as acceptable.
Failure to Implement Third-Party Inspections
Relying solely on the manufacturer’s internal quality checks is a significant risk. Independent third-party inspections during fabrication, welding, and testing stages are crucial for impartial validation. Skipping third-party involvement often results in undetected quality issues surfacing only after delivery or installation.
Inadequate Packaging and Handling Protocols
Even high-quality pipes can be damaged during transport if not properly protected. Missing or damaged end caps, improper bundling, or exposure to moisture can lead to corrosion or mechanical damage. A comprehensive IP should include pre-shipment inspection to verify packaging and handling meet project requirements.
By recognizing and addressing these common pitfalls, buyers can mitigate risks and ensure the delivery of reliable, code-compliant LSAW steel pipes for critical infrastructure projects.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for LSAW Steel Pipes
LSAW (Longitudinal Submerged Arc Welded) steel pipes are critical components in energy, infrastructure, and industrial projects. Their size, weight, and intended applications demand meticulous planning in logistics and strict adherence to compliance standards. This guide outlines key considerations for safe, efficient, and compliant transportation and handling of LSAW pipes.
Understanding LSAW Pipe Characteristics
LSAW pipes are typically large-diameter (often 16 inches and above), heavy, and manufactured to precise specifications. Key characteristics impacting logistics include:
* Dimensions: Lengths commonly range from 6 to 18 meters (20 to 60 feet), with diameters from 16 inches (406 mm) up to 60+ inches (1500+ mm).
* Weight: Individual pipe weights can range from hundreds of kilograms to several tons.
* Fragility: While robust, pipe ends (particularly bevels and coatings) are susceptible to damage during handling.
* Surface Coatings: Often coated (e.g., FBE, 3LPE, 3LPP) requiring protection to prevent damage that compromises corrosion resistance.
Transportation Planning & Method Selection
Selecting the right transportation method is crucial based on distance, destination, volume, pipe specifications, and cost.
* Ocean Freight (Containers & Breakbulk):
* Breakbulk/Project Cargo: The most common method for large-diameter LSAW pipes. Pipes are loaded onto flat racks, open-top containers, or directly onto the ship’s deck using heavy-lift gear.
* Containerization: Possible for smaller-diameter or shorter LSAW pipes fitting within standard or high-cube containers (20′ or 40′), but less common due to size constraints.
* Key Considerations: Stowage planning, lashing/securing according to CSS Code, protection from saltwater, and coordination with port facilities capable of handling heavy, oversized cargo.
* Rail Transport:
* Suitable for long overland distances, especially within continents.
* Requires specialized flatcars designed for heavy, long loads.
* Critical attention to axle load limits, bridge clearances, and route restrictions (curves, tunnels).
* Road Transport (Trucking):
* Prime Mover & Lowboy Trailers: Essential for oversized loads. Requires permits for weight and dimensions in most jurisdictions.
* Specialized Trailers: Extendable beam trailers (SPMTs – Self-Propelled Modular Transporters) or hydraulic modular trailers for exceptionally heavy or long pipes.
* Route Survey: Mandatory to identify obstacles (bridges, overpasses, power lines, narrow roads) and plan the safest, most efficient path. Escort vehicles are often required.
* Multimodal Transport: Complex shipments often combine methods (e.g., truck to port -> ocean -> rail -> final trucking). Seamless handoffs and coordinated documentation are vital.
Handling, Loading, and Securing Procedures
Improper handling is a primary cause of damage. Strict protocols must be enforced.
* Lifting:
* Use only approved lifting devices: Spreader beams are highly recommended to distribute load evenly and prevent deformation. Avoid slings directly on pipe body if possible; use padding if necessary.
* Never lift by the pipe ends or use chains/slings that can damage the coating or bevel.
* Ensure lifting points (if provided) are rated for the load.
* Loading/Unloading:
* Use cranes with sufficient capacity and appropriate reach.
* Maintain control during all movements. Avoid swinging.
* Place pipes gently on transport supports or storage racks.
* Securing (Lashing):
* Mandatory for all transport modes. Follow the IMO/ILO/UNECE Code of Safe Practice for Cargo Stowage and Securing (CSS Code).
* Use adequate number and strength of lashing straps, chains, or wire ropes with proper tension.
* Use dunnage (wooden blocks) and chocks to prevent rolling and absorb shock/vibration. Protect coatings with padding (e.g., rubber, felt) at contact points.
* Ensure the securing method prevents longitudinal, lateral, and vertical movement.
Storage Best Practices
Proper storage prevents damage and degradation before installation.
* Location: Level, well-drained, stable ground. Avoid areas prone to flooding or excessive moisture.
* Support: Use cradles or saddles with wide, rounded supports (minimum 4 points per pipe). Avoid direct contact with bare ground; use timber dunnage. Support points should be near the pipe ends and center.
* Stacking: Limit stack height based on pipe diameter, wall thickness, and support strength to prevent deformation. Use dunnage between layers. Avoid uneven stacking.
* Protection: Keep pipe ends capped (plastic or wooden) to prevent contamination and damage to bevels/coatings. Cover stacks with UV-resistant, breathable tarpaulins if stored long-term outdoors. Protect from direct sunlight, which can degrade certain coatings.
* Environment: Minimize exposure to corrosive environments (salt spray, chemicals). Keep storage area clean.
Regulatory and Compliance Requirements
Compliance ensures safety, quality, and legal shipment.
* International Standards:
* API 5L: The primary specification for line pipe, covering material, dimensions, testing, and marking. Compliance is often mandatory for oil & gas projects.
* ISO 3183: International equivalent to API 5L.
* ASME B31.4 / B31.8: Cover pipeline design and construction, influencing pipe requirements.
* Transportation Regulations:
* IMDG Code: For hazardous materials (if applicable, e.g., pipes with certain residues).
* International Road/Rail Regulations: (e.g., ADR for Europe, DOT for USA) covering vehicle weights, dimensions, safety, and documentation for oversized/overweight loads.
* Customs Regulations: Accurate Harmonized System (HS) codes, commercial invoices, packing lists, certificates of origin, and any required import permits.
* Certification & Documentation:
* Mill Test Certificates (MTCs) / Material Test Reports (MTRs): Mandatory, providing traceability and proof of compliance with specified standards (e.g., API 5L, ISO 3183).
* Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) Reports: Records of ultrasonic (UT), radiographic (RT), magnetic particle (MT) testing.
* Coating Inspection Reports: Verification of coating application and quality.
* Weight Certificates: For customs and load calculations.
* Packing List: Detailed list of contents, quantities, weights, dimensions.
* Bill of Lading / Air Waybill: Contract of carriage.
* Environmental & Safety:
* Comply with local and international environmental regulations (e.g., handling of waste coatings, spill prevention).
* Adhere to workplace safety standards (OSHA, local equivalents) during handling and storage.
Risk Mitigation and Damage Prevention
Proactive measures minimize costly delays and rejections.
* Pre-Shipment Inspection (PSI): Conduct thorough inspections at the mill or loading point to verify dimensions, coating integrity, end protection, and documentation.
* In-Transit Monitoring: For critical/high-value shipments, consider GPS tracking and shock/vibration monitoring.
* Insurance: Obtain comprehensive marine cargo insurance covering all risks (All Risks) for the full value of the shipment.
* Clear Communication: Maintain constant communication between buyer, seller, freight forwarder, carrier, and receiver regarding schedules, handling instructions, and potential issues.
* Training: Ensure all personnel involved in handling (mill, yard, port, transport) are trained in proper LSAW pipe handling procedures.
Conclusion
Successfully managing the logistics and compliance for LSAW steel pipes requires a detailed understanding of the product’s physical properties, adherence to stringent international standards and transport regulations, meticulous planning of handling and securing procedures, and comprehensive documentation. Prioritizing safety, quality assurance, and clear communication throughout the supply chain is essential to ensure these critical components arrive at their destination undamaged and compliant, ready for project integration.
Conclusion for Sourcing LSAW Steel Pipes
In conclusion, sourcing Longitudinal Submerged Arc Welded (LSAW) steel pipes requires a strategic and well-informed approach, considering factors such as material quality, manufacturing standards, supplier reliability, and project-specific requirements. LSAW pipes are essential for high-pressure and structural applications in industries like oil and gas, water transmission, and construction due to their superior strength, durability, and dimensional accuracy.
When sourcing LSAW pipes, it is crucial to partner with certified and experienced manufacturers who adhere to international standards such as API 5L, ASTM A53, A139, and ISO 3183. Conducting thorough due diligence—evaluating supplier track records, production capabilities, quality control processes, and logistics—ensures the procurement of reliable and compliant products.
Additionally, total cost of ownership should be considered over just the initial purchase price, factoring in lead times, transportation, potential tariffs, and after-sales support. Strategic sourcing, possibly through long-term contracts or supplier diversification, can mitigate supply chain risks and provide cost stability.
Ultimately, successful sourcing of LSAW steel pipes hinges on balancing quality, cost, and reliability to meet project timelines and performance standards, ensuring safe and efficient operations throughout the pipeline’s lifecycle.